What is the danger of breech presentation?
Obstetrics and gynecology encounter breech presentation in approximately 5% of cases of the total number of pregnancies.
In such a situation, qualified, highly professional assistance is needed for the mother and child. The main feature of the pelvic position of the fetus during childbirth is that the baby’s legs or buttocks pass through the birth canal first. At the same time, the cervix is not yet sufficiently smoothed and opened, so the advancement of the largest and densest part of the fetus - the head - may be difficult.
Breech presentation is becoming a common cause of the threat of miscarriage. In addition, incorrect position can provoke fetal malformations: disruption of the formation of the nervous and cardiovascular systems, bones, muscles and genital organs.
Causes and risk factors
The exact causes of fetal malposition are unknown. There are several risk factors:
- excessive fetal activity;
- restriction of fetal activity;
- obstacles to insertion of the head during childbirth;
- fetal malformations;
- abnormalities of the uterus.
Causes of excessive fetal activity:
- Polyhydramnios . With a large amount of amniotic fluid, the child’s activity increases, and the space for maneuvers increases.
- Flabbiness of the muscular corset of the anterior abdominal wall . Muscle failure leads to excessive stretching and the appearance of free space for fetal movements. The likelihood of this condition increases during the second and subsequent pregnancies.
- Prematurity . Incorrect fetal position is considered normal until 32 weeks. If labor starts prematurely, the baby may not have time to take the desired position. The shorter the gestational age, the higher the likelihood of developing the problem.
- Multiple pregnancy . When carrying twins, there is a high risk that one or both fetuses will take an incorrect position in the uterus.
- Fetal hypotrophy . A low birth weight baby occupies a small space in the uterus and can be positioned transversely or obliquely to its axis.
- Fetal hypoxia . Lack of oxygen forces the baby to actively move towards the uterus, changing its position. It may be unstable and change throughout pregnancy.
Reasons for decreased fetal activity:
- Low water . If there is a lack of amniotic fluid, the fetus has no room to maneuver and may remain in an abnormal position until delivery.
- Large fruit . After 30 weeks, excess weight prevents the fetus from moving in the uterus and can cause abnormal positioning.
- Threat of miscarriage . Increased tone of the uterus prevents the baby from moving in the womb, restraining his activity.
- Uterine fibroids . A tumor located in the fundus or body of the organ reduces the capacity of the uterus and reduces the motor activity of the fetus.
- Short umbilical cord . Incorrect fetal position may also be associated with umbilical cord torsion.
Obstacles to insertion of the head during labor lead to the baby being forced into an incorrect position. Risk factors:
- cervical uterine fibroids;
- placenta previa is a condition in which the fetal site blocks the exit from the uterus;
- anatomically narrow pelvis (including against the background of tumors, exostoses).
Anomalies in the development of the genital organs are a rare cause of fetal malposition. Problems arise with a bicornuate uterus, as well as with the presence of a septum. Less commonly, oblique or transverse position of the fetus occurs with a saddle-shaped uterus.
Fetal malformations can result in transverse and oblique position. The cause is excessive or reduced mobility, incorrect body proportions. This phenomenon often occurs with hydrocephalus and anencephaly.
Growth, fetal formation
The 22nd week of pregnancy has arrived, what happens to the baby during this period? The baby is actively growing, there is still plenty of space in the uterus, he is energetically turning over and pushing. The size of the fetus at the 22nd week of pregnancy reaches 270-290 mm. The spinal column, its vertebrae and intervertebral discs are intensively forming; the baby’s bone structures accumulate calcium. A woman’s diet must include products containing this element. The weight of a child at 22 weeks of pregnancy is close to five hundred grams. The world of baby's tactile sensations is expanding. A baby at 22 weeks knows how to play, he fiddles with the umbilical cord or his leg, and tries to suck his fingers. The baby has eyelashes and eyebrows on her face, and her head is starting to become covered with hair. The hair is almost transparent, but can be seen on an ultrasound. The baby's skin is all wrinkled, but with the thickening of the subcutaneous fat layer, the face becomes rounded. The nose and lips are drawn more and more clearly.
At 22 weeks of gestation, the baby acquired nails on its hands and feet. 2-3 weeks ago, mommy doubted whether the baby was moving. Fetal movement at 22 weeks of pregnancy cannot be confused with anything. The baby pushes very actively, especially at night. Excessively energetic and chaotic movements should alert the woman, perhaps the baby does not have enough oxygen. Children at this stage react to their mother’s bad mood and stress
Therefore, it is very important for her to remain calm. Sometimes pregnancy proceeds in such a way that the woman has not yet felt the kicks of her baby
A consultation with a gynecologist is necessary; if the doctor hears the baby’s heartbeat, there is no cause for alarm.
This is the 22nd week of pregnancy, the improvement of the fetus does not stop for a moment. All the most important organs and systems have already been established; their further development and improvement is underway. The baby's brain reaches a mass of 100 grams, its surface begins to become covered with convolutions, and grooves appear. All brain cells are already formed, new neurons and neural connections are developing. Connections are formed between different parts of the brain. The baby’s heart increases in size, the frequency of its contractions reaches 140-160 beats in 60 seconds.
The fetus at week 22 has a fairly developed nervous system, its movements become more and more coordinated.
Receptors appear on the baby’s skin and sweat glands form. All internal organs continue to function, the digestive system, pancreas and liver develop. The baby can open and close his eyes and squint. The eyes react to light, the baby hears a loud sound. The baby learned to yawn and hiccup.
The toddler actively swallows amniotic fluid. In this way he trains his lungs, this will make his first breath after birth easier. For a baby, the 22nd week of pregnancy is characterized by the fact that his body is covered with lanugo. Lanugo is a fluff that helps the vernix to stay on the skin. This lubricant protects the baby from direct contact with amniotic fluid. The closer the birth is, the less lubricant and hair remains on the baby’s body. It is believed that if the 22nd week of pregnancy ends in childbirth, the baby can survive with very long and difficult nursing. But he will not be able to avoid health problems. Monitor your well-being, take care of your health so that the baby is born on time.
Complications of childbirth and their prevention
A woman's risk of rupture of the cervix, perineum, and damage to the pelvic bones increases. Both in the case of natural birth and as a result of cesarean delivery, the likelihood of infectious complications, for example, endometritis, increases.
Perinatal outcomes for breech fetuses in case of timely surgery are favorable. Subsequently, the child grows and develops normally, unless he has a pathology that formed before birth.
Complications of childbirth:
- trauma to the cervical spine, spinal cord and brain;
- asphyxia (suffocation) of the fetus;
- prematurity and growth retardation;
- developmental defects;
- intrauterine infection with early rupture of amniotic fluid;
- respiratory distress syndrome (impaired lung function after birth);
- hip dysplasia.
Birth trauma is associated not only with damage to the cervical spine, but also with excessive pressure on the head during childbirth from the fundus of the uterus. It causes serious illness in the child in the future. There are motor dysfunctions (paralysis), strabismus, convulsive seizures (epilepsy), neuroses, endocrine pathology, hydrocephalus, and lag behind peers in physical and intellectual development.
The musculoskeletal system is affected. The baby may develop torticollis, hip dislocation, clubfoot, contracture (limited mobility) of the knee joints, dysplasia (impaired formation) of the hip joints.
At an older age, children born in a breech presentation, often regardless of whether this happened naturally or through surgery, exhibit increased excitability, restless sleep, decreased appetite, and hyperactivity syndrome. Subsequently, difficulties may arise when adapting to society and schooling.
To prevent complications during breech presentation, the following measures must be taken:
- formation of risk groups for breech presentation in the antenatal clinic;
- regular observation by a doctor;
- diagnosis and treatment of pregnancy complications such as gestosis, threatened miscarriage, placental insufficiency;
- prevention of postmaturity;
- use of therapeutic exercises;
- choosing the right method of childbirth;
- advance preparation for a planned caesarean section;
- proper management of natural childbirth, prevention of premature rupture of water, bleeding, disturbances in uterine contractility;
- diagnosis of complications during childbirth and timely decision on emergency surgery;
- careful delivery;
- thorough examination of the newborn child.
It is important to inform the expectant mother about pregnancy and birth tactics. Psychosomatics - disturbances in the functioning of internal organs associated with prolonged stress, anxiety, fear of the unknown - can negatively affect the baby’s condition
The more a woman knows about her situation, the less likely she is to develop complications. Therefore, it is recommended not only to ask the doctor about all the details of future childbirth that interest you, but also to read more about this pathology. It is necessary to prepare for a positive outcome in advance.
Characteristic signs and diagnosis
It is impossible to independently determine the location of the fetus. Breech presentation does not cause pain, the appearance of any nonspecific discharge or discomfort. Only a gynecologist can find out how the baby is positioned in the womb.
During an obstetric examination, the doctor may feel the large, soft presenting part. If the baby is positioned head down, there is a lower position of the uterine fundus above the pubis. The fetal heartbeat can be heard in the navel area.
During a vaginal examination, depending on the type of presentation, the gynecologist can palpate the baby’s feet, his tailbone, sacrum or soft volumetric part. Such an examination can be carried out closer to the middle of the third trimester.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing breech presentation is not difficult. For this purpose, external and internal examination is used, as well as additional research methods.
External inspection
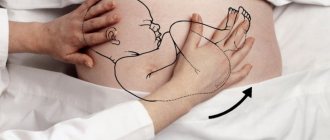
For this purpose, Leopold's techniques are used (determining the position and presentation of the child) and measuring the abdomen:
- Fundus height
The fundus of the uterus with this type of presentation is high, that is, it exceeds the physiological norm. This is due to the fact that the pelvic end is not pressed against the entrance to the pelvis before labor begins.
- Leopold's techniques
When palpating the abdomen, it is clearly determined that the dense and rounded part (the head) is located in the fundus of the uterus, and the buttocks (large, soft, irregularly shaped and non-balling, that is, the stationary part) is located at the entrance to the pelvis.
- Fetal heartbeat
With cephalic presentation, the heartbeat can be clearly heard on the right or left, but below the navel. When the pelvic end is presented, the heartbeat is heard at or above the navel.
Vaginal examination
This method is the most informative when carried out during childbirth:
- in case of presentation of the buttocks, the soft part and the gap between the buttocks, as well as the sacrum and genitals are palpated;
- if the presentation is purely gluteal, the inguinal fold is easily determined;
- in the case of a mixed breech presentation, the foot is felt next to the buttocks;
- with the foot, the legs of the fetus are determined, and in the case of a prolapsed leg, its main difference from a fallen handle is the sign that it is possible to “say hello” to the handle.
Additional Methods
- Fetal ultrasound
The presentation of the fetus is specified, as well as its weight, the presence or absence of congenital defects and umbilical cord entanglement, and the degree of extension of the head.
- CTG and ECG of the fetus
Allows you to assess the condition of the baby, hypoxia, entanglement or compression of the umbilical cord loops.
Breech presentation
In addition to transverse and oblique, longitudinal position does not always mean correct physiological placement. The baby can be vertical, parallel to the axis of the uterus, but not with his head down, but with his buttocks or legs. Then they talk about longitudinal pelvic presentation of the fetus. According to statistics, 3-5% of pregnancies occur with this diagnosis.
The choice of method of delivery for breech presentation depends on:
- on the gender of the child;
- mother's age;
- woman's pelvic size;
- fetal weight;
- subtype of presentation.
Childbirth in this case is considered pathological due to the high risk of complications. But the longitudinal position of the fetus with a breech presentation is not a mandatory indication for a cesarean section.
Doctors also take other factors into account when making decisions.
If the fetal presentation is pelvic longitudinal, then natural childbirth is carried out under the constant supervision of medical staff. The legs and buttocks are the first to emerge from the birth canal, and difficulties often arise with the advancement of the head. There is a high risk of intrauterine hypoxia, pinching and premature extension of the head, throwing back of the arms, and aspiration of amniotic fluid are possible.
If the fetal position is longitudinal and the presentation is breech, the second common complication of natural childbirth is a high level of trauma to the mother and child. A woman may experience severe bleeding when passing through a head that has not undergone configuration, that is, “not folded.” The newborn must be examined by an orthopedic traumatologist to rule out bone damage.
Pelvic longitudinal presentation of the fetus during pregnancy involves attempts to change it to a cephalic one. Special gymnastics are prescribed, and if necessary, an external preventive rotation is performed. If it is not possible to change the internal location, the woman is hospitalized to determine the risk group and select the appropriate method of delivery.
Labor management tactics
Childbirth through the birth canal in case of abnormal fetal position is practically not carried out due to the high risk of complications:
- early rupture of amniotic fluid with a high probability of infection of the fetus;
- loss of small parts of the fetus;
- loss of umbilical cord loops;
- acute fetal hypoxia;
- abnormal contractile activity of the uterus;
- rupture of the uterus when it is overstretched.
During childbirth, an advanced transverse position of the fetus may develop. This happens with early rupture of water and is accompanied by loss of mobility of the child. Further delivery through the vagina is impossible.
In modern obstetrics, oblique and transverse position of the fetus is an indication for cesarean section. The operation is performed at 37-41 weeks. The period is determined by the condition of the pregnant woman and child.
The expectant mother may refuse a cesarean section and insist on a natural birth. In this case, she needs to be aware of all the possible risks and understand that such a birth can be fatal. Death threatens the fetus as a result of asphyxia and the woman in labor due to uterine rupture.
The following conditions fall into the high-risk group for the development of complications:
- age over 35 years;
- multiple pregnancy;
- abnormalities in the structure of the uterus;
- large and multiple myomatous nodes;
- anatomically narrow pelvis;
- scar on the uterus;
- placenta previa;
- large fruit (more than 4000 g);
- change in amniotic fluid volume;
- threat of uterine rupture;
- loss of umbilical cord loops or fetal parts;
- neglected transverse position of the fetus.
In these situations, vaginal birth is not recommended.
A caesarean section can be planned for the first stage of labour. In this case, the woman begins to have independent contractions, and the cervix gradually dilates. There is a possibility that the fetus will turn over when labor begins. If this does not happen, a cesarean section is performed before pushing begins.
A planned caesarean section before the onset of labor is indicated in the following situations:
- gestational age 42 weeks or more (post-term);
- placenta previa;
- anatomically narrow pelvis;
- rupture of amniotic fluid before contractions begin;
- scar on the uterus;
- tumors of the reproductive organs.
Features of operative delivery:
- When the fetus is in a transverse position, it is necessary to expand access. It is not always possible to make an incision in the lower uterine segment. Often, the fetus is removed through a longitudinal incision.
- General anesthesia is often given for abnormal fetal position. Epidural anesthesia is not always possible.
- During surgery, there is a high risk of complications (including bleeding). A planned caesarean section should be performed by an experienced gynecologist in maternity hospitals that are fully equipped with everything necessary to provide care to the mother and newborn.
The surgical technique is determined after examining the patient. Early hospitalization in a maternity hospital at 38-39 weeks is recommended. It is important not only to re-evaluate the fetal position, but also to identify associated abnormalities. According to indications, cesarean section is performed before full-term pregnancy.
Correct fetal position
We have already figured out that the ideal is a longitudinal presentation of the baby. In this case, it should be head down and the back of the head should be turned towards the mother’s tummy. Firstly, in this position he feels more comfortable. Secondly, during childbirth, his chin comes into contact with the chest, which ensures:
- uniform and gentle pressure on the cervix, which stimulates its expansion and the production of hormones necessary at the moment in the woman’s body:
- turning the baby's head, allowing him to place the widest part of it at the most spacious point of the mother's pelvis
- the required angle of inclination of the baby’s head, ensuring faster and more comfortable passage of the baby through the birth canal
Thus, the longitudinal head position of the fetus allows mother and baby to meet faster and travel this path with the least loss. This is exactly the position of the child that is observed in most women in labor.
However, in approximately one out of ten cases, the baby may have the position described above, but at the same time be with the back of his head to the mother’s spine. That is, this is also the head position of the fetus, but less advantageous than when the back of the baby’s head is facing the woman’s stomach. The child, as a rule, is also born naturally, but this position can cause some problems, for example:
- premature release of water
- long and slow labor
- lower back pain in an expectant mother
- start pushing until the cervix is fully dilated
During childbirth, upon reaching the pelvic floor, the baby may turn around, which will require additional time. And in some cases, the reversal does not occur, and then doctors have to help him, using, for example, forceps.
This position of the child is called posterior and may be due to:
- anatomical features of the structure of the woman’s pelvis
- lifestyle of the expectant mother or professional factors
If you have a sedentary job, this increases the likelihood that your baby will take a back position. After all, when you are in this position, your pelvis is tilted back. Accordingly, the baby's head also leans back. But if you move a lot and spend most of the time on your feet, then the pelvis is tilted forward, and the baby has every chance to take the right position.
However, if the baby is in the rear position, you can try to turn him around. To do this, you need to tilt your pelvis forward, not back. For example:
when sitting, make sure that your knees are no higher than the level of your hips; when sitting on a surface that does not provide the desired posture; place a pillow under you; lift your pelvis; exercise with a fitball; lean over it; stand on all fours (this position ensures that the back of the baby’s head turns toward the tummy moms): you can just stand like that for 10 minutes or do some simple exercises, or you can wash the floors, putting the mop aside
Malposition
Incorrect positions of the baby include pelvic, transverse and oblique presentation. In the transverse position, it is always prescribed, and in the other two cases, much depends on various factors, but most often the woman is also sent for surgery.
There is also such a phenomenon as unstable fetal position. This means that the child “cannot decide”: at first he takes a longitudinal position, and then suddenly finds himself in a transverse or oblique position. Then the situation may change again. This happens when the baby is more mobile.
What can cause abnormal fetal position? This can be influenced by various factors:
- increased baby mobility
- decreased mobility of the child
- pathologies of uterine development
- pathologies of fetal development
- phenomena that prevent the insertion of the head (for example, a narrow pelvis, fibroids in the lower part of the uterus)
If your baby is in the wrong position, you can “persuad” him to turn around. To do this, you need to perform special exercises (which ones, better consult your doctor, because each case is individual). When the baby turns as needed, you can protect yourself from further changes in positions and wear it constantly, taking it off only in cases where you really cannot do without it. However, it is also better to talk to your doctor about the need for a bandage.
The position of the fetus is the stable location of the unborn child in the body of the uterus in which the child will be born. This position is characterized by the ratio of the uterine axis to the fetal axis. It is worth noting that the axis of the fetus is considered to be an imaginary line running along the back, from the back of the child’s head to his tailbone.
The fetal position is unstable, what does this mean?
In transverse and oblique positions, the position is determined not by the back, but by the head: the head on the left is the first position, on the right is the second position. The back is not always turned to the right or left, but it is usually turned anteriorly or posteriorly, so a distinction is made between the type of position - the relationship of the back to the anterior or posterior wall of the uterus. If the back is facing forward, then they talk about the front view of the position, if it is backward - about the rear view.
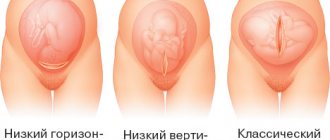
Fetal presentation. This is the relationship of the large part of the fetus (head or buttocks) to the entrance to the pelvis. If the head is above the entrance to the pelvis, the presentation is cephalic; if the pelvic end is located, the presentation is pelvic.
Presenting part. That part of the fetus that is located at the entrance to the pelvis and is the first to pass through the birth canal. With a cephalic presentation, the back of the head (occipital presentation), the crown (anterior cephalic), the forehead (frontal), and the fetal face (facial) can be presented. Typical is the occipital presentation (flexion type). With all other types, the head is in varying degrees of extension. With a breech presentation, the buttocks (breech presentation), the legs (foot presentation), and the buttocks together with the legs (mixed gluteal-foot presentation) can be presented.
Preliminary period
The processes of preparation for childbirth intensify in the last days of pregnancy, which is accompanied by an increase in signs of cervical maturity and the appearance of precursors of labor. This entire period is called preliminary. In addition, during this period the amount of estrogens, relaxins, oxytocin, and acetylcholine in the body increases significantly.
Date added: 2015-05-23; ; Does the published material violate copyright? | Personal data protection |
Didn't find what you were looking for? Use the search:
HomeObstetrics and GynecologyAnomaly presentation of the fetus
Biomechanism of labor in different types of presentation
The biomechanism of childbirth means a set of various movements performed by the fetus passing through the birth canal of the woman in labor. It directly depends on the design features of the female pelvis and the position that the baby takes at the beginning of labor.
Headlines
In this case, under the influence of rhythmic contractions of the uterus, the following occurs:
- The head bends, the chin presses against the chest and smoothly descends into the pelvis.
- The leading point is determined - the small fontanelle, which, under the influence of contractions and efforts, tends to the wire canal of the small pelvis.
Occipital
In the absence of concomitant diseases, this obstetric care is a standard procedure. The biomechanism consists of a combination of attempts that allow the fetus to be expelled through the pelvic area. The child is born at the main point - the back of the head and is the best outcome of childbirth.
Facial
It consists of maximum extension of the head before entering the small pelvis.
The face line is transverse or oblique. Then an internal rotation of the head is made at the bottom of the pelvis. Then it is fixed. As the baby is born, the head bends. Completion of the process consists of internal rotation of the shoulders and external rotation of the head.
Anterocephalic
The management of childbirth is similar to the management procedure for cephalic presentation, the difference lies in the active work of the obstetrician in the direction of preventing injuries to the newborn and ruptures in the mother.
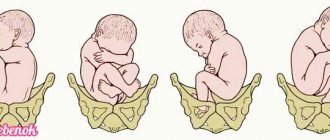
Pelvic
It consists of fixing the buttocks at the entrance to the pelvis, internal rotation of the buttocks, cutting in, cutting through, passing through the shoulders, and at the end the head cuts through.
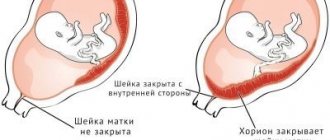
Low location of the placenta
The placenta, otherwise the baby's place, is the organ through which the fetus receives all the substances and oxygen necessary for development. The condition of the placenta is an extremely important factor for the proper development of the baby. Ultrasound may reveal low placentation during pregnancy. This means that the placenta is located below the internal os and can block the birth canal. This does not affect the course of pregnancy in the early stages; most often the placenta rises higher as the baby grows. She poses no threat to the child.
Quite rarely, the placenta completely closes the birth canal, preventing the birth of a child. But even in this case, natural childbirth is possible. It is bad if low placentation does not disappear before birth, and the baby is positioned with his legs down. A low-lying placenta can impede the supply of oxygen to the fetus and is more likely to be detached. A woman with this feature of the placenta should be under constant medical supervision, possibly in a hospital setting. A woman needs to avoid physical activity, get more rest, and avoid transport and crowds. She needs to protect her stomach from all kinds of injuries.
Exercise for the baby to take the correct position in the womb
If by the 36th week the fetal position is characterized as unstable, they speak of pathology. This is dangerous because the baby will not turn over longitudinally before birth and will settle in an oblique position, which will make it difficult for him to be born naturally. If at this stage it turns out that the fetus is not positioned correctly, prenatal correction is indicated. Effective:
The doctor will select a suitable complex. When performing gymnastics, the health status of the expectant mother is taken into account. Contraindications may include:
- gestosis;
- chronic diseases;
- placenta previa;
- risk of miscarriage.
If attempts to correct the situation fail, they resort to caesarean section. Otherwise, there is a high risk of umbilical cord prolapse during contractions and premature rupture of amniotic fluid. Not only medical interventions are important, but also the attitude of the expectant mother. You need to stroke the tummy and ask the baby to roll over. If he does this, the effect should be secured by wearing a bandage. The product can prevent changes in the correct position.
Unstable fetal position
I was also interested Girls, please share information
The baby turns around and this is normal, sometimes with his head down, sometimes with his butt, the main thing is that by the end of pregnancy he lies head down. In my exchange only in the last 2 visits (30 and 33 weeks) the position of the fetus was written “cont. Goal." those. head down. But even then the doctor said that everything could change, he still has time to turn around.
An ultrasound also showed that he was lying head down.
This doesn’t threaten anything, don’t think anything stupid about it. During pregnancy, the baby wraps around itself several times and develops in different parts of the body, and at 34-35 weeks you will have your last ultrasound, just to see if there is any wrapping.
Entanglement is dangerous only if it is repeated and tight, and this is not so common. So don't bother yourself with fears. Everything will be great.
This is also normal, during pregnancy the pressure decreases, in the first trimester this may cause headaches, but then the body adapts. Low blood pressure is called hypotension.
Until a certain period of time, the child constantly spins, especially if there is a lot of space in the belly; mine lay down head down quite early, and the doctor could determine this by feeling the belly with her hands.
As for rollovers, sometimes right before the birth the baby can feint with his ears and turn either with his butt (and before that lie with his head), or vice versa, turn his head (and before that lie with his butt). This happens all the time. I think you shouldn’t worry about this, especially since your time is not so long that the baby will be in a cephalic presentation.
yes, “the position of the fetus is unstable”
And you ask the doctor without leaving the cash register. She writes, and you: “What is this? And this?”
For example, I was “unestablished.” didn’t scare me, although I wanted to ask, but forgot, and about “cont. Goal." asked
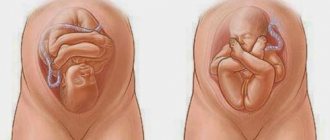
Breech presentation of the fetus
Breech presentation occurs in 3-5% of cases and is divided into foot presentation, when the fetal legs are presented, and breech presentation, when the baby seems to be squatting and his buttocks are presented. Breech presentation is more favorable.
Birth in a breech presentation is considered pathological due to the large number of complications in the mother and fetus, since the less voluminous pelvic end is born first and difficulties arise when removing the head. In case of pedicle presentation, the doctor delays the birth of the child with his hand until he squats to prevent the leg from falling out; after such assistance, the buttocks are born first.
Breech presentation is not an absolute indication for cesarean section. The question of the method of delivery is decided depending on the following factors:
- the size of the fetus (with a breech presentation, a large fetus is considered to be more than 3500 grams, while during a normal birth it is more than 4000 grams);
- maternal pelvic size;
- type of breech presentation (foot or buttock);
- sex of the fetus (for a girl, breech birth is associated with less risk than for a boy, since a boy may suffer damage to the genital organs);
- woman's age;
- the course and outcome of previous pregnancies and births.
To turn the fetus after 31 weeks, the following exercise is recommended: lie on the right side, lie down for 10 minutes, quickly turn over to the left side, after 10 minutes again to the right, repeat 3-4 times several times a day before meals. You need to stand in the knee-elbow position for 15-20 minutes a day. Exercises in the pool also contribute to fetal rotation. If the baby turns over on his head, it is recommended to wear a bandage to fix his correct position.
Contraindications for performing such exercises are complicated pregnancy (preeclampsia, threat of premature birth), a scar on the uterus after a cesarean section in the past, placenta previa, uterine tumors.
Previously, external rotation of the fetus was used (the doctor tried to move the fetal head down through the abdomen). Now it is not used due to low efficiency and a large number of complications, such as premature placental abruption, premature birth, and fetal impairment.
If breech presentation persists, then 2 weeks before birth the pregnant woman is sent to a hospital, where a delivery plan is drawn up.
Therapeutic exercises for abnormal fetal position
Therapeutic gymnastics allows you to gently push the baby and help him take the desired position in the uterus. Several methods have been developed, but it is difficult to speak unequivocally about their effectiveness. If a child has the ability to turn, he will do it without special exercises. If there are serious obstacles, gymnastics will not bring the desired result.
F. Dikan's scheme:
- A pregnant woman turns alternately on her left and right side. There should be no sudden movements - everything should be done smoothly, without straining the muscles of the back and abdomen.
- After each turn, the woman lies in the chosen position for 5-10 minutes. You can repeat the procedure 2-3 times. The entire lesson should take about an hour.
- Exercises are performed 3 times a day for 1-2 weeks. You can repeat the practice after a week break.
Methodology of E. V. Bryukhina, I. I. Grishchenko and A. E. Shuleshova:
- Lie on the side opposite to the position of the fetus (this question should be clarified with your doctor).
- Bend both legs at the knees and hips.
- Spend in this position for at least 5 minutes.
- Smoothly straighten your upper leg.
- As you inhale, press your overlying leg to your stomach, and as you exhale, straighten it. Give a slight push towards the back of the fetus. It is important not to make sudden movements - everything is done smoothly, without tension.
- Repeat the entire set of exercises after a short break (1-2 minutes).
- After completing the exercise, lie still for 10 minutes - this will allow the fetus to settle in the desired position.
- Take a knee-elbow position for 10 minutes after a short rest.
Exercises should be performed 3-5 times a day for a week. During this period, the fetus should turn. If the child takes a longitudinal position with his head down, the gymnastics stops. The woman begins to wear a support bandage before giving birth to keep the fetus in the desired position. If the child is positioned with his buttocks down, gymnastics are indicated for the breech presentation of the fetus.
Causes of breech presentation
All the reasons for the occurrence of such a diagnosis can be divided into two groups: factors depending on the mother’s body and developmental defects of the child himself.
Maternal factors include:
- Anomalies of the uterus: bicornuate, saddle-shaped and its duplication. Sometimes these defects can only be detected during pregnancy.
- Umbilical cord entanglement. If at the time of entanglement the baby was in a breech position, then the mechanical tension of the umbilical cord loop limits his movements. An umbilical cord that is too short also becomes an obstacle to achieving the head position.
- Polyhydramnios. An increased volume of amniotic fluid provokes frequent movement of the baby in the uterine cavity. Frequent changes in position can lead to the umbilical cord entwining the neck and body of the fetus.
- Multiple pregnancy. Lack of space in the uterine cavity often leads to the fact that one of the babies is positioned legs down.
- Uterine fibroids. The large size of the tumor prevents the fetus from turning its head down. The most dangerous are myomatous nodes located in the uterine cavity.
- Anatomical narrowing of the pelvis. Displacement of the pelvic bones or an anatomically narrow pelvis significantly limit the movement of the fetus and deprive it of the ability to change position.
Fetal-dependent factors include:
- Developmental defects. For example, hydrocephalus with an increase in the size of the head or a large goiter. Such developmental anomalies are quite rare, are diagnosed using ultrasound in the early stages and are a reason for terminating pregnancy for medical reasons.
- Prematurity. The fetal position is unstable until the middle of the 3rd trimester. Before such an early birth, the baby often does not have time to take the correct position.
- Intrauterine growth retardation. A small fetus moves and changes position in the womb much more often.
Types of presentation
The fetus is not static throughout the entire gestation period, but already at the 33rd week it is fixed in one position and remains there until birth.
A similar situation arises due to the increase in the size of the child, which makes it difficult for him to move. The 34th week is the beginning of preparation for childbirth. The fetus descends slowly, and ultrasound examination allows us to determine the presentation, which can be physiological, pathological and unstable.
Lower
This position is characterized by a close position to the exit from the uterine cavity, compared to the physiological one. When palpated, the fetus is identified in the small pelvis partially, and sometimes completely. This condition is a consequence of multiple births, weakness of the uterine muscles, physical activity and the characteristics of the pregnant woman’s body.
Headlines
The position is assessed by doctors as the most “correct” and is typical for most pregnancies. In this case, the baby makes his way into our world in the way that physiology and nature have prescribed - with his head. At the same time, the birth canal opens smoothly and harmoniously, under the pressure of the baby’s head. In turn, the rhythmically contracting muscles of the uterus press on the fetus. There are two types of cephalic presentation.
1st position
The position most favorable for successful delivery is also called flexion. The main characteristic is the maximum bending of the head before entering the birth canal, practically it is pressed to the chest, exit through the back of the head.
2nd position
The position is less favorable, the main feature is maximum extension of the head, pressing against the back. Exit from the birth canal by the forehead or face, which leads to injury to the woman and baby. It is diagnosed by an obstetrician during a prenatal examination through the vagina, after which an individual labor management strategy is developed.
Pelvic
The baby is positioned with his buttocks towards the exit of the pelvis. Birth occurs with the legs or buttocks. Presentation can be pathological, that is, pure gluteal, mixed or leg presentation. After diagnosis, the doctor chooses a tactic for conducting the process - either manual rotation of the fetus, or surgical obstetrics by cesarean section.
Transverse or oblique
This position is diagnosed when large parts of the fetus are not identified during a vaginal prenatal examination. The child is positioned obliquely or transversely in the large pelvis, which is a serious pathology. The cause is most often developmental abnormalities or trauma to the uterus.
Natural obstetrics when diagnosing this position is not possible. In all cases without exception, surgical intervention is prescribed before the amniotic fluid ruptures.
Unstable
An unstable posture is characteristic of polyhydramnios, when the child remains active until the last weeks of pregnancy. This or that position is also not recorded in cases where the fetus has malnutrition, that is, a weight lower than the theoretical one. Less common are cases of unstable presentation during intrauterine oxygen deprivation.
Ways to change the position of the fetus during pregnancy
If at the third planned ultrasound examination the examination shows that the baby has not changed its position, the woman can begin performing special exercises to turn the baby from pelvic to cephalic presentation.
Similar gymnastics are started from the 33rd week of gestation. If pregnancy proceeds with complications, you will have to stop doing the exercises so as not to harm the baby. Contraindications include scars on the uterus and low placenta previa.
If performing gymnastics does not give positive results, doctors hospitalize the pregnant woman to perform external rotation of the fetus in a hospital setting. Medical errors can cause rupture of the placenta, membranes, leakage of amniotic fluid and premature birth.
Pregnancy management
Considering the high risk of complications in pregnant women with breech presentation, preventive measures are prescribed to improve uteroplacental blood flow, prevent the threat of miscarriage and fetal hypoxia. Presentation with the pelvic end at 21 weeks is considered physiological, and the position of the fetus with its head down occurs by 22–24 weeks. Pregnant women are recommended to have a balanced diet (to prevent fetal hypo- or hypertrophy), as well as a gentle regimen (full sleep, rest).
Special gymnastics
Exercises for breech presentation of the fetus are recommended to begin at 28 weeks. But performing special gymnastics has a number of contraindications:
- scar on the uterus;
- bleeding;
- threat of interruption;
- gestosis;
- severe extragenital pathology.
Methods according to Dikan, according to Grishchenko and Shuleshova, as well as according to Fomicheva or Bryukhina are used. The simplest gymnastics are Dikan exercises. The pregnant woman lies first on one side or the other, turning over every 10 minutes. In one session, you need to make 3–4 turns, and perform the gymnastics itself three times a day. After the fetus is in a cephalic position, the abdomen is secured with a bandage.
External rotation of the fetus
If there is no effect from gymnastic exercises at 36 weeks, external rotation of the fetus is recommended. Manipulation is not performed in the following situations:
- existing scar on the uterus;
- planned cesarean section (other indications available);
- uterine defects;
- deviations on CTG;
- premature release of water;
- fetal defects;
- small amount of water;
- refusal of a pregnant woman;
- pregnancy with more than one fetus;
- placenta previa;
- oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- unstable position of the fetus.
Fetal inversion during breech presentation must be monitored by ultrasound and CTG; the procedure itself is carried out “under the cover” of tocolytics (ginipral, partusisten), and after the manipulation a non-stress test is performed and the ultrasound is repeated.
Complications of the procedure include:
- fetal hypoxia;
- placental abruption;
- uterine rupture;
- fetal brachial plexus injury.
Hospitalization of a pregnant woman
A woman is hospitalized with a breech presentation of the fetus at 38–39 weeks. In the hospital, additional examination of the pregnant woman is carried out:
- clarification of obstetric history;
- clarification of extragenital pathology;
- ultrasound examination (clarification of presentation, fetal size and degree of head extension);
- X-ray of the pelvis;
- amnioscopy;
- assess the readiness of the pregnant woman’s body for labor and the condition of the fetus.
Then they decide on the method of delivery. Caesarean section for breech presentation of the fetus is routinely prescribed for the following indications:
- fetal weight is less than 2 and more than 3.5 kg;
- narrowed pelvis, regardless of the degree of narrowing;
- curvature of the pelvis;
- excessive extension of the head;
- delayed fetal development;
- history of fetal death or birth trauma;
- post-maturity;
- placenta previa;
- breech presentation of the first baby with multiple births;
- scar on the uterus;
- foot presentation;
- “old” primigravida (more than 30);
- pregnancy after in vitro fertilization;
- extragenital pathology requiring exclusion of the second stage of labor.
Pain at the beginning of the second half of pregnancy
Pain at 22 weeks of pregnancy is caused by various reasons:
- A woman may periodically have a tummy tug. If they were irregular, not very strong, and disappear quickly, we can talk about training contractions. Some women begin to experience them during these periods. If contractions, acute pain, or bleeding are observed, urgent hospitalization is necessary. Such symptoms indicate the onset of premature labor.
- A pregnant woman's body weight steadily increases, therefore, the load on her legs increases. Many women report pain and swelling, especially in the evening. It's time to give up high-heeled shoes; you will feel more comfortable in sneakers or ballet shoes. It is useful to do contrasting foot baths before going to bed and massage them. During long walks, give yourself a rest, sit on a bench. When sitting, try to place your feet on some elevation.
- A woman’s belly is growing; in order to maintain her balance, she has to lean back when walking. All this cannot but affect the condition of the lower back and spine. Painful symptoms in the lower back can be reduced by wearing a prenatal bandage. It will hold your stomach and the load on your back will decrease.
- Many people face the problem of constipation during this period. They occur due to the fact that the uterus presses on the intestines. Try to include foods containing fiber in your diet - fresh vegetables and fruits, prunes, kefir, beet dishes. It is necessary to drink enough liquid.
- In the second half of pregnancy, blood vessels swell, including in the anus. This can lead to the appearance of hemorrhoids, and constipation will also contribute to this.