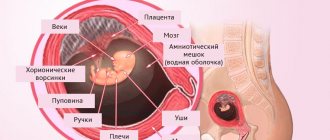
The more your belly grows and the more actively your baby makes itself known, the more often you think about how the birth will go. All pregnant women, without exception, ask this question, regardless of what kind of pregnancy it is. And if you become a mother for the first time, then you are even more concerned about the upcoming birth. And as the expected date approaches, every strange or suspicious sensation is ready to be considered as “it’s all begun!..”.
Women who have given birth tell their young friends that the onset of labor cannot be missed or confused with something: they say, when contractions begin, you will definitely understand that the process has begun. However, many expectant mothers arrive at the maternity hospital ahead of time. And all because of false contractions.
What are training contractions?
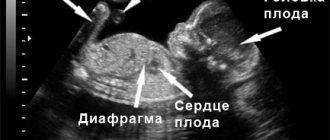
Training contractions are periodic contractions of the smooth muscles of the uterus. Another name for them is Braxton-Hicks contractions , named after the scientist who first described this phenomenon in 1872. Training contractions do not lead directly to childbirth; their purpose is to prepare the birth canal for the very process of giving birth to a child.
When do training contractions begin? They usually appear after the 20th week of pregnancy and often take women by surprise - after all, the period for childbirth is still short. And some expectant mothers do not encounter them at all or do not feel them or confuse them with a harbinger of miscarriage.
Symptoms and sensations during training/false contractions
Are training contractions painful? Braxton-Hicks contractions are completely painless and bring almost no discomfort to the expectant mother.
What do training contractions look like and how to recognize them? They are like a sharp uncomfortable compression or tension in the lower abdomen, not accompanied by pain. The lower abdomen and lower back may feel a little achy.
How long do training contractions last? The duration of training contractions ranges from several seconds to two minutes, and they are repeated no more than four times per hour. They, unlike prenatal contractions, appear irregularly, most often in the evening. Such contractions usually end very quickly, but the longer the pregnancy, the more discomfort they bring to the expectant mother.
The frequency of occurrence of such contractions in a particular woman is purely individual: the frequency varies from several times an hour to several times a day.
Reasons for appearance
According to scientists, training contractions occur in response to:
- increased physical activity of a woman (this can be not only playing sports, but also heavy housework or staying on your feet for a long time);
- regular stroking of her belly, including by herself (primigravidas are guilty of this);
- drinking alcohol or smoking;
- sleep problems, chronic fatigue;
- poor nutrition and deficiency of nutrients in the body;
- feeling hungry or, conversely, overeating;
- drinking carbonated water (it irritates the stomach, and this irritation is transmitted to the uterus);
- high fetal activity in the womb;
- a full bladder (it puts pressure on the uterus);
- deficiency of fluid in the body (it entails a decrease in the volume of circulating blood and, as a result, insufficient blood supply to the uterus);
- stressful situation, mother's worries;
- sexual intercourse and the orgasm that follows (this is explained by the fact that oxytocin is released into the blood, which provokes the appearance of muscle spasms);
- hot shower, bath.
Please note that some women experience contractions when a stranger touches their stomach.
How to distinguish real labor contractions from training ones
How to distinguish false contractions from real prenatal ones? Very simple:
- training contractions are irregular;
- the time intervals between them are not cyclical;
- false contractions can be easily stopped by changing body position or taking a shower;
- the cervix does not dilate;
- Gradually such contractions disappear completely.
Contractions that are precursors of labor , on the contrary, are regular and repeat at equal intervals, which gradually decrease. The contractions themselves become longer in duration. They continue until the baby is born. Pre-labor contractions are painful, and changing positions does not help relieve the attacks. The cervix gradually opens.
False contractions that occur after the 38th week of pregnancy are sometimes difficult to distinguish from real ones, but obstetricians-gynecologists advise to calm down and not panic : according to statistics, a woman always understands herself and with 100% accuracy that labor is beginning. Multiparous women usually do not have such questions about training contractions.
Signs of imminent labor
A woman's pregnancy lasts about forty weeks, and about fourteen days before the exciting event, the body signals about the upcoming birth with a number of signs and tips. By carefully observing some changes in the condition, you can accurately determine the time of birth of the baby. Such harbingers of some women are expressed quite clearly, while others may simply not pay attention to them, although completely in vain.
Nature has decreed that labor will not begin without warning, and it gives the woman the opportunity to prepare for it physically and psychologically. A pregnant woman may not immediately show all the signs of imminent labor, but the appearance of one or two warning signs should not frighten the expectant mother. On the contrary, they are designed to prepare her for the birth of a baby.
Nature suggests that childbirth is just around the corner with the following signs:
- false contractions. This is the name given to spontaneous contractions of the abdominal muscles, which most often appear after the thirty-sixth week of pregnancy, but can sometimes occur earlier, starting from the twentieth week. By the end of the thirty-eighth week of pregnancy, more than 70 percent of pregnant women experience this condition, and only some do not experience such phenomena;
- prolapse of the abdomen. A few weeks before giving birth, pregnant women giving birth to their first child experience a drooping belly, and for those women who give birth again, this can happen several hours before the joyful event. The baby's head, together with the uterus, descends to the entrance to the small pelvis, due to which the stomach moves to a lower position. At the same time, heaviness goes away from the gastric tract and respiratory system. The woman feels that it has become easier for her to breathe, but at the same time it becomes uncomfortable to sit and walk, so it is best for a woman to take a reclining position before giving birth. Having descended, the uterus stops putting pressure on the stomach, symptoms of heartburn and belching disappear, but pressure on the bladder leads to a more frequent urge to urinate. There is a movement of unpleasant sensations to the lower abdomen, a shift in the center of gravity affects the spine and lower limbs. Most often, a pregnant woman experiences tingling in her legs and pelvis, on which the baby’s head presses;
- removing the mucus plug. From the very beginning of pregnancy, the glands of the cervix begin to actively produce mucus. This thick fraction protects the uterus from microbes, thereby blocking the path of infection to the fetus and the waters around it. But before childbirth, under the influence of estrogen, the cervix loses its density and becomes softer. Softening the cervix allows you to gradually remove the mucus plug, because it has already fulfilled its function and is no longer needed. Clots in the form of jelly remain on the underwear and are transparent, white, yellowish and pinkish in color, and the release of mucus with blood clots becomes a harbinger of the onset of labor. The mucous plug comes out in one day immediately or gradually, the process of its separation takes place without pain, but slight pulling sensations in the lower abdomen may appear. For different women, the mucus plug may come off at different times - from two weeks to several hours before giving birth;
- a woman's weight loss. Two weeks before giving birth, under the influence of estrogen, excess fluid leaves the body, due to which swelling is eliminated. In general, due to water, the female body loses from 500 grams to 2 kg;
- changes in the excretory system. Due to the pressure of the baby's head on the rectum, a pregnant woman may experience constipation or, on the contrary, loose stools. The fetus also puts pressure on the bladder, causing frequent urination and difficulty holding urine, which becomes especially noticeable during physical activity;
- decreased frequency of fetal movements. Before birth, the fetus can hardly fit in the uterus, so it moves less often, thereby reducing its own physical activity;
- changes in the pregnant woman's mood. Towards the end of pregnancy, a woman’s mood often changes: her activity is sharply replaced by a loss of strength, and her good mood is replaced by apathy and drowsiness. These periods contribute to the accumulation of strength for the upcoming birth and are quite natural for a woman in the last stage of pregnancy.
We also recommend reading: How to quit smoking during pregnancy
As a result, false contractions appear
The tone of the muscular system of the uterus has a positive effect on the body of a pregnant woman - it does not allow the uterus to relax, it keeps it in a tense state all the time. The sensations of training contractions often appear at dusk, when the pregnant woman is resting. The result of their appearance is the flow of arterial blood to the fetus, thanks to which it is possible to fully provide it with nutrients. Thus, the tone of the uterine muscles in the last months of pregnancy has a positive effect on the fetus and ensures softening of the cervix.
False contractions can be triggered by external factors and often occur in the following situations:
- with high physical activity, including long walks;
- when a pregnant woman takes an excessively hot shower or bath;
- with excessive motor activity of the fetus;
- when a woman drinks strong tea or coffee. They stimulate the nervous system and, as a result, increase the tone of the uterus;
- Orgasm during sex also leads to increased muscle activity of the uterus;
- frequent manifestations of muscle tension of the uterus can be provoked by insufficient nutrition or dehydration of the body, which causes its blood supply to deteriorate;
- excessively high-calorie nutrition leads to contraction of the stomach walls, and along with it the uterus begins to experience muscle tension. Also, drinking carbonated drinks causes an overly full stomach to transmit its activity to the muscles of the uterus, which is located nearby;
- excess weight of the child or multiple births lead to the fact that any movement of the fetus irritates the walls of the uterus and increases its muscle tone;
- with strong emotional outbursts and stress, false contractions may also occur, accompanied by physical fatigue and sleep disturbances.
What to do during training contractions
What should an expectant mother do during training contractions, especially if they bother her? Use the following tips:
- Change your body position - squat, turn over, lie on your back. The most important thing is that you feel comfortable.
- Take a short walk around the street or house, moving smoothly and slowly.
- Taking a warm shower is a great way to stop training contractions.
- Go to the toilet, empty your bladder.
- Drink still water and fruit drinks.
- Take a break from contractions - take up your favorite hobby, listen to music or read.
- Just try to ignore false contractions.
By the way, you can use the phenomenon of false contractions to train before real birth - do breathing exercises . Expectant mothers are taught to breathe correctly during childbirth in childbirth preparation classes. And training contractions will help you learn to breathe without leaving home.
Do the following breathing exercises:
- Blow out the candles - inhale deeply through your nose and then exhale through your mouth. You should inhale slowly and exhale sharply and quickly.
- Breathe like a dog - shallow, quick inhalations and exhalations during a contraction. You should not breathe this way for more than 30 seconds to avoid dizziness.
- Save your breath - during a contraction, exhale slowly and then take a deep, full breath. then, after the fight is over, the exercise is repeated.
When should you see a doctor?
If normal training contractions occur, you should not panic and run to the doctor, but you should consult a specialist in the following cases:
- significant pain in the lower back and lower back;
- bloody issues;
- bleeding;
- water breaks;
- cramps and painful contractions;
- nausea and diarrhea;
- The fetus began to move noticeably less.
Do I need to go to a gynecologist?
“Workouts” are normal. But there are moments, having noticed which, you should still go to the residential complex.
- The appearance of blood or excessive vaginal discharge.
- Severe pain in the lower back.
- The baby has stopped moving (or barely moves).
- The waters are receding.
All these signs (plus duration, frequency, regularity of contractions) are not scary in the long term. Perhaps they are talking about the fact that the future dad needs to buy a stroller - you are going into labor.
Video about false and labor contractions
We invite you to watch a video where a specialist shares his knowledge about training contractions and how they differ from labor contractions. For those who are preparing to give birth for the first time, such knowledge will be very useful.
Even if you are going to become a mother for the first time and are faced with training contractions, and they frightened you, remember - do not panic and do not worry, because your excessive anxiety will negatively affect your general condition and the condition of the unborn baby. to discuss all your concerns here And experienced mothers will definitely give you advice on how to cope with training contractions, tell you what week and how long before birth they usually begin.