Possible reasons
The main factors causing this symptom are:
- occur after a gynecological examination by a doctor in a special chair;
- sexual activity in the final stages of pregnancy;
- the beginning of the cork separation process.
At 38 weeks they may appear after a visit to the doctor, when the cervix was examined. When visiting a doctor, a woman sits comfortably on a gynecological chair in a horizontal position. The gynecologist determines the condition of the external genitalia, using two mirrors to determine the maturity of the cervix and its readiness for childbirth. When using medical instruments, the mucous membrane of the genital organs may be injured, resulting in bloody or brown discharge in small quantities. The woman notices them several hours after the examination. They are not a dangerous sign, but, on the contrary, are considered normal preparation of the body.
During sex before childbirth, a woman’s blood supply to the genital organs increases and uteroplacental blood flow improves. The components of sperm affect the speed of dilatation of the cervix, and female lubricant smoothes and softens it. It is necessary to take into account the individual state of the pregnant woman, select positions with caution and observe the woman’s emotional background.
At the slightest painful sensation, you need to stop sexual intercourse. After careless lovemaking, after some time, brown discharge may appear before childbirth, that is, the body is stimulated to give birth, and contractions occur. Sometimes they appear simply as spotting mucus and may stop within 2-3 days. If bleeding occurs, you should immediately contact a medical facility for a full examination.
Mucous discharge indicates the removal of the plug. The pregnant woman definitely does not feel any changes in the development of the process. But sometimes there may be a gradual release of mucus, including pink discharge before labor. This means that blood is released along with the plug and the birth of the child will occur in the near future, or indicates premature expulsion of the placenta. At this time, the tone of the uterus increases, and nagging pain appears in the lower abdomen. Immediate hospitalization is required.
Normally, the volume of the released consistency reaches two tablespoons. The clot is dense or gel-like to the touch and visually has a white color with a yellowish tint. There is no specific smell. For each woman, the period between the removal of the plug and childbirth is different, the duration ranges from two hours to two weeks. Its main function is to protect the pregnant woman’s body from various infections.
With premature expulsion, the risk of infection increases; you must be extremely careful during this period before birth. You definitely need to give up intimate life and swimming in open water, visit the pool and take a hot bath. A woman can continue her normal lifestyle, but with minor exceptions. The main thing is to monitor your health and, if you have minor complaints, contact your doctor.
In most cases, if a woman expecting a baby notices brown discharge at the 38th week of pregnancy, that is, close to the expected date set by the doctor, this means that the plug has come off and you can prepare to be admitted to the maternity hospital.
Placental abruption. In the last trimester of pregnancy, placental abruption is considered the most dangerous pathology. It has different clinical manifestations depending on the stage of pregnancy.
The placenta is a special organ that provides communication between mother and child and provides immunological protection. The umbilical cord supplies nutrients and oxygen to the baby. Normally, it is separated only after the birth of the child. If a similar situation occurs in the later stages, then severe bleeding and dull uterine pain in the lower abdomen are observed. Immediate delivery is necessary for health reasons.
Recommendations
If you have alarming symptoms, so-called “red flags,” you should immediately call a doctor. These include:
- An increase in the volume of bloody discharge;
- Change in color of bloody discharge from brown to bright scarlet color;
- Deterioration of general condition - weakness and dizziness, flickering of spots before the eyes;
- Severe nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- Temperature increase;
- Nausea, vomiting.
And if a woman notices scant brown discharge, she will not be able to figure it out on her own. This should be done by an experienced specialist who, in the presence of other symptoms, can tell exactly what the cause is and whether there is cause for concern, or whether the mother can safely carry the child further and not have to worry about anything.
Excessive anxiety can negatively affect the well-being of the woman herself and affect the child.
Don’t panic in advance, contact the clinic, where they will advise you and give you the necessary recommendations. Share:
Leakage of amniotic fluid
Leaking amniotic fluid is a natural occurrence during childbirth, but it happens that amniotic fluid may leak prematurely. A colorless, sometimes greenish (during oxygen starvation of the fetus) and brown tint (during cervical injury or placental abruption), watery substance begins to be released from the vagina.
The rate of discharge of water is from 0.5 to 1.5 liters. May include white flakes - these are particles of lubricant that protect the skin of the fetus in the uterus.
If the gestation period is up to 32 weeks, and the secreted fluid is clear and in small quantities, then doctors try to prolong the gestation of the child as long as possible. When the 36th week arrives, further prolongation is stopped and stimulation is gradually introduced to develop labor.
If a change in the color of this substance is detected, you must urgently get to the maternity ward and tell the doctor about the characteristic abnormalities.
What to do in this case?
To reduce discharge and to prevent diseases, you must adhere to several rules:
- Stop sexual activity.
- Maintain intimate hygiene - shower your genitals several times a day, especially after visiting the toilet. Remove hair from the pubic area. Apply antiseptic treatment of the vagina.
- Use disposable sanitary pads.
- Underwear should be made from natural fabrics and not squeeze the woman’s body.
In order for your pregnancy to have a favorable outcome, you must carefully monitor your psychological and physical health, closely monitor the color, consistency, smell and volume of vaginal discharge, regularly visit your gynecologist and fully report any changes that have occurred.
The girls, after examining their cervix at 6:00 p.m. Sunday (the examination was very painful, 2 fingers were dilated and the cervix was soft), now at 4:30 a.m. Monday in the toilet they discovered brown discharge like a smear and one small blood clot. But from the descriptions it doesn’t look like a traffic jam. What is this? The discharge is not strong. Nothing seems to hurt now. But before that, before going to bed, everything hurt. And the baby inside often hiccups for 10 minutes (2 times yesterday). And strange sounds from the stomach after eating (not hiccups and it doesn’t look like gas), my husband and I listened to it as if some water was gurgling back and forth and a little frog was croaking (also happened 2 times) at first I was taken aback by the sounds, by the time I got to my husband everything went away, and then I managed to show him my eyes, they were worth five kopecks!!!)) What could this also be?
Discharge in late stages of pregnancy In later stages, spotting may indicate a threat of premature placental abruption, or mean premature onset of labor. In such cases, emergency assistance from gynecologists is necessary. However, the appearance of brown, not red, spotting in small quantities at 38-40 weeks is not a cause for particular concern.
In many women, such discharge occurs as a result of weak bleeding from the vessels located on the cervix. However, at the next scheduled visit to the gynecologist, a pregnant woman must tell him about the noticed vaginal discharge.
Causes of bleeding - normal or pathological
The cervix bleeds, as a rule, due to various pathological conditions of its integumentary epithelium. In addition to the fact that the cervix bleeds, symptoms such as pain during intercourse, pathological discharge, and problems with conception are noted. Signs are determined by the type of disease.
Inflammation
Inflammatory processes of the cervix and canal are initiated by the main pathogens:
- human papillomavirus;
- chlamydia;
- ureaplasma and mycoplasma;
- herpes simplex virus;
- Trichomonas;
- gardnerella;
- gonococci;
- opportunistic flora.
Genital infections cause inflammation of the cervical part - cervicitis and its canal - endocervicitis. The initial penetration of the pathogen into the tissue is accompanied by the appearance of true erosion. This pathology is accompanied by symptoms such as increased vaginal mucus, which acquires an unpleasant odor, yellow, greenish tint, foamy, purulent or mucous consistency.
The cervix bleeds or bleeds due to the fact that the erosion is a wound - a defect in the integumentary epithelium. But it is not uncommon for erosion to go unnoticed because it is not accompanied by symptoms. After it heals, the woman either recovers, or the process becomes chronic. Chronic cervicitis or endocervicitis is also accompanied by such manifestations as pathological discharge, pain during sex, and difficulty conceiving. The cervix bleeds on examination and there is contact bleeding.
If true erosion does not heal properly, when pseudo-erosion forms, the cervix also bleeds after sexual intercourse or examination by a gynecologist.
Polyposis
One of the variants of endometrial hyperplasia is its focal growth - a polyp. Polyps of this morphological nature appear in the uterine body. Depending on their size and shape, they can be visualized during an ultrasound examination. Often, polyps are not visible on ultrasound and are manifested by symptoms such as intermenstrual bleeding and spotting. Polyps have several types of structure. The adenomatous appearance is considered a malignant variant. Histological examination allows for an accurate diagnosis.
Polyps are the growth of glands of the columnar epithelium of the cervical canal. Polyps are benign in structure, however, they must be removed. Periodic bleeding is considered a sign of polyps. The cervix bleeds under any influence: during examination, after sexual intercourse. Outside of menstruation, the cervix rarely bleeds.
Erosion
Erosion is a focus of cylindrical tissue on the surface of the vaginal part. This type of tissue is normally located in the canal, but as a result of various provoking factors that lead to the formation of a wound, healing occurs with the transition of the columnar epithelium from the canal to the surface. This is how pseudo-erosion is formed.
Signs of pseudo-erosion include pathological discharge and pain during sexual intercourse. During a gynecological examination, the cervix bleeds. She also bleeds after sex.
The causes of the pathology are sexually transmitted infections. During the examination, condylomas are often observed.
During diagnostic studies and examination - colposcopy, scraping for cytology - it often turns out that the cervix is not erosion, but dysplasia.
The initial stages of cancer also have only one symptom: the cervical uterus bleeds under traumatic influences.
During pregnancy
The cervix of a healthy pregnant woman does not bleed either during examination or during pregnancy. However, sometimes, against the background of increased production of estrogen on the surface of the cervix, an ectopia forms in a pregnant woman - a displacement of the boundaries of the columnar epithelium to the vaginal part of the cervical region.
Upon examination, this condition of the cervix looks like a bright red rim around the external pharynx, the boundaries of which are clear. Signs of this condition boil down to the fact that a woman develops more abundant discharge, which has a white color and a mucous consistency. The cervix may bleed upon examination or during sexual intercourse. This is due to the proximity of blood vessels in the columnar epithelium.
Ectopia in pregnant women is a temporary normal state. Symptoms persist for some time after birth. Ectopia is observed and, if it persists for a long time, destruction is carried out with a laser, radio waves or liquid nitrogen.
If a pregnant woman has bleeding from the cervix, a colposcopy is performed to determine the cause of the bleeding. Since pregnancy is considered a period of decreased immunity, progression of human papillomavirus infection and cervical dysplasia cannot be ruled out. This disease occurs with similar symptoms as ectopia, so gynecologists show increased alertness.
| Dysplasia; |
What to do
In general, only one thing can be said for sure: in order not to risk your health and pregnancy, you need to see a gynecologist in any case and as soon as you notice brown discharge. There is no need to guess how normal they are, because most often there is nothing in common between brown discharge during pregnancy and the norm.
Abnormal, brown discharge in a woman before or after an examination by a gynecologist can signal minor injuries or illnesses, an ectopic pregnancy, or the risk of fetal loss. For expectant mothers, this is also a likely signal for the release of the mucus plug, which protects the cervical canal and the baby from unwanted microorganisms. And if this happens ahead of schedule, then pregnancy failure is possible.
When does brownish discharge appear?
A woman's vagina is an organ capable of self-cleaning. Periodic discharge from it signals natural processes in a healthy body.
Whether this is normal or pathological depends on the period when exactly they appeared. Brown ointments on underwear, not accompanied by painful sensations, smoothly turning into menstruation - this is a normal process.
A dark “ointment” that appears a week before the start of the cycle serves as a signal for alarm. This process indicates the presence of inflammation in the pelvic organs.
It can be:
- erosion - violation of the integrity of the surface - the cervix;
- endometrial hyperplasia - unnatural division of endometrial cells, leading to thickening of the walls of the uterus, and as a result, the inability to get pregnant;
- the appearance of polyps - benign neoplasms arising from glandular tissue;
- hormonal imbalance;
- benign tumor fibroid.
Brown discharge after a gynecological examination is a rare occurrence. Often occur as a result of microtrauma from a mirror during observation of pregnant women. They can also be obtained during sex or associated with the start of using new methods of contraception (IUD, intrauterine ring, oral contraceptives). Infection cannot be ruled out. In this case, the discharge continues for more than 2-3 days.
What factors can provoke bleeding?
The intensity of cervical bleeding may depend on the nature of the ongoing gynecological disease. The cause of the symptom is often injuries to the cervix, which are obtained in this way:
- having sex with a sexual partner;
- self-examination of the cervix;
- performing ultrasound transvaginally;
- gynecological examination in speculum or bimanual examination.
It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that bleeding from the cervix, which appears as a result of a gynecological examination or having sex, is not the norm. If a small drop appears once, we can talk about accidental damage, but if this is typical for each examination, the patient needs a comprehensive examination.
The intensity of bleeding of the cervix may vary depending on the degree of its damage or the nature of the progress of gynecological pathology. The discharge can be almost transparent, containing streaks of blood, and thick (brown or almost black). Women call them “daubs.” If there is an open, fresh wound on the surface of the cervix, the blood will be a rich scarlet color. The appearance of such a discharge really indicates bleeding resulting from an injury.
In general, bleeding from the cervix in women occurs in the following cases:
- a few days before or after menstruation;
- in the middle of the menstrual cycle;
- during the healing period after surgery;
- after a gynecological examination or sexual intercourse.
The list of main reasons that can provoke bleeding includes:
- taking hormone-containing drugs to prevent unwanted pregnancy;
- intrauterine device;
- hormonal disbalance;
- erosion;
- dysplasia;
- cervical endometriosis;
- myoma;
- papillomas on the cervix;
- adenomyosis;
- polyps of the cervical canal;
- endocervicitis;
- erythroplakia;
- leukoplakia;
- cervical cancer.
Bleeding that occurs during pregnancy indicates a threat of miscarriage or placental abruption. In the early stages, the appearance of non-standard discharge may indicate an ectopic localization of the fertilized egg.
It is impossible to determine the cause of blood discharge from the genital tract on your own. Since such a change is one of the symptoms of dangerous female diseases, the girl should seek medical help as an emergency. After conducting an examination and receiving the results of the required studies, the doctor can give an opinion and answer the question of why you are worried about bleeding that is not related to menstrual bleeding.
| Background and precancerous diseases that can provoke cervical bleeding | |
| Background | Precancerous |
| Ectopia; | |
Erosive lesion (true and false);
Cervicitis.
Condylomas.
The reason for the bleeding is that the violation leads to the destruction of the mucous layer lining the cervix, while the vessels are located close to the surface.
Features of the course of erosion and ectopia of the cervix
The reason for the appearance of erosion and ectopia of the cervix is infectious or traumatic, chemical damage to its mucous membranes. The causative agents of diseases are various sexually transmitted infections. By definition, erosion is a wound on the surface of the cervix that has a tendency to bleed.
The list of main pathogens includes:
- chlamydia;
- herpes;
- mycoplasmosis;
- ureaplasmosis;
- gardnerelez.
When multilayered squamous epithelium is destroyed as a result of increased activity of pathogenic microflora, necrosis of certain foci appears, desquamation occurs, and a bleeding surface forms at the site of the lesion - erosion.
Ectropion
Ectropion is a process of tissue deformation that can form after severe surgery and childbirth. The concept refers to inversion of the cervical canal. It can evert out due to internal ruptures of the cervix. When exposed to an unnatural environment, the columnar epithelium is attacked by the acidic environment of the vagina, which provokes cell destruction and leads to scarring.
In this case, after sexual intercourse or a gynecological examination, a woman discovers a few drops of fresh scarlet blood on her underwear. The next day, the discharge becomes spotty and disappears completely within 24 hours.
Papillomas and polyps
Polyps and papillomas can form on the surface of the cervix and cervical canal. There is no clear clinical picture for such changes. The only characteristic feature is the appearance of intermenstrual bleeding in a woman. During the entire cycle, ichor is released from the vagina; after examination in the speculum, bleeding becomes profuse. The reason lies in hormonal disorders, namely in the active production of female sex hormones.
Against the background of excess estrogen, proliferation and active growth of abnormal tissues is ensured, hyperplasia develops and polyps form. Genital warts are formed as a result of the activity of the human papillomavirus. With these neoplasms, the discharge is of a contact nature.
Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis is a disease of the female reproductive system, which is characterized by excessive growth of uterine tissue, accompanied by menstrual irregularities. With a long and uncontrolled course, the disease is dangerous not only with bleeding, but also with infertility. It is often detected untimely due to a blurred clinical picture.
The peculiarity is heavy menstrual flow, the duration of bleeding is more than 7 days, and symptoms of anemia can be observed. Extramenstrual bleeding, similar to ichor, is small and brown in color. Premenstrual syndrome manifests itself intensively, the stomach hurts before and during bleeding.
The main reason for the development of the disease is trauma to the cervix, which creates favorable conditions for the growth of endometriotic tissue. The risk of developing cancer against the background of adenomyosis is minimal; a particular danger lies in the development of infertility.
Endocervicitis
Endocervicitis is a pathology that causes bleeding that is not associated with menstruation. The disease affects the cervical canal and external os. The reason for the development is the addition of pathogenic microflora; progress can be traced against the background of the activity of bacteria and viruses.
What does brown discharge in a pregnant woman indicate?
During pregnancy, not only the woman’s hormonal background changes, but also the nature of vaginal discharge. Normally, in the second phase of the menstrual cycle, they become viscous and slightly cloudy (in contrast, in the first phase they are transparent, liquid, viscous). In pregnant women during this period, a different picture is observed.
So, only in the first three months of pregnancy do vaginal discharge have standard characteristics. Starting from the twelfth week, they become abundant and more liquid. During this period, as well as in subsequent periods, there should be no burning or itching on the external genitalia.
Brownish discharge is normal for a pregnant woman in the following cases:
- 1. The first few weeks after conception. Characteristics: in small quantities, odorless, light brown or beige-pink. Appear during the process of immersion of a fertilized egg into the wall of the uterus.
- 2. Changes in hormonal levels. Lasts for the first few months. If the discharge is cyclical (repeated consistently), a test for hormones is necessary; perhaps their level is higher than normal.
- 3. In the last weeks (from two weeks to several hours) before childbirth, due to the release of the mucus plug.
- 4. Microtraumas from gynecological examination devices. In this case, the discharge stops after a few days.
- 5. Due to the departure of one fertilized egg from twins.
Threat of spontaneous miscarriage
Brown discharge is a possible signal of a threatened miscarriage. In this case, they are accompanied by nagging pain in the lower abdomen, involuntary eruption of stomach contents, and loss of balance.
The egg with the embryo is rejected from the chorion (outer shell), causing damage that develops into a hematoma. A possible outcome is detachment and miscarriage.
Ectopic pregnancy or placenta previa
If brown discharge appears, pathological data are also possible. The fertilized egg is not always able to enter the uterine cavity. It happens that it migrates to another area, then an ectopic pregnancy occurs. The reasons for this process may be deformation of the fallopian tubes and adhesions. Pathology can also be localized in other areas of the pelvis.
In 90 percent of cases, the outcome of this situation is a miscarriage. Delayed diagnosis is likely to lead to malfunction of the reproductive organs.
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy:
- delayed menstruation;
- increased levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG);
- severe pain that feels like it occurs in the rectum (appears when the fetus is localized in an unnatural place);
- brown or bloody vaginal discharge;
- bleeding, dizziness.
Diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy is carried out using ultrasound. If detected, the fetus must be removed.
In extremely rare cases (occurs in less than 1%), placenta abruption or placenta previa occurs in the second trimester. Pathology occurs in the upper layer of the vessels of the uterus, and they begin to bleed. This happens for two reasons: due to the fetus being too close to this area or the uterus growing too quickly. Signs may include bleeding of various locations and brown discharge in copious amounts, which occur at the end of the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy.
To avoid pathology or start treatment on time, experts recommend ultrasound of the placenta.
Frozen fetus or hydatidiform mole
In some cases, fetal development may be arrested. This happens in the first trimester, 1-13 weeks. The provocateurs of this situation may be sexually transmitted diseases, genetic pathologies of the fetus, hormonal imbalance, rejection, blood clots in the blood vessels of the placenta and other natural causes.
- decrease in basal body temperature (in pregnant women it is 0.4 degrees higher);
- the appearance of brown discharge, weakly expressed;
- sharp cutting pain in the groin area;
- sudden stop of toxicosis, not related to the timing of pregnancy;
- changes in the condition of the breast, which stops swelling.
There is another type of embryo pathology in which normal development does not occur - hydatidiform mole. The placenta is overgrown with empty bubbles instead of fibrous chorions. This is accompanied by gagging from the gastrointestinal tract, physical malaise, high blood pressure, bleeding and severe headaches.
Premature birth
The period from week 20 - in the later stages - is the most dangerous for women who are constantly under stress, have chronic diseases or infections. The consequence may be opening of the cervix and premature birth. Accompanied by contractions and other pain in the abdominal area, the appearance of brown discharge.
In extremely rare cases, a woman manages to stop this process and continue pregnancy until the natural end of gestation.
Removal of the mucus plug
The mucus plug is designed to protect the body of the mother and child during pregnancy. Since it comes in different colors - transparent with bloody ointments, pink, beige, brown - for many women its loss becomes a cause for concern.
Removal of the mucus plug
The plug should come out on its own at 38 weeks of pregnancy, in whole or in part, with nagging pain in the sacral area. In some women, it comes out of the vagina at 40 weeks. For most, it happens directly on the day of birth.
After the 38th week, the local gynecologist must invite the expectant mother to an appointment. Often during the examination the vaginal walls are slightly injured. The result is discharge ranging from light brown to dark red. Continues for several hours after seeing a doctor.
Similar discharge can occur as a result of careless sex. There is no reason to worry if it lasts no more than two days.
Infectious diseases, pathologies
The embryo receives 50% of its genetic information from its father. In the mother's body it develops as a half-foreign graft. Because of this, a woman’s immune system is weakened during pregnancy. In the process of studying a number of clinical pictures, scientists found that pregnancy itself is a factor in the development of infectious diseases of the genitourinary system.
Diseases that lead to the appearance of brown or bloody discharge in the expectant mother can be either newly acquired, progressive, or “out of dormancy”, recurrent. These include:
- 1. Erosion of the cervix - “loose” surface of its mucous membrane. Discharge appears after sexual intercourse or examination by a doctor and passes without pain or other symptoms. They do not require medication or conservative intervention during pregnancy.
- 2. Sexually transmitted diseases or bacterial infections: at the embryonic stage or recurrent pathologies. In the context of changes in hormonal levels and reduced protective functions of the immune system, they develop and manifest themselves more strongly. In parallel with brown discharge, concern is caused by itching of the labia, discomfort in the pelvis/lower abdomen, and an unpleasant odor of viscous thick discharge.
- 3. Vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) is one of the likely causes of brown discharge. According to the study, about 40% of pregnant women suffer from this disease, with an increase in cases of up to 45% observed closer to childbirth. It is 2 or 3 times less common in non-pregnant women.
- 4. Benign abnormal growth of tissue over the mucous membrane (polyposis). It is detected by brown discharge during the development of the embryo, especially after examination by a gynecologist or sexual intercourse. Has no other symptoms. Removal of polyps after delivery is recommended. Although in a low degree of probability, they can develop into malignant ones.
Doctors strongly recommend that if any atypical discharge appears, you should consult a gynecologist. The consequence of inattention to oneself and the fetus can most likely be a pregnancy failure or complete or partial inhibition of a woman’s reproductive function.
Doctors insist that all girls and women undergo examinations at least once a year. It is not always possible to visit a doctor at such a time. Therefore, sometimes after rare visits and consultations with the doctor, unpleasant surprises begin. An unexpected “gift” - after an examination by a gynecologist, blood began to flow, accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen.
This happens under the influence of many factors - the occurrence of various diseases, including rare trips to the doctor. The most important thing to focus on is bleeding in pregnant women. This can be a serious sign of negative changes in the body.
After scraping
Discharge after uterine curettage is normal. The duration of discharge depends on the following factors:
- Reasons for curettage.
- Duration and scope of the procedure.
- The experience of the doctor and the quality of the manipulation performed.
If a small area of the uterus was scraped, the bleeding will last 1-3 days. If large-scale curettage was performed (surgery on several foci of the disease), bleeding will last from 5 to 8 days. Prolonged discharge after diagnostic curettage may occur due to poor blood clotting or as a result of hormonal imbalance.
The situation is considered normal when moderate bleeding lasts 5-7 days, gradually becoming less, gives way to bleeding and stops. In addition, there may be not very strong nagging pain in the lower abdomen associated with contractions of the uterus after diagnostic curettage and removal of part (or all) of the mucous membrane.
If the bleeding is profuse, accompanied by a rise in temperature, the appearance of an unpleasant smell of discharge, or severe pain in the lower abdomen, you should immediately consult a doctor!
The possibility of bleeding should not frighten you and make you refuse to visit a gynecologist. On the contrary, finding out the reasons for this phenomenon is the prerogative of this specialist. Perhaps this situation will force you to pay more attention to your condition and undergo a full examination, which will subsequently help you maintain your health.
Minor bleeding that stops within a few hours or one day is not a reason to worry. You need to lie down, rest and calm down. A repeated visit to the gynecologist will be necessary if the bleeding intensifies or if unpleasant symptoms occur (pain, itching, unpleasant odor of discharge).
During pregnancy, when there is a possibility of miscarriage, the appearance of blood should be taken more carefully. Especially if you experience nagging pain and/or dizziness. In these situations, you should contact a gynecologist immediately.
A regular visit to a gynecologist (it is recommended to visit at least once every 6 months) is a guarantee of timely detection of genital diseases and getting rid of them. However, often after examination by a doctor, women develop vaginal smear, which is sometimes accompanied by nagging pain in the lower abdomen. Why is this happening? And is discharge after an examination by a gynecologist a reason for a second visit to a specialist? Let's talk about it.
During a gynecological examination, the doctor uses special instruments that allow him to give an objective assessment of the condition of the reproductive organs. However, their use often causes mechanical injury to the mucous membranes of the vagina, cervix or uterus, as a result of which small capillaries are damaged and blood begins to be released from the vagina in small quantities. As a rule, the phenomenon is observed when a doctor uses gynecological speculums, with which he accidentally damages the integrity of the mucous membranes.
If a woman has brown discharge, the reason for this may be a vaginal smear, which is taken during examination for bacteriological examination. When taking it, the upper mucous layer of the vagina is scraped, which, naturally, also leads to damage to its small vessels. But in this case, minor bleeding occurs, which stops after 2–3 hours and does not require a second visit to the doctor.
In addition, the occurrence of brown discharge occurs not only due to the negligence of the gynecologist, but also due to the fault of the woman who, upon coming to the appointment, was very worried and made unnecessary sudden movements. It should also be noted that some women have increased fragility of blood vessels and for them, every gynecologist appointment ends with the appearance of a scanty smear that is dark or light brown in color.
The occurrence of bloody or pink discharge often occurs in cases where diagnostic or therapeutic procedures are carried out during use, which also compromise the integrity of the mucous membranes of the vagina or cervical canal. For example, this phenomenon is observed after cauterization of erosion or hysteroscopy. In this case, the discharge does not end as quickly as in the cases described above. They last from several days to a week; they can also pull in the lower abdomen and clots of clotted blood may come out.
In these cases, the appearance of atypical discharge after a gynecological examination is considered a completely normal condition and should not cause concern to the woman. However, if the daub is accompanied by an increase in temperature, severe abdominal pain, or bleeding is noted, then this has nothing to do with the norm. To determine the true cause of such symptoms, you will need to visit a specialist again and undergo a more detailed examination.
Pathological causes of atypical vaginal secretions
We can talk about pathological discharge in cases where it is observed for a long time (more than 2–4 days) and is accompanied by abdominal pain or other unpleasant symptoms. In this case, of course, it is necessary to make a second visit to the doctor in order to establish the factor that provokes their occurrence.
There are several reasons why atypical discharge may appear. More often, this role is played by infections obtained during an examination, during which unsterilized instruments were used, or by inflammatory diseases that the doctor could simply overlook.
If we talk about infectious diseases, the most common of them are candidiasis and bacterial vaginosis. They can also cause inflammation of the cervical canal, uterus or vagina, so you should never delay their treatment. However, if the development of infection is observed after visiting a gynecologist, then for a second examination it is better to choose another doctor or go to another clinic where sanitary standards are not violated.
Symptoms of the development of infectious diseases of the genital area are:
- Itching in the intimate area.
- The presence of beige, yellow, green or cheesy white discharge.
- Putrid, rotten or sour odor.
- Burning when urinating.
With the development of infectious diseases, the inner walls of the vagina become loose and any impact on them can lead to injury. However, when talking about why, after visiting a gynecologist, women develop a scarlet or brownish-colored smear, it is also necessary to note diseases in which neoplasms form on the cervical canal or inside the uterus. After mechanical impact, they can bleed, which will give a similar reaction. Such diseases include:
- endometriosis;
- adenomyosis;
- polyposis;
- uterine fibroids;
- uterine cancer.
Also, diseases that can produce a response in the form of bleeding include endometrial erosion and hypoplasia. Remember that these pathologies are dangerous to health and can cause not only the fact that a woman will not be able to get pregnant, but also serious complications that can be followed by death.
Important! If, after a gynecological examination, a woman begins to bleed from her vagina, along with nagging abdominal pain and other unpleasant symptoms, but upon examination the doctor does not reveal any changes, it is necessary to undergo a more detailed examination. It will allow you to get a complete picture of the condition and functionality of the reproductive organs, as well as identify the development of pathological processes in them.
Atypical discharge in pregnant women
If a woman has a delay and the test shows a positive result, then she needs to register with the antenatal clinic. But to do this, you also need to undergo an examination by a gynecologist. If the period is short, the appearance of discharge can be a serious reason to see a doctor or call an ambulance, since such a phenomenon indicates a threat of miscarriage.
In addition, the occurrence of discharge signals damage to the cervical canal, leading to the development of infectious or inflammatory diseases, which are dangerous in early pregnancy.
Also, if a woman experiences discharge in the first trimester after a medical examination, this may indicate abruption or placenta previa, which is also dangerous for the further development of the fetus.
Placental abruption in early pregnancy often occurs due to the doctor’s negligence when examining the patient. In this case, the woman experiences minor blood loss and severe abdominal pain. If such symptoms are present, you need to visit the doctor again.
As a rule, in later stages, gynecologists do not examine women in a chair. But there are situations when such an examination cannot be avoided. And in this case, if after examination a scarlet secretion is released from the vagina, we can talk about the risk of premature birth.
If no significant injuries were sustained during the gynecological examination, then vaginal discharge should stop within a few hours. However, if this does not happen, you should definitely consult a doctor. This will allow you to timely identify the problem and find adequate ways to solve it.
Abnormal, brown discharge in a woman before or after an examination by a gynecologist can signal minor injuries or illnesses, an ectopic pregnancy, or the risk of fetal loss. For expectant mothers, this is also a likely signal for the release of the mucus plug, which protects the cervical canal and the baby from unwanted microorganisms. And if this happens ahead of schedule, then pregnancy failure is possible.
Causes
Scanty bleeding in a woman after an examination by a gynecologist is not uncommon after a planned visit to the doctor, and there is no reason to be especially worried. Microtraumas of blood vessels and minor damage to the mucous membrane are why they occur after examination by a gynecologist.
Usually, the doctor takes a smear and uses a gynecological speculum during his manipulations. The analysis is taken from the mucous membrane, urethra and cervical canals of the uterus. In a word, they simply scrape off the test material from the vagina or other organ. Accordingly, the tissues are damaged and may bleed for some time. The main thing is that the bleeding is short-lived and stops very quickly. In any case, you need to monitor your health.
After an examination by a gynecologist, blood began to flow and did not stop bleeding for a long time, and it was also accompanied by itching in the groin, pain, and an incessant burning sensation, then you need to seek help immediately, accurately describing all the sensations. Perhaps this injury is making itself felt, or perhaps some kind of disease has manifested itself.
Treatment
The treatment regimen can be determined after receiving the results of basic examinations:
- gynecological examination in speculum and bimanual examination;
- determination of the concentration of female sex hormones in the blood;
- general blood analysis;
- ultrasound examination.
Basic rules of therapeutic intervention:
- If the disease has an infectious basis, the treatment regimen necessarily includes antibiotics. The required medication and its dose are determined by the attending physician after an accurate determination of the pathogen. To increase efficiency, you need to take immunostimulants.
- For the development of non-infectious diseases, vaginal suppositories and capsules are used.
- If the cause is erosive damage to the cervix, the woman needs surgery. Treatment is provided by laser therapy, cryodestruction and radio wave treatment.
- Polyps and papillomas are removed surgically. After surgery, the use of antibacterial agents is indicated.
If the bleeding is contact and appears after sexual intercourse, ultrasound or gynecological examination, there is no need to worry. There is probably some minor damage to the mucous membranes. If blood from the vagina begins to flow heavily, its volume is commensurate with menstrual blood loss, you need to visit a gynecologist. It is not always possible to stop bleeding on your own.
Attention! The drug Dicynon or Vikasol will help stop the bleeding. The compositions are produced by pharmaceutical companies in the form of injection solutions and tablets. The patient must understand that such drugs are not suitable for constant use and help reduce the intensity of bleeding without affecting its cause.
A disease that causes blood loss must be treated comprehensively. The course of therapy may include traditional methods, when properly combined with drug therapy. Douching or other procedures can only be done as prescribed by a doctor.
Is this normal
A woman’s uterus is intensively supplied with plasma and if it bleeds a little, then this is normal and there is no need to be upset. If this happened after using a speculum, then this is also not considered a pathology. It may be enough to change a specialist who will conduct the appointment more carefully. It is considered typical when pregnant women, after visiting a doctor, experience pain when emptying the bladder. This is associated with the collection of the test material for analysis and, most likely, injury occurred.
So, if, after an examination by a gynecologist, blood or light spotting begins to appear, this is normal in cases of physical damage from the speculum. There is no reason to worry. It is important to remember the duration of these processes. They must take place in the shortest possible time.
Regular gynecological examination is the main aspect of a woman’s health. In some cases, diseases detected in time are treated quickly and effectively. Any examination of a woman includes taking a smear. It is the cells of the mucous membrane that are studied in the laboratory. There are situations when careless examination causes serious problems in patients accompanied by pain in the lower back and abdomen. In such cases, immediate medical attention and follow-up therapy are required.
Each organism is individual. Therefore, it is believed that after consultation and examination, discomfort and slight spotting are normal. If a woman’s condition lasts for several days, then this is a serious danger and she urgently needs to consult a doctor. Everything is much more confusing when it comes to a number of certain diseases. Basically, the doctor personally determines whether there are any disorders and diseases or inquires about them in advance from the patient’s medical card.
There is a research method called a two-handed examination, when the location of the organs, their approximate parameters, the visibility of the adhesions of the fallopian tubes, and the chance of identifying any disease are felt. After these procedures, discomfort and pain may occur.
The danger of gynecological examinations is that unwanted outside intervention can become dangerous, especially if it is during pregnancy. Therefore, you need to approach the choice of a doctor extremely responsibly.
What to do if there is bleeding after a gynecological examination
If, after returning from the female doctor, bleeding begins, you should pay attention to its nature: color, thickness, frequency and volume. Short-term (several hours or one day) small bleeding caused by manipulation of the gynecological speculum is allowed
After returning from the doctor, you should carry out the necessary hygiene procedures, change your underwear, and lie down. If scarlet or dark blood continues to flow, you should not tolerate it, you need to go to the hospital immediately
Short-term (several hours or one day) small bleeding caused by manipulations with the gynecological speculum is allowed. After returning from the doctor, you should carry out the necessary hygiene procedures, change your underwear, and lie down. If scarlet or dark blood continues to flow, you should not endure it, you need to urgently go to the hospital.
Heavy discharge should alert you when it is accompanied by:
- significant pain in the lower torso or vagina;
- increased discomfort;
- burning sensation in the genitals;
- unpleasant odor;
- impurities of pus;
- heat;
- labored breathing;
- cardiopalmus.
In these cases, emergency assistance is required to identify the problem in a timely manner and correctly solve it.
Examination after examination in a chair can reveal the following pathologies:
- Endometriosis. It occurs in 10–15 percent of women of childbearing age and is characterized by painful periods, vaginal discharge, and uterine bleeding. The mucous membrane of the uterus grows into other organs and tissues of the pelvis, disrupting their function.
- Polyps are benign neoplasms into which a significant number of vessels grow, and at the slightest damage they begin to bleed. At the initial stage of development, they may not manifest themselves in any way and may not bother the woman, so they can only be detected during an examination by a specialist.
- Hyperplastic growth of the endometrium. The inner layer of the uterus grows, and there is a high probability of the process progressing to oncology.
- Cervical dysplasia. If left untreated, damage to the epithelial structure can lead to irreversible consequences, in particular cancer.
- Myoma, fibromyoma.
- A tumor of a malignant nature.
- Sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis).
All of these pathological abnormalities are characterized by bloody discharge.
Contact bleeding suggests the presence of problems in the female body. In rare cases, in the gynecological chair you can “catch” an unpleasant infection - bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis. This happens if the doctor neglects the rules of hygiene. Precursors of such infections, as a rule, are discharge mixed with blood immediately after examination.
In women who have not given birth, pain and discomfort after a medical examination are observed more often than in women who have children. Their vaginal muscles are less stretched, the cervix is quite narrow, and access to it has to be expanded with instruments. As a result of the increased sensitivity of the epithelial membrane to mechanical irritants, short-term bleeding may begin.
For a correct diagnosis, a complete history of all symptoms is needed. Light bleeding that ends quickly should not be a cause for concern. More voluminous ones require close attention and additional examination.
Excessive bleeding interferes with gynecological examination. In such cases, an ultrasound is performed, which is completely harmless even for pregnant women. With its help, you can diagnose the disease, determine the duration of pregnancy, and existing pathologies.
You should not, out of fear of possible consequences, refrain from visiting a gynecologist for preventive purposes. It would be much worse to discover that you have an already advanced disease, which will take a long time to treat. Each representative of the fair sex should approach the choice of “her” doctor individually and carefully. After all, if health-related problems arise, you will have to turn to a qualified specialist, often not even one. This facilitates correct diagnosis and timely treatment.
What to do
Many women do not know, and, being confused, begin to panic, especially after a gynecological examination. First you need to monitor your health - identify what the characteristic features of the discharge are. If little blood comes out and it stops quickly, there should be no cause for concern. You need to rest a little to calm your body.
And if it happens the next day, then that’s already bad. Then you need to make an appointment again. It is quite possible that a serious disorder has arisen or some disease has manifested itself.
It happens that the blood flows so much that it can be confused with menstruation. In this case; you must not hesitate, but call an ambulance, otherwise the blood loss will be too severe and life-threatening.
Indeed, as a result of careless manipulations during examination, significant injury to the internal genital organs could occur.
Emerging diseases
When blood starts to flow after an examination by a gynecologist, this is probably a harbinger of certain ailments. Endometriosis, for example, is accompanied by severe aching pain. This often manifests itself after visiting a specialist. And during menstruation, this torment is unbearable and the woman unknowingly takes painkillers.
Impurities of blood in a woman’s discharge can signal the growth of the endometrial layer. These pathological manifestations are caused not only by an appointment with a doctor, but also by a hormonal disorder with an excessive amount of estrogen in the body, obesity, etc. Before making a diagnosis yourself, you need to consult and undergo a series of tests.
If, after visiting a doctor, unexpectedly, then it is possible that uterine polyps have formed, consisting of endometrioid cells. These tumors, which are benign in nature at the very beginning, do not cause noticeable symptoms of the disease, pain or discomfort. Basically, they don't show up at all. Especially if your immune system is strong enough. Only a doctor, after conducting an examination, can reveal their presence.
Symptoms of endometrioid disease include pain after sexual intercourse, uterine pain, and disruption of the menstrual cycle. If treatment is not started immediately, you may encounter more serious diseases leading to infertility.
Sexually transmitted infections always manifest themselves as vaginal itching, burning, discomfort, pain after or during sexual intercourse, a fishy rotten odor and pain. If a woman exhibits the listed symptoms, she needs to seek help from a doctor and begin treatment. Many infectious diseases cause infertility, negatively affecting the functioning of the female reproductive system. , trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis.
Pathology
Sexually transmitted diseases are almost impossible to detect during examination. Based on the symptoms (smelly, purulent discharge) one can assume their presence, but the final diagnosis will be given by the smear result.
In addition, very often STDs that are not detected in time become chronic (latent). Inflammatory processes occurring in the tissues of the vagina and cervix make them more vulnerable. Therefore, after examining the cervix with the help of gynecological speculum, spotting appears. In this case, you need to be examined again by a gynecologist and take a smear for bacterial culture.
Cervical erosion is a very common disease. With erosion, ulcerations appear on the cervix, which begin to bleed under mechanical stress. Therefore, after a gynecological examination, small amounts of blood appear.
One of the methods for treating cervical erosion is a cauterization procedure, after which small brownish discharge may also appear. If heavy bleeding occurs, you should contact your gynecologist again.
Cervical polyps are benign formations that appear for a number of reasons (heredity, age 45-55 years, chronic inflammation, etc.). Polyps can be injured during a medical examination or sexual intercourse. In addition to bleeding, symptoms of pain (pulling in nature) in the lower abdomen and curdled discharge are characteristic. If you have these symptoms, you should get tested and begin treatment.
Endometriosis is another possible cause of spotting after examination. The disease is characterized by the proliferation of cells in the mucous layer of the uterus outside the usual growth sites.
It is not possible to diagnose the presence of this disease only through examination. A whole range of examination is required. However, there are quite specific symptoms that should alert a woman. The most common manifestations of the disease are disruption of the menstrual cycle and pronounced pain.
Uterine fibroids and endometrial hyperplasia. The presence of these diseases can also lead to the appearance of bleeding after examination, since both of these pathologies have a similar symptom - intermenstrual bleeding. An examination may coincide with such a phenomenon.
Diagnostics
If the girl’s bleeding is too serious and profuse, the examination will be extremely difficult. Therefore, the patient is sent to. It is harmless even during pregnancy. With its help, the timing of pregnancy, the position of the fetus, the presence of uterine pathologies and a number of other disorders are revealed. An ultrasound is prescribed after a routine examination by a doctor to clarify the diagnosis, if necessary.
This is a complex measure with the help of which the clinical picture of the course of pregnancy and the development of a particular disease is determined. Often this is an excellent diagnosis of diseases with bleeding, brown discharge and pathologies that the patient is not even aware of. If the discharge is not too abundant, then an examination by a doctor with a mirror is possible. As a rule, a small amount of bleeding does not interfere with clarifying the type of disease, establishing an accurate diagnosis and identifying the root cause of bleeding events.
Cervix bleeds during pregnancy
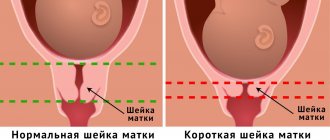
Cervical erosion is a rather dangerous gynecological disease, which at the initial stage of development can be asymptomatic.
In most cases, the disease does not affect reproductive functions. Patients with erosion may notice that the cervix bleeds during pregnancy. This symptom scares many people. There is no need to panic, but you should not delay a full gynecological examination. How dangerous is erosion during pregnancy, and does it need to be treated? We will talk about this in detail in this article.
In pregnant women
The most dangerous irreversible consequence of bleeding in pregnant women is self-abortion. This should be especially feared when bloody discharge appears in pregnant women after examination. If they are accompanied by dizziness, nausea, general malaise, weakness, or brown spots, then this is a sign of a threat. In cases where the doctor himself cannot determine the exact period of pregnancy, he gives a referral for an ultrasound examination.
Mild bleeding in a pregnant woman can be symptoms of other pathologies and disorders, which are also not recommended to be treated negligently. There are a lot of other unpleasant moments that are purely specific to each woman, so you should be more attentive to yourself and, having heard a doctor’s verdict about it, do not ignore his recommendations and prescriptions. Perhaps the patient will be sent to a hospital for preservation, where she will receive high-quality drug treatment and maintain the pregnancy until childbirth.
The danger that appears after a pregnant woman is examined by a gynecologist can be called a miscarriage.
In the practice of doctors, regrettable facts of a similar nature have occurred. When in the very early stages of about 10 days, the doctor, carelessly making sudden movements during the examination, provoked a miscarriage. As a result, the patient began to bleed after examination, sometimes only the next day. As a result, it is impossible to cure and save the fetus.
And if the patient and the doctor are aware of her situation, and after the examination, discharge and incessant viscous pain in the abdomen begin, then this is the main signal of negative changes and the threat of miscarriage.
If we focus more specifically on diseases, these can be erosion, papillomavirus, endometriosis and many others. This kind of illness can cause bleeding. The main thing is to start treatment on time when they are identified. Erosion is caused by many factors and their treatment cannot be delayed.
To keep a girl’s health in good condition, it is necessary to regularly visit the gynecological office as a preventive measure. Experts recommend being examined at least once a year, and much more often for pregnant women. But even with such a harmless procedure, bleeding may occur. Every girl of reproductive age should know why this happens and what to do in this case.
Causes
The most common provoking factors for the appearance of blood after a gynecological examination are:
- mechanical damage;
- microtrauma of uterine vessels;
- injury to other genital organs.
a gynecological speculum during the examination
, situations of accidental damage to the vaginal membrane cannot be excluded.
When taking a smear for analysis
Brown discharge often occurs. This procedure involves scraping out parts of the cervix, urethra or vagina. Vessels and epithelium are damaged, which provokes blood smear. Discharges, as a rule, are scanty. They disappear on their own in a short period of time. This condition is completely normal.