When is brown discharge normal?
There are two conditions in a woman when brown discharge refers to the normal (physiological) course of pregnancy, and they occur in 5-7% of expectant mothers.
Implantation of fertilized egg
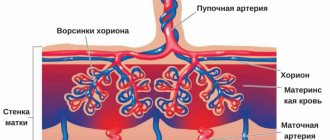
In the presence of a fertilized egg and favorable conditions, 7-10 days after sexual intercourse, the fertilized egg implants into the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium) - implantation . During this process, several capillaries (the smallest vessels) may be damaged, releasing a minimal amount of blood, which, when combined with physiological vaginal discharge, gives a light brown or beige color. Normally, this condition lasts 1-3 days and is not accompanied by pain or discomfort, but by cramps in the lumbar or abdominal area. The discharge goes away on its own and does not require any action.
Removal of the mucus plug
Refers to the normal course of the third trimester of pregnancy and can occur 2-3 weeks before the onset of labor. This is due to the fact that the cervix is already ready for childbirth, loose, shortened, with increased blood flow. The mucus plug, which protects the uterine cavity and the baby from external infections, comes off on the eve of birth, touches the outer surface of the cervix and can cause irritation of several capillaries and a brownish discharge. The duration of such discharge can be no more than 1 day. In this case, the woman should not feel any discomfort.
additionally The same effect occurs with any gynecological examination late in pregnancy or after sexual intercourse.
Can they be in the early stages?
Every healthy woman can periodically secrete mucus; all internal organs are covered with it. The cervix should always be moist. The genitals begin to work more actively during pregnancy.
After fertilization of the egg, a woman may notice a small amount of brown discharge. They appear when the embryo successfully attaches to the wall of the uterus. The process lasts no more than 40 hours. Spotting may be a one-time occurrence or occur periodically over a given period of time. Blood is released against the background of minor vascular damage. Implantation mucus may be absent or brown or beige in color.
In the first trimester
The first trimester can be called critical for a woman and her unborn child, because the body experiences stress and a number of changes, the fertilized egg quickly transforms into an embryo and fetus, and many organs are formed. That is why during this period any bleeding , including brown, most often develops in the presence of any pathology in a woman or a developing baby and is quite severe and dangerous .
Risk of miscarriage
The first and most common cause of brown discharge in the first trimester. For various reasons (most often from a lack of progesterone), the fertilized egg or embryo can detach from the endometrium, damaging blood vessels and causing brown vaginal discharge. Their quantity can vary from scanty to quite abundant, color - from light brown to brown-red. This depends on the severity of the threat of miscarriage and damage to the walls of the uterus.
The threat of miscarriage is accompanied by the following signs:
- nagging or cramping pain in the lower abdomen or lower back;
- nausea, vomiting;
- weakness;
- feeling unwell.
dangerous In this case, you should immediately call an ambulance and begin urgent treatment. Progesterone drugs, hemostatic agents and strict bed rest are usually prescribed.
Ectopic pregnancy
In rare cases, the fertilized egg may become fixed not in the uterine cavity, but in the fallopian tube (less commonly, in the ovary, on the cervix, in the abdominal cavity). This condition threatens the health and sometimes the life of a woman. As the embryo grows, the tube stretches and at some point ruptures, causing internal bleeding.
At the beginning of such a pregnancy, when the walls of the tube are traumatized, some vessels rupture and brown discharge appears. They are usually quite dark, streaked with red blood, and are accompanied by nagging or cramping pain in the lower back, lower abdomen, or on the side of the affected tube. In this case it is impossible ; treatment is only surgical - removal of the embryo and suturing of the fallopian tube.
Hydatidiform mole
A rarer pathology (1-2 cases per 1000 pregnant women), but no less dangerous. Occurs, as a rule, due to spontaneous genetic disorders in the fetal egg, when an additional set of chromosomes appears. In this case, the placenta cannot fully form; a huge number of cysts with clear liquid (looks like many bubbles) form on its surface.
Brown discharge bothers a woman periodically throughout the development of hydatidiform mole and is accompanied by:
- nausea;
- periodic vomiting;
- headaches;
- severe general weakness;
- increased blood pressure.
important In 95-99% of cases, an unborn baby dies in the early stages of development, often at the end of the first trimester.
The level of the hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) rises several times. Treatment is only surgical , in which the following is removed:
- embryo;
- the hydatidiform mole itself;
- sometimes part of the lining of the uterus.
A complication of this condition may be a malignant tumor , so the woman is carefully examined for 1.5-2 years after the operation and, if necessary, the uterus itself is removed. If the postoperative period is favorable, subsequent pregnancies are possible.
Non-developing (frozen) pregnancy
Frozen pregnancy occurs when a woman has infections, a lack of progesterone, and for other reasons. Leads to the death of the embryo. The woman remarks:
- scanty brown discharge;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- dizziness and headache;
- aching pain in the lower abdomen.
Most often, this condition is diagnosed on the first ultrasound at the end of the first trimester and is expressed by the absence of a heartbeat in the child.
information In more rare cases, a woman may experience inflammation of the internal genital organs. Surgical treatment - cleaning the uterine cavity by curettage.
Treatment
If the spotting is associated with progesterone deficiency, then the patient is usually prescribed Duphaston, with the help of which it is successfully possible to prolong pregnancy. But the causes of spotting in pregnant women are not always associated with hormonal disorders.
If the cause of the spotting is a frozen pregnancy, then surgical removal of the fertilized egg is necessary. If the frozen fetus is not removed in a timely manner, inflammation, infection and sepsis may begin, which can be fatal for the woman. Similar treatment is necessary for ectopic.
For spotting due to thrush, local drugs like Pimafucin, Nystatin are used, and in the last trimester Miconazole or Natamycin, etc. Many problems can arise with the treatment of sexually transmitted infections, because therapy is possible before 12 and after 22 weeks. The drugs are selected individually and taken strictly according to medical prescription. The main thing is to notice the problem in time and take the right measures to eliminate the probable threat.
Spotting in early pregnancy in rare cases is a physiological phenomenon associated with the attachment of the fertilized egg; more often they speak of pathologies. Therefore, if the pregnancy test is positive, the cause of any spotting should be determined by the doctor.
During pregnancy, spotting can occur at any stage, but is more common at the beginning of the first trimester and immediately before childbirth. After the 38th week and earlier, such discharge indicates the release of the plug, which precedes the imminent onset of labor.
In the first trimester, on the days of expected menstruation, such secretion more often indicates pathologies of fetal development. This can be an exacerbation of diseases in a woman, as well as possible complications that are dangerous to health and life. For example, an ectopic pregnancy or the onset of a spontaneous miscarriage.
There is a rarer phenomenon called memory of the female reproductive system. The condition is characterized by the fact that even with successful conception in the first months of pregnancy, short-term, scanty spotting occurs on the days when menstruation should begin. They are distinguished from ordinary menstrual discharge by their small volume, darker brown color, and mushy consistency.
In the second trimester
In the second trimester, brown discharge is a sign of the development of one or another pathology of fetal development and requires mandatory contact with a gynecologist for timely diagnosis and treatment. The main reasons are listed below.
Placental abruption
It is the most common cause of bloody discharge ranging from light brown and brown to bright red, from scanty and spotting amounts to heavy discharge. Abruption of a normally located placenta threatens the lives of both the mother (risk of extensive blood loss) and the developing baby (lack of nutrition and oxygen). May occur against the background of:
- stress;
- poor environmental situation in the place of residence;
- eating disorders;
- excessive physical activity;
- concomitant pathologies in women, etc.
The placenta can detach in areas of varying sizes:
- from a small area - with spontaneous development of a hematoma (practically does not affect the course of pregnancy and does not require serious treatment measures);
- to large areas - with continued progressive development of the condition (requires immediate treatment, up to cesarean section).
important This condition is most often accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen of varying severity, discomfort in the lumbar region, dizziness, fainting, etc.
Placenta previa
This is a condition of the pathological location of the placenta, when it completely or partially covers the uterine os (the area where the uterine cavity connects with the vagina - the place where the baby comes out during birth naturally). This leads to the fact that as the fetus grows, the load on the placenta and its vessels increases, which can cause periodic, spotting, brown discharge.
Presentation is most often accompanied by:
- intermittent, nagging or pain in the sacrum or lower abdomen;
- weakness;
- increased uterine tone;
- in rare cases - abruption of the low-lying placenta.
Throughout the entire period of gestation, it is necessary to carefully monitor the woman and baby to prevent the premature birth of an unformed child, bleeding, intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR), and intrauterine hypoxia.
Delivery with placenta previa is almost always carried out by cesarean section.
Premature birth
dangerous Starting from the 20th week of gestation, premature onset of labor is possible.
Most often it occurs due to infections in the mother and fetus, frequent stressful situations, concomitant pathology in women, etc. Brown discharge may occur when the cervix opens and precedes the appearance of red bloody discharge and the release of amniotic fluid.
This condition is also accompanied by severe cramping pain in the abdominal area and nagging pain in the sacrum. Requires immediate medical attention, hospitalization in an obstetric hospital and delivery. In an extremely rare case, with an immediate response from a pregnant woman, premature birth can be stopped and the gestation of the fetus can be extended as much as possible until it is more ready for independent life.
In the third trimester
The third trimester in 80-90% of cases is accompanied by brown discharge when the mucus plug is released, which is a harbinger of the readiness of the cervix for childbirth. However, the development of pathologies is also possible: premature birth, placental abruption or placental previa. All these conditions, in their course and tactics for managing expectant mothers and unborn children, are no different from those in the second trimester and also require the attention of the woman and medical personnel.
Regardless of the stage of pregnancy
At any stage of gestation, it is possible for a woman to develop or worsen an existing pathology, which is also often accompanied by brown discharge.
Cervical erosion
information It is a fairly common pathology in modern women and in almost all cases it occurs at a young (even teenage) age.
It is a violation of the structure of epithelial cells, ulcerations on the mucous membrane of the cervix. Brown, scanty, slightly spotting discharge during pregnancy occurs after contact of the damaged area with a foreign object (gynecological examination, sexual intercourse). Most often, they are not accompanied by any additional symptoms, disappear after 1 day and do not require medical intervention during pregnancy.
Inflammatory and infectious processes of the genital tract
Any sexually transmitted infections (both sexually transmitted and common bacterial) can cause brown spotting at any stage of gestation. A woman could become infected with an infection many years before conception and be a carrier of the infection, and against the background of hormonal changes and a somewhat reduced immune system, these bacteria became more active, their numbers increased, and a clinical picture of the disease arose.
A man who became a source of infection in a woman could get the disease not only through sexual contact, but also through illness:
- cystitis (inflammation of the bladder);
- prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate);
- urethritis (inflammation of the urethra), etc.
In addition to brown discharge, a woman may be bothered by:
- itching of the genitals;
- unpleasant odor of these secretions;
- viscous consistency;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen and pelvis.
information The most common treatment is antibiotics in the form of suppositories, vaginal tablets or oral tablets, with minimal exposure to the fetus.
Injuries to the vagina and cervix
This condition can occur due to domestic or violent damage. In cases where the injury is minor, the disruption of the integrity of the mucous membrane is insignificant, the discharge may be brown or brown-red, accompanied by discomfort in the area of the injury and itching. Examination by a gynecologist in the speculum also causes discomfort and increased bleeding. Treatment depends on the extent of the damage, ranging from disinfectant solutions to surgery.
Polyps in the vagina and cervix
Benign small neoplasms on a thin stalk can be present in the expectant mother both before pregnancy and can manifest themselves at any time during pregnancy. At the slightest touch to the polyp (sexual intercourse, examination by a gynecologist, etc.), it begins to bleed. This manifests itself as brown spotting and is not accompanied by additional symptoms.
Treatment during pregnancy is generally not carried out, but after delivery these tumors should be removed , because over time the process of degeneration of cells into malignant ones may begin.
What other discharges occur during pregnancy?
Vaginal discharge is an important diagnostic sign of the condition of a woman’s body. During pregnancy, double responsibility appears, so it is especially important to pay attention to all factors that may be informative for such an assessment.
White
White discharge is an option that can be observed during a completely natural course of events. After conception, a mucous plug forms, protecting the uterus from pathogenic microorganisms. During this period, the appearance of whitish discharge is a reflection of a natural process. It should not be accompanied by the appearance of an unpleasant odor or heterogeneous consistency. In this case, we are talking about the development of an infectious-inflammatory process.
Pink
Pink discharge is another possible pregnancy symptom. Their appearance is an alarming factor and often requires drug therapy with the antispasmodic papaverine. The occurrence of such discharge can be caused by mechanical damage to the vaginal mucosa, or the introduction of an egg into the wall of the uterus. Pale pink discharge is observed during exacerbation of thrush.
Any medications for treatment must be prescribed by a doctor
Bloody
The same circumstances that serve as factors for the release of brown secretions lead to the occurrence of bloody discharge.
Yellow
The appearance of discharge with a yellow tint is a clear sign of an inflammatory process. It can be caused by both pathogenic flora and irritation due to wearing synthetic underwear and pads.
Greens
Green discharge under no circumstances can be considered a variant of the norm. This symptomatology is characterized by the addition of other alarming signs: burning and itching in the perineal area, dysuric phenomena - painful, frequent urination. This picture suggests an infectious process.
Comments (3)
- Milana December 12, 2020 1:37 pm
In fact, any discharge is abnormal. I spent the entire pregnancy with my first child and had yellow discharge. And before giving birth it turned out that it was cocci, fortunately I had time to be treated with Metrogyl plus, otherwise I would have given birth in observation. You can't ignore them. - Polina Myazina 21 November 2020 02:39
I periodically have heavy discharge, but not brown, but transparent, without an unpleasant odor. Is this normal? Should I be worried about this?
- Baby-Calendar 21 November 2020 23:44
If you are under the supervision of a doctor, there is no need to worry. Just in case, check with your gynecologist about this issue, but heavy discharge is often a feature of the body, not a pathology.