General information
A cyst that affects brain structures is a benign neoplasm. It can form between the meninges in the right or left hemisphere and be localized in the frontal and temporal parts.
In appearance, the formation resembles a capsule, inside of which there is exudate. It can have different sizes.
The tumor is diagnosed in both children and adults. Treatment is with medications or surgical removal. In some cases, a wait-and-see approach is used, since the cyst may not provoke the development of complications.
Arachnoid cyst in a newborn baby
A formation of this type appears on the arachnoid membrane of the brain, the tissues of which are in close proximity to it. Such a cyst can occur as a result of inflammatory diseases of the newborn’s brain (for example, meningitis), as well as due to hemorrhage as a result of an injury. This pathology requires constant monitoring by a neurologist. In some cases, it can cause complications in the form of epileptic seizures in newborns.
Classification
In medicine, there are two main types of brain cysts: congenital and acquired. In the first case, they are diagnosed in newborns. According to experts, the main reason for their occurrence is a disruption of the process of intrauterine development.
Acquired cysts form at any age as a result of previous injuries or surgical intervention.
In addition, in newborn children, depending on the location of the neoplasm, three types of cysts are distinguished.
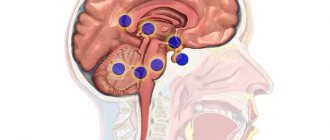
Arachnoid
Localized between the arachnoid membrane and the surface of the brain. It is capable of acquiring significant sizes.
On this topic
- central nervous system
How does a headache with a brain tumor hurt?
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 3, 2020
The main causes are mechanical damage. A feature of arachnoid cysts is rapid growth and a high risk of complications.
According to statistics, this type of brain cyst is diagnosed more often in boys.
Subelendemal
Occurs as a result of circulatory problems in the brain. It is considered the most dangerous, as it causes serious complications.
This type of cyst provokes oxygen starvation of the organ tissues, as a result of which the cells begin to die. Children experience neurological disorders and deterioration in general well-being due to compression of parts of the brain.
Formation of choroid plexuses
A brain cyst in a child, formed from a plexus of blood vessels, can be identified during the period of intrauterine development.
It is considered the safest, as it can dissolve on its own. In addition, formations are detected quite often during pregnancy during ultrasound examination.
In cases where the cyst has not disappeared, this indicates that during pregnancy the woman suffered a disease of an infectious nature.
Headache
A brain cyst in a newborn is nothing more than a tumor, often benign. Its appearance resembles a bubble filled with liquid. In most cases, a fetal cyst is diagnosed while still in the womb. However, by the time of birth it can disappear on its own, leaving no signs behind (the baby meets all standards of physical and mental development). But this happens extremely rarely.
The content of the article:
Why are such formations in the brain dangerous?
Children develop very quickly in the first year of life. Every day they make new movements, make more and more sounds, learn to sit, walk, etc. To assess whether the child is developing correctly, doctors advise seeing a neurologist at 1, 3, 6 and 12 months, who, based on the results of examining the baby, can be the first to determine the presence of cysts in a baby's brain. But it must be said that parents themselves can identify it by carefully monitoring the development and behavior of their baby.
The peculiarity of the cyst is that over time it can increase in size, squeezing the brain vessels and nerve endings. This, in turn, leads to disruption of blood flow and brain activity, as a result of which the child begins to lag behind in mental development.
In pediatrics, there are certain standards when a baby should begin to make the first sounds, roll over, independently hold objects in his hands, sit down, stand up, etc. For example, at 3 months a newborn should already be able to pronounce various sounds, hold his head well and respond to strangers noises. If this does not happen, you need to show him to a doctor. Since this indicates a developmental disorder and may be one of the signals for tumor formation.
Important! A brain cyst provokes pain in the head, as a result of which the baby becomes capricious, often cries and sleeps poorly. These conditions are a serious reason to contact a specialist.
However, it must be said that these are not the most dangerous consequences that this pathology leads to. A cyst in a newborn can cause impaired coordination, decreased quality of vision and hearing. As the tumor develops, more serious complications also arise. One of these is hydrocephalus. This disease is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the ventricle of the brain, which then causes serious disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system.
In isolated cases, such formations can lead to cerebral hemorrhage, which will lead to severe complications, including death. It is for this reason that doctors insist on a thorough examination of newborns up to 3 months, so that pathology can be identified in a timely manner and treatment can begin.
Classification and etiology
A cyst can form either inside the brain or on its surface. The liquid with which it is filled can also be of a different nature. And depending on these factors, such a tumor is divided into 4 types:
- Arachnoid. It is a formation filled with cerebrospinal fluid that occurs between the meninges. There are many reasons for the occurrence of such a cyst in newborns. Here the main role is played by head injuries received during passage through the birth canal. As a rule, such a tumor is detected in a baby 2 to 3 months after birth. In a child in the womb, an arachnoid cyst can form due to the rapid growth of the brain and as a result of infectious diseases suffered by the mother in the first or second trimester.
- Cerebral. This cyst forms inside the brain. It is formed from dead cells and more often due to head injuries received at birth. There are other factors in the formation of a cerebral tumor. Their role may be inflammatory and infectious diseases of the brain, in which massive death of brain cells occurs.
- Subependymal. Such a tumor can be multiple or single in nature. It occurs due to prolonged oxygen starvation (hypoxia), which leads to impaired cerebral circulation and death of brain cells. Such a cyst is usually detected at the age of 3–6 months.
- Choroid plexus cyst. This type of formation is detected during the embryonic stage. The reasons for its formation lie in physiological characteristics.
Clinical picture
When a cyst is small in size, it usually does not manifest itself in any way. If the formation is large, then it begins to compress nearby tissues, to which the body necessarily reacts, demonstrating malfunctions in almost all internal organs.
A tumor in the head of a newborn child can increase after an increase in fluid pressure in the cavity or when the baby’s body is exposed to negative factors that provoke its rapid growth - various infectious and inflammatory processes.
The rapid growth of a cyst can lead to headaches of varying intensity and nature (dull, throbbing, regular, periodic, etc.). In this case, the functionality of the sense organs is impaired - the child experiences a decrease in hearing, vision and smell.
Children whose cyst progresses become anxious, drowsy and moody. Their coordination of movement is impaired and muscle hypertonicity is noted. If the formation is too large, it almost always leads to an increase in intracranial pressure, which manifests itself in the form of tinnitus and strong pulsation in the head.
Important! A cyst of the posterior cranial fossa can cause frequent convulsions, fainting, tremors and disruption of the digestive system in a 3-4 month old baby, resulting in vomiting and regurgitation. Such a formation can even manifest itself as epileptic attacks and paralysis of the limbs!
Diagnostics
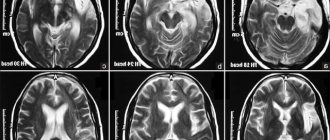
Since in children under 1 year of age the fontanel is not yet closed, the cyst is diagnosed using an ultrasound of the brain. This study is recommended for behavior in newborns up to 3 months who were born prematurely or are at risk of developing cystic formations (for example, the mother suffered severe infectious diseases during pregnancy).
Ultrasound not only reveals the presence of a tumor, but also assesses the general condition of the brain, its blood circulation and disorders that are already present at the research stage. To clarify the diagnosis, diagnostic methods such as CT or MRI can be used.
It is also mandatory to carry out various blood tests that can reveal the level of blood clotting, the concentration of cholesterol in it, as well as the presence of infectious and autoimmune diseases.
Treatment
Cyst therapy depends on several factors - the nature of the formation and the presence of complications in the baby to which it led. The causes of the tumor also play an important role.
Important! If a choroid plexus cyst has been identified in an infant, then the small child does not need special treatment, since tumors of this kind resolve on their own.
Also, therapy is not required if the formation is small and the infant feels well. In this case, the child needs constant monitoring. In other situations, surgical treatment is performed. Unfortunately, this is the only way to cure such a pathology.
Surgical treatment is carried out in several ways:
- Radical. During the operation, craniotomy is performed and the formation is completely removed.
- Palliative. This type of operation is a bypass surgery, during which the tumor is removed through a special shunt system.
- Endoscopic. Removal of the formation is carried out through punctures made in the skull.
If a cyst has been identified in a newborn baby, do not panic. These formations, with timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, do not pose a threat to the baby’s life. After their removal, the child begins to develop and grow in the same way as his peers.
Source: StopKista.ru
By
Causes
Congenital cysts in children and adolescents arise as a result of exposure to external and internal factors. Experts have identified a number of reasons why a cyst can form in the head.
Circulatory disorders
Insufficient blood flow provokes oxygen starvation, as a result, organ cells begin to die.
Over time, cystic cavities form in place of the affected tissues.
Injuries
When blows received during or after birth, damage to brain structures is observed.
Even minor injuries can lead to the formation of cysts and the development of serious consequences.
Inflammatory diseases
A pathological process that affects brain structures leads to dangerous diseases such as meningitis or encephalitis.
Inflammation spreads to large areas of the organ, and healthy tissues die. As a result, cystic formations are formed.
The causes of cysts can also be various changes in the functioning of the central nervous system of the congenital type. A similar process is provoked by difficult pregnancy, constant stress, toxicosis, genetic predisposition, and the use of medications during pregnancy.
Subependymal cyst in a newborn baby
This pathology is considered much more serious than the one we are considering above. In this case, the cyst appears near the walls of the lateral ventricles of the brain, and if it increases in size, it can cause disruption of its structure.
The reason for the appearance of formations of this type can be hemorrhage due to birth trauma, infection of the embryo, asphyxia, etc., or a circulatory disorder in the area of the ventricles of the brain, which leads to the death of some areas of its tissue, in the place of which cysts form. What complicates the situation is that such cysts cannot be treated with drug therapy.
Clinical picture
A cyst in the head in children in the early stages of formation does not show signs. Unpleasant symptoms occur when the formation begins to put pressure on neighboring brain structures.
The clinical picture depends on where the formation is located. In cases where it affects the occipital region, vision deteriorates. Nebula and double vision are noted.
When the cerebellum is damaged, dizziness and loss of coordination of movement are observed. When the cyst is located in the pituitary gland, the body's hormonal levels are disrupted, which negatively affects the physical development of the baby.
Common signs of a cyst in the head include frequent regurgitation, constant restlessness, sleep disturbances, nausea and vomiting.
Diagnostic methods
Cysts affecting brain structures in newborns are detected randomly during diagnosis. Vascular type formations are detected during pregnancy.
To determine the exact location, type and size of the tumor, the specialist prescribes a number of instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods.
Blood tests
Blood tests can reveal changes in hormonal levels, levels of leukocytes, red blood cells and sugar.
The analysis also allows you to determine the presence of an infectious lesion and determine the type of pathogen.
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging is the most informative method for diagnosing neoplasms affecting brain structures.
Thanks to the possibility of layer-by-layer scanning, a specialist can determine the structure and location of the cyst. But the method is used only for children aged 5 years and older.
X-ray examination
The technique allows you to determine the location and size of the tumor. It is considered a fairly safe method of research.
X-rays are used to identify cysts in teenagers.
Neurosonography
A type of ultrasound that is used to diagnose the disease in newborns. The study is carried out through the fontanel, which reduces the ionizing load on the entire body.
The technique is prescribed only for diagnosing pathology in children under one year of age, until the bones of the skull converge.
Features of treatment
In cases where the cyst does not increase in size and does not show symptoms, it does not require medical intervention. Experts use a wait-and-see approach.
When the tumor grows, medications are used or surgical removal is prescribed.
Drug therapy
When diagnosing a cyst, medications are used to restore blood circulation in the brain. Such drugs as Actovegin, Cerebrolysin, Cortexin are used.
If the cause of the formation is an infectious lesion, the doctor prescribes antiviral or antibacterial agents.
The duration of therapy and dosage of medications is determined by the doctor.
Surgery
To remove a cyst in the head in children, radical or palliative surgery is prescribed. In the first case, craniotomy is performed.
On this topic
- central nervous system
What are the dangers of a porencephalic cyst of the brain?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- May 27, 2020
The operation is quite complicated. The disadvantage of the technique is the high likelihood of serious complications such as visual impairment, hearing impairment, decreased intelligence, or deformation of the skull.
Palliative intervention can be performed using bypass surgery or an endoscopic device.
The advantages of the procedures are low trauma and a short rehabilitation period. The methods are used in cases where the cyst is small.
Characteristic features of a brain cyst
A brain cyst that occurs in a newborn is a fluid-filled volumetric structure (spherical cavity), which replaces dead areas of the brain and can be located in any part of this organ. It can be both single and multiple. This pathology is common and is diagnosed in approximately 40% of newborns.
A cavity with fluid located in the brain area can form in the fetus in the womb or after the birth of the child. Sometimes it becomes so small that it does not affect the child’s condition in any way, and the neoplasm itself resolves on its own over time. But, if the cysts are numerous and large in size, children experience delayed psychomotor development, slow growth, poor weight gain, and deterioration in visual function.
Dr. Komarovsky will talk about the causes and treatment of the disease in children:
After childbirth, examination for the presence of a scalp cyst in a newborn is mandatory in the following cases:
- If there was a birth injury;
- If the mother was infected with a herpes infection during pregnancy;
- If the pregnancy proceeded with complications (large fetus size, oligohydramnios).
If the cyst is single and small in size, timely treatment begins to guarantee a favorable outcome. Otherwise, the consequences become irreversible: the child lags behind in physical and then sexual development, suffers from hearing and vision impairment. There is a high risk of disability, and in the most severe cases, death occurs.
Can it develop into cancer?
A brain cyst is a benign formation that does not always require removal. But in the absence of therapy, certain consequences may occur in some cases.
The most dangerous complication is the likelihood of the neoplasm degenerating into a malignant tumor. A similar process is observed under the influence of certain factors. These include exposure to chemicals, trauma to the skull, and genetic predisposition.
The transformation of a cyst into a cancerous tumor is established in rare cases. But, despite this, it requires careful diagnosis, constant medical supervision and therapy.
Consequences
In cases where a cyst in a child’s head enlarges and is accompanied by symptoms, but there is no treatment, certain consequences may occur.
As the tumor grows, it puts pressure on brain structures. As a result, the child begins to lag behind his peers in mental, mental and physical development.
A brain cyst can cause hearing and vision impairment. There is a loss of coordination of movements. In severe cases, children experience convulsive seizures and possible paralysis of the limbs.
According to research results, it is noted that in newborn children complications arise in exceptional cases. Most often, the cyst does not require treatment. Only expectant therapy is carried out.
Forecast
If a cyst is detected in the head of a newborn, the prognosis in case of timely treatment is favorable. Typically, neoplasms are established in the early stages of development. Severe consequences after surgery are observed in rare cases.
Often, a cyst that affects brain structures does not require therapy. In this case, specialists use a wait-and-see approach.
A person can live their whole life with a diagnosed cystic neoplasm. It has virtually no effect on life expectancy.
An unfavorable prognosis is established in cases where the cyst transforms into a malignant tumor. Life expectancy in this case depends on the stage of its development at which treatment was carried out and the characteristics of the course of the pathology.
Birth tumors in infants
The most dangerous for a child during its embryonic development are viral and inflammatory diseases that the mother suffers. It is worth noting that among the many causes of congenital pathologies and brain defects in a baby, one of the main ones are viruses or bad habits of the mother. Due to the extremely strong blood connection between mother and fetus, the child absorbs useful substances from the carrier’s body, as well as bacteria, which in his fragile body can provoke many disorders and diseases.
The second most important reason for the formation of 3 mm cysts in the head of a newborn is considered to be childbirth. Often, during a complicated or extremely painful birth, the baby stops halfway and cannot push the head through for a long time. This period of childbirth is considered to be the most dangerous for the brain, since prolonged compression of brain tissue leads to slow necrosis and death of gray matter tissue, as well as to multiple hemorrhages and lesions. Due to such complicated births, cysts in the head of a newborn of 2 mm or more are registered annually in 30% of all newly born children in the world.
The only effective option to protect your baby during childbirth is to choose a cesarean section instead of a natural birth. However, not every mother agrees to such an operation. A caesarean section requires special permission from a doctor, as well as relatively good health and the absence of defects and heart diseases that can be aggravated by anesthesia.