Diarrhea during pregnancy in the second trimester is a common problem. Sometimes the disorder not only causes discomfort to the expectant mother, but also threatens the fetus. Only a doctor can determine the exact causes and treatment of prolonged diarrhea in pregnant women. But with a mild form of the disorder, the expectant mother can alleviate her condition at home.
For every pregnant woman, the support of her husband is of great importance
Etiology
If your intestines hurt during pregnancy, this may be a consequence of pathological processes such as:
- constipation;
- dysbacteriosis;
- acute food poisoning;
- intestinal flu;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- Crohn's disease;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- proctological diseases, if the rectum hurts during pregnancy;
- exacerbation of existing gastroenterological diseases.
In addition, the intestines hurt during pregnancy due to natural physiological changes in the body during this period, namely:
- hormonal changes in the body of the expectant mother;
- a large amount of progesterone, which leads to relaxation of the muscles of the internal organs;
- compression of internal organs due to the growing uterus.
In addition, it should be noted that pain in the rectum during pregnancy can be a consequence of poor nutrition:
- binge eating;
- incorrectly composed diet;
- habit of eating before bed or while lying down.
There are quite a few factors that can provoke this symptom during pregnancy, and this is not always a consequence of diseases. However, due to the fact that there is no specific clinical picture in this case, you should consult a doctor for advice rather than carry out treatment yourself.
Stomach flu or rotavirus infection
The so-called intestinal flu during pregnancy is very insidious, and everyone from a baby to an old man can catch it. Unwashed hands or stale food, contaminated water, or contact with someone carrying this virus can cause infection. And during pregnancy you need to be extremely careful and take all measures to prevent such a disease.
It is very difficult to identify symptoms, as they can easily be mistaken for toxicosis. They do not pose a particular threat to the child, but for the expectant mother this is fraught with dehydration and weakening of the body. If such a problem occurs, then the pregnant woman needs to adhere to a diet and adhere to the regime. It will take about a week to overcome this virus.
Symptoms
The nature of the clinical picture will depend mainly on the underlying factor.
The collective symptomatic complex can include the following clinical signs:
- rumbling in the stomach, increased flatulence;
- heartburn, belching with air or an unpleasant odor;
- nausea and vomiting - in most cases, these symptoms follow each other, occur after eating, and vomiting does not always bring relief;
- unstable bowel movements - prolonged diarrhea can alternate with constipation of an almost chronic nature;
- During the act of defecation, unpleasant sensations may be present, feces may contain impurities of blood, mucus, and undigested food;
- abdominal pain, the nature and location of which will depend on the underlying factor;
- increase in temperature to low-grade levels, and in some cases to high levels (38-39 degrees);
- decreased appetite;
- pallor of the skin, general deterioration of health;
- weakness, increasing malaise.
A similar clinical picture occurs in almost any gastroenterological disease, so it is strongly not recommended to carry out treatment on your own in this case. It is even more dangerous to take any medications, since you can cause irreparable harm to the baby.
Important! If there is pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy, you should urgently consult a doctor, since such a symptom may be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy, threatened miscarriage, placental abruption and other extremely dangerous disorders during pregnancy.
Pain in the lower abdomen in the second trimester of pregnancy: normal or pathological?
What explains pregnancy pain in the second trimester?
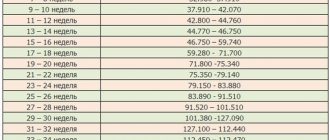
From the 13th to the 28th week, the level of progesterone in the body remains in the range of 71.5–303.1 units. This is several times higher than its concentration before conception, although in the first weeks it is no longer so high. Progesterone is a pregnancy hormone. At this time, it still actively contributes to the successful gestation of the fetus: under its influence, the uterus enlarges and stretches, and its muscle tone decreases. Such regulatory functions of the organ can provoke a slightly nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
By the end of the 2nd trimester, the baby’s weight reaches 650 g. Along with this indicator, others also increase: the baby reaches 9 cm in length. Together with the placenta and the volume of amniotic fluid, they stretch the walls of the uterus, causing it to move deeper and rise slightly. At the same time, muscles and ligaments are stretched - this is another cause of discomfort. A sprain of the round ligament, which supports the organ, is characterized by short sharp attacks, and the muscle fibers are characterized by longer-lasting pulling sensations.
Intestinal dysfunction is a common cause of pain during pregnancy in the second trimester. Constipation and flatulence, which almost all expectant mothers experience, can be caused by various factors.
- Poor nutrition. Excessive consumption of legumes, eggs, milk, cabbage, kvass and carbonated drinks. Lack of porridge. Abuse of sweets.
- Pain worsens against the background of chronic colitis (inflammation of the intestinal mucosa) and dysbiosis (imbalance of intestinal microflora).
- Another cause of discomfort is the growing uterus, which puts pressure on regional organs, including the intestines. Not only does his motility decrease under the influence of progesterone, the uterus compresses his walls, interfering with the natural movement of feces.
Most women associate painful sensations with physical activity: fast walking, forced bending, turning the body - everything related to professional activities and daily activity.
Incorrect body position during rest, sleep, and sedentary work.
Quite often, women who have previously undergone surgery experience abdominal pain during pregnancy in the second trimester. This is optimal for mature mothers who gave birth by caesarean section.
How to deal with pain?
The cases described above do not require drug treatment.
Usually it is enough to rest, give yourself a light massage with circular stroking movements, and drink warm tea. Things are a little different with flatulence and constipation. Enemas, suppositories and castor oil, laxatives based on rhubarb, buckthorn and senna are strictly prohibited during pregnancy. To alleviate the condition and prevent it, you need to reconsider your diet: replace regular bread with whole grain bread, eat a spoonful of flaxseed in the morning on an empty stomach, drink more liquid. And also, if possible, do gymnastics.
When should I see a doctor?
Pain during pregnancy in the second trimester can be symptoms of gynecological diseases. There may be an exacerbation of chronic forms due to weakened immunity or the appearance of new ones for the same reasons.
Another reason to immediately consult a doctor is excessive discharge. Yellow or greenish leucorrhoea with an unpleasant putrid or sour odor may indicate the addition of sexually transmitted infections. If the discharge is brown or scarlet, there is a suspicion of a threat of termination of pregnancy.
Diagnostics
The first step is a physical examination of the pregnant woman. In this case, you will need to consult a gynecologist, gastroenterologist, or nephrologist.
During the initial examination, the doctor should:
- find out the full clinical picture;
- collect personal and family history;
- review the patient's medical history.
In addition, they carry out:
- laboratory tests - general and biochemical blood tests, general stool analysis, general urinalysis;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- in particularly difficult cases, an MRI is performed.
Endoscopic examinations during pregnancy are strictly prohibited, as this can harm the baby.
Treatment
The course of therapeutic measures will be aimed at eliminating the root cause, if any. The use of medications is kept to a minimum, since in the late stages of pregnancy, as in the early stages, they are contraindicated. In the most extreme cases, the doctor may prescribe mild painkillers and antispasmodics. If diarrhea occurs, astringents are prescribed.
The basis of treatment is the normalization of nutrition and daily routine.
Regarding the first, the following recommendations can be made:
- nutrition should be balanced;
- it is necessary to exclude fatty, fried, salty foods, sauces and marinades;
- sweet carbonated drinks, packaged juices and similar liquids should be excluded;
- optimal culinary processing - baking without fat, steaming, stewing, boiling;
- meals should be small and frequent - the time interval between meals should be at least two hours;
- Be sure to have a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals in your daily diet.
In addition, a pregnant woman needs to take daily walks in the fresh air, avoid stressful situations, and undergo regular medical examinations.
The above nutritional recommendations can also be used as a preventive measure. The prognosis in most cases is favorable - timely correct therapy eliminates the development of serious complications.
Self-medication in this case is excluded, and the use of traditional medicine is possible, but only on the recommendation of a doctor. You need to consult a doctor in a timely manner, as soon as the first clinical signs begin to appear.
Nagging pain in the abdomen and intestines, bloating, nausea and bowel irregularities accompany most pregnancies - but they do not always indicate a normal course. Atypical abdominal pain in an expectant mother may indicate various diseases or pathologies - from dysbiosis to serious inflammation, and even the threat of miscarriage. So there is no way to ignore the pain.
Is diarrhea dangerous during pregnancy?
Treatment for loose stools during pregnancy depends on identifying the cause that provoked the disease. In any case, if diarrhea appears at this stage of pregnancy, the woman should consult a doctor.
In some cases, diarrhea is a short-term phenomenon caused by nervous overstrain or a minor error in nutrition.
Then, in order to cope with this problem, the expectant mother needs to calm down or make changes to her diet.
The need for relaxation therapy arises when a woman is under stress for a long time during pregnancy.
Then she may experience diarrhea regularly. This can negatively affect the balance of hormones in her body. What to do in this case?
A psychotherapist will help the girl return to a state of psychological comfort at this time. During psychotherapy sessions, the expectant mother will be able to determine the cause of her worries, as well as find a way out of a depressive state.
If a woman’s prolonged diarrhea is accompanied by symptoms such as fever, nausea, dizziness and abdominal pain, there is a need for urgent hospitalization.
If you have an upset stomach, it is important to follow a diet
Only a doctor can determine how to treat diarrhea. Much depends on the cause of this phenomenon. If diarrhea is caused by any disease, then it is important not only to eliminate the problem of loose stools, but also to treat the underlying disease. This is the only way to minimize the risks of subsequent complications.
If diarrhea is not accompanied by alarming symptoms, then it can be dealt with at home. Diet, safe medications, and traditional medicine methods will help. If the expectant mother has doubts about her health, if she has frequent and profuse loose stools, vomiting and fever, she should definitely consult a doctor. The main thing is not to harm yourself and the baby by self-medicating.
An intestinal disorder that is not a symptom of an illness should be tried to be eliminated with the help of diet. This is the easiest and safest way. Sometimes adjusting your diet is enough to get rid of the problem, and you won’t have to resort to medication. It is important to follow simple rules:
- Refuse food for 10 hours. It is necessary to give the intestines a rest; overloading it when upset is strictly prohibited - you can worsen the situation. The right decision would be to take a “break” for at least 10 hours. If you feel hungry, you can satisfy it with crackers and tea.
- Drink plenty of fluids. To replenish fluid loss, you need to drink at least two liters of still water. You can drink unsweetened herbal tea. It's better to brew it lightly.
- Correctly plan the next day's diet. The next day, you can eat chopped boiled meat (lean), oatmeal, buckwheat, rice, and low-fat cookies. Raw vegetables and unheat-treated fruits, fermented milk products, fried and salty foods, and smoked foods are strictly prohibited. Taboo – strong tea, coffee, sweet carbonated drinks. You should be careful with rich broths: they can make you weak.
As a rule, the condition improves after just a few hours of fasting. But this is only on condition that the expectant mother drinks a lot of fluids to replenish losses. Preparing the right diet for the next day will consolidate the result. It is recommended to follow a gentle menu for a couple more days so that intestinal function returns to normal.
If diarrhea does not go away after a day, blood is visible in the stool, vomiting and fever appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Delay can cost your child's health.
Medicines in an “interesting situation” should be treated with caution. The active substances contained in medications can adversely affect the child's condition. It is best to discuss taking medications to relieve diarrhea with your doctor. There are only a few drugs that pregnant women can use without fear of risks:
- "Regidron". The action of the drug is aimed at restoring the water-salt balance in the body, which is disturbed by diarrhea. The product prevents dehydration and prevents beneficial substances from being “washed out”.
- Sorbents. Activated carbon, Atoxil, Smecta, Enterosgel are considered safe. The drugs perform a cleansing function. They are especially effective if diarrhea is caused by poor quality foods.
If you have additional symptoms, you need to consult a doctor about what you can do for diarrhea. For diarrhea, drug therapy can be different, much depends on the cause that provoked this condition. At the turn of the trimesters (26th – 27th week) you should not experiment with self-medication: it is believed that during this period the fetus is more exposed to danger than usual.
Traditional methods
Although the second trimester is considered a safe time, it is better not to take risks with alternative medicine during this period. It is advisable to discuss the possibility of turning to traditional methods with your doctor. However, there are three safe recipes that will help get rid of diarrhea. They can be used only when diarrhea is a one-time occurrence and there are no threatening symptoms.
- Infusion of pomegranate peels. You need to grind 15 g of pomegranate peels using a blender. Pour a glass of boiling water over the raw materials and let it brew for half an hour. You need to take a tablespoon three times a day.
- Rosehip and blackberry decoction. Grind the rose hips. Mix them with blackberry leaves in a 1:1 ratio. Pour two tablespoons of the prepared mixture with a glass of boiling water. The product should be boiled in a water bath for 15 minutes, and then left for half an hour. The strained decoction should be drunk a day, after dividing the volume four times.
- Rice water. To prepare the decoction, you need to pour two teaspoons of washed rice with 500 ml of water. Cook the mixture for an hour, stirring regularly. Then you need to strain and take the liquid three times a day.
Expectant mothers should remember that diarrhea in the second trimester can be dangerous. To prevent the condition, you need to avoid stress, monitor the quality of food, and not drink pharmacological agents (even if they are vitamins) without a medical prescription. If diarrhea does not stop for more than a day, or there are alarming symptoms, then you should immediately consult a doctor. Delay, just like illiterate self-medication, can cost the baby’s health.
- Regidron;
- Smecta;
- Activated carbon;
- Entergosgel.
It is important to understand that these drugs can be used only after thoroughly studying the instructions, and only when the diarrhea is not severe and does not cause much concern. In the serious cases described above, self-medication is strictly not recommended.
- Remember personal hygiene standards.
- Take prenatal vitamins.
- Eat right, focusing on fresh and healthy foods.
- Eat only at home, refusing to visit cafes and restaurants with dubious cuisine.
Diarrhea during pregnancy can be a real test of endurance. But all's well that ends well. And by taking simple measures to eliminate the problem of diarrhea, you can continue to enjoy the anticipation of the birth of your baby. Be healthy!
Pregnant women have to bravely endure all the hardships and deprivations of their current condition - from mood swings and, to put it mildly, strange taste preferences to bowel disorders in the form of constipation and diarrhea. It is the latter that will be discussed in the information below.
You are invited to find out why diarrhea may appear during the second trimester and the entire period as a whole, whether it is dangerous, how to cope with such an unpleasant condition and whether its occurrence can be prevented.
Why does my intestines hurt during pregnancy?
There are many reasons for the appearance of different types of pain in the intestinal system in the expectant mother:
- during conception and the formation of the fetus, the entire female body is reconstructed thanks to the hormone progesterone (it is also called the “pregnancy hormone”) - it stretches the walls of the stomach and places it in the required position, preparing the place for the future baby;
- immediately after conception, the egg begins its “journey” into the uterine cavity, which is almost always accompanied by characteristic colic in the intestines;
- The general hormonal changes in a woman’s body always affect the state of the intestinal system, because the main “restructuring” occurs precisely in the abdominal cavity - the place where the child will develop: hence the nagging and stabbing pain in the abdomen, bowel movements, etc.
Physiological reasons
Problems with the intestines also arise due to the rapid growth of the fetus - the uterus enlarges, stretches, and puts pressure on surrounding organs.
How the intestines hurt during pregnancy - symptoms of the disease
When an expectant mother has a stomach ache in the intestinal area, you need to find out exactly what sensations the woman is experiencing. Thanks to a detailed analysis, the main signs of certain pathologies associated with the stomach are revealed. Perhaps the cause of discomfort is excessive gas formation in the stomach or changes in hormonal levels.
When experiencing colic in the stomach, you need to pay attention to the following nuances:
- Nature of the discomfort: spasms or pain.
- Severity: mild, moderate or acute colic.
- Location of the lesion: around the navel, in the hypochondrium, lower abdomen, in the side.
- Frequency: sharp short stabbing feelings or constant.
- Duration: Short and sharp or long lasting.
To understand why a pregnant woman’s stomach hurts, you need to study both external and internal manifestations. It is important to determine what exactly causes the pain and how to get rid of the discomfort without harming the child.
Colic in pregnant women can be caused by the following reasons:
Physiological aspect
During pregnancy, both in the early and late stages, hormonal changes occur in the body. The level of estrogen and progesterone increases, because of this the muscles of the internal organs relax and cause slight discomfort.
Incoming food begins to be absorbed worse; due to the stress state in the woman’s body, the muscles of the organs contract, this causes cramps and cramps in the abdomen, either on the right, then on the left, or in the epigastrium. The stomach will stop hurting after hormonal levels normalize. In this case, it is better to consult a gynecologist and take a vitamin complex for pregnant women.
Miscarriage
Aching, pulling sensations with muscle spasms may indicate premature birth or miscarriage. What exactly happens in the body depends on the trimester.
During premature birth, a girl experiences the following symptoms:
- bleeding from the vagina;
- aching pain radiating to the lower back;
- a sharp increase in uterine tone;
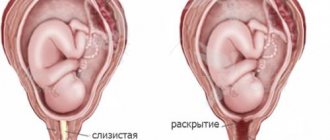
- slow dilatation of the cervix.
If these symptoms are not treated promptly, a miscarriage may occur. If pregnancy is terminated, fragments of the fetus or placenta may remain in the uterus, which increases the risk of thrombohemorrhagic pathologies and infection of the mother. Therefore, if you have nagging pain in the lower abdomen, you should contact your doctor and undergo an examination in order to protect your health and the fetus.
Placental complications
In case of injury, toxicosis or viral diseases, parts of the placenta may move away from the uterus. The child begins to be in danger, as the blood supply and supply of nutrients are disrupted. A woman develops the following symptoms:
- Acute pain in the uterine area.
- Internal bleeding opens (can be either weak or pronounced).
- The condition of the fetus is disturbed.
If the placenta begins to exfoliate in the center, then there will be no external bleeding, since the blood discharge penetrates the walls of the uterus. Such abnormalities usually occur in the initial stages of pregnancy. If treatment is not started, the pathology will progress and the fetus will die in the womb in the first weeks of development.
Intestinal diseases
If you have pain in the stomach area, the organ itself may be bothering you. This is associated with inflammatory or infectious pathologies. In addition, poor nutrition in pregnant women often disrupts the functioning of the digestive tract, which is characterized by colic in the abdominal cavity. If the expectant mother had gastritis or an ulcer before pregnancy, this can also cause the development of the disease.
Chronic inflammation is observed only in the presence of colitis or Corn's disease. Infectious lesions appear due to the ingestion of viruses and E. coli.
Problems with the organ make themselves felt by the following symptoms:
- stitching pain in the navel and sides;
- rumbling and cramping in the stomach;
- diarrhea;
- discharge of mucus, blood or bile formations along with excrement.
If the intestinal mucosa is irritated, the stool will be normal without additional discharge, and discomfort does not appear at night. With infectious lesions, girls develop a fever and diarrhea.
Inflammatory processes
Pain syndrome in the lower abdominal cavity most often indicates inflammatory processes in the female genital organs.
In this case, the following symptoms appear:
- drawing dull unpleasant sensations in the sacral area radiating to the rectum;
- a sharp increase in temperature.
- painful feelings when examined by a gynecologist and during palpation of the abdominal cavity.
Acute manifestations in the abdominal cavity may indicate peritonitis, a dangerous inflammation of the peritoneum. Therefore, at the first signs of ill health, treatment must be started immediately to avoid complications.
Even more interesting:
Causes of sores on the labia
Which doctor should you contact?
Of course, a woman during pregnancy (especially if this is her first pregnancy, or if there are any complications) should constantly maintain contact with a doctor and regularly undergo the necessary tests - this will help prevent many diseases and make sure that the baby in the womb is developing correctly, and his there is no threat to health.
If discomfort in the stomach occurs that is not associated with natural physiological causes, a pregnant woman must:
- Visit a gastroenterologist: he may prescribe manometry (a test that reveals the ability of the esophagus to contractile activity), spectrophotometry and various other diagnostic studies of the esophagus.
- Donate blood for a general analysis, feces and urine for the presence of infection in the genitourinary system.
- In case of late toxicosis of a pregnant woman, accompanied by severe stomach pain, you will need to visit an endocrinologist - perhaps this condition is the result of abnormal levels of hormones (including sugar) in the blood.
- In case of stomach pain resulting from food poisoning, strong activity of the child and other physiological reasons, you must first contact your leading therapist - he will analyze the intensity of the pain, identify the root cause of its occurrence, and prescribe appropriate treatment (correction of nutrition, daily routine, etc. .).
- If you have stomach pain associated with diseases of the genitourinary system, first of all contact an obstetrician-gynecologist: in this case, you will need to submit urine and a smear for microflora examination, as well as undergo an additional ultrasound examination.
What are intestinal pains?
It would seem that pain is pain, however, intestinal pain can be different, and the cause and method of treatment depend on what particular case the woman is faced with.
We also recommend reading: Pain in the vagina during pregnancy
Cramps in the intestines
With spasms, the pain changes with a change in posture, with every movement, and even with sneezing. As a rule, after visiting the toilet there is a temporary improvement in the condition. In this case, the painful sensations are associated with excessive gas accumulations, as well as with the problem of inconsistent stool.
With pain in the lower part, we can talk about more serious problems - diseases of the intestines or abdominal cavity. This could be appendicitis, ulcers, liver or kidneys, hernia, as well as various inflammatory processes occurring in the body. In addition, in women it is fraught with inflammation of the reproductive system.
Another type of pain, which usually radiates in the lower abdomen, can signal intestinal obstruction and even volvulus. In men, such pain is accompanied by painful urination and indicates a problem associated with prostate function.
At a time when a woman carries a baby under her heart, her stomach becomes an object of special attention. As soon as she senses any deviations from the norm, she immediately sounds the alarm. And here, the main thing is not to panic, but to visit a doctor in a timely manner in order to understand whether these are just spasms or something serious.
If we are talking about abdominal pain in a pregnant woman, then it can be classified as obstetric or non-obstetric
Obstetric pain:
- when there is a threat of interruption;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- placental abruption.
Non-obstetric pain:
- problem with the digestive tract;
- sprain of abdominal ligaments and muscles;
- various surgical pathologies.
If we are talking about the risk of losing a child, a woman feels a characteristic nagging or constantly aching pain in the lower back and lower abdomen. There may even be a discharge mixed with blood.
An ectopic pregnancy is characterized by sharp pain, sometimes going away, sometimes appearing with renewed vigor. The pain can be so severe that a woman can even lose consciousness. However, it also happens that there is practically no pain, and bleeding is barely noticeable. Then the woman may not be aware of her problem for a long time. The fallopian tubes usually rupture between eight and twelve weeks.
If premature placental abruption occurs, sharp pain inside the abdomen may appear, internal bleeding and even hypoxia may occur. The body of a pregnant woman goes through difficult trials. Hormones are raging, the body is being rebuilt literally brick by brick. Constipation, dysbacteriosis, flatulence, vomiting - you name it, and most of this is considered within the acceptable norm. The child grows in the mother’s womb day by day, as a result of which it inevitably affects all the internal organs of the mother, causing discomfort and even pain. It is during this period that many chronic diseases worsen, from problems with stool to appendicitis.
The body of a pregnant woman goes through difficult trials. Hormones are raging, the body is being rebuilt literally brick by brick. Constipation, dysbacteriosis, flatulence, vomiting - you name it, and most of this is considered within the acceptable norm. The child grows in the mother’s womb day by day, as a result of which it inevitably affects all the internal organs of the mother, causing discomfort and even pain. It is during this period that many chronic diseases worsen, from problems with stool to appendicitis.
You should know that, no matter where and how the stomach hurts, until the exact cause of what is happening is established, in no case should you resort to any physical influence. Even a simple harmless massage can lead to internal bleeding.
We also recommend reading: Glucose tolerance test during pregnancy
It happens that the stomach hurts simply because a woman has eaten too much and any pressure on it can provoke excessive formation of gases, as well as difficulties with digesting food. In addition, a woman may face the problem of lactose intolerance. If the problem was due to the above reasons, then after some time, all the discomfort will simply go away.
It happens that a woman does not even fully understand what and where she is hurting. Pain in one place can be felt on the completely opposite side. For example, with pneumonia, many patients complain of pain in the upper abdomen, although it would seem that there is no connection here.
Pain in the upper abdomen
Pain in this part of the abdomen, as well as in others, does not cause very pleasant sensations. But in order to get rid of them it is necessary to find the cause of what is happening. Regarding this part of the abdomen, the most common reason is that the shrinking uterus puts pressure on the liver and gallbladder. All this provokes a malfunction in the process of bile secretion.
Many expectant mothers experience discomfort due to the baby’s movements, especially if we are talking about a multiple pregnancy or a large child. As a result of the pressure on the internal organs, a woman loses her appetite, suffers from heartburn, bloating and even vomiting; this is what many call toxicosis.
Pain in the left side of the abdomen
If the cause of pain on the left side is in the intestines, then most likely this is due to problems with stool - diarrhea or constipation. Then there may be blood in the stool, and the temperature becomes higher than normal.
If the cause of pain on the left side is in the intestines, then most likely this is due to problems with stool - diarrhea or constipation. Then there may be blood in the stool, and the temperature becomes higher than normal.
The stomach can also respond on the left side after poor nutrition, drinking alcohol or taking a strong antibiotic. However, as a rule, the stomach hurts in this part not very much, but for a long time. In this case, vomiting and attacks of nausea are also possible.
In addition, a hernia may appear in this part, then the pain may spread and partially affect the chest. It should be noted that the diagnosis of “hernia” cannot be made by anyone except a specialist, and in no case should you delay in solving this problem. Therefore, at the first suspicion, you should immediately go for examination to a professional. Many diabetics, smokers and alcohol abusers suffer from pain on the left side.
Pain in the right side of the abdomen
Pain in this part of the abdomen is usually associated with the functioning of the liver, gallbladder, pancreas and duodenum. Problems with these internal organs can occur in the shoulders (biliary tract), back (duodenum or pancreas), and in men, in the ovaries (kidneys). In addition, appendicitis, right kidney and genitals may hurt here.
Based on the above, it is clear that there are enough reasons for discomfort in the intestines in pregnant women. Not all of them are associated with any serious diseases, and some do not even require special treatment. However, if we are talking about any pain that does not stop for a long time, you should definitely see a specialist. In addition, you should immediately visit a doctor if intestinal problems are accompanied by additional symptoms, such as fever, vomiting, or problems with stool. It is not recommended to use any medications or traditional methods of treatment without a doctor’s recommendation.
What to do: bowel treatment
When the symptoms and nature of stomach pain indicate a certain ailment, and a doctor’s examination and tests confirm the diagnosis, optimal treatment is prescribed, which takes into account the nature of the pregnancy, the presence of additional complications and other factors.
Approved drugs
Drug treatment of intestinal pain in a pregnant woman is always gentle - antibiotics are prescribed only in extreme cases.
Approved medications that relieve stomach discomfort include:
- adsorbents (white and black activated carbon, Espumisan, etc.);
- enzymes - Creon, Cisapride, Mezim, Metoclopramide, etc.;
- drugs that improve intestinal microflora - Hilak forte, Biosporin, Mutaflor, Lactium, etc.;
- some herbal preparations are based on extracts of chamomile, coriander, mint, caraway, and St. John's wort.
When choosing a drug for treatment, many factors should be taken into account: individual intolerance to the components, the nature of the intestinal disease, the composition of the vitamin complex that the pregnant woman takes - therefore, it is highly not recommended to prescribe the dosage and course of treatment yourself.
Nutrition correction
Nutrition correction will depend on where and how exactly the stomach hurts:
- in case of gastritis and increased acidity of the stomach, foods high in acid should be excluded from the diet: fermented milk products, canned foods and pickles, fried and spicy foods;
- in case of flatulence, heavy foods, legumes, and foods high in starch should be avoided;
- To get rid of heartburn, you will need to eliminate carbonated drinks, some juices and spices, and to improve the microflora, add natural yoghurts with healthy enzymes to the menu.
Of course, there is no need to completely give up the listed products (only if the intestinal disease is not in a progressive form), but you will definitely have to reduce the consumption of such products. And, of course, nutritional correction, as well as the choice of medications, must be agreed upon with a doctor.
Prevention
Most diseases are easier to prevent than to treat - and intestinal discomfort during pregnancy is no exception.
To minimize the risk of complications in the intestinal system, it is necessary:
- create an optimal diet, do not overeat, avoid junk food that can irritate the intestinal walls;
- prevent the decline of the immune system: include more seasonal vegetables and fruits in the diet, do not forget about vitamin preparations;
- wash vegetables and fruits thoroughly before eating;
- subject food to proper heat treatment (do not eat rare steaks, half-cooked mushrooms, etc.);
- drink only high-quality water - mineral or boiled (it is better not to drink water from springs or wells during pregnancy);
- avoid stressful situations, spend more time in the fresh air, ventilate the room before going to bed;
- avoid injury during sexual intercourse;
- exclude any overexertion or heavy physical activity.
Pain in the intestines in pregnant women occurs quite often, and the causes can be of a different nature: from natural physiological to dangerous, therefore, if uncharacteristic acute pain appears, changes in stool, general weakness or high temperature, you should urgently consult a doctor.
Prevention of intestinal diseases, proper nutrition, a healthy lifestyle and a positive attitude will help you bear a healthy baby.
Intestinal pain during pregnancy is a symptom familiar to many women. The cause of the problem is a hormonal imbalance in the body, a change in hormonal levels - especially in the early stages. At the end of the second and third trimesters, the intestines hurt mainly due to the pressure exerted by the growing uterus. Symptoms require attention, the problem can be serious, and incorrect diagnosis in the early stages risks missing a dangerous change. It is important to understand where the sensation is localized and what organ it is associated with.
Digestive disorders in the first trimester
Often in the early stages women have stomach and intestinal pain. During pregnancy, this phenomenon is considered normal. After all, it is at this moment that a woman’s nutrition radically changes. Due to toxicosis, expectant mothers strive to eat something unusual. More salty foods and spices appear in the diet. Women have a sweet tooth: they can spend hours eating cakes and chocolate.
This diet certainly affects digestion. The lack of fiber and indigestible fibers inhibits intestinal motility. In addition, progesterone is actively produced at this time. It relaxes muscles, including the intestines. Expectant mothers begin to experience constipation, fermentation increases and the amount of gas increases. Often, bloating is noticeable to the naked eye.
This problem can only be treated by correcting the diet. Women should give preference to vegetables and fruits and eat more greens. Distribute your daily protein and fat intake correctly. Avoid empty carbohydrates. If you have a tendency to constipation, then it is permissible to use mild laxatives, for example Duphalac.
Symptoms and problems
When the intestines or stomach hurt during pregnancy, a woman may think that there is a threat to the unborn child, and termination of pregnancy may occur. A danger to the baby is indicated by strong cramping sensations, during which blood is released. What to do if a pregnant woman experiences these symptoms? You must call an ambulance immediately.
Ordinary intestinal discomfort should not be associated with high risks; the body goes through a restructuring, which can cause stomach pain and colic. When planning to visit a doctor, it is necessary to talk about symptoms that are obstetric and non-obstetric in nature. Typical problems in pregnant women include:
Causes
Pain in the intestines in a pregnant woman can occur for the following reasons:
- Pressure of the uterus on the intestines.
- A gut disorder caused by bacteria or viruses often has pain as one of its symptoms.
- Non-infectious intestinal diseases.
- Intestinal colic also causes pain and discomfort in the intestinal area in a pregnant woman.
Such diseases and conditions often cause not only pain, but also nausea, vomiting, headaches in a pregnant woman, and sometimes this even becomes the basis for termination of pregnancy. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor at the first signs of pathology, and not try to treat the problem yourself, since the body of a pregnant woman requires a more attentive attitude towards itself.
Pressure of the uterus on the intestines
Since the intestines are located near the uterus, and it grows larger every month, this creates pressure. The intestines are pinched, stagnation of feces and gases is formed. This leads to pain and constipation. Intestinal problems for this problem most often begin in the third trimester, but can appear already in the second, especially if a woman is carrying several babies.
Causes of colic in pregnant women
The future child puts forward new requirements for the diet. Whims arise, food preferences change dramatically, which irritates the digestive tract. Not having time to separate the food received, sweet and salty, fruit and dairy, incompatible things, the body reacts with intestinal disorders.
Another risk factor is hormonal changes. Progesterone relaxes smooth muscles, slows down the digestive tract, causing stagnation and pain. Factor number two is the growing uterus, squeezing the internal organs.
The main method of prevention to avoid treatment of the gastrointestinal tract is adherence to the diet and regimen. It is necessary to eat regularly without overeating, in small portions, excluding things that irritate the intestines. Alcohol, coffee, spices are excluded, salty and sweet foods are taken during periods of normal functioning of the tract. To avoid becoming a victim of stagnation, you need to maintain a positive mood, walk, and move moderately.
Diarrhea and intestinal disorders
It is worth understanding that diarrhea and constipation are frequent companions of pregnancy; the obstetrician usually warns expectant mothers. Constipation occurs more often, diarrhea is less common and more dangerous. The very type of disorder signals a possible infection or poisoning. Pain on the left or right, accompanied by loose stools, indicates a lack of enzymes, worms, problems with microflora, infections, and nervous disorders. A symptom that does not go away within two to three days is a reason to consult a doctor. Diarrhea accompanied by pain, fever, or a sharp deterioration in health is a reason to call a specialist to your home.
Short-term disorders, periodic pain of low intensity, one-time attacks of diarrhea, nausea are a relatively normal phenomenon caused by temporary disruptions in the functioning of the body. There is no point in worrying about this.
Diets to normalize the gastrointestinal tract
Diets help normalize the condition of the intestines and stomach and digestive processes. By adhering to them, a woman minimizes risks to health and well-being. We are not talking about strict diets; it is necessary to adjust the diet in a minimal way.
By consuming foods rich in fiber, it is possible to eliminate stagnation in the intestines, ensuring its complete cleansing. Fruits and vegetables, nuts are an essential part of the diet for a pregnant woman. Bran and baked potatoes help soften the intestinal walls and increase permeability. Nutritional supplements should be taken with caution or completely avoided throughout pregnancy.
Pectin soothes abdominal pain and relieves nausea. It is found in currants, rose hips, papaya, and citrus fruits. You should not take viburnum, as the risk of miscarriage increases. In the early stages, drink milk with caution, choosing fermented milk products - to avoid the occurrence of pain. You need to drink a lot of water, up to 8 glasses a day - with its abundance, the intestines work more actively, quickly cleansing themselves. It is wise to exclude caffeine.
Constipation and risks
Some women ignore constipation that is not accompanied by pain. This phenomenon is common for pregnant women - progesterone slows down the intestines, the uterus compresses the organ. Constipation leads to clogging of the body with toxic substances, which is harmful for mother and child. This symptom also leads to cracks, hemorrhoids, and tumors. If you have problems with stool, measures must be taken. If you pass blood in your stool, you should visit a gynecologist.
You should not use medications that relax the intestines and stimulate bowel movements. They also stimulate the uterus, causing it to contract, which can lead to miscarriage.
Irritable bowel syndrome in pregnant women
Many people know firsthand that chronic diseases can worsen during pregnancy. These include irritable bowel syndrome. These are specific intestinal disorders of a functional nature, which are accompanied by pain and problems with stool.
Causes of the disease
The reasons why irritable bowel syndrome manifests itself are not fully understood today, but there are some factors that suggest that the disease develops from the following criteria:
- stressful situations;
- excessive consumption of fatty and spicy foods, carbonated and sweet drinks;
- lack of fiber in the diet;
- constant overeating;
- genetic predisposition;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- hormonal imbalances.
Symptoms of irritable bowel
In expectant mothers, this syndrome can be calculated by the following signs:
- pain, mainly in the lower abdomen, subsiding after bowel movements and release of gases;
- alternating diarrhea and constipation, which can occur several times a day or once or twice a week;
- altered consistency, color, or amount of stool that is hard, watery, with mucus, or hard lumps;
- constant rumbling in the stomach;
- feeling of incomplete bowel movement, frequent desire to defecate;
- unpleasant bloating after eating and causeless flatulence.
If irritable bowel syndrome is present for a long time, about a month, for example, then we can conclude that the pregnant woman is suffering from a progressive stage of this disease. Symptoms can also include a general condition, such as increased fatigue, causeless anxiety, migraines, painful urination and discomfort during sexual intercourse, unpleasant taste in the mouth, insomnia, and irregular heart rhythms.
The need for additional research may be appropriate if there are signs indicating that irritable bowel syndrome is causing serious pathologies:
- unexplained weight loss;
- discharge with blood clots from the anus;
- swelling in the abdomen and hardening of the anus;
- development of anemia.
Diagnosis of the disease
To be sure that a pregnant woman has irritable bowel syndrome, a number of tests should be performed, namely:
- coprogram;
- general blood analysis;
- blood test for celiac disease;
- examination using colonoscopy;
- if necessary, computed tomography.
Treatments for Irritable Bowel Syndrome
After a full examination and a series of tests, the specialist must prescribe treatment. It is better to forget about self-medication as a method right away, because your health and the health of your baby is more important than any lotions and infusions.
Correct recommendations and compliance with all prescriptions will help eliminate problems such as irritable bowel syndrome:
- Firstly, it is a proper balanced diet. You need to eat 5-6 times a day in small portions. And since some people suffer from intolerance to certain foods, they should be completely excluded, as well as chocolate, dairy products, coffee and sugar substitutes. Therefore, listen carefully to your body when planning your diet.
- Secondly, leave stress and worries in the past. Breathing exercises will help you cope with this.
- Thirdly, exercise. Active mom, active baby. Sufficient physical activity is the best way to prevent irritable bowel syndrome. Ideal in this case are yoga for pregnant women, swimming, and for more active ones – race walking and long walks.
Please note that in case of severe gas formation, the use of drinking straws and chewing gum is excluded, as they contribute to excessive entry of excess air into the intestines when swallowed.
Experts also resort to drug treatment. But the use of medications is necessary only in emergency cases, as there is a risk to the health of the expectant mother and her child. The best drugs to suppress irritable bowel syndrome are antispasmodics, laxatives, antidiarrheals, and antidepressants.
Preventive measures for the disease
Irritable bowel syndrome requires preventive measures, which include not only a balanced diet and exercise, but also a positive psychological atmosphere that gives positive emotions and completely eliminates anxiety and fear. Stress and anxiety are contraindicated for a pregnant woman, especially in this problem. Moreover, during severe anxiety or a stressful situation, a portion of adrenaline is released into the blood, and this hormone can negatively affect intestinal motility. Therefore, calm and once again, calm.
So, if you find signs that are similar to irritable bowel syndrome, do not put off your visit until better times and do not be embarrassed about the problem that has arisen. If you miss an important point, then there is a high probability of more serious diseases that will require immediate treatment. Pregnancy is a time to enjoy your situation, not waste it on treatment. Be attentive to your health and take timely measures to preserve it.
Risks of intestinal disorders at different stages of pregnancy
The changing periods of pregnancy introduce changes into the body associated with fetal growth, hormonal levels, and other factors. The uterus, its rate of increase, size, and position have a great influence on the intestines and the functioning of the organ. Even with a healthy digestive system, its growth affects digestion and bowel movements. Spasmodic growth and weight gain of the fetus affect the woman’s well-being, causing pain, cramps, discomfort, and digestive problems of various types.
In the first two months, the uterus is small in size, not extending beyond the pelvis. It does not interfere with the digestive tract; its functioning is influenced by hormonal levels and food preferences.
By 9-10 weeks its size increases. The uterus does not interfere with the natural functioning of the body, but needs become increased, and the gastrointestinal tract must satisfy them. By 13 weeks, the uterus softens, takes on a spherical shape, and the intestinal muscles relax. There is gas formation and a constant urge to urinate. Pain in the intestinal area usually appears at 15-16 weeks. Problems increase even at 17-18, there is noticeable pressure on the internal organs, heartburn torments. There is a feeling of incompleteness of defecation, the reason is pressure on the large intestine.
At longer periods, they complain of congestion caused by the size and pressure of the uterus; other problems are rare. Women who do not overeat, maintain moderate activity during the period of bearing a child, and follow a diet, rarely complain of problems in the final stages. Heartburn in the first and second trimester haunts many, regardless of lifestyle. The stomach also experiences pressure from the uterus, and dietary whims affect it first.