A woman's periods stop, her breasts swell, and her uterus increases in size. And suddenly the development of pregnancy suddenly stops, the fetus dies.
According to statistics, on average, frozen pregnancy occurs in 10-15% of women. The frequency of pathology is directly proportional to age. If among pregnant women aged 20-30 years, intrauterine fetal death is observed in 10% of cases, then after 45 the figure increases to almost 15%.
In most cases of arrest, the embryo stops developing in the early stages, but in medical practice, later pathologies occur that lead to death, calcification, mummification of the embryo and frozen pregnancy.
When is pregnancy terminated?
The greatest risk of fetal death is the first trimester of pregnancy, and the woman may not notice anything. Based on the results of long-term observations, it was found that most often intrauterine development of the fetus stops at 3-4, 8-11 and 16-18 weeks.
If a frozen pregnancy is terminated in the early stages, then usually no external symptoms are observed. In the late period of gestation, a woman may notice that the tenderness of the mammary glands and toxicosis of pregnancy have disappeared. When the fertilized egg begins to exfoliate, the lower third of the abdomen may hurt and bloody discharge may appear. Other manifestations of frozen pregnancy: hyperthermia and decreased basal temperature. In general, no pronounced symptoms are observed, so suspicion of the development of a frozen pregnancy in the early period is a reason to immediately perform an obstetric ultrasound.
In addition, the woman must donate blood for hormones. The absence of an increase or decrease in the level of hCG in the first weeks after conception most likely indicates a missed abortion.
Why pregnancy freezes
The most common cause is genetic abnormalities of the fetus , causing disorders that are incompatible with further development. The “culprits” of this are not always the mother, the father, or both at once - there are also random mutations, while genetically both parents are absolutely healthy.
” Most often, such pregnancies are terminated at the earliest stages: 75% of genetically abnormal pregnancies are terminated at 6-7 weeks, another 20% at 12-17 weeks, and no more than 7% of such babies develop up to 28 weeks.
In second place are hormonal disorders in the mother’s body : lack of progesterone, diabetes mellitus, hyper- and hypofunction of the thyroid gland, hyperandrogenism - increased levels of male sex hormones and a number of other pathologies. It should be noted that most of them are not an absolute obstacle to a successful pregnancy, but require mandatory correction, and preparation should begin before the moment of conception.
Autoimmune diseases also play a role in spontaneous abortion , in particular antiphospholipid syndrome, which provokes blood clots. This is the main cause of embryo death after the 10th week of pregnancy. It should be noted that timely therapy reduces the negative impact of this factor and allows you to carry and safely give birth to a healthy child.
Infections. Contrary to popular belief, pregnancy does not end with a runny nose. The main infectious culprits of frozen pregnancy are rubella and influenza, especially when accompanied by complications. However, other diseases are also named among the reasons: cytomegalovirus, herpes, toxoplasmosis (especially if the infection occurred during pregnancy), all types of sexually transmitted diseases.
In vitro fertilization. For an as yet unknown reason, absolutely healthy embryos implanted in the uterus of an ideally prepared woman can stop their development at an early stage.
Among the indirect reasons are also the age of the parents , especially the mother. Most likely, this is due to the fact that with age, the risk of genetic “errors,” the burden of infections, and the number of chronic diseases “accumulate.”
” At 20 years of age, approximately 10% of women face spontaneous termination of pregnancy, at 35 years old - 25%, at 45 years old - 50%.
Causes of frozen pregnancy
Regardless of the period at which a frozen pregnancy was discovered, its reasons can be completely different.
The main ones include:
- Genetic abnormalities. This is the main cause of freezing (about 60% of all cases). Genetic anomalies can be inherited to a child, with the genes of the parents, or arise for the first time, under the influence of various internal or external factors.
- Age. The risk of fetal death and miscarriage increases with age. According to statistics, in women of forty years of age or older, miscarriage occurs in a third of all pregnancies. Cytogenetic examination of a dead fetus in most cases reveals genetic disorders.
- Infections. The presence of a number of infectious diseases in the mother, including those transmitted through sexual contact, is a common cause of fetal death. That is why gynecologists recommend that women undergo all the necessary examinations when planning a pregnancy. Particular attention should be paid to latent viral infections (Epstein-Barr virus, herpes and cytomegalovirus).
- Hormonal disbalance. It is known that a low level of progesterone in a woman’s blood can lead to the cessation of fetal development. But if this is detected in time and the patient is prescribed medications containing progesterone or hCG, the risk of interruption is reduced. The ability to bear a fetus can be affected by the increased content of male sex hormones in the female body.
- Metabolic disease. Women diagnosed with diabetes mellitus (uncompensated), obesity or PCOS have an increased risk of miscarriage.
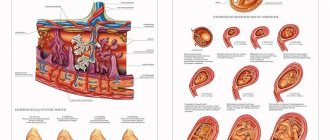
- Uterine abnormalities. In approximately 10% of cases, freezing occurs due to deformation of the uterine cavity. Miscarriage can occur with pathologies such as endometrial polyps, fibroids, congenital anomalies of the uterus, adhesions and intrauterine septa. In these cases, surgical intervention is necessary to restore reproductive ability.
- Antiphospholipid syndrome. In some cases, women with miscarriage are diagnosed with antibodies to lupus anticoagulant and cardiolipin. To confirm the diagnosis, a repeat study is carried out, but not earlier than one and a half months after the first.
- Thrombophilia. Hereditary bleeding disorders increase the risk of developing the disease due to impaired microcirculation and the formation of microthrombi in the fetoplacental system.
- Male factor. It has been proven that sperm DNA fragmentation has a bad effect on the development of the embryo, increasing the risk of miscarriage.
As can be seen from the above, the causes of missed abortion in the early stages are different, so it is recommended to start planning your pregnancy in advance, undergo an examination to exclude or cure diseases that may contribute to this, and carefully prepare the body for conception. Moreover, both spouses should take part in this, since the cause of abnormalities in the embryo can be either a defect in the egg or sperm.
An important point is the age of the future parents. The older they are, the higher the likelihood of pathologies in the fetus, frozen pregnancy, and early miscarriages. It has been proven that the eggs of young women are easier to fertilize and implant, and there is less risk of developing anomalies. Therefore, if a woman is planning to postpone pregnancy, trying to climb the career ladder, achieving financial well-being, or for any other reason, she should consider how much the risk of difficulty conceiving increases and take certain steps.
It is now possible to preserve your eggs by cryo-freezing at a young age, and then use them to get pregnant through IVF. This is a good way to reduce the risk of pathologies and embryo death.
Causes of fading
The reasons that lead to the condition of “frozen pregnancy” are very numerous. These include:
Hormonal imbalance
A lack of the pregnancy hormone, progesterone, inhibits the progression of pregnancy, which ultimately leads to the death of the fetus.
Androgens, or rather their excess or hyperandrogenism, may also be to blame. Accordingly, diseases such as sclerocystic ovaries, diseases of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands, and other endocrine pathologies can lead to intrauterine death of the embryo/fetus.
Genetic disorders
Chromosomal aberrations of the fetus or inheritance of an abnormal gene from one of the parents leads to the formation of a karyotype of the unborn child, with which life is impossible. That is, nature itself eliminates defective embryos.
Infections
Sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, herpes and others), as well as common infectious diseases (rubella, influenza, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus infection) in the early stages lead to fetal death, and in the later stages to gross malformations. It is to identify infections and reduce the risk of miscarriage that women undergo flora smears three times.
ECO
Often, after IVF, pregnancy “freezes,” which is most likely due to the reasons that prompted the woman to turn to this method of becoming pregnant.
Age
The older the woman, the higher the likelihood of a frozen pregnancy. The risk of this condition is especially high in primiparous women over 35 years of age.
Autoimmune conditions
Antiphospholipid syndrome, in which the number of antibodies to blood phospholipids increases, leads to thrombosis, including in the uterus, as a result of which the fetus does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients and dies.
Immunological factor
The fetus inherits equal amounts of genetic material from the father and from the mother; due to some conditions, the mother’s body perceives the unborn child as a foreign agent and kills him.
Unfavorable environment
Inadequate nutrition, harmful production, climate change and much more are also the causes of missed abortion.
Bad habits
Alcohol, smoking, and drug use are the cause not only of fetal deformities, but also of failed miscarriage.
Abortion
Numerous abortions lead to the formation of defective endometrium in the second phase of the menstrual cycle, which prevents the implantation of the fertilized egg after conception. In the event that implantation does occur, the defective mucous membrane of the uterine cavity cannot satisfy all the embryo’s needs for nutrients and oxygen.
Frozen pregnancy after IVF
Freezing may occur after IVF. This is due to the fact that ART only contributes to the successful fertilization of the egg. Modern medicine cannot yet fully control the processes that occur in a woman’s body after the transfer of embryos to the uterus. Nervous strain and stress also contribute to miscarriage.
Predisposing factors are bad habits, physical inactivity, and poor nutrition. Careful pregnancy planning will help to avoid repeating mistakes, during which the woman’s body will be prepared for the upcoming pregnancy.
Before starting an IVF cycle, all risk factors must be eliminated. Infectious processes must be eliminated, hormonal balance restored, chronic pathologies that cannot be cured must be transferred into remission.
If you have hereditary diseases, you should plan a pregnancy only after consulting a geneticist. In difficult cases, you can consider using donor material (sperm, eggs). If unfavorable factors are not excluded, the likelihood that the patient will have a repeat miscarriage is high.
Diagnosis of frozen pregnancy
Very often, a pregnancy that is frozen before 3-4 weeks remains undiagnosed. However, there are several nuances here that you should pay attention to. Firstly, the next menstruation comes with some delay, often not exceeding a few days.
Secondly, your periods may be more painful and heavier than usual. The pain is localized in the lower abdomen, can radiate to the lower back, and is cramping in nature. Thirdly, very sensitive women, even at such early stages, can feel that they are pregnant. With the arrival of menstruation after a frozen pregnancy, the manifestations disappear.
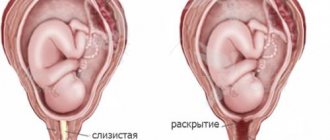
In the period up to 18-20 weeks, a frozen pregnancy is diagnosed, as a rule, by chance, during a regular visit to the gynecologist. During the examination, the doctor notices that the size of the uterus does not correspond to the gestational age. The cervix becomes pink, while one of the signs of developing pregnancy is cyanosis of the mucous membrane.
After 20 weeks, the lack of fetal movements is a cause for concern. During an objective examination, the doctor does not hear a heartbeat, and the child does not react with jerks to the examination. Of the instrumental diagnostic methods, ultrasound is the main one.
With its help, the doctor sees the following signs of a frozen pregnancy:
- Empty fertilized egg (anembryony).
- No heartbeat.
- No movement.
- Inconsistency between the size of the fetus and the gestational age.
Laboratory tests to confirm the diagnosis recommend determining the levels of the following substances:
- Chorionic gonadotropin.
- Trophoblastic b-1-glycoprotein.
- Placenta-specific a-1-microglobulin.
Differential diagnosis of frozen pregnancy is carried out with spontaneous abortion and trophoblastic disease. These pathological conditions have a similar clinical picture, but their treatment tactics are completely different.
Treatment
The consequences of a frozen pregnancy for a woman’s health can be unfavorable. If timely measures are not taken, then decomposition of the fetus is possible, which will lead to the development of intoxication and sepsis. Sometimes bleeding occurs. In case of fetal death before 16 weeks of pregnancy, curettage is performed. This is a surgical intervention during which the gynecologist removes the fetus, amniotic structures and the functional layer of the endometrium using a curette - a sharp surgical instrument. The cervical canal is first expanded using dilators of different diameters. So the operation is quite painful, it is performed only under general anesthesia.
Abortive material is sent for bacteriological examination and histology. To establish the causes of miscarriage, it is recommended to conduct a cytogenetic study of the obtained abortive material. If a frozen pregnancy is detected in the early stages, then a medical abortion may be performed. However, if the uterus does not empty completely, then curettage will have to be done. In addition, it is possible to perform vacuum aspiration, which is performed under general anesthesia.
After 16 weeks, medications are used to expel the fetus, after which the uterine cavity is curetted.
What to do
A frozen pregnancy at more than 7 weeks, which was not detected in a timely manner, is a risk of the spread of fetal decay products through the mother’s bloodstream. This condition is the most dangerous for a woman’s life. Therefore, if dangerous symptoms are detected, in the presence of bloody discharge, you must immediately consult a doctor.
After the study, when an accurate diagnosis is established, the doctor will suggest the best way out. Unfortunately, the only option for future developments is curettage. The uterus itself is not able to cope with the removal of such a large fetus, and therefore muscle contractions bring pain to the woman.
Curettage is performed under general anesthesia intravenously; the woman will not notice any painful complications in the future.
Preparing to remove the fertilized egg
Before removing the fertilized egg from the uterine cavity, the patient should undergo the following tests:
- General blood analysis.
- General urine analysis.
- Smears to determine the degree of vaginal cleanliness.
- Examination for carriage of HIV, syphilis, viral hepatitis.
- Coagulogram.
- Biochemical screening.
If necessary, the patient is consulted by a therapist or specialists. Immediately before the operation, the woman is examined by an anesthesiologist-resuscitator.
The examination allows you to assess the general condition of the patient and exclude infectious diseases. In addition, the doctor will receive objective information about the functioning of internal organs and systems, and, if there is an increased risk of complications, will take preventive measures.
Possible consequences
Unfortunately, no matter at what stage a frozen pregnancy is discovered, its consequences are not always favorable. All complications that accompany intrauterine fetal death and related gynecological manipulations can be divided into two groups - early and late.
The first group includes:
- perforation of the uterus during curettage;
- intense bleeding;
- infectious diseases of the internal genital organs.
Late complications include:
- chronic inflammatory processes;
- disruption of ovarian function;
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- infertility.
Hello girls everyone! I'll tell you my further development of events. After my ultrasound on December 29, the next day the doctor called me and said that since the ultrasound was not done by a doctor, but, let’s say, a laboratory assistant, and if I don’t have discharge, then I should wait for the next ultrasound, and if there is blood, then immediately to the hospital. Well, I didn’t wait for the ultrasound, because... On Wednesday there was blood. In the evening after work, my husband took me to the emergency department at the hospital. We sat for 5 hours and accepted. They took blood and urine tests. I lay there on the bed until 8 am, and in the morning they did an ultrasound. The fetus died at the 8th week, and that day it was already exactly 12. Then the emergency doctor called my gynecologist, it turned out that my gynecologist also works in this hospital and was there that day, delivering the baby. She came, looked at me and offered 3 options: wait until the body itself rejects everything, the second is to do a cleansing and the 3rd take medication and within 24 hours everything will come out of there. Of course, I chose the 3rd one, and she was more inclined towards it. I arrived home on Thursday from the hospital at half past noon, immediately administered these 4 tablets, and after 2 hours it started happening...... The main thing is that she didn’t tell me anything about the pain!!!! And then, imagine, my stomach starts to hurt, not so much at first, but then more and more. I tried to call her, she is not at the reception today, but at the birth. Of course, they didn’t call her to the phone, and in the emergency department they also refused to give me advice over the phone. Here are the rules, they say, if you want, come and wait for an appointment (well, it will be 3-4 hours!!!!) But time goes by, and the pain becomes more and more intense. I quickly go to the Internet, I read what kind of medicine this is. It turns out that it is given to stimulate labor and soften the uterus. In short, here I realized that I was having real contractions!!! The contraction lasts for 30-40 seconds, and then releases for 30-40 seconds. It’s good that I at least read stories about childbirth and roughly understood what it was. By 8 pm the pain became absolutely terrible. I couldn’t stand it and called the phone where they give medical advice, and they sent me an ambulance. An ambulance picked me up and at half past ten brought me to another hospital. There I was just climbing on the walls and asking for painkillers. As a result, around 10:30 I was given an IV. I felt better and they were going to send me home. While back and forth, the effect of the drip wore off and the pain reappeared. They gave me 3 tablets, nothing helped, then an injection and again on the drum, then 2 more tablets, the nurse told me that these would definitely help because... they just bring down the pain like an elephant. This is his expression. And it really helped. In short, my husband took me home at half past four in the morning. I just woke up now. I was so exhausted during these 2 days. It seems like a week has already passed. That's it. Now we will try to understand why this happened, that we need to heal and after a while we will return to battle for
And most importantly, I have never seen anywhere on the forums that they give such drugs to induce a miscarriage. Who has encountered this? By the way, I found a jar called Apo-misoprostol 200 mgg. I inserted 4 tablets intravaginally. If everything really works out and everything is fine, then this is better than cleaning?!!!???
Further tactics
A non-developing pregnancy is a reason for a comprehensive examination of the couple. It is imperative to find the cause of fetal death and, when planning the next pregnancy, exclude it. Statistics show that the probability of having a healthy child in such women exceeds 90%.
Termination of pregnancy is a huge stress for any woman. Unfortunately, the symptoms of a frozen pregnancy are not always noticeable. This can lead to a late visit to a specialist. If you have any suspicions, you should immediately contact a gynecologist. A woman can receive psychological help not only from her close people, but also from friends in misfortune. One of the places for communication is the forum about frozen pregnancy. There you can get moral support for women who have experienced the same situation.
After a missed pregnancy, you should plan your next attempt no earlier than six months later. The body needs to recover. If conception occurs earlier, then the likelihood of repeated spontaneous abortion is high.
To reduce the risk of miscarriage, contact the AltraVita clinic. The best gynecologists in the country are ready to monitor your pregnancy from the first to the last week so that nothing happens to you and your baby. If this is not the first time this happens, we will find out the cause of the unsuccessful pregnancy and, if possible, eliminate it so that your next pregnancy ends safely in childbirth.
How to avoid a frozen pregnancy, and what is the likelihood of its recurrence
Alas, it is impossible to completely guarantee yourself against an unfavorable outcome, since, as emphasized above, a number of genetic “breakdowns” are the result of chance. And yet, if the first pregnancy was frozen, it is recommended to submit the remains of the fetus for genetic research to find out whether such a result could be the result of heredity.
” The risk of repeated spontaneous abortion if there is a history of one miscarriage is about 8% (that is, exactly the same as for any woman, regardless of the number of successful births).
However, if subsequent pregnancies end in miscarriages, then most likely the risk is due to serious genetic disorders. So, the probability that after three miscarriages the fourth pregnancy will be terminated early is 40%, the fifth – more than 60%. You should not experiment with your own health and risk the opportunity to become a mother. After two interrupted pregnancies, be sure to contact geneticists and, if necessary, use the IVF procedure. Choosing a genetically healthy embryo will significantly increase your chances of bearing and giving birth to a healthy child.
” If you have not been identified with any genetic abnormalities or diseases that affect bearing a child, then you can plan a new pregnancy 3-6 months after the frozen one.
If it turns out that the reason for the miscarriage of pregnancy was non-genetic disorders, then it is necessary to pay attention to treatment and preparation for conception. Don't rely on chance.
Infertility after a single frozen pregnancy is a fairly rare complication (less than 10%), but repeated frozen pregnancies themselves become a risk factor, causing hormonal imbalances.