Pregnancy does not always proceed smoothly, without complications. Every expectant mother takes care of the health and condition of her baby even before his birth.
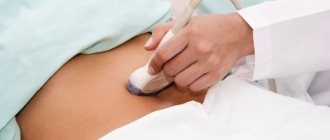
Every visit to the doctor and every ultrasound diagnosis is a joyful event, since it is at these moments that you can learn a little more about the condition of the fetus. If a pregnant woman no longer feels previously noticeable movements and tremors in the abdomen, which mean that the baby is comfortable and nothing is bothering him, it is recommended to consult a specialist to exclude the diagnosis of a frozen pregnancy .
What does fetal freezing mean in the second trimester?
The period of waiting for a baby from the 13th to the 27th week is called the golden time of pregnancy: toxicosis has already subsided by this period, the tummy does not yet cause any particular inconvenience - the woman can partially return to her usual routine, that is, receive moderate physical activity, meet with friends , go to theaters, cafes, etc. For the fetus, the second trimester is the stage of completion of the formation of the child’s place and the birth of internal organs and systems. Fading pregnancy during this period, as a rule, is an infrequent phenomenon, in contrast to earlier periods, but nevertheless it still happens. This means that a woman needs to know why this happens and what to do.
Starting from the second trimester, the organs and systems of the fetus begin to work independently
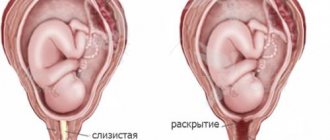
Frozen pregnancy is the cessation of intrauterine development of the fetus with its subsequent death, accompanied by inertia of the uterus, that is, the absence of its ability to contract.
Diagnostics
Objective studies are carried out by a gynecologist based on the patient’s condition. An oral survey of the patient is conducted regarding the subjective sensations described above. The clinical picture may be completely absent, apart from individual manifestations. It is important to collect anamnesis and find out what kind of life the patient leads. To detect signs of fetal fading in the second trimester, studies are carried out:
- Determination of the size of the uterus. Often women are interested in whether the belly grows during a frozen pregnancy in the second trimester. Usually, during a frozen pregnancy, the size is significantly smaller than normal and does not correspond to the gestational age.
- Visual assessment of the reproductive tract. The passages are pale, insufficiently colored. Carrying out an ultrasound examination of the uterus.
- Detection of fetal heartbeat.
Diagnosis should be carried out as early as possible. Intense uterine bleeding is possible, often fatal. It is important to consult a doctor at the slightest suspicion; this is a guarantee of a quick and effective response to the problem. We are talking about the life of not only the fetus, but also the woman herself.
Signs of a frozen pregnancy
Interruption of intrauterine development of a baby does not manifest itself instantly (!), so when the first symptoms of pregnancy fading occur, a woman should immediately seek help from a specialist:
- the appearance of vaginal discharge (red and brown confirm that the uterus is trying to “expel” the dead fetus, yellow, green and gray are indicators of the development of infection due to the decomposition of the dead fetus);
- weakness, chills, trembling;
- heat;
- aching pain, as during menstruation;
Pain in the lower abdomen is an alarm signal for a pregnant woman at any stage
- a sharp stop in the manifestations of toxicosis, if it was still present at this stage (most often in the second trimester, toxicosis no longer exists), as well as a cessation of enlargement of the mammary glands.
The manifestation of symptoms depends on the stage of pregnancy at which the fetus died, as well as on the time that has passed since the cessation of embryonic activity.
Fetal freezing after 18–20 weeks: absence of movements
The most obvious and early symptom of fetal pathology is the absence of movement: if a woman is pregnant for the first time, then tremors can be felt from the 20th week, if not the first, then already from the 18th. The average frequency of movements is 10 series of tremors with an interval of 1.5–2 hours. If the intervals between movements increase to an interval of 3-4 hours or more, you need to urgently contact a gynecologist: perhaps the fetus is experiencing a lack of oxygen.
Symptoms of freezing before the first movements
If freezing occurred before the fetal movements began, that is, from the 13th to the 18th–20th week, then you should pay attention not only to vaginal discharge and pain in the lower abdomen, but also to the condition of the breasts. On the 3rd–6th day after the death of the embryo, the breasts decrease in volume, become softer, and colostrum may even be released.
Decrease in basal temperature
Another symptom of the cessation of pregnancy at any stage is a decrease in basal temperature below 37ºC. But here it is important to consider the following nuances:
- basal temperature is an informative source of the course of pregnancy only if measured regularly;
- the basal temperature indicator is an unreliable source of diagnosis, since sometimes it decreases only a few weeks after pregnancy ends, which is associated with the continued production of the hormone characteristic of pregnancy by the cells of the chorionic membrane;
- a decrease in basal temperature even by 0.2ºC in the absence of other signs is a reason to contact a gynecologist - perhaps the body produces little progesterone, which can lead to miscarriage.
Basal temperature readings are informative only when measured constantly and at the same time
Other signs
In addition, one of the obvious signs of fading pregnancy, including before the period when the fetus begins to move, is the lack of progress in the growth of the woman’s abdomen. However, this symptom appears several weeks after the death of the fetus and is usually accompanied by a whole complex of signs of intoxication in the woman’s body:
- profuse sweating;
- nausea, vomiting;
- malaise;
- weight loss;
- increased heart rate;
- sepsis, caused by the fact that microorganisms from a dead fetus enter the blood of a pregnant woman, provoking an inflammatory reaction.
Signs of concern
The symptoms of the disease are very diverse, the appearance of at least one is a reason to sound the alarm and contact your gynecologist. Most common symptoms:
- Changes in the process of the baby moving in the womb. From about 16-18 weeks, the first activity appears in the form of movements - first weak, barely noticeable, then stronger. They appear constantly throughout the day, every hour or two. Ideally, there should be 10-15 series of pushes from the baby. If suddenly there are no movements for 4-6 hours, and even more so for a day or longer, you must definitely inform the doctor, who will conduct an examination and listen to the beating of the small heart.
- Condition of the mammary glands. Usually during this period the breasts swell and become dense. Sometimes women complain of pain, but this is normal, especially in the early stages up to 8-9 months. And if the mammary glands become softer, the painful sensations suddenly go away - this is an indication that the level of hormones has dropped. You should pay attention to this.
- The appearance of atypical discharge from the genital tract. Not necessarily bloody; during a frozen pregnancy, yellow, brown, light pink, foul-smelling vaginal discharge is possible. Most often abundant, liquid. The reason for their appearance is that the frozen fetus begins to be rejected from the endometrium, provoking inflammation.
- Painful symptoms of varying degrees of intensity. The pain is often nagging and dull. Occasionally there are sharp, shooting ones. Location: lower abdomen.
- Bad feeling. What symptoms should alert you - headache for several days in a row, fever up to 37-37.5 degrees, so-called low-grade fever, signaling inflammatory processes. Possible loss of appetite, sudden hot flashes, surges in blood pressure, sudden changes in mood, irritability for no reason, tearfulness. All this indicates changes in hormonal levels.
Pathology indicators during medical examination
They are the most accurate - they allow you to determine 100% whether the embryo is viable or not.
- Ultrasound - the specialist will immediately see whether there are heartbeats. According to this procedure, indirect symptoms of the pathological process are visible - undeveloped organs, lack of movement, strange position, deformities of the arms, legs, and spine.
- Drying the heartbeat through the abdomen with a stethoscope. The procedure is generally applied at every visit of a pregnant woman who is registered. A stethoscope is a long tube made of wood, one end is placed on the stomach, the other to the doctor's ear. Sometimes the heart rate is not heard due to the special location of the placenta, a large layer of fatty tissue on the abdominal wall. Therefore, this method should be combined with ultrasound diagnostics to avoid inaccuracies and misdiagnosis.
- There is no change in uterine height readings. With regular appointments, its height is measured with a tape applied to the stomach. The height should increase in accordance with the obstetric period. If the child freezes, this indicator remains unchanged. Again, you need to confirm the accuracy of the diagnosis with other tests and examination.
- Gynecological examination. With pathology, it is clear that the cervical canal and cervix are open - normally this should not be the case. Plus, thick brown discharge mixed with blood is visible.
It is important to establish the death of the fetus as early as possible in order to avoid severe intoxication of the body from decaying tissues, therefore it is unacceptable to ignore the signs of a frozen pregnancy in the 2nd trimester.
An important difference between a frozen pregnancy in the early stages and a similar condition in the 2nd trimester is the combination of the absence of heart rhythms and the discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the set period. In the first weeks, the primary indicator is an empty fertilized egg.
Causes of frozen pregnancy at 13–27 weeks
The cause of pregnancy loss can be determined only after carefully carried out diagnostic procedures. There are four most common causes of fetal death in the womb.
There are several reasons for pregnancy fading in the second trimester
Genetic “breakdown”
As a rule, genetic disorders cause intrauterine fetal death in the first couple of months, at 6–7 weeks. Very rarely, chromosome deviations due to dysfunctional combination of the genes of the father and mother appear so late.
In medical practice, it is believed that if a woman experiences more than three miscarriages, the reason lies precisely in unsuccessful genetic combinations.
Hormonal imbalance
The amount of hormones during the period of waiting for a child must be balanced, and an excess of androgens or a lack of progesterone leads to the fact that the fetus ceases to form and dies. This usually also appears in the first trimester, before the 10th week, but can sometimes occur in the 13th or even 14th week.
Violations can be identified in advance if you take the necessary tests at the planning stage of the baby - the imbalance of hormones can be eliminated with competent therapy.
Infections
The immune system during pregnancy is very vulnerable. And despite the fact that the fetus is protected by the placenta, there are a number of factors that nullify this protection. Firstly, the activation of the vaginal flora, which makes the body open to a wide variety of bacteria. When the infection worsens, the fetus becomes infected, which provokes its death. Secondly, the consequences of the body’s fight against the pathogen are very dangerous: high temperature and intoxication of the body lead to the disruption of the blood supply system, which means that the fetus does not receive the volumes of oxygen and nutrients that it needs to live - from this the embryo and is dying.
Sexual infections that enter the uterus from the vagina are also a factor that provokes fetal death. Syphilis, chlamydia, toxoplasmosis, and cytomegaly are especially dangerous.
Untreated infections often cause fetal death
Pathologies of the structure of the reproductive organ
In the second trimester, the reasons for fetal freezing may be structural features of the uterus:
- “baby uterus”, that is, underdeveloped, which can be accompanied by hormonal deficiency and lead to the death of the embryo, but if a woman is registered for pregnancy at term, then hormonal correction will be carried out in a timely manner;
- bicornuate uterus, that is, with one cervix, the reproductive organ diverges into two chambers (with such a pathology, placenta previa is usually diagnosed, which is a direct threat of its detachment and death of the embryo);
- fibroids (if the placenta is adjacent to areas of fibroids, this can lead to detachment of the baby’s place and death of the embryo).
Antiphospholipid syndrome
This is an autoimmune condition characterized by the formation of blood clots. Blockage of the placental vascular network leads to disruption of blood flow and hypoxia of the embryo.
Lifestyle
Pregnancy imposes a taboo on some pre-pregnancy habits, which, if not eliminated in time, can cause fetal fading:
- wearing tight underwear, sedentary work at the computer (the blood vessels of the pelvic organs are pinched, which provokes circulatory problems in the fetus);
- improper diet, as a result of which the embryo does not receive all the substances necessary for full growth and stops developing;
- drinking alcohol and smoking provoke thinning of the placenta, its ultrastructural changes, as well as impaired blood flow, which makes the growth and development of the fetus impossible;
- intense physical activity, which affects the functioning of the respiratory system of a pregnant woman, which, due to a decrease in lung volume caused by the displacement of internal organs by an enlarging uterus, already requires a larger volume of oxygen, which, in turn, has a significant impact on the proper development of organs and systems of the embryo ;
- lack of moderate physical activity also affects the respiratory system and blood flow of the pregnant woman and fetus;
- stress, lack of sleep, lack of fresh air and positive emotions (the weakening or strengthening of the fetal heartbeat depends on the emotional state of the pregnant woman, which affects the functioning of its circulatory system and the enrichment of tissues with oxygen).
The reason that the fetus stops developing may be an injury received by a pregnant woman.
Uncontrolled medication use can also cause fetal death
Who is at risk
No one is immune from fetal death, but the risk increases even more if a woman has exceeded the age threshold of 35 years and/or has a history of:
- abortion performed by medication;
- experience of miscarriage;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- pathological conditions of the organs of the reproductive system.
Women who become pregnant through IVF are also at risk: based on research in recent years, experts have concluded that the risk of miscarriage in cases of such pregnancies is much higher.
Video: causes of frozen pregnancy - expert opinion
Common causes of pathology
A similar tragedy happens even to completely healthy parents who carefully planned their pregnancy and underwent all the prescribed tests and studies.
The most common causes of pregnancy loss include the following pathologies and conditions:
- Fetal pathologies incompatible with life.
- Infectious disease of the mother in a latent or acute form. Similar infections that can have a detrimental effect on the fetus include the following diseases: toxoplasmosis, rubella, chickenpox, cytomegalovirus, influenza. Pregnant women are more susceptible to infections and viruses than non-pregnant women, this is caused by suppression of the immune system.
- Lack of the hormone progesterone, which is involved in maintaining pregnancy.
- Genetic mutations of the fetus.
- Bad habits.
- Taking medications that are contraindicated during pregnancy, as they penetrate the placental barrier.
After suffering a frozen pregnancy, it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination of the whole body, visit a geneticist and check compatibility with a partner.
Diagnosis of frozen pregnancy in the second trimester
To establish a frozen pregnancy, three diagnostic methods are used in medical practice. To draw final conclusions, a woman is prescribed at least two types of tests, sometimes repeated after 7-14 days.
Examination by a gynecologist and ultrasound
During a gynecological examination, the following indicators will be informative for a specialist:
- correspondence or discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the gestational age (the gynecologist measures the height of the fundus of the uterus, that is, the distance from the pubic bone to the area along the midline of the abdomen, where dense tissue becomes soft, that is, to the border, fundus, uterus), but due to the growth of the fetal bladder the uterus can continue to grow for some time even after the fetus has died;
- change in the color of the vagina, or rather, the absence of cyanosis - blue discoloration of the mucous membrane, which is a characteristic sign of pregnancy;
- decrease in basal temperature;
- absence of fetal heartbeat.
Listening to the fetal heartbeat is done using a stethoscope. But sometimes listening to the heart is prevented by a layer of fat or the anterior location of the child’s seat. Therefore, the most accurate diagnostic procedure is an ultrasound examination, which allows you to accurately determine whether the fetal heart is beating or not.
The most accurate diagnostic procedure for detecting a frozen pregnancy is ultrasound
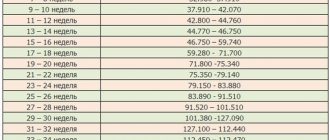
Table: norms for fundal height of the uterus during pregnancy in the second trimester
| Week of pregnancy | Length in mm (+/- 10 mm) | Width (+/- 10 mm) | Height of the uterus relative to the pubic line, cm | Position of the uterine fundus |
| 12 | 120 | 70 | 11 | Reaches the pubic line |
| 16 | 140 | 80 | 14 | The organ is located between the navel and pubis |
| 18 | 180 | 90–100 | 16–18 | 6–7 cm above the pubic line |
| 20 | 200 | 110–120 | 18–20 | The fundus of the uterus is located 2 fingers below the navel |
| 22 | 210 | 120–140 | 21–24 | Almost reaches navel level |
| 24 | 230 | 140–160 | 23–26 | Raises to the level of the navel |
| 26 | 250 | 160–170 | 25–28 | Rises just above the navel |
| 28 | 280 | 170–180 | 26–30 | 2–3 fingers above the navel |
HCG level analysis
The concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in the blood of a pregnant woman is also considered one of the diagnostic procedures for determining fetal freezing.
HCG in the body of a pregnant woman performs three functions: it stimulates the production of hormones designed to adapt the body to bearing a child (from the 1st to the 6th week, hCG ensures the functioning of the corpus luteum), is responsible for the production of progesterone, which supports pregnancy, and also promotes proper work of the placenta.
In pregnant women, the level of the hCG hormone is high compared to the pre-pregnancy period, so a decrease in levels can be caused, among other things, by the death of the fetus. However, the analysis for hCG levels has one caveat: if the fetus died recently, then the hormone level will still be normal, since the woman’s body has not yet had time to react to this.
Blood for hCG level analysis is taken from a vein
Table: hCG level in the second trimester
| Week of pregnancy | Normal range |
| 12–16 weeks | 6140–103000 IU/l |
| 17–21 weeks | 4720–80100 IU/l |
| 22–39 weeks | 2700–78100 IU/l |
In no case should you rely solely on hCG level data to make a diagnosis. The fact is that hormonal levels in women are very individual, and the hCG normal range is very wide, so what is low for one pregnant woman may be normal for another, and completely elevated for a third. Moreover, in the second trimester, at the stage of completion of the formation of the placenta, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin decreases for a short time, and then increases again.
How is diagnostics carried out?
The diagnosis of “frozen pregnancy” is made only by a gynecologist after a series of examinations:
- inspection . During a gynecological examination, the doctor notes a deviation from the norm in the size of the uterus, a change in the color of the cervix, its dilatation and a decrease in basal temperature;
- hCG analysis . During the normal development of a child, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin constantly increases. If it is at a level below normal for a certain period of time, it may indicate fetal death;
Important! HCG levels may remain within normal limits for several weeks after fetal development has stopped.
- general blood analysis. This is an additional examination that can help identify the inflammatory process if the fetus has died for a long time;
- Ultrasound. This is the most accurate method for determining a frozen pregnancy. It can be used to determine whether the baby's heart is beating.
What to do after diagnosing a frozen pregnancy
The sentence “frozen pregnancy” sounds when the child can no longer be saved. Therefore, it is paramount to remove the fetus as quickly as possible, otherwise inflammation and bleeding may begin, the consequences of which can threaten the woman’s life. After studying the anamnesis, the gynecologist chooses one of three strategies for removing the fetus.
Waiting strategy
In other words, the doctor leaves the patient under observation until she experiences spontaneous rejection of the dead fetus, that is, a miscarriage. For this strategy, it is important to control the level of hCG: a decrease in the hormone provokes a decrease in the amount of progesterone, which, in turn, leads to contractions of the uterus and the expulsion of a foreign body. However, a wait-and-see strategy can be very dangerous for a woman's health, as the dead fetus begins to decompose in her body. Therefore, it is important to monitor the state of health, and in case of manifestations of intoxication (nausea, vomiting, fever, chills) to choose a different method of extracting the fetus.
Scraping
The most common method of fetal removal is from the 14th to the 16th week. And even if a woman has a miscarriage, she cannot do without curettage, since the membranes of the fetus remain in the uterus, which, due to their immaturity, cannot exfoliate on their own. Gynecological cleansing or curettage (curettage) is performed under local anesthesia. The doctor opens the cervix with a special dilator, then, using instruments, removes the fetus in parts and cleans the mucous layer from the uterine walls.
Vacuum aspiration
Removal of the fetus before the 15th week can also be done by vacuum aspiration, but sometimes particles of membranes remain in the uterine cavity, and then curettage is also necessary.
After removing the fetus using any of these methods, the woman remains in the hospital for one to two weeks. After 7 and 14 days, she has an ultrasound to see if the uterus has cleared of non-viable tissue.
Artificial birth
There are several options for performing an artificial birth procedure (possible from the 12th week), that is, provoking premature birth.
The method of artificial childbirth is selected individually by the doctor after a thorough study of the woman’s medical history.
Taking prostaglandin
One of the outdated methods of artificial childbirth up to the 20th week. Its essence lies in the fact that in order to stimulate the opening of the cervix, a woman is prescribed to take the hormone prostaglandin in the form of suppositories, tablets or gels that are inserted into the vagina. In addition, oxytocin is prescribed, which is responsible for contractions of the reproductive organ. This is a long and painful procedure. Today, to alleviate a woman’s condition, prostaglandin is used in combination with Mifegin, which speeds up labor.
C-section
The operation is called a “minor caesarean section” and is prescribed when the patient is in serious condition. For example, if a woman begins to become intoxicated due to the decomposition of a dead embryo. The procedure is no different from a regular cesarean operation: the abdominal cavity is dissected, an incision is made in the uterus, the fetus is removed, the uterus is cleaned, sutured, and stitches are also placed on the abdominal wall.
Administration of sodium chloride and glucose
This method is considered the least dangerous in the later stages of fetal death. Its essence lies in the fact that sterile solutions of sodium chloride and glucose are injected so that the liquid is between the uterus and the placenta. The solution triggers the mechanism of detachment of the amniotic sac, which causes a reflex contraction of the uterus and thereby starts the birth process. Before this procedure, the woman is prescribed drugs that soften the tissue of the cervix and promote its opening, for example, no-shpu. Or kelp is introduced into the cervical canal - seaweed, which after 3-4 hours swells and mechanically opens the cervix.
After termination of pregnancy by any method, the tissues of the embryo and uterine mucosa are sent for histology to determine the reasons that caused the death of the fetus.
Treatment
When you have already learned one of the most unpleasant news in life, you should think first of all about your personal health. A fetus that has stopped developing can cause poisoning in a woman. Therefore, you have to use medications that cause a miscarriage or perform an operation (something like an abortion that cleanses the uterine cavity). And there are cases when spontaneous abortion occurs and then no special treatment is required. But specialist supervision is necessary in any case.
Consequences of a non-developing pregnancy in the second trimester
Delay in carrying out the procedure for removing a dead embryo can be fraught with the following consequences for the woman’s body:
- development of infection - if the fetus is not removed on time, then the woman may develop sepsis or disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, which provokes the formation of blood clots - both complications are life-threatening;
- retention of fetal membranes in the uterine cavity, which leads to disruption of the contractile function of the reproductive organ and bleeding;
- mechanical damage to the uterus during curettage or vacuum aspiration procedures, which, in turn, can cause infertility, especially if curettage was performed repeatedly;
- psychological problems associated with concerns about the ability to bear a child in the future.
The experience of fetal death may cause a couple to fear becoming pregnant again
Treatment and prevention
Intrauterine fetal death is a great psychological stress for the mother, but negative emotions only make the situation worse. In this situation, a woman should try to calm down, trust the doctors and carry out quality treatment. Sometimes specialists are able to identify the cause of the pathology and eliminate it. After a few months, the woman can try to have a baby again.
After a diagnosis of “frozen pregnancy” is made, the doctor selects treatment. Sometimes he uses expectant tactics, hoping that a drop in placental hormones will provoke a spontaneous miscarriage. This method is possible only if the woman is in good health and the dead fetus remains in the uterus for a short period of time.
If the fetus does not leave the uterine cavity on its own, the woman has an abortion for medical reasons. It can occur under either local or general anesthesia. If all manipulations are followed correctly, this intervention is safe for women. After the procedure, antibacterial therapy, diagnostic ultrasound after 14 days and routine examinations by a gynecologist are required. In rare cases, parts of the fetus remain in the uterine cavity, then the woman is advised to undergo repeated curettage to prevent infection.
What to do after a frozen pregnancy
After the fetus is removed, treatment is carried out. Broad-spectrum antibiotics, for example, Ceftriaxone, are usually prescribed, and preventive measures are also taken. You can plan your next pregnancy no earlier than six months after completion of treatment.
During the treatment process, measures are taken to identify the reason why the embryo froze. To do this, both partners:
- take tests to study hormone levels (sex and thyroid hormones);
Both partners should be tested for infections and hormones
- take smears to detect the presence of sexually transmitted infections;
- do an ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- are being examined by a geneticist.
Why is this happening?
- Problems with genetics are a common reason why a child loses the opportunity to develop adequately. Due to abnormalities in the combination of chromosomes, the embryo loses its viability, most often for up to 9-12 weeks.
- Violation of adequate hormone production. Progesterone is responsible for the safety of the embryo; if it is deficient, there is a high chance of pathologies appearing. Excessive androgen production negatively affects fetal growth, causing either congenital diseases or stillbirth.
- Diseases of an infectious nature. If the expectant mother gets sick with a harmless cold, the consequences may affect the condition of the fetus, since with a banal acute respiratory infection, intoxication occurs and the flow of blood, oxygen and nutrients is disrupted. As a result, the baby may die.
- Leading an unhealthy lifestyle - it is impossible or unwillingness to give up smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages - even low-alcohol ones - leads to inhibition of the normal functioning of the unborn child.
There is a risk group, or women who are more susceptible to miscarriage:
- persons whose age is over 35-40 years, the optimal age for having children is from 20 to 30 years;
- those who have already had the problem of miscarriages;
- have undergone an abortion;
- with a burdened heredity in terms of genetics and other diseases that are difficult to treat.
Prevention
To prevent recurrence of miscarriage, you must:
- get rid of sexually transmitted infections at least three months before conception;
- take care of vaccination against chickenpox, rubella (especially if one of the parents works in a children's team);
- visit a geneticist;
- take vitamins (in particular, folic acid);
- eat a balanced diet, including vegetables and fruits in your diet;
- spend more time in the fresh air;
- give up unhealthy habits.
A healthy lifestyle throughout the entire period of expecting a baby is an important condition for a successful pregnancy.
Reviews from women
For women who have experienced a frozen pregnancy, this remains a trauma for life, but does not become an obstacle to subsequent conception and successful childbirth.
I had a miscarriage at 22 weeks(((((((...artificial birth, cleaning...further treatment with antibiotics...they did histology and found nothing...only after I was examined...and they eventually found out that I had elevated hormones: testosterone and DEG... because of this everything happened... after 6 months I became pregnant and gave birth to a girl, 5 kg 58 cm.
Fox
https://deti.mail.ru/forum/v_ozhidanii_chuda/planirovanie_beremennosti/podskazhite_u_kogo_byla_zamershaja_bermennost_by_281288miaus_mail_ru/?page=2
I had 4 frozen babies and I searched for the cause myself for 5 years, all the doctors said I was healthy, by the way, I need to do karyotyping of the fetus, for example, in one of my unsuccessful pregnancies a triple set of chromosomes was discovered, as a result I discovered genetic thrombophilia and hypothyroidism, All this was corrected, and only then was it possible to bear it.
Anonymous
https://www.u-mama.ru/forum/family/health/697598/
I had terrible bleeding, I had to throw out the mattress, absolutely no pain. At 14 weeks.
Remedios
https://eva.ru/static/forums/49/2008_4/1285415.htm
2 weeks ago, during a routine ultrasound, they discovered that the child had died. The term was 17-18 weeks, but she froze at 15-16. Histology is not ready yet. This was our 3rd child, the older ones were born without problems. I had herpes in the first weeks, I think it was his fault. Let's get treatment and hope that next time everything will work out.
Lelka
https://deti.mail.ru/forum/v_ozhidanii_chuda/planirovanie_beremennosti/podskazhite_u_kogo_byla_zamershaja_bermennost_by_281288miaus_mail_ru/?page=2
I had 2 missed pregnancies. The first one froze at 14 weeks: brownish discharge appeared, I went to my doctor, and she urgently went to the hospital. There they immediately did an ultrasound, and then they did a cleaning. Then everything was “written off” to the thyroid gland (I have a goiter). The gynecologists immediately shouted that I couldn’t give birth, and in the first weeks I took hormonal tablets L-thyroxine. Endocrinologists argued that this could not have any effect. In addition, I was a student then, living in a dormitory: poor nutrition, nerves, etc. The second pregnancy was almost three years later. I registered and at 11 weeks, heavy brownish-red discharge appeared. I went to the doctor and had an ultrasound; the pregnancy had already stopped for 3 weeks. Cleaning again. To find out the reason, it was necessary to undergo a ton of tests for torch infections. I passed a few, everything was fine. There was not enough money for the rest; they are not cheap. I read a lot of literature on this topic, there could be all sorts of reasons: something went wrong in development - that’s all. During my third pregnancy, the first thing I did was go to a private clinic for an ultrasound. A week later - discharge again! I go to the doctor, she urgently goes to the hospital. I drove with 95% confidence that cleaning was waiting for me again (the period was 3-5 weeks). But fortunately, everything worked out, and my happiness turned 4 years old yesterday.
LTLiana
https://kinder.sumy.ua/forum/index.php?topic=9508.0
Reviews
Larisa
“The doctors sent me for cleaning, but until the very end I believed that everything was fine with my baby. I had to visit four doctors and do several ultrasounds to make sure that the pregnancy was developing. Girls, when making such a diagnosis, do not give up.”
Lisa
“Indeed, most of the symptoms of a frozen pregnancy coincide with the manifestation of toxicosis . I will go to my gynecologist more often.”
Nastya
“You wouldn’t wish this experience on your enemy, but I went through it. Indeed, everything is as described in the article. It is very important to consult a doctor in a timely manner, otherwise there is a risk of not getting pregnant again.”