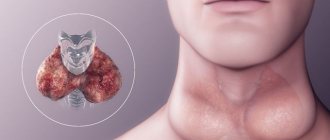
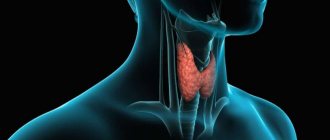
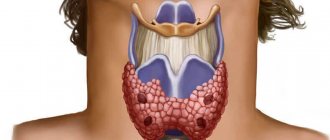
The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland. It releases its products (hormones) into the blood. This gland is located on the front surface of the neck above the thyroid cartilage of the larynx, which is why it is called so. The main function of the thyroid gland is the production of thyroid hormones - thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which ensure the normal functioning of almost all organs and functional systems of the body. Therefore, doctors pay special attention to her.
The cells of the thyroid gland are the only ones in our body capable of extracting iodine from food and creating such important hormones from it. Disruption of the thyroid gland can lead to the development of mentally retarded children. Thyroid diseases are closely related to a woman’s ability to become pregnant and give birth to a healthy child, and a man’s ability to become a father. The main role in this is played by the hormonal background and the specificity of the processes in the body that are triggered when it is disrupted.
Every woman planning to have a child, regardless of whether she suspects infertility or not, should have her thyroid gland examined, the same applies to men. After all, the problem is that disturbances in the functioning of this organ are not always noticeable, but manifest themselves nonspecifically, as in many other diseases.
How does the functioning of the thyroid gland affect the possibility of conception?
The thyroid gland produces thyroid hormones, which contain iodine. Thyroid hormones are vital for normal growth and development of the body. They also actively interact with sex hormones. In order for the reproductive system in men and women to function normally, it is necessary that there are no malfunctions in the thyroid gland. If it produces too many hormones (thyrotoxicosis) or too little (hypothyroidism), this will affect the ability to conceive in both men and women.
The effect of prolactin on a woman’s body
What is prolactin?
Prolactin is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland in the anterior part of the brain. The formation of the female body is impossible without the active participation of prolactin in all metabolic processes and the activity of internal organs. With a normal prolactin level, a girl’s mammary glands and figure develop during adolescence. During pregnancy and breastfeeding, prolactin is responsible for the production of lactation. But it is also worth knowing about the negative effects of this hormone.
Cause of hair loss and excess weight
There is an opinion that hair loss and excess weight are somehow connected with increased levels of prolactin in the body. To understand whether this is so, it is necessary to undergo a series of tests and come to a diagnosis.
The normal level of prolactin in a woman’s body should be 4-23 ng/ml. During pregnancy, this value increases hundreds of times.
If you have complaints about hair loss and excess weight, then you need to prepare and take a blood test to determine the level of prolactin in the blood. In women, blood is drawn three times a month on different days of the cycle. Before the study, you must limit your food intake, do not drink or smoke. It is unacceptable to take prolactin and progesterone in the form of hormonal drugs.
If two out of three tests show prolactin levels exceeding the norm, then it is necessary to undergo instrumental analysis methods. These are ultrasound of the mammary glands and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. Abnormalities in the production of prolactin by the pituitary gland may indicate that the cause of hair loss is excess levels of the hormone.
Hyperprolactinemia is a disease characterized by an increase in prolactin in the blood. Another symptom of hyperprolactinemia is excess body weight. This is due to the fact that excessive synthesis of prolactin in the body provokes an increase in appetite. At the same time, metabolic and metabolic processes are disrupted; accordingly, all beneficial substances from food are completely absorbed by the body.
The woman rapidly begins to gain excess weight. This can occur despite excessive exercise and diet. All that needs to be done in such a situation is to consult a doctor for professional advice. But remember that the main cause of excess weight is poor nutrition, and only 10% out of 100 are the result of hormonal imbalance in the body.
How does prolactin affect conception?
You are not ovulating due to high prolactin levels. Appropriate treatment is necessary. Every second woman hears these words in the gynecologist’s office.
If you do not ovulate, have an irregular menstrual cycle, and cannot conceive a child within a year, then the cause may be a benign brain tumor or pituitary microadenoma. To confirm the diagnosis, a woman needs to be tested for prolactin levels.
If the hormone norm is exceeded by several tens or even hundreds of times, the diagnosis is confirmed. Do not be alarmed if hair loss, excess weight and acne on the face are added to the problem of conception.
If the excess of prolactin is insignificant, then the doctor looks at the level of macroprolactin. Prolactin and macroprolactin differ from each other in their effect on the body. There is a huge connection between an increase in prolactin and the onset of ovulation. While microprolactin does not affect any processes in the body.
With an increase in the lactation hormone, the synthesis of progesterone is blocked, and this entails the cessation of ovulation and the menstrual cycle. If the diagnosis of pituitary microadenoma is confirmed after an MRI of the brain, ultrasound of the pelvis and mammary glands, the doctor prescribes a drug to reduce prolactin in the woman’s blood. As a rule, these are prolactin inhibitors - dostinex or bromocriptine.
Drug treatment must be carried out for 12 months. At this time, it is prohibited to plan a pregnancy. After a repeat test for prolactin levels, showing a decrease in the hormone, you can plan to conceive a child.
If egg fertilization is carried out using IVF, the gynecologist is also obliged to refer the patient for blood tests. Prolactin and conception are associated not only with direct fertilization, but also with assisted reproductive technology IVF. Increased prolactin during the transport of the fertilized egg to the uterus can interfere with implantation. There is also a risk that the embryo will not develop normally.
For IVF to be successful, it is necessary to take Dostinex and carry out estrogen hormone therapy. Only after this will there be a chance that the IVF protocol will show successful implantation.
Hormone and milk secretion
Galactorrhea is the secretion of milk from the mammary glands, unrelated to pregnancy or lactation. Galactorrhea is accompanied by painful sensations over the entire area of the mammary glands. But you shouldn’t run to the pharmacy for drugs that reduce prolactin in a woman’s body.
You need to know that a number of hormones are responsible for the formation and stimulation of milk in the glands. First of all, it is prolactin, followed by insulin, thyroxine, somatropin and cortisol. Do not forget about estrogens - hormones that directly affect the menstrual cycle, ovulation and fertilization of a woman.
Galactorrhea can manifest itself in various forms. If the discharge from the nipples is quite profuse, then you should consult a doctor. One or two drops of colostrum is not a cause for concern; this amount is normal.
Galactorrhea can be either unilateral or bilateral. Despite the fact that galactorrhea is a fairly common disease, its causes are quite difficult to establish. If the accompanying symptoms are hair loss, excess weight, acne, then it can be argued that prolactin is increased in the woman’s body.
If prolactin is normal, then it is worth excluding diseases such as:
- Tumor formations in the brain;
- Consequences of taking antibiotics;
- Hypertriosis – hormonal deficiency;
- Polycystic ovary syndrome;
- Obesity and overweight.
Only after confirmation or elimination of other possible causes of discharge from the mammary glands can appropriate treatment be prescribed. Galactorrhea is cured in 80% of cases with drug treatment.
Prevention of hyperprolactinemia
Hair loss, a woman's weight above normal, galactorrhea, acne, problems with ovulation and conception - these are all the effects of prolactin on a woman's body. Therefore, to avoid such consequences, it is necessary to carry out timely prevention.
Ovulation, conception, and planning a child through IVF depend on the woman’s hormonal background. Prolactin and macroprolactin are the first analysis that a woman needs to do. An increase in these hormones will allow for timely treatment. Maintaining the balance of progesterone and estrogen will allow a woman to monitor her health.
Only such a decoction will trigger REGENERATION of the thyroid gland
The goiter will disappear in 3 days! This remedy has become a sensation in the treatment of the thyroid gland!
Excessive weight of a woman can also cause difficulties in conceiving IVF and fertilization using the natural method. Therefore, a balanced diet is recommended for all girls of reproductive age. A lack of vitamins, minerals and trace elements can also cause acne and poor hair condition.
Before using any form of contraception, you should consult a gynecologist. It has been proven that the intrauterine device stimulates the production of prolactin in a woman’s body. You should not risk your health and self-medicate.
If a woman takes a blood test for hormones twice a year and undergoes a preventive examination of the whole body, then the risk of developing any diseases is reduced several times.
Norm for men
| Name | Norm |
| FSH (mIU/ml) | 1-10 |
| LH (mIU/ml) | 0,8-8,3 |
| Testosterone (nmol/l) | 5,77-27,14 |
| Progesterone (nmol/l) | 0,8-4,2 |
| Estradiol (pg/ml) | 7,63-42,6 |
| Prolactin (mIU/ml) | 106-530 |
It is difficult to overestimate the importance of substances such as hormones in conscious family planning and pregnancy. They affect a person’s emotional state, his appearance, and his ability to reproduce. Not only women, but also men need to monitor their hormonal levels. Any imbalance can lead to irreparable consequences, which can be avoided if you get tested on time and seek help from specialists.
Pregnancy and thyroid diseases
In most cases, pregnancy becomes a pleasant surprise for expectant parents.
But there are situations when the desired conception cannot occur, despite the efforts of both partners.
The longer an infertile marriage continues, the greater the tension in the family.
Partners begin to sound the alarm, consult with all sorts of doctors, apply special diets and much more, but rarely does it occur to any of them to visit an endocrinologist.
Is it possible to get pregnant if you have thyroid disease?
The reproductive system is a complex mechanism.
The process of egg formation, the ovulatory cycle, the activity of the corpus luteum, conception, the readiness of the uterine mucosa to receive a fertilized egg and pregnancy itself - all this is under the control of the neuroendocrine system.
Its representatives are the adrenal glands, ovaries, pituitary gland, hypothalamus and thyroid gland.
All these organs are interconnected, and if any problems arise in one of them, the entire reproductive system will suffer.
You can find out the cause of the disease and cure it through a comprehensive examination of the woman.
What thyroid pathologies affect conception?
Chronic lack of iodine in the body in childhood or adolescence with hypothyroidism or endemic goiter in a girl leads to the fact that these endocrine diseases negatively affect the entire process of her puberty, in particular the formation of menstrual function, up to its absence.
Subsequently, this can lead to infertility, chronic menstrual irregularities, and problems with miscarriage.
Not only with hypothyroidism, but also with hyperthyroidism, a completely different disease in which thyroid hormones are produced in greater quantities than necessary, a woman’s reproductive function suffers.
Menstrual irregularities may also occur, usually characterized by prolonged bleeding and menopause.
This kind of bleeding has a negative impact on the female body, causing exhaustion and diseases of the internal organs, which also leads to the inability to get pregnant, as with hypothyroidism.
Diseases of the thyroid gland cause the following gynecological diseases:
- uterine fibroids;
- endometriosis;
- polycystic disease;
- mastopathy.
If the disease is autoimmune thyroiditis, conception from a practical point of view can be allowed, but often the pregnancy that has begun ends in an unfavorable scenario - fetal death or spontaneous miscarriage.
This can be explained by the synthesis of specific antibodies to the thyroid gland and autoantibodies to the circulatory system, against this background problems arise when planning pregnancy and during its subsequent bearing.
Women with autoimmune thyroiditis should be screened for hormones when planning to conceive to identify possible risk factors.
Half of women who are unable to get pregnant suffer from pathologies of the thyroid gland, often existing in an erased phase, without showing clinical symptoms of the disease, but at the same time negatively affecting reproductive capabilities, including conception.
Thus, thyroid hormones are one of the main organs of the neuroendocrine and reproductive system in a woman’s body.
Lack of iodine in food and the environment, unfavorable environmental conditions, genetic predisposition, and bad habits are to blame for this.
But the frequent detection of diseases of the endocrine system can be considered a well-deserved stage in the development of the diagnostic field of research, because in their absence, previously, thyroid diseases could be detected only at a late stage of development.
In addition, there has been a qualitative improvement in the field of gynecological endocrinology.
That is why partners who turn to specialists with problems of infertility, spontaneous miscarriage and missed pregnancy, these days receive a specific comprehensive study of the condition of the thyroid gland and its ability to produce hormones.
However, many of them suffer from a lack of ovulation.
Hypofunction of the thyroid gland, which occurs with hypothyroidism, is associated with insufficient synthesis of hormones that affect a woman’s fertility.
Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism, which also affects the maturation of female germ cells, which is explained by impaired sensitivity of the ovaries to gonadotropin.
In addition, with hypothyroidism, disturbances occur in estrogen metabolism.
As a result, estradiol is not able to convert into estrone, as it should happen under conditions when thyroid hormones are normal.
Most experts are confident in the close relationship between the thyroid gland and the woman’s reproductive system, which is disrupted against the background of negative processes in the central part of the regulation of the neuroendocrine system.
Since the functioning of the thyroid gland and the reproductive system depend on the pituitary gland, and the hormones of this organ are controlled by the hypothalamus, as a result of all these problematic chains, a woman faces problems when planning pregnancy and infertility.
When to contact an endocrinologist?
Despite the diseases listed above, infertility cannot be considered a death sentence.
The modern pharmaceutical industry and medicine do not stand still, including in the field of endocrinology.
Nowadays, specialists can cope even with such a serious diagnosis as autoimmune thyroiditis, so a woman has real opportunities to safely conceive and bear a healthy child.
You can contact an endocrinologist already when planning conception, if any problems arise with this.
What is autoimmune thyroiditis
Autoimmune thyroiditis is a chronic inflammation of the thyroid tissue. The prefix “autoimmune” means a malfunction of the immune system when the body, for some reason, begins to perceive thyroid cells as foreign and produces antibodies to them. The result is inflammation and a gradual decrease in gland function.
Another name for the disease is Hashimoto's thyroiditis (Hashimoto's). The peculiarity and main danger of this pathology is destructive changes in gland cells - thyrocytes.
The disease is sometimes asymptomatic and suddenly manifests itself during any sudden changes in the body (stress, taking medications, decreased immunity, hormonal changes).
Most often, the disease progresses and leads to the development of hypothyroidism. Less commonly, hyperthyroidism occurs - increased function of the thyroid gland, when the organ begins to produce excessive amounts of thyroid-stimulating hormones.
Most often, Hashimoto's thyroiditis occurs in women of reproductive age, and pregnancy and childbirth are provoking factors that aggravate the course of the pathology.
Is it possible to get pregnant if you have thyroid disease?
When a woman is preparing to become a mother, her attitude to health must be attentive, since the body works under great stress. The thyroid gland and pregnancy is something that every expectant mother should remember, since this organ largely determines how successfully this condition will pass.
During pregnancy, a woman’s endocrine system is subjected to increased stress; it produces large quantities of hormones necessary for the body. The amount of hormones increases because it is necessary to provide them not only to the body of the expectant mother, but also to the body of the fetus.
It is clear that the thyroid gland functions with increased intensity during pregnancy, its size may increase, but this phenomenon is temporary. There is no reason to worry in such cases, since after the baby is born everything will quickly return to normal.
The thyroid gland in pregnant women - its importance
This organ belongs to the internal secretion; it produces hormones that are of vital importance, especially thyroxine. Metabolic processes in the body are regulated, so that a person’s intellectual and physical abilities are not impaired.
In order for the organ to function normally, a sufficient amount of iodine is needed, this is important for the normal bearing of a child. If iodine is present in the required amount, then the required amount of a thyroid-type substance is produced, so there are no obstacles to the normal functioning of all human organs.
Such substances play a significant role in ensuring that the fetus in the mother’s womb develops normally, so that there are no problems with the formation of important body systems of the future baby. All this affects the condition of not only the fetus, but also the mother.
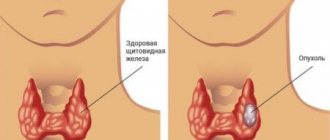
Thyroid diseases and pregnancy are the most common phenomenon among other pathological processes that are related to the endocrine system. This has a significant impact on pregnancy. But is it possible to get pregnant with such pathologies? Everything is individual, and the prognosis for diseases is also different. Some things do not threaten future motherhood, while others pose a serious danger. An enlarged thyroid gland often does not mean anything terrible, but there are symptoms that should force a woman to take the necessary measures in time.
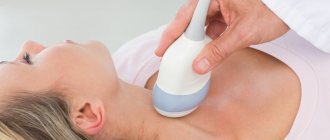
It is clear that when a woman soon plans to experience the joy of motherhood, she must carefully monitor the condition of this organ. This is not difficult to do - you need to check the amount of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream in a timely manner and on a regular basis.
Pregnancy planned with thyroid gland
In order for everything to be in order, it is necessary to take care of the condition of the organ at the pregnancy planning stage, and it is even better to do it earlier. The physical and intellectual development of the child depends on the amount of thyroid hormones in the body. If the thyroid gland is enlarged, then the consequences can be different, it all depends on what reasons caused the change in the size of the organ.
It is necessary to undergo an examination of the organ using ultrasound, then the hormonal status can be determined: it can be high or low, but it is better that it corresponds to the norm. If hormonal levels are elevated, the expectant mother should immediately see an endocrinologist. He will determine the cause of the disorder, the necessary therapy and a special diet that contains a large amount of iodine will be prescribed.
Only after all the substances return to normal can you safely go on to conceive a child, if everything is in order in the thyroid gland. There is no need to worry about the thyroid gland, even if it grows in size, but you should definitely undergo a medical examination. If a woman says, I can’t devote so much time to examinations, then everything can end badly, problems with the thyroid gland are serious. And here it is not only an enlargement of the thyroid gland, but the pathology of the thyroid gland can be more serious. The connection between this organ and the reproductive organs is close; with increased hormonal activity, the organ increases in size for various reasons.
Sick thyroid during pregnancy
Pregnancy and female thyroid disease have a significant impact on how this process occurs. At this time, problems with the endocrine system are revealed that were not visible before. At this time, the body undergoes hormonal changes; it occurs in such a way that the fetus is born in the most comfortable conditions.
Children are then born healthy, nothing prevents the baby from developing normally, all conditions are created for the child. But under the influence of pathologies, everything can change.
The thyroid gland and pregnancy involve the following pathologies:
- when a woman’s body lacks iodine, a goiter begins to form, which is also influenced by the unfavorable state of the environment. The ecology is in an unsatisfactory condition, ultraviolet and radioactive radiation are active, people work in hazardous production conditions. With goiter, the consequences are negative;
- organ tissues undergo an inflammatory process, that is, thyroiditis begins;
- the gland begins to function with increased activity, thyrotoxicosis begins;
- Tumor-like processes begin to form in the thyroid gland, which are both benign and malignant.
The thyroid gland in healthy pregnant women at the initial stage does not have any serious disorders. Pregnancy and the nodes of the female thyroid gland are interconnected, the latter often begin to change in size.
In some cases, the organ becomes larger in size, this is because the hormonal load is exceeded. But this phenomenon is reversible, so there is no reason to worry.
The thyroid gland is enlarged in pregnant women
As already noted, the organ often increases in size, but this does not always happen for physiological reasons. Pregnancy and various diseases of the thyroid gland can lead to a large size of this organ, various kinds of disorders in the endocrine system, when pathological conditions develop. Often, the expectant mother had certain disorders even before she conceived, but in this state they become obvious.
An enlarged female thyroid gland during pregnancy is observed in the following diseases:
- in the presence of hypothyroidism, this pathology occurs in a chronic mode, the functional activity of the organ is inhibited. This disease is difficult to diagnose, since the symptoms of the disease are largely similar to the general symptoms of pregnancy. The woman feels constantly tired, her nerves are out of order, and she constantly feels sleepy. Diagnostics is possible only in laboratory conditions. The danger of such a disease is great - there may be premature birth, the baby is born with anomalies, his endocrine system is affected. The symptoms here can be different, but often the symptoms have much in common with the condition of the expectant mother.
- in the presence of thyrotoxicosis, the activity of the organ significantly exceeds the norm, but such pathology is not observed so often in expectant mothers. Problems with conception begin, which entails the inability to become a mother. If you succeed in conceiving a child, then the risk of his being born with pathologies increases significantly.
Nodes in the female thyroid gland during pregnancy can also increase in size, this is influenced by hormones and developing pathologies. Therefore, it is important to know about pathologies even before conceiving a baby is planned, then it is possible to identify and cure all disorders in time.
Absence of the thyroid gland during pregnancy
Such conditions seem strange and even impossible at first, but in fact they can be observed quite often. People whose organs have been surgically removed due to cancer and other serious illnesses. It is possible to plan motherhood in such situations, but this can be done no earlier than a year after all the necessary rehabilitation measures have been completed and if the pathology does not show a relapse.
If such conditions are met, the doctor prescribes hormone replacement therapy, after which the woman will be able to conceive a child. In this case, the patient should be observed by highly specialized specialists in endocrinology and gynecology.
Thyroid nodules during pregnancy
Rarely in this condition do nodes form initially; often a woman already has them; if hormonal levels are elevated, then this situation is almost always observed. Such nodes can be benign or malignant. If they are benign, then there is no danger to the health of the expectant mother and child, but if we are talking about malignant formations, then timely medical intervention is necessary. If we are talking about increased hormonal levels, then such intervention should be immediate. A diseased node can lead to serious problems; such nodes must be dealt with in a timely manner.
If large nodes develop, then this is not a reason to terminate the pregnancy. But in this condition, a woman needs to regularly visit an endocrinologist, take the necessary tests, and undergo appropriate medical therapy so that nodal changes are under constant control.
Thyroid adenoma
We are talking about a benign formation in which the synthesis of thyroid hormones is exceeded. But for this condition no serious problems arise. The problem is that diagnosing an adenoma is difficult, since its symptoms have much in common with the general signs of the health of the expectant mother. A sick woman often doesn’t even understand what’s wrong with her; she doesn’t find any connection with her unhealthy thyroid gland.
If we are talking about a benign neoplasm, then there will be no problems, but if a malignant tumor begins to form, a serious danger arises. In order to detect the very beginning of such a pathology, it is important to undergo a timely examination by an endocrinologist.
Autoimmune type thyroiditis
This disease begins to form due to the inability of the human immune system to recognize its cells; the reasons here are the influence of negative factors. As a result, the thyroid tissue is attacked by the immune system, which negatively affects the woman’s health and the child’s development as well.
If you have autoimmune thyroiditis, you should not plan to conceive a baby; first of all, you undergo special therapy using iodine and hormonal drugs.
Organ removal
Such an organ should not be removed, otherwise the female body will be negatively affected. If a woman is diagnosed with a disease when there is a need to eliminate the endocrine organ, then it is necessary to undergo a medical abortion; premature birth can also be caused.
If sudden changes in hormonal levels are observed, then the pregnancy will proceed normally, not only the health, but also the life of the baby is at risk, so the most radical measures must be taken.
Preventive measures
If a woman is aware that she has AIT or has a family history of thyroid disease, she should undergo a thorough thyroid examination long before planning a pregnancy.
It is important to understand that pregnancy itself is a stress for the body, and the endocrine system is under a lot of stress, which it cannot always cope with.
If an atrophic or hypertrophic form of autoimmune thyroiditis is diagnosed, it is necessary to undergo a full course of treatment with medications. During therapy, pregnancy should be avoided, so the doctor usually prescribes hormonal contraceptives.
After 1.5-2 years, it is necessary to stop taking hormones and medications for the thyroid gland to ensure stable remission of the disease. If the therapy is successful, the doctor allows you to plan a pregnancy one year after treatment.
If pregnancy occurs against the background of AIT, then it is important to observe the following measures:
- visit an endocrinologist monthly;
- Check T4 levels every month.
If the indicators are reduced, the doctor prescribes premium thyreostatics, which the woman takes with constant monitoring of T4 levels. If it decreases excessively, the medication should be temporarily stopped. After childbirth, AIT usually returns, and medications are also resumed. At small doses (up to 100 mg/day) of the drug, breastfeeding is not contraindicated.
Chronic autoimmune thyroiditis
It is also called Hashimoto's thyroiditis and lymphocytic thyroiditis. It is a chronic disease of the thyroid gland of autoimmune origin. There are much more cases of chronic autoimmune thyroiditis among women (and young women are more likely to suffer from it) than among men. Cases of manifestation of AIT in the form of familial forms are often known. Relatives of most patients with AIT have circulating antibodies to the thyroid gland. It is not uncommon for the same patient diagnosed with AIT, or members of his family, to have other autoimmune diseases.
For a long time, chronic autoimmune thyroiditis may not show any symptoms. Its first symptoms are an increase in the size of the thyroid gland, changes in the structure: tuberosity, density. Patients often complain of a feeling of neck compression, a lump in the throat, difficulty swallowing; if the gland is greatly enlarged, the patient may experience difficulty breathing.
The consequence of progressive thyroiditis is hormonal disturbances. Hormones are elevated in hyperthyroidism. The patient is often irritable, has a rapid heartbeat, feels general weakness, fever, sweating, and loses weight.
In most cases, chronic AIT is manifested by a decrease in the amount of gland hormones - hypothyroidism.
In both cases, cases of infertility, weakened attention, and poor memory are identified. If children suffer from chronic AIT, they experience a slowdown in development and lag behind their peers.
Thyroiditis after childbirth
After pregnancy, the clinical manifestations of AIT increase, which is associated with the restoration of the functions of the immune system. The main reason for the exacerbation of the pathology is auto-aggression to the thyroid gland, caused by the activation of protective cells after prolonged suppression.
In 2% of women, Hashimoto's thyroiditis first appears after the birth of a child. Endocrinologists identify a number of factors that increase the risk of autoimmune disorders:
- diabetes;
- hereditary endocrine diseases;
- early and late toxicosis;
- repeat pregnancy.
Pregnancy and childbirth are key factors provoking relapses of thyroiditis in women.
If the disease is detected in patients at the stage of pregnancy planning, then after the birth of the child, drug therapy is started. For classic triphasic thyroiditis, symptomatic medications (beta blockers, NSAIDs), triiodothyronine substitutes or iodine-containing drugs are prescribed. Timely therapy prevents postpartum depression, myxedema, and heart failure.
The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland and is part of the endocrine system. It synthesizes two iodine-containing hormones - thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), and a peptide hormone - calcitonin.
Thyroid hormones are the main regulators of body homeostasis. They take part:
- in the main metabolic processes of tissues and organs;
- in the formation of new cells;
- in structural differentiation.
Another important function of thyroid hormones is maintaining a constant body temperature and producing energy. Thyroid hormones regulate the oxygen consumed by tissues, the processes of oxidation and energy production, and control the formation and neutralization of free radicals. Throughout life, the influence of thyroid-stimulating hormones on the development of the body in physical, mental and mental terms does not cease. Due to a deficiency of hormones during pregnancy, underdevelopment of the brain during intrauterine development is possible, therefore, the risk of cretinism in the child increases. Thyroid hormones are also responsible for the proper functioning of the immune system.