Why amniotic fluid is needed
Amniotic fluid is necessary for the normal development of the child in the mother's womb; it is needed for
- protecting the child from loud sounds and impacts (water absorbs noise and acts as a shock absorber);
- maintaining a comfortable temperature (amniotic fluid has a temperature of 37 degrees);
- protection from external threats (the amniotic fluid bladder is sealed, which allows the child to be protected from external influences);
- providing nutrition to the baby (water does not allow the bladder to shrink, preventing the umbilical cord from being compressed);
- freedom of movement of the baby (in the 1st-2nd trimester the baby can move freely and swim in the amniotic fluid).
At birth, leaving his native environment, the child experiences stress, which water helps relieve. When the birth ligament is washed off from a newborn baby, he relaxes. This is very important for preparing for the new stage of his life.
What is oligohydramnios?
In obstetrics and gynecology, insufficient amniotic fluid is called oligohydramnios.
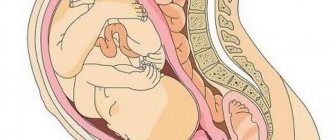
Amniotic fluid (or amniotic fluid)
- the liquid environment in which the fetus is located during pregnancy.
This biological fluid performs several important functions. These include:
- protective function
- the water shell protects the child from the penetration of infections (due to the tightness of the shells and immunoglobulins included in the water), from mechanical influences from the outside (for example, from blows and shocks), loud sounds (water muffles them), external fluctuations in pressure and temperature (maintaining optimal pressure and constant temperature of 37 ºС, of course, if mommy is healthy and her body temperature does not exceed 37.8 ºС); - metabolic function
- the child absorbs amniotic fluid, enriched with nutrients, and releases it back. In addition to all this, fetal fluid ensures free movement of the baby inside the womb. Therefore, with a normal amount of amniotic fluid, the baby is cozy and comfortable, he is protected and provided with everything he needs.
Composition and norm of amniotic fluid
The fetal membranes begin to form after the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus.
Then a complex process begins. A protective bladder with sterile fluid inside is formed from the membranes (amnion and chorion). As the fetus grows, the bubble enlarges. Amniotic fluid is formed due to the “leakage” of maternal blood plasma. In the later stages, the child himself, his lungs, and kidneys also participate in the production and renewal of amniotic fluid.
Amniotic fluid consists of water (97%) with proteins and mineral salts (calcium, sodium, chlorine) dissolved in it. Skin cells, hair cells, and aromatic substances can also be found in it.
There is an opinion that the smell of amniotic fluid is similar to the smell of mother's milk, so a newborn baby can easily find his mother's breast, because he drank a liquid similar to milk in the womb.
Norm and pathologies
The normal amount of amniotic fluid at the end of pregnancy is 600-1500 ml. For a number of reasons, these figures may deviate more or less from the norm. Then doctors talk about polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios.
Oligohydramnios is diagnosed when the expectant mother has less than 500 ml of amniotic fluid. The reason for the decrease in the amount of water lies in the insufficient development of the endometrium (water membrane) or a decrease in its secretory ability. Among other reasons causing pathology are called
- abnormalities in the development of the child’s genitourinary system;
- mother's hypertension;
- inflammatory diseases of women;
- metabolic disorders, obesity;
- fetoplacental insufficiency.
Oligohydramnios in one fetus when carrying twins is explained by the uneven distribution of blood in the placenta.
With oligohydramnios, severe abdominal pain, painful movements of the child are observed, the uterus is reduced, and the size of its fundus does not correspond to the gestational age.
With polyhydramnios, the secretory function of the aqueous membrane is increased. Polyhydramnios can result from:
- diabetes mellitus, infectious and viral diseases of the mother;
- heart disease, kidney disease;
- incompatibility of the Rh factor of the blood of mother and child;
- multiple pregnancy (polyhydramnios in one fetus, oligohydramnios in the other);
- diseases of the placenta.
Signs of polyhydramnios are heaviness in the abdomen, swelling of the legs, breathing and blood circulation become difficult, and the child’s movements become too active.
Oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios are dangerous pathologies. To eliminate them, the help of a specialist is required. At the slightest suspicion, you should consult a doctor.
Deviations in the color of amniotic fluid
Normally, amniotic fluid is colorless and transparent. The consistency is similar to water and has no odor. Most often, expectant mothers are concerned about changes in the color of the amniotic fluid.
You can judge the color of amniotic fluid during its outpouring, which occurs during childbirth. In most cases, if the pregnancy is full-term, the waters are clear or cloudy yellow. This is their normal color and is not dangerous. The woman’s task after her water breaks is to get to the maternity hospital within 2-3 hours.
Amniotic fluid may be a different color.
- Red speckled. A slight admixture of blood in a fluid of normal (light or cloudy yellow) color is considered normal, since it indicates dilatation of the cervix.
- Green color. The baby's original feces turn the water greenish or swampy. The child experiences oxygen starvation; swallowing such water is dangerous for the development of pneumonia in the baby.
- Red. Dangerous color indicates internal bleeding in the mother or fetus. The best decision is to take a horizontal position and urgently call an ambulance.
- Dark brown. This color indicates the death of the fetus; you should immediately consult a doctor.
Possible risks when a problem is detected
A discrepancy between the norms of the amniotic fluid index by week of pregnancy indicates the occurrence of polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios in a woman.
The manifestation of such conditions is quite dangerous, even threatening serious complications. Dangers of polyhydramnios:
- possible placental abruption;
- development of infection of the birth canal;
- fetal development disorder;
- miscarriage is possible.
Most often, oligohydramnios is detected after 26-30 weeks or after post-term pregnancy at 41 weeks. In addition, oligohydramnios threatens serious fetal diseases.
Ultrasonography
If the amniotic fluid index at 31 weeks is 66, with an average value at 31 weeks of 14 cm, then you need urgent specialist intervention.
Dangers of oligohydramnios:
- disorders of the respiratory and genitourinary systems;
- hypodynamics and pressure on the fetus, which can cause various anomalies: changes in fetal weight, dislocations, deformations of bones and spine;
- the occurrence of hypoxia;
- possibility of premature miscarriage;
- risk of bleeding after childbirth.
Excess amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios) is detected in 1 to 3% of women in labor. For example, at week 34 your AFI is more than 278 units, this indicates a critical level of amniotic fluid. The causes of polyhydramnios are influenced by the presence of certain factors.
From the mother's side:
- Rh factor, blood group;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- the presence of infections or inflammatory processes in the body.
According to placenta analysis:
- when a benign tumor of the fetal membrane occurs;
- with swelling of the placenta.
Diagnosis of the fetus:
- multiple pregnancy;
- hereditary pathologies or diseases.
Causes of oligohydramnios:
- abnormalities of the fetus inside the womb;
- various pathologies: infections, chromosomal abnormalities, poor fetal development, etc.;
- the presence of diseases in a woman: problems with the heart, blood vessels, inflammatory and infectious symptoms, kidney disease;
- placental insufficiency, defects, heart attack;
- post-maturity of the fetus;
- placental abruption;
- premature death of a child inside the womb.
People in white coats
Polyhydramnios can be of different types.
- In moderate condition, the size of the inner pocket ranges from 7 cm to 18.
- With severe polyhydramnios, the value appears in the range from 18 to 24 cm.
- In chronic cases, the indicator is slightly higher, but stable.
- In borderline and acute conditions, the index value varies between the average and the highest. In this case, inpatient treatment is recommended.
- In case of acute excess fluid, specialists will prescribe an amniotomy; in case of chronic excess, complex therapeutic treatment.
Self-treatment is not recommended at all. Only observation by specialists and compliance with all doctor’s instructions guarantee the safety of the mother and fetus.
These recommendations also apply to oligohydramnios; in case of acute symptoms, the pregnant woman will be offered hospital treatment. For example, your amniotic fluid index is 5 5, this indicates critical oligohydramnios, which can become a threat to the life of the fetus.
Recommendations for moderate polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios:
- everyone without exception is prescribed Curantil, Actovegin;
- minimum physical activity;
- healthy diet, diet in combination with a vitamin complex;
- preventive treatment to protect against the formation of infectious and inflammatory processes;
- in case of postmaturity – stimulation of labor.
As the baby grows
In traditional treatment, antibiotics are usually used to restore hypodynamic functions. For various infections, immunomodulators are prescribed. Diuretics are required.
Water research methods
Today, there are several ways to obtain information about the state of the amniotic fluid before the onset of labor. All methods are divided into invasive (requiring direct sampling of material) and non-invasive (not requiring penetration into the uterine cavity).
The only non-invasive method is ultrasound. This study can provide information about the amount of amniotic fluid and allows you to diagnose oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios.
Other research methods (invasive) are associated with high risks, therefore they are carried out for serious indications.
- Amnioscopy. Inspection of amniotic fluid using an amnioscope. This device is a tube with a lighting device at the end. The examination of the expectant mother is carried out on a gynecological chair by inserting the device into the cervix. The doctor pays attention to the color and consistency of the water. An examination is possible after 37 weeks if there is a suspicion of fetal hypoxia or Rhesus conflict.
- Amniocentesis. Unlike amnioscopy, amniocentesis is performed after 16 weeks of pregnancy, when the fluid volume reaches 150 ml. A needle is inserted into the amniotic cavity under ultrasound guidance and a small amount of fluid is withdrawn. To perform amniocentesis, serious indications are needed: suspicion of genetic diseases or intrauterine infections, Rh conflict, insufficient oxygen supply, chronic diseases of the mother.
Invasive diagnostic methods are associated with risks of miscarriage, premature rupture of amniotic fluid, miscarriages, and placental abruption. Only a doctor can prescribe the procedure.
Indications for the study
If there are any factors from the list of reasons, it is recommended to undergo all examinations regularly. Their types and frequency should be determined by the observing gynecologist.
Low or polyhydramnios can be determined using an ultrasound scan.
Oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios are not accompanied by any pronounced symptoms, so the lack of fluid can only be confirmed during an ultrasound examination. The doctor can suggest the presence of a problem after assessing the dynamics of the increase in the volume of the abdomen and raising the fundus of the uterus upward.
Amniotic fluid norms by week of pregnancy
As pregnancy progresses, the amount of amniotic fluid increases. Approximate calculations look like this:
- 30 ml at 10-11 weeks;
- 100 ml for 13-14;
- 400 ml at 17-20;
- 1200ml for 36-38;
- 600-800 a few days before birth.
The amount of amniotic fluid is individual for each expectant mother; the calculations given are approximate, so doctors do not measure the amount of amniotic fluid in milliliters using the definition of “amniotic fluid index.” It is measured using an ultrasound machine starting at 16 weeks. The norms look like this:
- 73-201 mm (average 121) at 16 weeks;
- 77-211 (127) at 17;
- 80-220 (133) by 18;
- 83-230 (137) at 19;
- 86-230 (143) by 20;
- 88-233 (143) at 21;
- 89-235 (145) at 22;
- 90-237 (146) at 23;
- 90-238 (147) at 24;
- 89-240 (147) at 25;
- 89-242 (147) at 26;
- 85-245 (156) at 27;
- 86-249 (146) at 28;
- 84-254 (145) at 29;
- 82-258 (145) at 30;
- 79-263 (144) at 31;
- 77-269 (144) at 32;
- 74-274 (143) at 33;
- 72-278 (142) at 34;
- 70-279 (140) at 35;
- 68-279 (138) at 36;
- 66-275 (135) at 37;
- 65-269 (132) at 38;
- 64-255 (127) at 39;
- 63-240 (123) by 40;
- 63-216 (116) at 41;
- 63-192 (110) at 42.
These figures can be seen in the medical card; the average figures for each stage of pregnancy are given in brackets. Only a doctor can correctly decipher the data, since the norms of the amniotic fluid index depend on the individual characteristics of the body.
What are the causes of oligohydramnios?
Depending on the severity of the pathology, moderate and severe oligohydramnios are distinguished.
You can often find an inscription in an ultrasound report: “a tendency towards moderate oligohydramnios.” This means that the expectant mother may have health problems and needs more careful monitoring.
Moderate oligohydramnios
– this is a slight deviation in the amount of fetal fluid from the norm. This type of deviation may be caused by the individual characteristics of the pregnant woman’s body or, in the worst case, may be a prerequisite for the occurrence of a more severe form of this pathology. In any case, doctors recommend preventing fetoplacental insufficiency (FPI).
Moderate lack of water is not a critical situation, because the amount of water is not constant and can change several times a day. Perhaps there was an error in establishing the diagnosis and the fault was with the doctor who made a not very accurate calculation during the ultrasound, because determining the amniotic fluid index is a subjective and approximate matter. Therefore, there is no need to panic; in 8 out of 10 cases, pregnancy ends in the successful birth of a healthy baby.
Severe oligohydramnios
poses a danger to the health of the fetus, so you must follow all the instructions of the doctor monitoring the pregnancy.
The causes of oligohydramnios, regardless of the degree of its severity:
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- problems with the cardiovascular system in a pregnant woman (hypertension and others);
- diseases of the fetal urinary system (kidneys, for example);
- leakage of amniotic fluid (if the integrity of the membranes is violated);
- pathology in the development of membranes;
- bacterial infections suffered during pregnancy or shortly before its onset;
- diabetes;
- late gestosis.
Most often, oligohydramnios occurs due to metabolic disorders in a pregnant woman, as well as after viral diseases (acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, etc.) and with fetoplacental insufficiency.
Personal practice shows that ultrasound doctors often exaggerate the scale of the problem, and a slight deviation from the norm is already a disaster for them. Such pseudo-oligohydramnios causes unnecessary stress for the expectant mother, but in fact the babies are born relatively healthy.
The only thing is that childbirth with oligohydramnios (even slight) can occur with some complications (poor opening of the cervix, painful contractions and prolonged labor due to pelvic or breech presentation of the fetus, which arose due to oligohydramnios). Although complicated childbirth can occur in any woman in labor, regardless of the amount of water.
obstetrician-gynecologist A. Berezhnaya
The occurrence of oligohydramnios during post-term pregnancy is considered a common occurrence, since the placenta has grown old and can no longer fully perform its functions, so it exfoliates. Then doctors prescribe induction of labor or perform a planned caesarean section.
What is IAF and its measurement
The amount of amniotic fluid is assessed in two ways:
Subjective. A sonographer (ultrasound specialist) carefully examines the amount of amniotic fluid in transverse and longitudinal scans and identifies polyhydramnios (an increase in amniotic fluid between the fetus and the anterior abdominal wall) or oligohydramnios (accordingly, the volume of water is reduced along with spaces free from echo structures).
Objective. This method is the determination of the amniotic fluid index. To do this, the ultrasound specialist divides the uterine cavity into 4 quadrants by drawing perpendicular lines. The transverse line runs horizontally at the level of the navel, and the vertical line runs along the linea alba of the abdomen. In each “compartment”, a vertical pocket is determined and measured, that is, the deepest pocket without echo structures. By summing the 4 values, which are expressed in centimeters, the IAF is obtained.
Optimal treatment
The optimal treatment is determined individually for each pregnant patient, taking into account the diagnosis, characteristics and cause of the problem.
Let's say you are 32 weeks pregnant and your amniotic fluid index is 77. This means you have borderline oligohydramnios.
Polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios are far from a tragedy, but with oligohydramnios you will have to spend most of your time in hospital.
If you take medications correctly and strictly follow the doctor's recommendations, the level of polyhydramnios will decrease, and the value of oligohydramnios will increase to the required numbers. In this case, your index of AF - amniotic fluid will remain at a stable value.
A good mood, positive emotions, a positive attitude, and strict adherence to all doctor’s recommendations guarantee minimal risk to the mother’s health and the normal development of the child.
| Medical Center | Address | Price |
| 1st Clinical City Hospital | Minsk, Nezavisimosti Ave., 64 | 6200 rub. |
| Medicine plus | Moscow Volgogradsky pr., 64 | from 1500 rub. |
| Alpha Health Center | Ekaterinburg, st. Maxim Gorky, 17 | from 1500 rub. |
| Nadiya Reproductive Medicine Clinic | Kyiv, st. Maxim Krivonosa, 19 A | from 490 rub. |
About the author : Borovikova Olga
Water is the first thing a child gets acquainted with. While still in the womb, it floats in a fluid called amniotic fluid. Find out what amniotic fluid looks like and what the norm is by week (table) of pregnancy from the article.
Amniotic fluid norms by week
The amniotic fluid index depends on the stage of pregnancy, and starting from 16 weeks, its value gradually increases, reaching a peak at 32 weeks, and then AFI values decrease.
Amniotic fluid index norms:
- 16 weeks – 73-201mm (average 121mm);
- 17 weeks – 77-211mm (average 127mm);
- 18 weeks – 80-220mm (average 133mm);
- 19 weeks – 83-230mm (average 137mm);
- 20 weeks – 86-230mm (average 141mm);
- 21 weeks – 88-233mm (average 143mm);
- 22 weeks – 89-235mm (average 145mm);
- 23 weeks – 90-237mm (average 146mm);
- 24 weeks – 90-238mm (average 147mm);
- 25 weeks – 89-240mm (average 147mm);
- 26 weeks – 89-242mm (average 147mm);
- 27 weeks – 85-245mm (average 156mm);
- 28 weeks – 86-249mm (average 146mm);
- 29 weeks – 84-254mm (average 145mm);
- 30 weeks – 82-258mm (average 145mm);
- 31 weeks – 79-263mm (average 144mm);
- 32 weeks – 77-269mm (average 144mm);
- 33 weeks – 74-274mm (average 143mm);
- 34 weeks – 72-278mm (average 142mm);
- 35 weeks – 70-279mm (average 140mm);
- 36 weeks – 68-279mm (average 138mm);
- 37 weeks – 66-275mm (average 135mm);
- 38 weeks – 65-269mm (average 132mm);
- 39 weeks – 64-255mm (average 127mm);
- 40 weeks – 63-240mm (average 123mm);
- 41 weeks – 63-216mm (average 116mm);
- 42 weeks – 63-192mm (average 110mm).
Indicator table is normal
AFI, the norm by week during pregnancy is within fairly wide limits, can additionally change down or up. Therefore, the given data are averaged; the presence or absence of a problem must be determined by the observing gynecologist.
| Gestational age in weeks | Range of indicators | Average |
| 16 | 75-200 | 120 |
| 17 | 76-210 | 126 |
| 18 | 80-219 | 133 |
| 19 | 84-229 | 136 |
| 20 | 85-229 | 140 |
| 21 | 89-232 | 142 |
| 22 | 89-234 | 144 |
| 23 | 90-236 | 145 |
| 24 | 90-237 | 147 |
| 25 | 90-239 | 147 |
| 26 | 90-241 | 147 |
| 27 | 85-244 | 155 |
| 28 | 87-248 | 145 |
| 29 | 85-253 | 146 |
| 30 | 83-257 | 146 |
| 31 | 80-264 | 146 |
| 32 | 78-268 | 145 |
| 33 | 75-273 | 145 |
| 34 | 73-277 | 143 |
| 35 | 71-278 | 139 |
| 36 | 69-278 | 138 |
| 37 | 67-274 | 124 |
| 38 | 66-268 | 133 |
| 39 | 65-254 | 128 |
| 40 | 64-239 | 124 |
| 41 | 64-215 | 115 |
| 42 | 64-189 | 109 |
When carrying monochorionic diamniotic twins, fluid deficiency is recorded more often. In this case, doctors recommend carrying the pregnancy to at least 32 weeks.
In the future, depending on the criticality of the particular case, a planned caesarean section may be required. For monitoring, ultrasound examinations are recommended every 10 days for the remainder of the pregnancy.
Doctors must also determine the height of the vertical pouch - the distance of free space between the fetus and the inner wall of the amniotic bladder. Based on this indicator, one can assume the development of feto-fetal syndrome during pregnancy with twins or triplets.
Feto-fetal syndrome is a serious complication of multiple pregnancies, in the presence of which the blood flow of individual fetuses differs significantly. In severe cases, mortality can reach 100%. The syndrome is accompanied by the development of polyhydramnios.
To treat and correct the condition of the woman and fetus, it is recommended to carry out the procedure of amnioreduction, or removal of excess amniotic fluid.
Additionally, the production of surfactant is monitored - a substance that allows the lungs to open after the birth of a child and prevents them from collapsing in the future.
The biological role of amniotic fluid in the body of a pregnant woman
Amniotic fluid is the environment that surrounds the baby from the first weeks of his life. It has an optimal temperature regime, chemical and biological composition for the development and vital activity of the embryo at all stages of its development.
From a physiological point of view, the amniotic fluid is transparent or slightly cloudy; during analysis, particles of epithelium, a certain amount of lubricant, fluff and fetal urine can be detected in it.
It is not constant - every 2.5-3 hours, due to the secretion of fluid by the membranes, a partial change (resorption) of amniotic fluid occurs in several systems:
- “mother – fetus – amniotic fluid” (about 30-50% of the total volume of water is replaced, while some of it is absorbed by the fetus itself);
- “mother - amniotic fluid” (renewed to 75-80% of the fluid).
The maximum formation of amniotic fluid is observed in the first 5 months of pregnancy, but as labor approaches, its volume rapidly decreases and in the prenatal period is only 0.5-2 liters.
Studies of the waters themselves have shown that they contain a variety of biological substances and components:
- vitamins;
- microelements in various proportions;
- enzymes;
- antibodies and antigens;
- hormones and immunoglobulins;
- proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
Analysis of amniotic fluid can help determine the sex and blood type of the fetus, as well as provide comprehensive information about the state of its development.
Reasons for the development of oligohydramnios
There are many reasons for the formation of oligohydramnios. The main ones are:
- underdevelopment of membranes or reduced secretion of water;
- abnormal development of the fetus (its kidneys, skeleton);
- increased blood pressure in the expectant mother, especially with significant deviations from the norm;
- bacterial infections that penetrate not only through the genital tract, but also directly into the amniotic fluid;
- multiple pregnancy, with uneven development of the placenta, giving different blood flow to each fetus;
- post-maturity;
- impaired metabolism in a woman’s body, especially if she is overweight.
Methods for studying amniotic fluid
Amniotic fluid is not only the environment and nutrient medium for the embryo, it performs a number of important functions, for example:
- prevents pressure on the fetus from the outside;
- creates intrauterine silence, protecting the embryo from loud sounds and noises;
- prevents infections from entering the uterine cavity;
- participates in the formation of vital systems, including initial coordination of movement, since the fetus moves relatively freely in the amniotic fluid;
- protects against mechanical influences.
To assess the cytological and biological composition of amniotic fluid, various research methods have been developed:
- Ultrasound (to determine the homogeneity and amount of amniotic fluid);
- amnioscopy;
- amniocentesis.
Amniotic fluid plays an important role in the birth process itself - biological substances contained in the amniotic fluid stimulate the dilation of the cervix, therefore their qualitative and quantitative composition is important, and anomalies are unacceptable.
What function do they perform?
During pregnancy, the water membrane protects the baby from mechanical damage (injuries, bruises, blows), creates a comfortable living environment, participates in metabolism, protects the umbilical cord from compression, prevents the formation of adhesions between the baby’s skin and the walls of the uterus, protects against infections from the genital tract . The baby constantly swallows liquid, training the digestive, excretory and respiratory systems.
During labor, the amniotic sac presses on the cervix, causing it to dilate. During physiological childbirth, the amniotic sac ruptures in the first stage of labor with full or almost (5-6 cm) full dilatation of the cervix. Timely rupture of the membranes not only contributes to the normal process of effacement and dilatation of the cervix, but also maintains favorable conditions for the fetus during labor. As long as the membranes are intact, the baby is not in danger of infection. In addition, the contracting walls of the uterus do not directly envelop the fetus and do not disrupt the blood circulation between the mother and the fetus. The breaking of water after cervical dilatation of 3 cm or more rarely changes the normal course of labor. The absence of an amniotic sac at the onset of labor can lead to the development of labor weakness.
Amniotic fluid index
The amniotic fluid index (AFI) is a quantitative indicator of the volume of amniotic fluid at a specific stage of pregnancy.
But given the fact that each organism has its own characteristics, IAF is usually called “floating”.
The amount of amniotic fluid is determined using an ultrasound machine.
To do this, the uterine cavity is conventionally divided into 4 sectors (pockets), one section runs along the white line of the abdomen, and the second is perpendicular to it through the navel.
In each sector, the maximum vertical pocket is measured - the free distance between the fetus and the uterine wall. The resulting values are added together, and the indicator is expressed in millimeters (mm).
Table. Norms of amniotic fluid index by week of pregnancy
| Gestation period, weeks | Index value (10th percentile), mm | Index value (50th percentile), mm | Index value (95th percentile), mm |
| 16 | 73 | 121 | 201 |
| 17 | 77 | 127 | 211 |
| 18 | 80 | 133 | 220 |
| 19 | 83 | 137 | 225 |
| 20 | 86 | 141 | 230 |
| 21 | 88 | 143 | 233 |
| 22 | 89 | 145 | 235 |
| 23 | 90 | 146 | 237 |
| 24 | 90 | 147 | 238 |
| 25 | 89 | 147 | 240 |
| 26 | 89 | 147 | 242 |
| 27 | 85 | 156 | 245 |
| 28 | 86 | 146 | 249 |
| 29 | 84 | 145 | 254 |
| 30 | 82 | 145 | 258 |
| 31 | 79 | 144 | 263 |
| 32 | 77 | 144 | 269 |
| 33 | 74 | 143 | 274 |
| 34 | 72 | 142 | 278 |
| 35 | 70 | 140 | 279 |
| 36 | 68 | 138 | 279 |
| 37 | 66 | 135 | 275 |
| 38 | 65 | 132 | 269 |
| 39 | 64 | 127 | 255 |
| 40 | 63 | 123 | 240 |
| 41 | 63 | 116 | 216 |
| 42 | 63 | 110 | 192 |
The results of the study are not always 100% correct, since they directly depend on the qualifications of the diagnostician and the condition of the equipment.
Oligohydramnios during pregnancy
Oligohydramnios is a rather unpleasant and very common phenomenon during pregnancy. If the deviation of the amount of amniotic fluid from the norm of the amniotic fluid index by week is insignificant, a diagnosis of “moderate oligohydramnios” is made. In order to correct it, you can use diet, proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle. After some time, the amount of water returns to normal and does not in any way affect the child’s condition.
The diagnosis of “severe oligohydramnios” is made when the deviation from the norm of the amniotic fluid index over the weeks is large. With this diagnosis, urgent hospitalization and inpatient treatment are required. This is due to the high probability of dire consequences for the child.
If the amniotic fluid index at 20 weeks (normal) is in the range of 86-230 ml, and ultrasound results indicate a much smaller actual volume of amniotic fluid, in the absence of treatment this can provoke underdevelopment of vital organs, deformation of skeletal bones, and the development of various fetal pathologies. Therefore, it is very important to start treatment of severe oligohydramnios on time.
When a low amniotic fluid index is determined at 34 weeks (the norm is on average 142 ml), and there are already well-defined deviations in the development of the child, the question of terminating the pregnancy often arises, since treatment in this case is pointless and will not bring any benefits. results.
Norm and pathologies of amniotic fluid
It is important to understand that only a qualified specialist can make an accurate diagnosis, based on ultrasound data, amniotic fluid index and examination of the patient.
If you average the amount of amniotic fluid, you get the following picture:
- at 10-11 weeks 30 ml;
- 13-14 weeks – about 100 ml;
- 17-20 weeks – up to 400 ml;
- 36 week – approximately 1200 ml;
- a few days before birth – 600-800 ml.
A sufficient amount of amniotic fluid allows a woman to give birth independently and without complications.
AFI is higher than normal
An amniotic fluid index of more than 25 cm is considered polyhydramnios.
Amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid) is a biologically active liquid medium that surrounds the fetus during pregnancy. It consists of water and contains small amounts of mineral salts, fetal cells, fragments of sebaceous glands and epidermal scales. The formation of amniotic fluid begins in the third week of pregnancy and reaches 1-1.5 liters by the time of birth.
Amniotic fluid not only allows the baby to move freely in the womb, but also maintains a constant body temperature and protects it from infection and mechanical influences from the external environment. Towards the end of pregnancy, the kidneys and lungs of the unborn child begin to take part in the production of amniotic fluid.
Reasons for deviations from the norm
Deviations from the norm of AFI, up or down, make it possible to diagnose polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios.
Polyhydramnios
Polyhydramnios occurs in 1-3% of cases of the total number of births (data vary significantly among different authors). This pathology is caused by 3 groups of factors:
1. From the woman's side
- immunization based on Rh factor and blood group;
- diabetes;
- various infectious and inflammatory processes;
2. From the placenta
- Chorioangioma (benign tumor of the fetal membrane, the outcome of pregnancy depends on its size; if detected, regular monitoring is recommended);
- according to ultrasound, “placenta surrounded by a cushion” (edema);
3. From the fetus
- multiple pregnancy;
- congenital anomalies of fetal development (with polyhydramnios, it occurs in 20-30% of cases);
- chromosomal pathology and hereditary diseases;
Low water
The share of oligohydramnios is 0.3-5.5% and the causes of its occurrence include:
- intrauterine anomalies of fetal development (malformations of the genitourinary system);
- fetal pathology (developmental delay, intrauterine infection, chromosomal diseases);
- maternal diseases (preeclampsia, pathology of the cardiovascular system, kidney disease, infectious and inflammatory processes);
- pathology of the placenta (fetoplacental insufficiency, placental defects, heart attacks);
- post-maturity;
- placental abruption;
- intrauterine fetal death.
Important! All materials are for reference purposes only and are in no way an alternative to face-to-face consultation with a specialist.
Preparing and conducting analysis
Ultrasound examination is recommended for all pregnant women to exclude developmental pathologies, determine the sex of the child and assess his general health and current condition.
During the examination, an ultrasound sensor, a transducer, generates special vibrations that are directed into the tissue. There they encounter various obstacles and are repelled by them. As a result, a two, three or four-dimensional image is displayed on the monitor.
According to medical standards, an ultrasound examination must be performed several times:
- 11-14 weeks;
- 20-24 weeks;
- 32-35 weeks.
For the first time, the correct formation of the fetal body and its internal organs is assessed. Gender can most often be determined starting from the 12th week of pregnancy. Sometimes errors occur due to the fact that the external genital organs of boys and girls at such an early stage of development have many similarities.
Therefore, if the mother really wants to know who she is carrying, the ultrasound specialist may recommend an additional visit after 2 weeks. In private clinics, you do not always need to pay extra for this service separately.
dangers, causes, treatment tactics, consultation
Around the baby in the womb there is amniotic fluid, which is vital for its safety and development. These waters protect the fetus from mechanical shocks, infections, temperature changes; they are important for the formation of breathing and digestion processes, as well as for the development of the baby’s bones and muscles. What is polyhydramnios? This is when too much amniotic fluid accumulates in the uterus; this diagnosis occurs in 1% of all pregnancies.
Types of polyhydramnios
Relative - not dangerous if the doctor is absolutely sure that the pregnant woman does not have any infection. It is most common in women who are expecting a large child.
Idiopathic - polyhydramnios, the cause of which remains unclear.
Moderate - the size of the vertical pocket is 8-18 cm.
Pronounced - the size of the vertical pocket is above 18 cm, and the IAF is more than 24 cm.
Borderline, tendency to polyhydramnios - when the level is at the borderline between normal and elevated levels. Observation required.
Acute - when the amount of water increases at a high speed. Quite dangerous for the life of the fetus if no measures are taken by doctors.
Chronic - the amount of fluid is higher than normal, but stable.
Causes of polyhydramnios during pregnancy
Experts say that it is possible to find out the causes of polyhydramnios only in 2 out of 3 cases. It turns out that one third of pregnant women with this diagnosis have idiopathic polyhydramnios (for no apparent reason). Why might a woman have this problem?
- Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus in a woman.
- Multiple pregnancy. In most cases, it happens that one child receives more blood and nutrients than the other, which leads to complications.
- Anomalies of fetal development. In this case, it may be difficult for the child to swallow and process the amniotic fluid. This occurs due to a cleft lip or palate, hydrocephalus, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, nervous system or heart.
- Fetal anemia.
- Cardiovascular diseases in pregnant women.
- Incompatibility of blood between mother and child.
- Problems in the functioning of the placenta.
Signs and diagnosis
If we are talking about a mild form, then usually the woman does not feel any suspicious abnormalities.
If the case is severe, shortness of breath, swelling in the lower abdomen and rare trips to the toilet occur.
Polyhydramnios is usually diagnosed after an ultrasound. It may be prescribed unscheduled if the gynecologist suddenly notices some signs - high blood pressure, a urinary tract infection suddenly appears, the stomach becomes larger than normal and swelling appears.
Treatment methods
If polyhydramnios is acute, an amniotomy will be prescribed to remove excess water. If it is chronic, it would be better to prolong the pregnancy until the due date and prescribe complex therapy.
Is it possible to cure yourself at home using folk remedies? I strongly recommend that you follow your doctor's instructions and not use any herbal remedies or homeopathy. There are a number of drugs that are used depending on the cause of polyhydramnios, we will discuss them in detail below. Leave folk remedies for treating colds.