Amniotic fluid index: weekly norms and causes of deviations
In the mother's womb, the baby is in an environment that is ideal for its development and growth. The environment that provides the baby with protection, nutrition, and maintenance of a stable temperature is water. Amniotic fluid is located inside the amniotic sac and its quantity at different stages of pregnancy is an important indicator that allows us to judge how well the baby is developing. The amount of water is usually measured using the amniotic fluid index ( AFI).
What it is?
The amniotic fluid index is a special value that is determined during an ultrasound scan during pregnancy. It indicates the amount of amniotic fluid. At different stages of pregnancy, the amount of aqueous medium cannot be the same, because the pressure inside the uterus must, like the temperature, be maintained at a constant level. The membranes secrete water, the baby takes part in this process by swallowing it and peeing with it, renewal occurs every three hours.
But the baby grows, gains weight, the placenta grows, the umbilical cord becomes longer, and if the amount of water remained at the same level throughout the entire gestation period, the woman’s uterus would simply burst before the time came to give birth.
That is why, as the baby grows, the amount of water gradually decreases, the amniofluid index decreases, the pressure remains stable, and overstrain of the uterus and amniotic sac does not occur. Fluid normally leaves the amniotic sac already at the end of the first stage of labor, before pushing at the peak of labor contractions. Earlier rupture before childbirth is considered a complication of childbirth. And leakage of water due to a violation of the integrity of the fetal bladder, tears and microcracks of the membranes, when the liquid comes out literally drop by drop gradually, is considered a serious complication of pregnancy.
That is why IAF is a permanent column of the ultrasound diagnostic protocol. Both scheduled and unscheduled surveys always include determining the amount of water.
Doctors calculate the volume of fluid inside the amniotic sac in two ways. The first one is subjective. In order to understand how much water is present inside the fetal sac at that particular period of gestation, the doctor takes longitudinal and transverse measurements of the internal cavity of the uterus. However, the error in such a calculation is quite high, and therefore the amniotic fluid index was created. This method of determination is also considered subjective, but still its accuracy is somewhat higher.
In order to calculate the IAF, several mathematical values are needed, obtained after visually dividing the uterine cavity into quadrants. The doctor sees the reflected ultrasound signal on the monitor - an image of the uterine cavity. He draws two straight lines - across and along so that they intersect at one point in the center of the uterus. This results in four quadrants.
In each of the four quadrants, the sensor measures a vertical pocket, which is considered the deepest. It is important that there are no fetal limbs or umbilical cord at the measurement site. We get four numbers, their addition in total determines the index we are looking for - IAZ.
This value is not considered absolutely accurate. It all depends on how prepared and qualified the doctor conducting the examination is, as well as on the quality and resolution of the ultrasound diagnostic device itself. This means that if a woman undergoes two ultrasound examinations on the same day by two different doctors using different machines, she will receive different results from each other. True, not so much that one doctor sees the pathology and the other does not. To avoid discrepancies and confusion, it is customary to consider quite significant ranges of acceptable values as norms.
When is it necessary to take an amniotic fluid test?
Amniocentesis is performed at different stages of pregnancy and, depending on the period, is divided into two types.
- Early amniocentesis: performed in the first trimester of pregnancy (from 10 to 14 weeks).
- Late amniocentesis: performed after the 15th week of pregnancy.
There are two techniques for accessing the amniotic sac:
- use of a puncture adapter;
- "free hand" technique.
Why is amniocentesis performed?
- Intrauterine diagnosis of congenital diseases and hereditary pathologies.
- Amnioreduction (removal of excessive amounts of amniotic fluid due to polyhydramnios).
- Intravesical administration of drugs to terminate pregnancy in the second trimester.
- Monitoring the condition of the fetus in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy: determination and assessment of the severity of hemolytic disease of the fetus (HDF), degree of lung maturity, synthesis of surfactant in the lungs, diagnosis of intrapartum infections.
- Fetotherapy (drug treatment of the fetus).
- Fetosurgery (surgical treatment of the fetus).
Under what conditions is amniocentesis prescribed in the early stages of intrapartum fetal development?
- is over 40 years old or under 20.
- Burdened hereditary history (the presence of hereditary diseases in one or both spouses that can manifest themselves in the baby).
- The mother has previously given birth to a child with a hereditary disease.
- Changes in laboratory parameters or instrumental examination, requiring more detailed diagnosis.
Regardless of the stage of pregnancy, there may be other indications for puncture of amniotic fluid.
- Suspicion of intrauterine fetal hypoxia or developmental pathology.
- Needs for assessing fetal lung development and diagnosing intrapartum infection.
- The use of fetotoxic drugs or the use of toxic substances by a pregnant woman.
- Excessive amount of amniotic fluid. is performed for the purpose of amnioreduction . The procedure is not one-time, it is carried out until the amount of amniotic fluid stabilizes to a volume that does not impede the growth and development of the fetus.
- If the result of at least one screening test is positive.
- The need for intrauterine treatment .
- For medical termination of pregnancy (if there are strict indications).
- Surgical treatment of the fetus .
Contraindications to amniocentesis
This procedure has a small number of contraindications due to its high diagnostic value and the subsequent possibility of maintaining pregnancy or fetal health.
What are the main contraindications?
- Threat of spontaneous abortion or placental abruption.
- Increased body temperature in a pregnant woman.
- Exacerbation of chronic pathologies in a pregnant woman.
- The presence of acute inflammatory processes, regardless of their location.
- Large tumor formations of the muscular layer of the uterus (fibroids).
In case of pathology of blood coagulation function, amniocentesis is not contraindicated, but it is advisable to carry out the procedure under the control of coagulants.
Why amniotic fluid is needed
Amniotic fluid is necessary for the normal development of the child in the mother's womb; it is needed for
- protecting the child from loud sounds and impacts (water absorbs noise and acts as a shock absorber);
- maintaining a comfortable temperature (amniotic fluid has a temperature of 37 degrees);
- protection from external threats (the amniotic fluid bladder is sealed, which allows the child to be protected from external influences);
- providing nutrition to the baby (water does not allow the bladder to shrink, preventing the umbilical cord from being compressed);
- freedom of movement of the baby (in the 1st-2nd trimester the baby can move freely and swim in the amniotic fluid).
Composition and norm of amniotic fluid
The fetal membranes begin to form after the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus.
Then a complex process begins. A protective bladder with sterile fluid inside is formed from the membranes (amnion and chorion). As the fetus grows, the bubble enlarges. Amniotic fluid is formed due to the “leakage” of maternal blood plasma. In the later stages, the child himself, his lungs, and kidneys also participate in the production and renewal of amniotic fluid.
Amniotic fluid consists of water (97%) with proteins and mineral salts (calcium, sodium, chlorine) dissolved in it. Skin cells, hair cells, and aromatic substances can also be found in it.
There is an opinion that the smell of amniotic fluid is similar to the smell of mother's milk, so a newborn baby can easily find his mother's breast, because he drank a liquid similar to milk in the womb.
Norm and pathologies
The normal amount of amniotic fluid at the end of pregnancy is 600-1500 ml. For a number of reasons, these figures may deviate more or less from the norm. Then doctors talk about polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios.
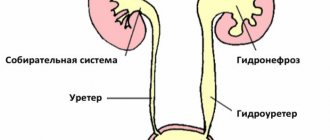
Oligohydramnios is diagnosed when the expectant mother has less than 500 ml of amniotic fluid.
The reason for the decrease in the amount of water lies in the insufficient development of the endometrium (water membrane) or a decrease in its secretory ability. Among other reasons causing pathology are called
- abnormalities in the development of the child’s genitourinary system;
- mother's hypertension;
- inflammatory diseases of women;
- metabolic disorders, obesity;
- fetoplacental insufficiency.
Oligohydramnios in one fetus when carrying twins is explained by the uneven distribution of blood in the placenta.
With oligohydramnios, severe abdominal pain, painful movements of the child are observed, the uterus is reduced, and the size of its fundus does not correspond to the gestational age.
With polyhydramnios, the secretory function of the aqueous membrane is increased.
Polyhydramnios can result from:
- diabetes mellitus, infectious and viral diseases of the mother;
- heart disease, kidney disease;
- incompatibility of the Rh factor of the blood of mother and child;
- multiple pregnancy (polyhydramnios in one fetus, oligohydramnios in the other);
- diseases of the placenta.
Signs of polyhydramnios are heaviness in the abdomen, swelling of the legs, breathing and blood circulation become difficult, and the child’s movements become too active.
Oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios are dangerous pathologies. To eliminate them, the help of a specialist is required. At the slightest suspicion, you should consult a doctor.
Deviations in the color of amniotic fluid
Normally, amniotic fluid is colorless and transparent. The consistency is similar to water and has no odor. Most often, expectant mothers are concerned about changes in the color of the amniotic fluid.
You can judge the color of amniotic fluid during its outpouring, which occurs during childbirth. In most cases, if the pregnancy is full-term, the waters are clear or cloudy yellow. This is their normal color and is not dangerous. The woman’s task after her water breaks is to get to the maternity hospital within 2-3 hours.
Amniotic fluid may be a different color.
- Red speckled.
A slight admixture of blood in a fluid of normal (light or cloudy yellow) color is considered normal, since it indicates dilatation of the cervix. - Green color.
The baby's original feces turn the water greenish or swampy. The child experiences oxygen starvation; swallowing such water is dangerous for the development of pneumonia in the baby. - Red.
Dangerous color indicates internal bleeding in the mother or fetus. The best decision is to take a horizontal position and urgently call an ambulance. - Dark brown.
This color indicates the death of the fetus; you should immediately consult a doctor.
If the color of the amniotic fluid changes, the mother and baby may be in danger. Therefore, it is better not to get to the maternity hospital on your own; you should call an ambulance and report the color of the water.
What problems can arise during low water conditions?
Low water levels occurring during the first and second trimesters are more likely to cause serious complications than when they occur during the third trimester.
- Birth defects: fetal or complete absence of any external or internal organs in newborns (hip dysplasia, club leg)
- premature birth
- miscarriage: death of a baby in the uterus before 20 weeks of pregnancy
- stillbirth: death of a baby in the womb after twenty weeks of pregnancy
- death of a child shortly after birth
Low water levels that occur during the third trimester can lead to the following problems:
- Fetal growth restrictions
- Compression of the umbilical cord during labor or birth (the umbilical cord is responsible for carrying oxygen and food to the fetus, so its compression prevents the baby from receiving sufficient nutrition and oxygen)
- Caesarean section (a surgical method to deliver a baby through an incision in the mother's abdomen and uterus)
Water research methods
Today, there are several ways to obtain information about the state of the amniotic fluid before the onset of labor. All methods are divided into invasive (requiring direct sampling of material) and non-invasive (not requiring penetration into the uterine cavity).
The only non-invasive method is ultrasound. This study can provide information about the amount of amniotic fluid and allows you to diagnose oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios.
Other research methods (invasive) are associated with high risks, therefore they are carried out for serious indications.
- Amnioscopy.
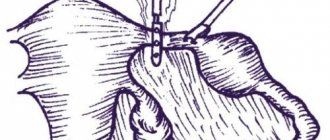
Inspection of amniotic fluid using an amnioscope. This device is a tube with a lighting device at the end. The examination of the expectant mother is carried out on a gynecological chair by inserting the device into the cervix. The doctor pays attention to the color and consistency of the water. An examination is possible after 37 weeks if there is a suspicion of fetal hypoxia or Rhesus conflict. - Amniocentesis.
Unlike amnioscopy, amniocentesis is performed after 16 weeks of pregnancy, when the fluid volume reaches 150 ml. A needle is inserted into the amniotic cavity under ultrasound guidance and a small amount of fluid is withdrawn. To perform amniocentesis, serious indications are needed: suspicion of genetic diseases or intrauterine infections, Rh conflict, insufficient oxygen supply, chronic diseases of the mother.
Physiological and pathological rupture of water
Amniotic fluid, the leakage of which is a pathology along with oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios, during the normal course of pregnancy flows out only with the onset of labor. When contractions occur, the process of bursting the bubble and the subsequent leakage of fluid is called effusion.
What amniotic fluid is and what functions it performs can be learned from this video:
It should not occur earlier than 38 weeks. The flow of water before this period is an early outpouring.
Amniotic fluid can leak simultaneously, when the membrane ruptures in the center of the fetal sac, or gradually, when its integrity is violated above the uterus. This option is more successful if there is leakage before the preliminary due date.
There are several types of rupture of amniotic fluid based on the time of occurrence:
- timely - after the onset of labor contractions with sufficient dilatation of the cervix;
- premature - before the onset of active contractions at 39-42 weeks;
- earlier - after the onset of precursor contractions during the process of delivery with a closed cervix;
- delayed - occurs when the density of the amniotic membrane is high, and occurs after the start of pushing.
Amniotic fluid norms by week of pregnancy
As pregnancy progresses, the amount of amniotic fluid increases. Approximate calculations look like this:
- 30 ml at 10-11 weeks;
- 100 ml for 13-14;
- 400 ml at 17-20;
- 1200ml for 36-38;
- 600-800 a few days before birth.
The amount of amniotic fluid is individual for each expectant mother; the calculations given are approximate, so doctors do not measure the amount of amniotic fluid in milliliters using the definition of “amniotic fluid index.” It is measured using an ultrasound machine starting at 16 weeks. The norms look like this:
- 73-201 mm (average 121) at 16 weeks;
- 77-211 (127) at 17;
- 80-220 (133) by 18;
- 83-230 (137) at 19;
- 86-230 (143) by 20;
- 88-233 (143) at 21;
- 89-235 (145) at 22;
- 90-237 (146) at 23;
- 90-238 (147) at 24;
- 89-240 (147) at 25;
- 89-242 (147) at 26;
- 85-245 (156) at 27;
- 86-249 (146) at 28;
- 84-254 (145) at 29;
- 82-258 (145) at 30;
- 79-263 (144) at 31;
- 77-269 (144) at 32;
- 74-274 (143) at 33;
- 72-278 (142) at 34;
- 70-279 (140) at 35;
- 68-279 (138) at 36;
- 66-275 (135) at 37;
- 65-269 (132) at 38;
- 64-255 (127) at 39;
- 63-240 (123) by 40;
- 63-216 (116) at 41;
- 63-192 (110) at 42.
These figures can be seen in the medical card; the average figures for each stage of pregnancy are given in brackets. Only a doctor can correctly decipher the data, since the norms of the amniotic fluid index depend on the individual characteristics of the body.
Leakage of amniotic fluid
Leakage of amniotic fluid is quite difficult to notice; this problem occurs most often in the last stages of pregnancy, when the uterus puts pressure on the bladder and slight urinary incontinence may occur. Before giving birth, natural discharge becomes thin and can also be mistaken for leakage. How not to make a mistake? Read more about how to detect leakage of amniotic fluid and what to do.
You can determine the leakage of amniotic fluid at home. There is a special test pad for this. The method is quite popular, but such a gasket is quite expensive (400-600 rubles), and the result is not always reliable. So, not only leaking water, but also inflammatory diseases can show a positive result.
The exact result can be obtained in the maternity hospital after examining the discharge.
The most informative way to determine water leakage is amniocentesis. A safe dye is injected into the amniotic sac using a needle, and a tampon is placed in the pregnant woman's vagina. Dyeing the swab will show leakage of amniotic fluid. This method is used in special cases when the child's life is at risk.
Causes of leakage
Amniotic fluid, the leakage of which is often confused with other secretions, becomes clearly noticeable in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy. In the early stages and mid-pregnancy, the fluid may mix with the cervical mucus and not stand out against its background.
The first instance of water leakage is usually mistaken for involuntary urination, but the later the pregnancy, the more obvious the problem becomes. The release of amniotic fluid most often occurs when there is a change in position or tension in the pelvis.
Among the most common causes of amniotic fluid leakage are:
- infection of the mother's reproductive system, which leads to softening of the walls of the bladder;
- underdevelopment or pathology of the cervix, which increases the risk of infection;
- narrow pelvis of a pregnant woman;
- Rhesus conflict;
- chronic and autoimmune diseases;
- incorrect position of the fetus in the womb;
- multiple pregnancy;
- abnormal structure of the uterus;
- thrombophilia;
- anemia;
- uterine fibroids;
- defects in fetal development;
- diabetes;
- excessive drinking and smoking;
- mechanical damage during invasive diagnostics.
In addition, in the 1st and 2nd trimester, rupture of water occurs during a miscarriage. In the early stages it goes unnoticed due to bleeding, and in the middle of pregnancy it indicates the onset of premature labor.
Obstetrics research indicates that women at risk for amniotic fluid leakage include:
- who have already experienced early rupture in a previous pregnancy;
- suffering from anemia and connective tissue diseases;
- smokers;
- experiencing severe physical and emotional stress.
Normal amniotic fluid index during pregnancy
During their first pregnancy, many are faced with the concept of amniotic fluid index, abbreviated as AFI. To fully understand what it is and how important it is to adhere to IAL standards, it is necessary to consider all aspects of this issue.
Amniotic fluid is the official name for the amniotic fluid in the womb of a pregnant woman, which provides the biological environment for the normal development of the child.
Basic functions of the biological environment.
- Child nutrition. The composition of amniotic fluid contains many necessary and beneficial substances for the fetus. During the period of maturation, they enter the child’s body by absorption through the skin. As the baby matures, it begins to consume the required amount on its own.
- Ensuring normal pressure and temperature.
- Protection of the fetus from external environmental factors.
- The composition of amniotic fluid includes the required amount of immunoglobulin fractions, which create a sterile barrier, preventing the occurrence of infections. This is due to the fact that amniotic fluid has the ability to constantly renew itself; the process will stop after childbirth.
- An important factor is the complete sealing of the bladder, as well as the movement of the fetus in space.
Amniotic fluid: living water
Amniotic fluid (or amniotic fluid as it is also called) surrounds your baby for the first nine months of his life. For him, they provide training for all basic functions (breathing, swallowing), shock-absorbing protection, and a nutrient medium. Where do they come from, what are they made of, why are they analyzed?
As soon as the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus, the formation of not only the child’s body begins, but also its complex life support system: the membranes, placenta and umbilical cord.
Where do membranes come from? They develop from the same cells as the embryo! So, as soon as the fertilized egg begins to divide, new cells receive their “specialization”, initially there are only three types: ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm - these layers are called germ layers. The ectoderm ultimately produces the nervous system, sensory organs, skin epithelium, and tooth enamel; endoderm gives rise to the epithelium of the midgut, digestive glands, and epithelium of the lungs; Well, the mesoderm is the future muscle and connective tissue, the circulatory system, the kidneys, and the gonads. The membranes are also formed from the germ layers; the inner layer, the amnion, is from the ectoderm, and the outer layer, the chorion (as well as the embryonic part of the placenta) is from the mesoderm.
“The membranes form a sealed bladder, which begins to fill with fluid due to the secretion of the amniotic layer (that’s why the fluid is called amniotic) and sweating of the mother’s blood vessels: during pregnancy, their permeability increases, and the liquid component of the blood, plasma, begins to leak through their walls. At the end of pregnancy, the baby also joins in the production of amniotic fluid - after all, his kidneys begin to work, and the volume of amniotic fluid reaches one and a half liters.
The composition of amniotic fluid is quite complex: proteins and mineral salts, fats, hormones, enzymes, immunoglobulins (they protect the child from diseases), group antigens corresponding to the fetal blood type are dissolved in them, and in addition, particles of the child’s epidermis and vellus hair accumulate (approximately 1.5%). There is an opinion that the smell of amniotic fluid is similar to the smell of human milk, and this allows the newborn to immediately find the mother's breast.
The child actively interacts with the amniotic fluid: up to 14 weeks, the fluid seeps into his body through the skin, then (when keratin accumulates in the skin and it becomes thicker) the child, like a fish, begins to “inhale” the fluid, doing the first and very important exercise for the lungs. During childbirth, the lungs are compressed, the remaining amniotic fluid is squeezed out, and immediately after this the baby takes his first breath.
Table of values
Different modulations of the norms of the AF-amniotic fluid index by week indicate the development of an anomaly or pathology in the fetus. To avoid unfavorable situations, pregnant women need to be constantly examined.
Check with a gynecologist
To ensure correct diagnostic results, doctors carry out a number of preparatory measures.
- Analysis of the cytological and biochemical composition of amniotic fluid.
- Checking transparency and shade.
- Accounting for hormones contained.
- Checking, studying the volume. The gestational period affects the volume of amniotic fluid, which is calculated relative to the trimesters of pregnancy.
There is a special table that describes the norms of the amniotic fluid index by week in mm.
As can be seen from the table, the calculation principle is quite simple. For example, you need to find out the normal amniotic fluid index at 19 weeks of pregnancy. The table values show 83-137-225, where the first value is the minimum, then the average value and the maximum allowable quantity are indicated.
How is it measured?
Modern diagnostic practice offers 2 ways to determine the amount of amniotic fluid during pregnancy:
- ultrasound examination of the uterus;
- Ultrasound diagnosis of the uterine cavity with quadrant measurements.
In the first case, the doctor uses a sensor to examine the uterine cavity in the longitudinal and transverse directions.
Based on the data obtained, the possible amount of amniotic fluid is determined.
This diagnostic method is imperfect and does not provide accurate information about the fluid content.
Quadrant research provides more accurate information.
When examining the uterine cavity, the doctor conventionally divides it into 4 sections using vertical lines. These areas are called quadrants.
The next step in the study is to determine the free pocket in each quadrant. This is the most free area where there are no limbs or parts of the child’s body.
The doctor analyzes the pockets in 4 quadrants and, based on the information received, makes a conclusion about the amount of amniotic fluid.
The method makes it possible to diagnose pathologies such as polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios.
In addition, amniotic fluid can be examined using the following procedures:
- amniocentesis;
- amnioscopy.
Possible risks when a problem is detected
A discrepancy between the norms of the amniotic fluid index by week of pregnancy indicates the occurrence of polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios in a woman. The manifestation of such conditions is quite dangerous, even threatening serious complications.
Dangers of polyhydramnios:
- possible placental abruption;
- development of infection of the birth canal;
- fetal development disorder;
- miscarriage is possible.
Most often, oligohydramnios is detected after 26-30 weeks or after post-term pregnancy at 41 weeks. In addition, oligohydramnios threatens serious fetal diseases.
If the amniotic fluid index at 31 weeks is 66, with an average value at 31 weeks of 14 cm, then you need urgent specialist intervention.
Dangers of oligohydramnios:
- disorders of the respiratory and genitourinary systems;
- hypodynamics and pressure on the fetus, which can cause various anomalies: changes in fetal weight, dislocations, deformations of bones and spine;
- the occurrence of hypoxia;
- possibility of premature miscarriage;
- risk of bleeding after childbirth.
Excess amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios) is detected in 1 to 3% of women in labor. For example, at week 34 your AFI is more than 278 units, this indicates a critical level of amniotic fluid. The causes of polyhydramnios are influenced by the presence of certain factors.
From the mother's side:
- Rh factor, blood group;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- the presence of infections or inflammatory processes in the body.
According to placenta analysis:
- when a benign tumor of the fetal membrane occurs;
- with swelling of the placenta.
- multiple pregnancy;
- hereditary pathologies or diseases.
Causes of oligohydramnios:
- abnormalities of the fetus inside the womb;
- various pathologies: infections, chromosomal abnormalities, poor fetal development, etc.;
- the presence of diseases in a woman: problems with the heart, blood vessels, inflammatory and infectious symptoms, kidney disease;
- placental insufficiency, defects, heart attack;
- post-maturity of the fetus;
- placental abruption;
- premature death of a child inside the womb.
People in white coats
Polyhydramnios can be of different types.
- In moderate condition, the size of the inner pocket ranges from 7 cm to 18.
- With severe polyhydramnios, the value appears in the range from 18 to 24 cm.
- In chronic cases, the indicator is slightly higher, but stable.
- In borderline and acute conditions, the index value varies between the average and the highest. In this case, inpatient treatment is recommended.
- In case of acute excess fluid, specialists will prescribe an amniotomy; in case of chronic excess, complex therapeutic treatment.
Self-treatment is not recommended at all. Only observation by specialists and compliance with all doctor’s instructions guarantee the safety of the mother and fetus.
These recommendations also apply to oligohydramnios; in case of acute symptoms, the pregnant woman will be offered hospital treatment. For example, your amniotic fluid index is 5 5, this indicates critical oligohydramnios, which can become a threat to the life of the fetus.
Recommendations for moderate polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios:
- everyone without exception is prescribed Curantil, Actovegin;
- minimum physical activity;
- healthy diet, diet in combination with a vitamin complex;
- preventive treatment to protect against the formation of infectious and inflammatory processes;
- in case of postmaturity – stimulation of labor.
As the baby grows
In traditional treatment, antibiotics are usually used to restore hypodynamic functions. For various infections, immunomodulators are prescribed. Diuretics are required.
Polyhydramnios: types, symptoms, causes, danger of the condition
A conclusion about polyhydramnios is made by a specialist if the fluid volume exceeds 1.5-2 liters during normal pregnancy. Polyhydramnios is usually diagnosed at the end of the second or beginning of the third trimester.
There are acute polyhydramnios with a sudden increase in the volume of water, which is accompanied by shortness of breath, a feeling of heaviness and pain in the abdomen, severe swelling, and chronic, in which the amount of amniotic fluid increases gradually, without worsening the well-being of the pregnant woman.
Among the causes of polyhydramnios are the following:
- presence of diabetes mellitus in the mother
- an acute or chronic infectious process was detected in the mother’s body
- diseases of the cardiovascular system
- various fetal developmental anomalies
- Rhesus conflict between mother and fetus
Ultrasound is the main tool in diagnosing this condition. The main criterion for assessing the amount of amniotic fluid is the size of the vertical pocket. If during the examination the specialist determined its value to be 8-11 cm, this is a mild degree of polyhydramnios. We can talk about the average degree of this condition when the size of the vertical pocket is from 12 to 15 centimeters, but if this figure reaches 16 cm, then a conclusion is made about pronounced polyhydramnios.
Upon manual examination of the pregnant woman, a significant increase in the circumference of the abdomen, as well as the height of the uterine fundus, is noted. The uterus itself is in good shape, which is why parts of the fetus are difficult to palpate. Excessive motor activity of the child is noted, heart sounds are heard indistinctly.
The danger of polyhydramnios is that a large amount of water greatly stretches the uterus, as a result of which it contracts poorly during childbirth. This leads to a protracted labor and possible bleeding in the postpartum period. Polyhydramnios can cause placental abruption and prolapse of the umbilical cord, which poses a great danger to both the mother and the unborn child.
The birth strategy for polyhydramnios involves performing an amniotomy (puncture of the amniotic sac) at the very beginning of labor. Amniotic fluid is then slowly released through a needle or catheter to reduce the volume of the uterus and tighten its walls. After the baby is born, the mother in labor is prescribed medications to stimulate contraction of the uterine muscles.
Mild chronic polyhydramnios has virtually no effect on the course of pregnancy; childbirth usually occurs on time and is not complicated. However, parallel treatment of the disease that causes polyhydramnios is required.
Severe polyhydramnios often provokes premature birth. If there are symptoms indicating circulatory disorders in the expectant mother with severe swelling and severe shortness of breath, the question of artificial termination of pregnancy is raised.