Amniotic fluid is an active biological environment in which the unborn baby develops in the mother’s body. This medium is also called amniotic fluid because it fills the amniotic sac, the membrane that surrounds the fetus. There is an opinion that the smell of amniotic fluid resembles the smell of mother's milk, and this is what helps a newly born baby easily find his mother's breast.
Composition and volume of amniotic fluid
The volume of amniotic fluid directly depends on the gestational age of the baby's mother. For example, in the tenth week of pregnancy the volume is on average 30 ml, in the thirteenth-fourteenth week the volume is 100 ml, in the eighteenth week - 400 ml. The maximum volume of amniotic fluid is observed at 37-38 weeks of pregnancy: from 1000 ml to 1500 ml. That is, the norm of amniotic fluid should be judged by taking into account the duration of pregnancy. At the end of pregnancy, the volume of amniotic fluid may decrease and amount to approximately 800 ml.
Now let's figure out how amniotic fluid is renewed. During a normal pregnancy, approximately 500 ml of amniotic fluid is exchanged in 1 hour. Absolute renewal of amniotic fluid occurs every three hours.
Amniotic fluid contains many components. Each component is important for the normal development of the fetus. The main component, of course, is water, which contains carbohydrate-containing substances, proteins, mineral salts, fats, hormones, enzymes, and immunoglobulins.
But as the baby grows, in addition to these components, fetal urine, epithelial skin cells, secretions of the sebaceous glands, and hair cells begin to appear in the amniotic fluid. The concentration of components depends on the stage of pregnancy. But the quantity and quality of amniotic fluid can change for various reasons, which can lead to oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios.
In order to determine the volume of amniotic fluid, special calculations are made. The amniotic fluid index is calculated using ultrasound. Based on the amniotic fluid index, one can judge the amount of amniotic fluid.
Amniotic fluid color
From the broken amniotic fluid you can get a lot of information about the condition of the baby. Let's try to understand what the color of amniotic fluid indicates.
Yellow color of amniotic fluid.
If a woman’s amniotic fluid is slightly cloudy or yellow in color, then there is no reason to worry. This is exactly the color they should be.
Yellow color of amniotic fluid with red streaks.
If you notice red streaks in your broken water, but you feel fine and begin to feel contractions, then you have no need to be alarmed. Basically, these veins indicate the dilation of the cervix.
Dark brown color of amniotic fluid.
Unfortunately, this color almost always indicates that the baby has died intrauterinely. In this case, you should already take care of saving the mother’s life.
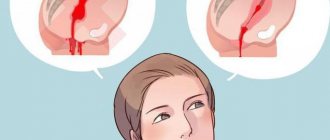
Red color of amniotic fluid.
This color indicates serious danger, both for the child and for the mother. This color indicates that the mother or baby has started bleeding, and the blood has entered directly into the amniotic fluid. This is a fairly rare case, but if it happens, you should immediately call an ambulance, and then take a horizontal position and not move.
Amniotic fluid is green.
In this case, the forecasts are disappointing, since this color means serious problems for the baby. Why amniotic fluid is green is easily explained. Green color occurs if the volume of amniotic fluid was too small or intrauterine bowel movement occurred. Therefore, if you notice that the waters have a green tint, try to get to the hospital as soon as possible.
Meconium aspiration of amniotic fluid
Aspiration of amniotic fluid occurs when meconium enters the amniotic fluid. Meconium in the amniotic fluid is the baby's first stool, when the baby defecates while still in the mother's womb. It happens that during childbirth the child swallowed amniotic fluid, along with which meconium entered his respiratory tract. Such cases are quite common, so you shouldn’t worry too much, because the newborn receives timely assistance and usually everything ends well.
Have an easy birth and healthy babies!
Among the things that all women know about pregnancy, of course, is amniotic fluid, which may break in due time. Poor knowledge. Moreover, a process is “boiling” inside you, which directly affects the development and health of the unborn child.
With the end of cell division, the internal cells of the fertilized egg form a sealed bladder - the amniotic sac with sterile fluid inside. As the unborn child grows and develops, his “house” also grows, and the volume of amniotic fluid increases.
More than just water
Despite the coincidence in name and composition (97% distilled water), amniotic fluid (also known as amniotic fluid) is more than water. This is a biologically active environment surrounding the fetus, which contains proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, hormones, vitamins, enzymes and other biologically active substances. From a physiological point of view, this is a filtrate of the mother's blood plasma. In dissolved form, it contains oxygen and all other components (electrolytes) of the blood of the mother and fetus.
At the beginning of pregnancy, amniotic fluid is colorless and transparent. But with increasing pregnancy, its composition changes significantly. Due to the secretions of the sebaceous glands of the fetus, epithelial scales (upper layers of skin), and vellus hairs that have entered it, it gradually becomes cloudy. However, despite the fact that from a chemical point of view the composition of the amniotic fluid changes, its pH is always interconnected with the pH of the blood of the unborn baby and, with a normal pregnancy, does not upset its balance.
Harbingers of childbirth
The first signs of the onset of labor appear two to three weeks before its onset: the woman feels that it has become easier for her to move and breathe, and there is a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen and lower back. This is explained by the fact that the fetal head has dropped somewhat downwards and the uterus itself is no longer supported in the hypochondrium.
Doctors call this condition harbingers of childbirth. Signs of labor also include irregular, slightly painful contractions of the uterine walls, which are felt by the woman in the form of minor short-term pain. At this time, the woman should arrive at the maternity hospital, because no one knows how many hours or days after such warnings regular, long contractions will begin.
If even slight bloody discharge appears from the external genitalia or the water breaks, or a pelvic, oblique, transverse position of the fetus is established, the pregnant woman must urgently go to the maternity hospital. Women who have undergone inflammation of the uterine appendages, abortion, gynecological or obstetric surgery should be admitted to the maternity hospital in advance, that is, two weeks before the due date.
If a woman has late periods (after 17 years), painful, scanty or heavy, then with the onset of pregnancy she may have a miscarriage, and if the pregnancy is carried to term, complications in childbirth may occur. To avoid this, a woman should regularly visit an antenatal clinic and, if necessary, be observed in a hospital 2-3 times during pregnancy.
At all speeds
Amniotic fluid is not in a static state, and throughout pregnancy it is renewed due to circular exchange. The metabolic rate is quite high and is approximately 500 ml/hour during a normally developing pregnancy. Since the total volume of amnifluid is normally 1-1.5 liters by 37-38 weeks, a complete exchange of water occurs on average in 3 hours. Exchange occurs through the placenta, as well as through extraplacental membranes. The fruit itself is involved in renewing more than 30% of its habitat!
In addition to the fact that the fetus swallows amniofluid, up to 22-24 weeks it reaches it through the skin. However, as the epidermis grows and becomes keratinized, the skin approaches its natural state and becomes almost impermeable to the liquid environment. The cutaneous metabolic pathway is replaced by another, and already in the third trimester of pregnancy, thanks to breathing “exercises,” the fetus “distills” 600-800 ml of water per day through its lungs.
Consequences of green waters during childbirth: what to expect in the future?
Let's be frank and speak frankly. Green waters during labor are a bad sign. Due to the fact that the child may have drunk contaminated liquid, he will subsequently develop a weak immune system. But these are isolated cases, which are accompanied by a number of other significant indicators.
There is no direct relationship between green waters and fetal health. You should carefully monitor your health and undergo examinations on time.
It is important to know!
If a pregnant woman’s green water breaks, it is necessary to immediately sound the alarm and urgently deliver the baby into the world. Panic, fuss and simple ignorance of what needs to be done can lead to oxygen starvation of the fetus, which causes irreparable harm to it. At this moment, the behavior of the doctor is important, who will correctly carry out cleansing procedures of the respiratory tract at the moment the baby’s head appears.
If meconium contamination occurred during childbirth, then there is no need to worry about the baby’s health. In 100% of cases, this will not lead to any consequences and a healthy baby will be born.
A pregnant woman should understand that many factors occur during childbirth that can significantly affect the health of the baby. But for nine months you can show maximum attention to your health, rest, nutrition, and positive emotions. Take care of yourself and your child!
Protection
- provide warmth by maintaining the ambient temperature at 37 degrees Celsius;
- due to the content of immunoglobulins, they protect the fetus from possible pathogenic influences;
- being a kind of buffer, they protect the unborn child from any pressure from the outside. First of all, this eliminates compression of the umbilical cord by the fetal body and the walls of the uterus and ensures proper functioning and interchange between mother and fetus along this main “transport” channel;
- thanks to the tightness of the bladder, nutritious and beneficial nutrients can reach the fetus through the only “checkpoint” - the placenta, but uninvited “guests” (infections) will be delayed;
- prevent the fusion of parts of the body of the unborn child with the amnion (fetal membrane);
- absorb shocks and muffle noises coming from the outside world.
Development
- create conditions for the proper development of children's lungs, ensuring the “breathing” of the fetus after its chest has formed and begins to move. “Inhaling” liquid is an important exercise for the lungs and excellent preparation for breathing in a normal atmosphere;
- they start the work of children's kidneys and digestive system due to the fact that already from the 10-14th week of pregnancy the fetus slowly begins to swallow water, process it and excrete it along with urine;
- participate in metabolism, ensuring the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus;
- supply the fetus with everything necessary for its formation: proteins, fats, glucose, enzymes, hormones, etc.
- create optimal physical conditions for the child: he is free in his movements (especially in the early stages) and swims in the amniotic fluid;
- take care of the proper formation and functioning of the fetal blood system (especially its coagulation) thanks to the factors contained (thromboplastin, fibrinolysin, etc.). In addition, due to its own clotting properties, it can prevent bleeding during complicated pregnancy and even during childbirth.
Further actions
If the water broke while the woman was at home, then it is necessary to call an ambulance so that she can take her to the maternity hospital, no matter how far along the pregnancy she is. In the event that the rupture of amniotic fluid occurs in the early stages of pregnancy, it is necessary to consult a doctor as quickly as possible, since the sooner you can turn to specialists for help, the greater the likelihood of maintaining the pregnancy and carrying a healthy child without pathologies.
If you notice that your waters broke on time, and the approximate date of birth set by your attending physician is one of these days, then this indicates that labor will begin in the next six to twelve hours. At least, doctors will make every effort to ensure that this happens, since it is this period of time after the water breaks that is considered optimal for both the newborn and the woman in labor.
What will the waters tell us?
Amniotic fluid is the baby’s environment, which, like a “marker,” reacts to any change in his physical condition. Of course, doctors actively use this property for diagnostic purposes when monitoring the expectant mother and her baby. During pregnancy, various methods are used to monitor the condition of amniotic fluid. Ultrasound allows you to determine the amount of water, thanks to which you can promptly recognize such deviations from the norm as low and polyhydramnios.
Amnioscopy (examination of the lower pole of the amniotic sac through the cervical canal) and amniocentesis (puncture of the amniotic cavity through the abdominal wall, posterior vaginal fornix, or cervical canal) allow one to evaluate the color of the amniotic fluid.
To assess the maturity of the child’s lungs, the expectant mother may be offered an amniofluid test to determine the level of phospholipids. Only with an optimal ratio of lecithin and sphingomyelin concentrations (2:1) are conditions created for easy expansion of the lungs during the first extrauterine breath. This is the only way the baby will be able to breathe on his own without experiencing difficulties. The level of creatinine content can determine the degree of maturity of the fetal kidneys.
And finally, based on the state of the waters, doctors monitor the condition of the child during a post-term pregnancy (assessment of fetal overmaturity according to Clifford).
All narrow diagnostic studies are carried out for expectant mothers only according to strict indications, if ultrasound or test results give doctors reason to doubt the successful course of pregnancy.
What is it and what are its functions?
Amniotic fluid is a liquid medium produced by the inner part of the membranes in pregnant women. The amnion produces fluid, which is why it is called amniotic fluid. It surrounds the baby, being a completely natural habitat for him. The course of pregnancy and the prognosis for childbirth depend on the state of the water.
They depart in the first phase of labor, when contractions reach their peak. But this is a classic version of the norm. In practice, departure may be earlier.
Nature assigns several key functions to water.
- The liquid medium nourishes the baby, since it contains lipids, proteins, glucose, and hormones. In the early stages, the embryo absorbs these substances through the skin, and later begins to swallow water, digest it and write. The composition of the waters is updated every 3 hours.
- Thanks to them, constant temperature and pressure are maintained in the uterine cavity.
- Water is a shock absorber that softens any external influences, such as shocks and pressure. The water prevents the umbilical cord from being pinched.
- The amniofluid contains antibodies, and the bubble is sealed - this protects the baby from bacteria and viruses from the outside.
- Thanks to the liquid medium, the baby is able to move.
- Amniofluid protects the baby from loud sounds, of which there are many on the other side of the mother’s belly.
During childbirth, the breaking of water is of additional importance - enzymes in the fluid help accelerate the dilatation of the cervix and facilitate the birth process.
Dangerous leak
Normally, the amniotic sac retains its integrity until the onset of labor. But situations are possible (for example, due to physical injury or a fall) when the bladder ruptures and amniotic fluid leaks. This can cause panic in the expectant mother. But you shouldn’t rush to conclusions, because during pregnancy, both vaginal discharge and slight leakage of urine are possible due to relaxation of the muscular system (the result of preparing the body for childbirth). To clarify the situation, you need to empty your bladder, wash and dry yourself, and lie down on a dry sheet. If after 10-15 minutes a wet spot is found on the sheets, you should consult a doctor. Deformation of the amniotic sac can lead to infection in the fetus, so action must be taken immediately. In addition, if the pregnancy is less than 34 weeks and the baby's lungs are not yet mature enough to breathe on their own, the doctor will try to prolong the pregnancy. In this case, the expectant mother will be prescribed antibiotics in order to protect the baby in utero. If the situation cannot be brought under control, water leakage continues, fetal hypoxia is suspected, or the expectant mother’s temperature rises (risk of intrauterine infection), the woman is given an amniotomy (artificial puncture of the amniotic sac) and labor is induced.
Why does premature rupture of membranes occur?
Normally, rupture of the membranes occurs before birth.
The mechanism of childbirth is still not well understood; it is believed that this occurs under the influence of several reasons that trigger the process of childbirth. Premature rupture of membranes most often occurs due to infectious diseases of the mother - these are infections of internal organs, foci of chronic infection, infectious blood diseases, and sexually transmitted diseases. For this reason, doctors always insist on treating thrush, even if the treatment has a short-term effect. Toxins released by microorganisms thin the membranes, which leads to microcracks and subsequent ruptures. With a clinical narrow pelvis, transverse or breech presentation of the child, a contact belt is not formed, there is no clear division of amniotic fluid into anterior and posterior, and the entire volume of amniotic fluid presses on the lower part of the bladder. The shells often cannot withstand the pressure and rupture.
Water traffic light
And yet, most expectant mothers are close to the ideal, when the amniotic fluid drains and labor begins at the scheduled time, i.e. no earlier than 37 weeks. It would seem that you can relax, but this is not entirely true. After all, the further actions of the woman in labor should directly depend on the color of the departed amniotic fluid.
Yellow color – no danger. If the broken water has a cloudy yellowish tint, the only thing that needs to be done is to get to the maternity hospital within 2-3 hours. This color of water at the end of pregnancy is natural and does not pose any danger to you.
Red speckled. An admixture of blood streaks in the amniotic fluid of a normal color (i.e., cloudy yellow) with the mother in good general health is the result of dilatation of the cervix and a reason to go to the maternity hospital.
Green does not tell you to relax. Greenish and gray-greenish shades can have two reasons: insufficient amniotic fluid or fetal defecation. You need to go to the maternity hospital immediately, since in this situation the child may experience severe oxygen starvation.
In addition, meconium (a product of defecation) swallowed by a child, entering the lungs, can provoke the development of pneumonia or pulmonitis in the newborn.
Dark brown is the color of misfortune. And this misfortune is intrauterine fetal death. There may be many reasons, but now you need to take care of yourself as soon as possible.
Red is a dangerous color. Internal bleeding in a woman or fetus can turn amniotic fluid reddish or red. At the slightest suspicion, take a horizontal position and do not move.
Instructions for relatives
: It is necessary to urgently call an ambulance, reporting the color of the broken water. Under no circumstances should you lift, sit down, or turn a woman in labor. It is prohibited to deliver a woman to the maternity hospital on your own! In this case, we are often talking about saving the lives of a woman and a child!
What does amniotic fluid look like, how does it differ from vaginal discharge, and can it be confused with urine leakage? Amniotic fluid is a prerequisite for the full development of the child. In it, it is inside the mother's womb until the onset of labor (this is normal). It protects the fetus from any possible injury due to bruises in the mother's abdomen. And an intact amniotic sac, which is filled with amniotic fluid, is a guarantee that an infection from the vagina will not penetrate into the baby. This is why it is so important to notice the rupture of the amniotic sac in time, and even better, to do everything to prevent it.
How can you protect yourself from premature discharge of amniotic fluid? It is advisable to think about this long before pregnancy. Sexually transmitted infections are one of the main causes of intrauterine death of a child, which occurred, among other things, due to water leakage. That is, a woman does not need to be promiscuous. And pregnancy should be planned by first checking for various infections and, if necessary, treating them.
Another common cause of this pathology is isthmic-cervical insufficiency, as a result of which the cervix begins to shorten and open much earlier than the onset of labor. As a result, the child sinks lower and the bladder bursts under pressure. And the most common cause of isthmic-cervical insufficiency is abortion. This means that avoiding them and reliable contraception is another preventive measure that will help prevent premature rupture of the membranes during pregnancy.
Ultrasound specialists also monitor the amniotic fluid. It is mandatory to determine its quantity. Polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios are common pathologies. Some experts still define it and in conclusion reflect it with the word “suspend”. Many Russian experts consider them a marker of chromosomal pathology or intrauterine infection. In fact, it is the vellus hair of the fetus, the epidermis, etc. And as pregnancy progresses, the amount of suspensions usually becomes larger. Especially if the pregnancy is post-term.
Very important information is what color the amniotic fluid is, but you can only find out after the rupture of the membranes. If the child feels well, there are no obvious pathologies - the amniotic fluid does not have an unpleasant odor, it is generally odorless and colorless. The color of the amniotic fluid is slightly whitish - this is also a variant of the norm. Since they may contain small amounts of white flakes. In some cases, the color of the amniotic fluid is a signal for an emergency ultrasound examination and, possibly, even an unscheduled cesarean section. This is if green amniotic fluid is released from a pregnant woman. This is one of the clear signs of oxygen deficiency in the fetus. They are green because a child with intrauterine oxygen deficiency spontaneously releases original feces - meconium, which colors the amniotic fluid. What consequences can green colored amniotic fluid have for the baby? If acute hypoxia occurs, it will most likely be neurological disorders. Much will depend on the amount of time during which the child lacked oxygen, as well as on the extent to which resuscitation measures were carried out in the maternity hospital.
It remains to understand the external difference between amniotic fluid and vaginal discharge (which normally increases during pregnancy) and urine. In fact, with a slight tear in the bladder, when the water literally comes out of the vagina in droplets, it is almost unnoticeable. Therefore, all expectant mothers who notice a wet panty liner, sanitary pad or underwear should consult a doctor. A simple examination on the chair and an amniotic test for the composition of the discharge will help to accurately say whether there is amniotic fluid there.
Cervical diseases
In women who have undergone cervical surgery or have developmental defects, the cervix often cannot withstand the load and the amniotic sac protrudes into the canal.
Often, in case of cervical insufficiency, special manipulations are performed, applying sutures or putting on a special cap. This prevents protrusion of the amniotic sac and allows you to maintain the pregnancy. In women with pathologies and abnormal development of the uterus, water leakage is diagnosed more often. Drinking alcohol, drugs, and smoking during pregnancy is almost always fraught with complications, including not only rupture of membranes and premature birth, but also fetal developmental abnormalities. Many patients refuse amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling, as this procedure increases the likelihood of rupture of the membranes. Obstetricians also believe that these procedures should be carried out strictly according to indications. However, in pregnant women who are indicated for such procedures, other risk factors for premature rupture of membranes are often identified, so there is no clear opinion on this matter.