The health and life of the unborn baby depends on a huge number of factors.
Heredity plays a role, as does the mother’s behavior during pregnancy, her diet, daily routine, the presence of infectious diseases, and congenital developmental abnormalities.
But not all pregnant women know that the success of bearing a child depends on the nature of the attachment of the fetus to the wall of the uterus.
Most often, expectant mothers who are faced with a diagnosis of chorion presentation find out about this.
What is chorion
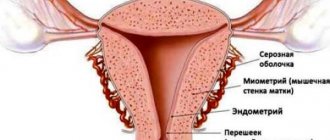
Chorion is one of the membranes that surrounds the baby in the uterus and provides communication with the mother’s body. This structure provides nutrition and breathing to the child, as well as the removal of its metabolic products.
It is also a kind of barrier that protects the small organism from harmful influences.
The period of active functioning of the chorion is the first trimester, later it is replaced by the placenta, which will ensure the connection between mother and child until the moment of birth.
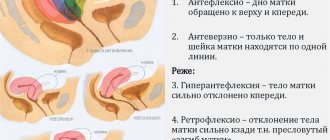
How the chorion attaches to the wall of the uterus
The chorion has many outgrowths called villi, which are embedded in the wall of the uterus. They are penetrated by a dense network of capillaries and come into contact with the mother’s blood vessels.
Normally, the chorion is attached to the fundus of the uterus or its walls in the upper part.
This arrangement is the most favorable: when the uterus stretches during the baby’s growth, neither the chorion in the first trimester nor the placenta in subsequent stages will be damaged or peeled off, and the blood vessels will maintain integrity and ensure uninterrupted nutrition and breathing of the baby.
What it is?
The chorion is a temporary organ that performs the functions of a pharmacist. It is formed from the moment the fertilized egg is implanted from the fallopian tube, where the egg and sperm meet, into the uterine cavity. As soon as the blastocyst (which is what the fertilized egg turns into by 8-9 days after ovulation) reaches the uterine cavity, it strives to gain a foothold in it. It is this process that is called implantation.
At the site of attachment of the blastocyst shell, special enzymes are secreted that make the mucous membranes of the uterus more pliable and allow the fertilized egg to “grow.” A chorion is formed at the site of attachment. It is necessary to supply the fertilized egg with useful substances from the mother’s blood. A little later, the placenta appears in its place. But until the 12-13th week we are talking specifically about the chorion, since the placenta is still forming and does not function.
If implantation is successful, the fertilized egg is fixed in the fundus of the uterus (this is its upper part). If, for some pathological reason, the blastocyst fails to implant in the upper or middle part of the uterus, it may descend into the lower uterine segment. And then the chorion will form low.
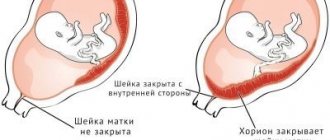
Chorionic presentation refers to its location relative to the cervical canal, a thin passage inside the cervix that connects the uterine cavity and vagina. There is no talk of presentation only if the chorion has formed in the area of the fundus of the uterus or in its middle part (in the body of the uterus).
If the chorion is low, there are several types of presentation.
What is chorionic presentation
In some women, the chorion is attached to the lower part of the uterus. In this case, they talk about presentation. Based on the nature of its localization, they are distinguished:
1 Low position
– the chorion is attached to the lower segment of the uterus, but does not block the cervical canal (that is, it does not block the path along which the baby will move during childbirth).
In this case, severe bleeding may occur, feeding and breathing of the fetus becomes impossible. Recommended.
3
Constant disruption of the connection between the placenta and the maternal body can cause fetal hypoxia (oxygen starvation), delayed growth and development, and in severe cases, death.
4
Although a low-lying placenta is considered the least dangerous for mother and baby among all presentation options, it can cause complications during labor.
5
With complete placenta previa, natural childbirth provokes heavy bleeding, which can lead to death of the mother and fetus.
Therefore, a caesarean section would be the only reasonable solution.
6
In case of complete and partial presentation, vaginal examination is not recommended during a gynecological examination, as it can cause bleeding.
Thus, placenta previa, especially complete one, is a truly dangerous phenomenon that causes a lot of difficulties.
But if this problem is detected on time, in the early stages of pregnancy, a woman has a high chance of having a healthy baby. However, control over the condition of the expectant mother and her child should be more careful.
Interesting! Fourth month of pregnancy: development continues
Causes of chorionic presentation
The doctor may not be able to determine the factor that played a decisive role in the incorrect location of the placenta. The most common causes of presentation are:
1
Congenital anomalies of the structure of the uterus, scars and defects in its wall, which arise due to previous surgical operations, cesarean section or frequent inflammatory processes.
2
Presentation occurs more often in women who have a large number of children, or in those who encountered this problem during a previous pregnancy.
3
A woman's age over 35 years is also a risk factor; the likelihood of placenta previa increases if the woman has bad habits (smoking is especially dangerous).
What awaits a pregnant woman if she is diagnosed with chorionic presentation
The expectant mother should be aware that in the case of placenta previa, she must be more careful and attentive. Most likely, you will have to spend some time in the hospital.
Some women with this diagnosis are forced to spend quite a long time in the hospital, but the health of the child is more important, so you will have to be patient.
This diagnosis cannot be eliminated by treatment. If the placenta itself does not change its location during pregnancy, then no external factors will be able to influence it.
All medications that are prescribed to a woman for breech presentation are designed to eliminate complications (for example, stop bleeding) or support the condition of the mother and her baby (multivitamins are often recommended, which can reduce the risk of decreased development).
Throughout pregnancy, a woman should follow a more gentle daily routine, rest more, and avoid physical and mental stress that can cause bleeding. Sexual contacts are often prohibited. If bleeding occurs, bed rest is recommended.
During pregnancy, many things frighten the expectant mother. The words about the attachment and presentation of the chorion at the first ultrasound sound especially scary. In most cases there is nothing to fear. But some situations require careful follow-up and treatment.
The fertilized egg with the embryo developing in it consists of two membranes. The chorion is the external one, which at 12-14 weeks turns into the placenta.
A feature of the structure of this structure is the abundant amount of villi on the surface. With their help, the fetus is attached to the wall of the uterus. This is an important stage affecting a normal pregnancy.
Types of chorion attachment, some features
The uterus is conventionally divided into three parts: the lower segment, the anterior and posterior walls. When the chorionic villi attach to one of them, the full development of the embryo and placenta begins. There are the following types:
- Along the front wall.
- On the back wall.
- Bottom view.
If the chorion is on the back wall of the uterus, then this is not a pathology, but the most favorable development option. This is related to:
- good blood supply to the area;
- low stretchability;
- the absence of mechanical impact on the fetus when it moves its legs.
Doctors also regard the localization of the chorion along the anterior wall as a variant of the norm. Pregnant women with this diagnosis are included in the high-risk group for bleeding. They are given general recommendations and are not prescribed medication.
Be sure to visit a specialist on an individual schedule!
When treating pregnant women with chorion located on the anterior wall of the uterus, doctors may encounter some difficulties:
Such problems can be easily solved through in-depth monitoring, including more frequent ultrasound and tocography (the baby’s heartbeat is assessed).
Attachment of the chorion in the lower segment of the uterus is a prognostically unfavorable sign. If it is located more than 3 cm above the cervix, then the pregnant woman is treated on an outpatient basis with more careful dynamic monitoring. It is worth considering that such terminology is appropriate only for very short periods. After 12 weeks they talk about placenta previa.
What to do?
As already mentioned, marginal chorionic presentation is diagnosed in approximately 4-5 women out of ten pregnant women up to 12 weeks. However, not all of them immediately fall into the risk group and are listed as patients for planned cesarean section. The prognosis is favorable, and in 90% of cases the chorion, and then the placenta, which forms in its place, migrates higher along with the growth of the uterus.
The baby in the mother's womb is growing rapidly. To meet his needs for comfort, the walls of the uterus and the ligamentous apparatus are forced to stretch. Together with them, the placenta, which at the beginning of pregnancy was in a marginal presentation, will “crawl” upward. The placenta will migrate along the anterior or posterior wall of the uterus - it does not matter. It is important that in most cases it actually rises, and all the threats and risks associated with low placentation remain a thing of the past.
Medicine cannot influence the migration process, speed it up or stimulate it. A woman diagnosed with marginal chorionic presentation must follow all the recommendations of her attending physician, exclude physical activity, heavy lifting, jumping, sudden movements, and squats. She will have to visit her doctor more often and have an ultrasound done to monitor the process of chorion (placenta) migration. Sex during marginal presentation is prohibited, since orgasm associated with contraction of the muscles of the uterus can contribute to rapid traumatic detachment of the chorion and the occurrence of severe bleeding, in which the child can die in utero, and the woman can lose a lot of blood and die from this.
The process of placental migration is usually completed by 18-20 weeks of pregnancy. By this time or a little later (by 35-28 weeks), the true state of affairs becomes clear - if the placenta has risen, the restrictions will be lifted, if not, the pregnant woman will be classified as at risk for premature birth and will be guided further with increased attention and trepidation.
Chorionic presentation: what is the danger?
Attachment of the chorion is a natural process necessary for the further good development of the embryo. Against this background, a situation may arise when the fertilized egg is located very low (close to the internal os, less than 3 cm), covering the natural birth canal. This condition is called chorion presentation. The following types are distinguished:
- marginal;
- central;
- incomplete (partial).
Regional presentation is considered more successful. In this case, the chorion touches the area of the internal os and the cervix. As the fetus grows and the uterus enlarges, the placenta may migrate. At an ultrasound scan at 18 weeks, this situation usually changes to a normal location.
With central presentation, the chorion completely blocks the cervical canal. This is the most dangerous type, in which massive bleeding often develops and fetal death occurs.
Partial presentation is characterized by the fact that the chorion covers the lumen of the cervical canal by 2/3 or less. The advantage of this type is that when the placenta migrates, it moves to the marginal localization, and then to the normal position.
The danger of any kind lies in the possible occurrence of complications. These include bleeding of varying degrees of intensity and antenatal fetal death. If medical care is not provided in a timely manner, a woman’s life is at risk. Such complications are due to the development of a good blood supply system when the fertilized egg is attached to the uterine wall.
As a result of certain factors (intense physical activity, high blood pressure, uterine hypertonicity), a slight detachment of the chorionic villi occurs, which is accompanied by the development of bleeding. Depending on the area of the damaged area, it will vary in intensity.
Chorionic presentation at 12 and 13 weeks of pregnancy: marginal
You are here: Home > Articles > Pregnancy and childbirth > Pregnancy
April 27, 2020 | views: 33,649
The very first trimester of pregnancy is ending. The expectant mother is already beginning to adapt to her new position. The first fears have passed, but I am increasingly concerned about the state of the baby’s development. And he has already grown enough that it would be possible to determine the presence of pathologies of fetal development. At 12-13 weeks of pregnancy, the first ultrasound examination is prescribed.
It is carried out in order to detect abnormalities in the structure of the embryo and chorion - this is how the fetus and placenta are commonly called in gynecology at this time. And suddenly in the description of the study the phrase “chorion presentation” appears. What does chorion presentation mean at 12 weeks? What does it mean for you and your baby? Many mothers panic and look for an answer to their question from relatives, friends, and even on the Internet. We must not forget that the excitement of a pregnant woman can adversely affect a small, not yet strong body. You need to calm down and figure this out.
Types of presentation
Typically, the first ultrasound during pregnancy monitoring is scheduled at the end of the trimester, the 13th week of pregnancy. Then you can see the diagnosis of chorion presentation at 13 weeks. The chorion is a continuation of the umbilical vein of the embryo, ensuring attachment of the fetus to the wall of the uterus. A few more weeks will pass, and it will already be called the placenta. The nutrition that the baby receives depends on its development. The location of the chorion in the uterus can be varied. It can attach to the fundus of the uterus (this is its upper part), to the side walls, or in the cervix. The place where the uterus meets the cervix is called the internal os. If the chorion is located in the area of the bottom or side walls, then such localization is considered normal. In 10-12%, the chorion is attached to the wall next to the internal os, and can even overlap it; this arrangement is considered chorion presentation. Depending on the exact location of attachment, there are:
- Central chorion presentation. The chorion is attached to the opening located at the border of the body and the cervix. It covers the internal pharynx completely.
- Incomplete chorion presentation. The chorion is attached along the edge of the internal pharynx, and partially covers it.
- Low chorion presentation. The chorion is located within a three-centimeter zone from the internal os of the uterus and does not overlap it.
As the fetus grows, the uterus increases in size, so the place of attachment of the chorion changes. By the time of birth, placenta previa is observed in only 0.5% of cases. This is sometimes called "migration" of the placenta. Therefore, the diagnosis of chorion presentation at 12-13 weeks of pregnancy is not always as scary as expectant mothers imagine.
If, during chorion presentation, no more than one third of the internal pharynx overlaps, then they speak of marginal presentation of the chorion. Unlike central presentation, which requires observation in a hospital, marginal chorionic presentation is one of the most favorable forms. Most often, the placenta migrates towards the end of pregnancy.
Causes
It is believed that chorion presentation can occur against the background of:
- Inflammatory processes of the uterus. They lead to deformation of its walls.
- Abortions and surgical interventions. May also cause scar tissue to form in the uterus.
- Repeated birth, especially if chorionic presentation was also observed in the previous case.
- Anomalies in the development of the uterus or the development of the embryo itself.
Symptoms
Usually, chorionic presentation is detected by a doctor during an ultrasound. But sometimes a pregnant woman herself turns to a gynecologist if she detects spotting or bleeding of varying intensity. Usually its appearance is associated with physical stress (hot bath, sexual activity).
Complications
There are a number of complications that can result from marginal chorion presentation, although they are much less common than if the chorion presentation is central. Miscarriage, fetal death, developmental anomalies that occur against the background of hypoxia are complications that can occur in a child. The most common complication of a pregnant woman may be blood loss and anemia. Chorionic presentation may be an indication for caesarean section. If a pregnant woman diagnosed with marginal chorionic presentation starts bleeding after 12 weeks, she should urgently visit a doctor.
Treatment
In cases not complicated by bleeding, marginal chorionic presentation does not require treatment. But if bleeding occurs, the pregnant woman needs to be monitored in a hospital. An important role is given to the prevention of complications in chorion presentation. Pregnant women with this diagnosis should be more attentive to themselves and avoid:
- Physical and mental stress.
- Monitor your diet.
- Limit sex life.
There is no need to worry and worry if an ultrasound has revealed marginal placenta previa, especially considering that emotional balance is necessary not only for you, but also for the baby. The likelihood of complications occurring is low if you follow the gynecologist's recommendations and are more attentive to your well-being.
Leave your comment: Cancel
Causes of presentation, diagnosis and treatment
The true reason for the development of such situations has not yet been found. Background factors for the occurrence of presentation are:
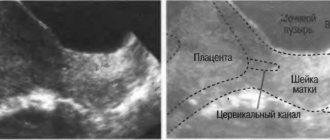
The only method for diagnosing chorionic attachment and presentation is ultrasound! It is carried out in the early stages, when it is already possible to diagnose abnormalities and prevent the development of complications.
Pregnant women with central chorionic presentation must be hospitalized in a specialized hospital. It is impossible to cure this condition! The actions of doctors are aimed at preventing the development of complications. Therapy for all patients is comprehensive. It includes general recommendations and prescription of medications. A positive result largely depends on the pregnant woman herself.
Drug therapy is aimed at reducing uterine tone, pressure, and treating stress. Antispasmodics include No-shpa in tablets, Papaverine in rectal suppositories, Magne B6, and ginipral. The dose, duration of use and specific medicine are selected by the doctor!
It is possible to carry and give birth to a child with different localizations of the chorion. Many girls give birth naturally without any complications. If placenta previa persists, delivery is carried out by planned cesarean section. This is done to prevent complications during childbirth and preserve the life of the mother and baby.
During a routine ultrasound examination, which is carried out after the 12th week of pregnancy, among other factors, the functional diagnostics doctor pays attention to the position of the chorion. In most cases, this parameter does not cause any concern to the specialist. However, there are situations when the expectant mother is diagnosed with chorionic presentation. Is this phenomenon dangerous? What types of chorionic presentation are there? Which of them require therapeutic measures? How is chorionic presentation diagnosed and treated?
What is chorion: its structure, functions and connection with the placenta
The chorion is the outer membrane that surrounds the embryo and is its connecting link with the mother’s body. Its formation begins after the second week of pregnancy. The chorion is attached to the inner wall of the uterus with the help of villi. Its structure is presented in the form of a white ring with wavy outlines, located on the outer edge of the fertilized egg.
Without chorion, the vital activity of the fetus is impossible. This is because through this shell:
- gas exchange occurs between the embryo and the pregnant woman;
- excretory and trophic functions are carried out;
- the child is protected from the negative influence of pathogenic agents.
If in his conclusion the functional diagnostics doctor indicates that the structure of this organ has not been changed, the process of bearing a child proceeds in a standard manner. Otherwise, disruptions in the course of pregnancy occur.
The chorion retains its ring-shaped form until 9 weeks of gestation. Then its structure changes, it becomes smooth and branched. After this, the placenta is formed from the chorion. This happens after 13 weeks of pregnancy.
Location in the uterus
Dear reader!
This article talks about typical ways to solve your issues, but each case is unique! If you want to know how to solve your particular problem, ask your question. It's fast and free
!
The chorion can occupy different positions in the uterus. The most favorable localization is considered to be its attachment to the fundus of the uterus or its walls in the upper region. This arrangement prevents damage and detachment of the chorion and placenta during the stretching of the uterus during fetal growth, and also prevents damage to the integrity of the vessels that are responsible for the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to the embryo.
During pregnancy, the location of the organ may change. This phenomenon is called migration. In situations where the chorion is not properly attached to the walls of the uterus, we are talking about presentation.
The phenomenon in which this organ is located in the lower part of the uterus and partially or completely blocks the pharynx of the cervical canal that passes into it is considered conditionally pathological.
Types of pathologies
If placental tissue is detected directly at the site of the internal os, then this clinical condition is defined as presentation. It can be partial, complete and marginal. Each type of presentation is determined by the location of the placenta relative to the internal os.
It is necessary to determine the abnormal position of the placental tissue. This allows doctors to prevent quite a few dangerous pathologies that can develop during pregnancy.
Obstetricians-gynecologists identify several clinical variants of this pathological condition:
- Central . In this situation, the placental tissue is located in the lower part of the uterus and also covers the internal os.
- Lateral. In this situation, the placental tissue is also located in the lower part of the uterus, but the pharynx is not completely blocked.
- Regional . In this case, the placental tissue and pharynx practically touch their edges.
Types of chorion presentation during pregnancy
Previa of the future placenta occurs:
- Full (central). It completely covers the opening of the cervical canal. When diagnosing such an arrangement of the villous membrane of the fetus, in the vast majority of cases, immediate hospitalization is indicated.
- Incomplete. This type is divided into partial and marginal presentation of the chorion. In the first case, the overlap of the pharynx is determined by 2/3. With marginal presentation of the chorion, the third part of the internal os is covered by the membranes of the embryo, and the edge of the future placenta is located on the periphery.
- Low. The villous membrane of the fetus is located less than 3 cm from the pharynx, and the situation does not reach its complete overlap.
There are also such types of chorion localization as:
- Rear. If the doctor’s report on functional diagnostics includes the phrase “predominant localization is posterior,” you should not be alarmed. Chorion on the posterior wall is not a pathological phenomenon. Here we are talking about one of the most common types of fastening of this organ.
- Front. If the future placenta is not located on the back wall of the uterus, then it is attached to the front. This localization is considered normal, but requires observation. If precautions are not observed, the anterior type of attachment of the chorion is fraught with detachment of the membranes of the embryo.
- Side. We are talking about a side position. It always comes down to the front or the back. In this case, the conclusion of the study will indicate that the chorion, for example, is located behind and to the right.
Chorion covers the pharynx by 21 ml
The girls had an ultrasound. The impression is twofold. Firstly, my impression of the doctor, many people praise her, maybe she’s such a professional and it’s worth listening to her, but what I didn’t like was that: she praises herself too much, it somehow immediately repels her, belittles her colleagues (for example, she spoke very disapprovingly of Kashlevskaya , how is it that all the doctors and patients praise her) and somehow reacts sharply to questions. Next, the procedure was done vaginally, and it was very unpleasant, i.e. somehow painful. Kashlevskaya did it all so carefully, I didn’t even feel it, but today I was all tense... every movement hurt. Maybe, of course, because the deadline is different or the device is different, I don’t know.
Result: - the placenta (as it turned out it is not correct to call it that yet, for now it is the chorion) has risen, now it is 18 ml above the pharynx, and before it overlapped by 21 ml. This made me happy, but the doctor said that it most likely would not rise to normal, it would be slightly below normal. But she can give birth on her own :-)) - but there is a threat of miscarriage, and she said that it is very serious, because... the neck is open at 4.6 a.b. at 3.3 maximum. Those. They treated me wrong all this time, noshpa and papaverine are garbage. For treatment, it is necessary to identify the cause, it is either rhesus, hormones or infections. She took my exchange card to look at it, this is of course a plus for the doctor, because... She’s not obligated to do this at all, it’s her job to do the ultrasound...do it and get out. After looking at the card, she was surprised that the infectious disease specialist sent me with the words that I was healthy and did not need treatment. I have high numbers there for G CMV (1:1600 and toxoplasmosis (296.8 this garbage is from cats, my parents have 2 of them at home). No one paid my attention to these numbers, I’m healthy and healthy. And then it turns out that I’m in danger of miscarriage just because of these infections, that the baby can be born with various abnormalities, heart, nervous system, etc. I was terribly upset, tomorrow I will show these numbers in the hospital. Maybe now they won’t be discharged... I was hoping that tomorrow .
This is such bullshit. Maybe I should go to another infectious disease specialist, my Yarovaya is still on vacation, I don’t even know... Now I’ll go to Simashko for an EMG. And tomorrow at 7 am back to the hospital...
She also said that because of the threat she couldn’t climb much, but most likely it would be a girl, but this is not certain, because... difficult to view :-)) All this time I was sure that Egor was there, now we’ll choose another name to be on the safe side :-))
Symptoms and diagnosis
There are no signs that would directly indicate an abnormal location of the future placenta (marginal, partial, complete, low). The pathological course of gestation can be determined only by a number of indirect manifestations:
- bleeding;
- occasional spotting;
- weakness;
- attacks of dizziness;
- clouding of consciousness;
- pulling or cramping pain in the lower abdomen.
This pathology can be detected only after 12 weeks of gestation. In modern medicine, chorionic presentation at 13 weeks can be diagnosed exclusively using ultrasound.
How are they treated?
The main task in case of chorionic presentation is to take measures to maintain pregnancy. In case of heavy bleeding, when conservative methods of therapy are powerless, emergency delivery is resorted to. The table contains information about what procedures are provided for placenta previa.
| Methods for maintaining pregnancy if the placenta is located incorrectly | Drugs used | Purpose of use |
| Medication | Papaverine (rectal suppositories), tablets Drotaverine, Nosh-Pa, Duphaston, Utrozhestan | Decreased uterine tone |
| Vitamin complexes | Strengthening the immune system, improving metabolic processes in the body | |
| Iron-containing medications (Totema, Maltofer, Ferrum-Lek) | Preventing and eliminating signs of anemia | |
| Sedatives (valerian tincture, motherwort tincture) | Relief of psycho-emotional disorders | |
| Hemostatics (sodium ethamsylate) | Stop bleeding | |
| Non-drug | Bed rest | |
| Limiting physical activity. Sudden movements, lifting heavy objects, and playing sports are prohibited. | ||
| Complete sexual rest | ||
| Avoiding stress | ||
| Using a bandage in late pregnancy | ||
| A balanced diet, excluding foods that can lead to disruption of the bowel movement process | ||
The pregnancy process is a very delicate chemistry that affects the entire female body. In order for a child to grow up, you need to take good care of yourself, eat well and not miss doctor’s examinations.
Not all women know what is happening in the world, and this is a rather important point. Every month, a follicle matures in the female body, which ruptures and releases the egg. This period is considered the most favorable for conception. During fertilization, the egg moves through the tubes and enters the uterus, where it is firmly attached to her body. There it develops for quite a long time. Localization of the chorion, chorionic detachment and its presentation can cause a number of problems during the preservation of the fetus and its birth.
What is chorion and what is its role
Throughout pregnancy, the embryo develops in a membrane that protects it from external damage and contains the nutrients the baby needs. Composition of the membrane: amnion and chorion. Where the outer part is the main one, as it is attached to the reproductive organ. Localization of the chorion, chorion detachment is one of the many problems encountered during pregnancy.
This matter is vital for the normal development of the fetus. The chorion appears at the very beginning of the period and exists until that moment. The correct location of the chorion and its uniform distribution are important. It should be located on the back wall of the uterus. Chorionic presentation is when it is located in the lower part of the reproductive organ.
To diagnose problems in this area, it is necessary to carry out, since a simple gynecological examination will not give results.
Types of chorion depending on the duration of pregnancy
Chorionic presentation may occur at different stages of pregnancy. Its location is shown by ultrasound. At 6 weeks, the fertilized egg is usually attached in a ring shape over the entire area. At the 8th week it becomes circular.
Most often, chorion presentation is detected at 12 weeks, since at this time the first planned ultrasound examination is performed. This pathology requires bed rest and hospital treatment. If the placenta rises up, the threat will be eliminated. Chorionic presentation at 12 weeks can only be eliminated through drug treatment. Also, pregnant women are prescribed complete rest and...
Expectant mothers are wondering about chorionic villi: what is it and are they normal. The outer membrane of the fetus has small villi that help attach it to the wall of the uterus, so this structure of matter is considered completely normal.
Localization of the chorion
Experts determine several main positions of placenta concentration:
- Localization of the chorion along the posterior wall. This location of the tissue suggests less deviation from the norm than others.
- The predominant anterior localization of the chorion is a deviation from the norm that requires medical intervention.
- When the chorion blocks the internal os, not only the development of the fetus is hampered, but also its birth.
All problems associated with incorrect presentation can only be solved medically. Women should not resort to traditional methods of treatment.
There are several places where amniotic tissue attaches to the uterus and they all require separate consideration. Localization of the chorion along the posterior wall is most common. This condition is typical in early pregnancy. The primary localization of the chorion is considered to be in the posterior part of the reproductive organ. It is clearly visible during ultrasound examination. In this case, there is no need to panic. The posterior localization of the chorion will not and will not cause spontaneous abortion. The state of matter may change, so specialists prescribe an examination in the early stages. Expectant mothers must clearly understand that the posterior localization of the chorion is a normal development of pregnancy. Usually, in this case, there are no problems with the health of the woman and the unborn child.
The chorion can be located along the anterior wall of the uterus. Experts consider this arrangement of matter to be normal, but warn that expectant mothers should be extremely careful. Chorion along the anterior wall of the uterus can threaten placental abruption, so you must follow all doctor’s instructions. However, this is not a reason to panic, since matter has a specific ability to migrate. Chorion along the anterior wall is not a death sentence, but minor complications that can be eliminated.
Some women experience attachment of the amniotic sac to the side of the reproductive organ. In this case, doctors say: chorion on the front wall or on the back, and on the right or left. This is also determined by ultrasound. Anterior localization of the chorion with lateral deviation is also not a pathology and can change.
The examination results sometimes contain information about the different location of the site of attachment of matter to the wall of the uterus. The low location of the chorion means that the attachment site is in close proximity to the cervix. The distance separating them is no more than 3 centimeters. Low location of the chorion is not a pathology. It is completely acceptable for medical reasons. Low chorionic attachment may change. The uterus enlarges with the growth of the fetus, so the insertion site rises upward. Low chorion attachment can be considered normal if it does not close the pharynx.
There are several types of presentation that are detected by ultrasound.
- Regional chorion presentation;
- Partial;
- Complete.
Complete presentation means that the matter is localized near the cervix and closes the exit for the fetus. The chorion blocks the internal os and interferes not only with spontaneous childbirth, but also threatens arbitrary termination of pregnancy. This may lead to surgery during childbirth. Medicine has not yet developed a way to solve the problem when the chorion blocks the internal pharynx. But experts advise complete rest and proper nutrition for this diagnosis.
With partial closure, one part of the cervix remains open.
The marginal presentation of the chorion involves minimal closure of the exit from the canal and only along one edge. This problem does not contribute to miscarriage, unlike the other two.
Chorionic villus biopsy and indications for it
Many women wonder why a chorionic villus biopsy is performed. You should know that this matter has the same genetic structure as the fetus. In this regard, the procedure can be carried out in order to detect diseases in early pregnancy.
Chorionic villus biopsy is performed for the following indications:
- Late pregnancy;
- Previously born children have diseases associated with chromosomes;
- The genes contain these diseases;
- Echography indication.
Chorionic villus sampling can have complications. This is bleeding, pain or miscarriage. In this regard, the duration of the procedure should not exceed 12 weeks.
Chorionic villus biopsy has its contraindications. If a woman has chronic diseases in the acute stage, the material is not available, there are visible deviations from the norm in the cervix, the presence of fibroids, bloody discharge and other equally serious indications, the procedure is not performed.
Chorionic villus biopsy reviews are quite contradictory. First of all, you need to know that this is a small but painful operation. The procedure is performed through the cervix or abdominal cavity, depending on the location of the matter. In addition, certain complications may arise as the pregnancy continues. No matter what reviews a chorionic villus biopsy has, it should only be carried out due to urgent need and medical indications. The operation is performed under constant ultrasound monitoring.
During the mandatory ultrasound after 12 weeks, the location of the chorion is assessed, among other things. Sometimes an ultrasound specialist diagnoses chorionic presentation. What does this mean and how dangerous is it?
what does it mean “the chorion covers the internal os. “???
What is low chorion presentation, and why is it dangerous? This location of the baby's place is said to be if it is located at a distance of less than 6 cm from the internal os of the uterus. This threatens with several consequences at once: abruptions (and consequently bleeding), pelvic or oblique presentation of the fetus, which can lead not only to a cesarean section, but also to a miscarriage. Severe bleeding can be fatal if not stopped quickly. Complete chorion presentation threatens placental abruption over a large area, which is dangerous because of bleeding for the mother, and the child at this time experiences acute hypoxia, which can cause death in a matter of minutes. That is why such pregnant women are preferred to be managed in a hospital setting. This location of the placenta is also called central chorion presentation, that is, the baby’s place closes the internal os.
But not everything is so scary, the placenta migrates during pregnancy, simultaneously with the growth of the uterus. Thus, in many cases, even complete placenta previa can become normal by the third trimester.
As for operative delivery, it is an absolute indication if there is a complete or partial marginal presentation of the chorion (that is, the placenta at one end is in contact with the internal os). If the distance from the internal os to the placenta is at least 2-3 cm, childbirth can take place naturally, and as statistics show, they are not more problematic than those that occur when the placenta is high in the uterus.
What are the causes of low chorion presentation, and can it be avoided using any preventive measures? The best prevention is regular visits to the gynecologist and early detection and treatment of gynecological diseases, as well as reliable contraception if pregnancy is not yet desired. This is very important, since the cause of this pathology is precisely inflammatory diseases as a result of curettage and abortion. The uterine tissue is damaged, and the egg cannot be implanted in the most physiological place for it (the back or front wall of the uterus). In addition, chorion presentation along the posterior or anterior wall can occur due to multiple neoplasms of the uterine cavity (multiple fibroids), due to polyps. Therefore, all women with fibroids should consult a gynecologist before pregnancy regarding the likelihood of a successful pregnancy outcome with existing tumors. In some cases, it is recommended to remove them (but then you can become pregnant no earlier than 1.5-2 years after the operation), and in some, on the contrary, to postpone the operation. It is also necessary to take into account that during pregnancy, fibroids tend to increase due to the growth of the hormone estrogen. Typically, a sharp increase in tumors is observed in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Women over 35 years of age and multiparous women have an increased risk of low chorionic presentation. But often it occurs without obvious reasons. The main thing in this situation is the correct, very careful way of life until the placenta rises. It is recommended to stop sexual relations and reduce physical activity, be sure to regularly visit a gynecologist and have ultrasound examinations. In this way, complications can be identified in time and placental abruptions can be prevented.
What is chorionic presentation and why does it occur?
Until the placenta is formed, the embryo is surrounded by a villous membrane, which grows into the lining of the uterus. Until the 16th week of gestation, this is the chorion (from the 17th week - the placenta), which performs the following main functions:
- Nutrition of the embryo;
- Respiration - delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide;
- Isolation of metabolic products;
- Embryo protection.
During the normal course of pregnancy, the chorion attaches to the fundus of the uterus and grows along the anterior, posterior and lateral walls, but this does not always happen.
Chorionic presentation is its incorrect location, in which there is complete or partial overlap of the internal os of the cervical canal.
Why this condition occurs is not completely clear. But a connection has been established with some factors:
- chronic inflammation of the uterus;
- previous operations;
- abnormal development of the uterus;
- a large number of pregnancies and births;
- low attachment of the placenta in the previous pregnancy.
What is the attachment of the placenta and chorion?
Sometimes it happens that the placenta is attached to the anterior wall of the uterus or in the lower segment, partially or completely blocking the internal os of the cervical canal.
Sometimes you can come across the term “chorion presentation”, which from an obstetric point of view is incorrect, since the chorion is the middle membrane in relation to the others. The exception is the first trimester of pregnancy, when the placenta is not yet fully formed.
Types of chorion location
Based on the attachment of the chorion relative to the internal os, presentation occurs:
- Complete - a condition in which the chorion completely covers the internal os. This will subsequently develop into placenta previa.
- Incomplete - characterized by overlap of part of the uterine os. If the villous membrane comes out up to a third, then this is called marginal presentation.
- Low - the chorion is located at a distance of 3 cm or less from the pharynx, but does not overlap it.
Chorionic presentation at 12 weeks is not the final verdict. As the uterus and fetus grow, migration may occur, and the condition will return to normal. A more favorable prognosis is noted for the posterior location of the chorion and presentation along the anterior wall.
Complete blocking of the uterine pharynx by the chorion is a dangerous type of pathology that threatens massive bleeding.
How is chorionic presentation manifested?
Most often, pathology is detected during ultrasound.
Bloody discharge can also be caused by presentation, especially if a hot bath, sauna, or sexual intercourse took place shortly before. In this case, you need to urgently consult a doctor.
Complications
The pathology is dangerous:
- premature miscarriage;
- uterine bleeding;
- intrauterine death of a child.
Chronic blood loss leads to the development of anemia and fetal hypoxia. If complete occlusion of the pharynx remains, natural childbirth is impossible.
Treatment of chorionic presentation
Partial chorionic presentation without bleeding does not require hospitalization. Isolation of any amount of blood is an indication for treatment in the hospital.
It is impossible to artificially change the location of the villous membrane, so the main task facing doctors is maintaining pregnancy. A protective treatment regime is created in the hospital:
- The woman is in a calm environment, on bed rest;
- Physical activity is limited;
- A balanced diet is provided with the exception of foods that strengthen or relax the stool.
Drug treatment is as follows:
- Suppositories with Papaverine, Drotaverine tablets to relieve uterine tone;
- Iron preparations, for example, Totema, Maltofer - for the prevention or treatment of anemia.
In the presence of bleeding, the hemostatic drug sodium etamsylate is additionally used. At the beginning of therapy, it is administered intravenously or intramuscularly. Then you can switch to tablets.
Massive bleeding that cannot be treated with conservative methods is an indication for termination of pregnancy.
After discharge from the hospital, at home it is necessary to adhere to a measured lifestyle, eliminate stress and increased workload. It is forbidden to have sex, because this may cause new bleeding and miscarriage.
What is the prognosis for the pathology?
Chorionic presentation at 8-14 weeks can transform into a normal location of the placenta or persist in the form of low placentation.
If the presentation does not disappear, but turns into an anomaly in the location of the placenta, then by the time of birth the baby may be transverse in the uterus or with the buttocks down. In such cases, to reduce the risk, it is recommended to deliver the baby through.
Prevention
Women should take care of their reproductive health as early as possible:
- Hypothermia should be avoided and inflammatory diseases of the genital area should be treated promptly.
- Do not resort to abortion, this is not a method of family planning.
- It is important to eat properly and nutritiously and lead a measured lifestyle.
If you follow these simple rules, you won’t have to become familiar with pathologies from personal experience.
Yulia Shevchenko, obstetrician-gynecologist, especially for the site
Treatment
It should be noted that there is no specific treatment for this pathology.
: It is impossible to artificially change the location of the chorion, therefore all therapeutic measures are aimed only at maintaining pregnancy and treating possible complications.
However, diagnosing chorionic presentation does not mean that in the future the formed placenta will also occupy an incorrect position. Due to the growth of the uterus, upward migration of the chorion and placenta is possible
.
Tactics for further management of pregnancy
when chorion previa is detected, it depends on the presence of bleeding and its volume.
If chorionic presentation is diagnosed by ultrasound and there is no bleeding, it is advisable to hospitalize the woman in a hospital, where a complex of therapeutic measures is carried out
:
- Complete bed rest;
- Strict limitation of physical activity;
- Constant monitoring of medical personnel;
- Ultrasound control;
- Complex of vitamins for pregnant women;
- Compliance with a diet with strict exclusion of foods that cause loose stools or constipation;
- Drugs to reduce uterine tone (Papaverine);
- Iron supplements to prevent the development of anemia (Sorbifer).
If the treatment results are positive , the woman can be discharged home, but she must strictly follow a number of recommendations
:
- Strict limitation of physical activity
(heavy lifting, jumping, fast walking, running are completely excluded); - Avoiding sexual contact
; - Elimination of stressful situations and increased mental stress
; - Following a diet
to prevent constipation and diarrhea; - At the first sign of bloody discharge from the genital tract, an emergency visit to the gynecological department
.
When bleeding occurs
They carry out similar treatment (
necessarily in a hospital setting
!), but in addition they prescribe hemostatic drugs (sodium ethamsylate). In most cases, therapeutic measures are effective, and pregnancy can be maintained further.
Important For massive bleeding
the development of conditions that threaten the woman’s life is possible; in this case, regardless of the gestational age, the pregnancy is urgently terminated.