Often, at an appointment with a gynecologist, a woman receives a referral for a cervical biopsy. At first glance, this analysis is quite unusual, which is why many patients are scared when they hear about it for the first time. But it’s enough to understand the nuances - and it will become clear that the procedure is not worth the worry if you approach its preparation and implementation correctly.
- What it is
- Can it be done during pregnancy?
- Indications for cervical biopsy
- Methods: Puncture (simple)
- Endocervical curettage
- Electrosurgical and radio wave
- Conization or wedge-shaped
- When to do it
What it is
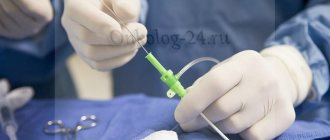
A cervical biopsy is a diagnostic method that reveals unhealthy pathologies in the organ. Such a study is traditionally prescribed when doctors suspect a serious illness in a patient. Its essence lies in pinching off (cutting off) microscopic sections of tissue from the neck, which are sent for detailed study. Based on the results of this laboratory analysis, the attending physician makes a final diagnosis and also determines a course of treatment, if necessary.
Today this is one of the safest ways to determine the state of women's health. Due to their specificity, many diseases of the reproductive system behave unnoticed for the time being, and symptoms begin to appear only in the last, advanced stages of development, when it is very difficult to cope with them. However, a biopsy reveals such pathologies at the earliest stages, which is why it is so important to undergo timely examinations by a specialist.
Did you know? Oddly enough, the word “vagina” was first used in cinema thanks to Walt Disney. In 1946, Walt Disney Productions produced the animated film The Story of Menstruation, intended for health education classes in public schools. The film contained useful advice in case of “critical days”, which at that time was not known to everyone.
Can it be done during pregnancy?
Doctors try to avoid biopsies during pregnancy, so as not to additionally burden the female body. Usually it is postponed until childbirth and is recommended to be done 10-12 weeks after the birth of the baby. If the procedure is done too early, the results may be false. Samples are taken for analysis during pregnancy only when doctors have serious concerns about the health of the expectant mother. In such conditions, the procedure is prescribed for the second trimester, when the risk of negative consequences from it is minimal.
Find out how to treat ectopia, leukoplakia and cervical dysplasia.
If the test results of a pregnant woman show the presence of cancer cells, then most often a decision is made to terminate the pregnancy in order to save the woman. However, there are many cases when a pregnant woman carried and gave birth to a baby without problems, and treatment was carried out after. Each case is individual, so doctors weigh all the risks before offering a choice to the patient.
Cordocentesis
This diagnostic method involves puncture of the fetal umbilical cord for the purpose of drawing blood or administering medications. Although it is possible to carry out such a procedure after the 18th week of pregnancy, the optimal period is considered to be 22-25 weeks. The advantage of this method is that the risk of miscarriages is minimized, but at the same time a high percentage of information content is maintained in relation to the detection of gene and chromosomal diseases.
A pregnant woman may have many questions related to the recommended diagnostic measures, and the doctor is obliged to answer them in detail
Indications for cervical biopsy
Doctors rarely prescribe a biopsy without reason, even though it is quite safe for health. Reasons for performing a biopsy include:
- unsatisfactory results of smear cytology;
- the presence of polyps on the cervix;
- condylomas;
- changes in tissues during colposcopy;
- leukoplakia;
- cervical erosion.
Important! If the sampling technology is followed, the analysis results are error-free.
Methods of carrying out
Modern gynecology has in its arsenal various types of cervical biopsy, differing only in how the procedure is performed. The method in this case does not affect the result, but is important for the woman’s comfort.
Puncture (simple)
When using this method, a thin needle is used, and the instrument itself is in the form of a syringe. The tip is inserted into the organ being examined, then when the piston is pressed, the microscopic branches are cut off and the material to be examined is placed in the hollow space of the needle. This type of biopsy has several disadvantages:
- there is a risk of piercing the vaginal wall or damaging neighboring organs;
- It is especially dangerous to carry out it in the presence of cancer cells: the doctor must be careful when taking material so that diseased particles do not get on healthy tissue and create a new focus of the disease.
Depending on the size of the needle, the procedure is divided into fine-needle (aspiration) and thick-needle (trepanobiopsy).
The difference between them is the amount of material the tool can handle. Did you know? 30% of women during pregnancy experience the desire to try inedible things.
Endocervical curettage
Curettage is used when there is no clear boundary of the suspicious area, so doctors take samples from all tissues of the cervical canal. There are several types of curettes (special blades) of different sizes specifically for this purpose. Given the painfulness of the procedure, it is performed under local anesthesia. The instrument is inserted into the canal and the material is scraped back and forth. This method is quite common in the USA, but in Europe they prefer to avoid it for a number of reasons:
- the quality of the material in this case is not the best; it contains impurities, which makes analysis difficult;
- pain relief does not always help during the procedure;
- there is a risk of bleeding.
Electrosurgical and radio wave
An electrosurgical biopsy is performed using a loop of thin wire through which a current is passed. The procedure is not so much painful as simply unpleasant. Its main disadvantage is the risk of getting a scar on the cervix, which is undesirable for nulliparous women. Radio wave biopsy of the cervix is carried out using a radiosurgical knife, which clearly and quickly separates tissue. Ideal for women planning pregnancy.
Conization or wedge-shaped
The essence of this method is to cut out a cone-shaped piece of tissue on the cervix or cervical canal. Conization has its own subspecies:
- laser;
- loopback (using radio waves);
- knife (no longer used today).
The procedure takes an average of 15-30 minutes and is performed after pain relief. There is no risk of bleeding or infection. A special subtype of conization is called a circular biopsy. It is distinguished by the fact that materials are taken for analysis not only from the suspicious area, but also from the healthy areas surrounding it. This move allows doctors to see a more complete picture of what is happening. A circular biopsy is necessarily performed under anesthesia (sometimes under general anesthesia) and the site where the material is taken may bleed for several weeks. However, if the discharge is heavy, you should contact your doctor.
Technique
A biopsy will reflect the true state of affairs only if the rules of the procedure are followed. Therefore, it is important to adhere to the timing of its implementation, requirements for tools and preparation.
When to do it
The date of the procedure is agreed upon with the doctor, based on the patient’s menstrual cycle. The best time for the procedure is 7-13 days of the period. However, it can be carried out immediately after the end of menstruation, then before the start of the next cycle the flesh will have time to heal completely.
How to prepare
As for preparation, it occurs in several stages. It's worth starting with getting tested. Since the procedure is invasive, the risk of complications from infections must be checked before undergoing it. For this purpose they rent:
- general blood analysis;
- blood clotting test;
- smears for flora and cytology;
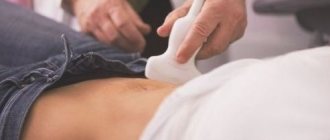
- colposcopy is required;
- tests for HIV, hepatitis, hidden infections.
Important! The exact list of tests is always provided by the doctor, based on the patient’s health characteristics.
Immediately before the procedure itself, you must follow a few simple rules:
- two days before the biopsy, you must stop having sex;
- at the same time, you need to give up tampons and stop douching;
- if you are taking any medications, it is better to consult a specialist about whether you can continue the course before and after the procedure;
- If possible, before going to the doctor for the procedure, it is advisable to take a shower, adhering to the rules of intimate hygiene.
You can eat before the biopsy if you are not planning to use general anesthesia.
Taking material for analysis
Depending on the type of biopsy, the procedure may vary. Before the procedure, it is advisable to discuss it with your doctor so you know what to expect and what the process will be like. An in-office biopsy involves local anesthesia as needed and usually lasts no more than 15-30 minutes. In this case, as at a regular appointment, the patient takes a seat in the gynecological chair, and the doctor introduces a mirror for viewing and illuminates the area where the material is planned to be taken.
You may also find it helpful to learn more about endometritis, fibroids, and uterine metroendometritis.
Then the procedure itself occurs, after which the samples taken are packaged for transfer to the laboratory, and the patient can be free.
In more complex cases, when there is a high probability of detecting infected areas that will need to be removed immediately, the procedure is carried out in a hospital setting. To do this, the woman is admitted to the hospital one day before the biopsy. Doctors perform the procedure using:
- epidural (spinal) anesthesia: under its influence, sensitivity in the lower half of the body is lost;
- general anesthesia, when the patient falls asleep.
In a hospital setting, a biopsy lasts from 40 minutes to 2 hours, depending on the complexity of the case.
Important! Once completed, the doctors monitor the patient for a short period of time (sometimes the woman is left overnight in the hospital).
If there are no complications, then you can go home.
Results and transcript
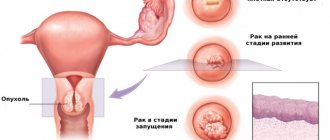
The results of a cervical biopsy will be ready within 10-14 business days, depending on the type of procedure and the laboratory where the study was performed. It is better to entrust the interpretation of analyzes to a specialist . The research protocol is usually full of terms and abbreviations that will mean nothing to an untrained person. However, in general terms there are four possible results:
- Normal: no atypical cells or neoplasms of any kind were detected in the sample.
- Inconclusive/contradictory findings indicate problems with the procedure and the biopsy must be repeated.
- Benign cells are available. This means that there are harmless formations in the body, there is no threat of cancer.
- Oncological cells were detected . In addition to confirmation, the results will inform you about the type and stage of the disease, the size of the affected area and its location. The doctor needs all this data to formulate a course of treatment.
In studies that were conducted to study the effectiveness of biopsy, it was found that in 98% of the analysis was true, only in 2% of cases an error was detected.
What to do after
The effects of a biopsy may take some time to be felt. They will appear as follows:
- Bleeding. Their duration and abundance depend on the type of analysis performed. The longest discharge (5-7 days) will occur after conization and loop biopsy. In other cases they last no more than 3 days.
- Pain in the lower abdomen, in the vaginal area. These unpleasant sensations have a pulling, aching character and usually disappear within a few days, when the biopsy mark completely heals.
- Possible increase in temperature. Most often, it is caused not so much by the biopsy itself as by excitement and anxiety about it. However, if the temperature rises above 37.5°C, consult a doctor: this is already a sign of infection.
Important! Using a tampon during this period is strictly prohibited; replace it with a gasket.
After the procedure, the doctor usually gives recommendations to the patient on how to avoid complications:
- do not take a bath, only a warm shower;
- You cannot swim in open waters or pools;
- It is advisable to begin sexual activity no earlier than 7 days after the procedure (sometimes this period extends to 10-14 days);
- exclude physical activity, weights, and any training during the recovery period;
- taking vaginal medications must be replaced with analogues in tablets;
- give up medications that thin the blood (the most popular of them is aspirin), otherwise there is a risk of increasing the amount of discharge and delaying the healing process of the wound.
As for pregnancy after a cervical biopsy, the procedure itself does not affect the process in any way if the test results are normal.
Preparation
In order for the operation to go smoothly and the expected result to be obtained, it is necessary to carry out preliminary preparation. First of all, a woman should undergo a gynecological examination and additional examination:
- General blood and urine tests.
- Blood test for biochemistry: antibodies to infections (herpes, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, syphilis, HIV, hepatitis), coagulogram.
- Smear from the cervical canal (for cytology and microflora).
- Analysis of secretions (bacteriological, PCR).
- Colpocervicoscopy.
- Ultrasound of the pelvis (transvaginal).
- Electrocardiogram.
The research results make it possible to confirm the diagnosis and exclude conditions that are a limiting factor for curettage. For a week, a woman should not take medications that affect the blood coagulation system. On the eve of the procedure, you must refrain from sexual intercourse and use intimate hygiene products (use only water), and immediately on the day of the procedure, come to the doctor on an empty stomach.
Contraindications
Despite the effectiveness of a biopsy, there are cases when it is not recommended by specialists. The reasons for this decision by doctors may be different:
- The presence of inflammation in the vagina or cervix. In such cases, the doctor conducts additional tests as necessary, prescribes a course of treatment, and only after the disease has resolved, performs a biopsy.
- It should not be done during menstruation.
- If there is a suspicion of pregnancy, the procedure is postponed until this fact is clarified. If confirmed, the procedure is not performed in the first trimester without compelling reasons.
Did you know? The hormones cortisol and progesterone are responsible for the feeling of danger. Their increased concentration in the female body makes the weaker sex more susceptible to anxiety and panic compared to men.
Chorionic villus biopsy
The chorion is the outer membrane of the embryo. Chorionic villus biopsy (CVS) is a study of cells of the outer membrane of the fetus containing the same hereditary material (karyotype) as the developing fetus. Karyotype analysis makes it possible to identify severe pathologies of embryo development in the 1st trimester, when other medical procedures associated with penetration through the natural external barriers of the body are strictly contraindicated.
BVS is performed at 8-12 weeks of pregnancy. Later, it is not recommended to do this procedure, since at 13 weeks the placenta develops from the chorion. But before the 11th week, there is a risk of impaired development of the baby’s limbs.
This diagnosis is carried out in the following cases:
- If a woman becomes pregnant over the age of 35. In old-time mothers, the likelihood of developing fetal pathologies increases.
- One of the parents has genetic abnormalities (developmental defects, hereditary diseases, chromosomal rearrangements).
- The child was conceived as a result of incest (the parents are siblings).
- The medical history noted primary infertility, miscarriages occurred, previous children were born still or with genetic disorders.
- In the early stages of pregnancy, the woman took embryotoxic drugs, had x-rays taken, or inhaled toxic vapors.
Chorionic villus biopsy makes it possible to detect Down syndrome, trisomy 18 chromosome, the presence of an additional 13 chromosome in the cells and other diseases at the genetic level in the fetus, as well as determine gender and establish paternity.
Collection of material for such diagnostic studies is contraindicated in the following cases:
- existing threat of miscarriage;
- a pregnant woman has inflammatory diseases on the skin of the abdomen, vagina or cervix;
- the woman is a carrier of HIV infection.
BVH is not without risks and consequences. The main ones:
- In 1-2% of cases, a miscarriage occurs after the manipulation.
- In 0.1-0.5% of cases, intrauterine infection occurs.
- The fertilized egg exfoliates due to the formation of a retrochorial hematoma.
Doctors do not insist on a chorionic villus biopsy and future parents always have a choice.
Possible complications
Like any major procedure, a cervical biopsy can have complications. They can occur for various reasons, but it is worth knowing about them in order to be able to seek medical help in a timely manner. This should be done if:
- bleeding after the procedure is brightly colored, in large quantities or has dark clots;
- discharge lasts more than 7 days or has an uncharacteristic, unpleasant odor;
- More than two weeks have already passed, and there are still brown smears;
- body temperature above 37.5°C;
- I am worried about acute pain in the lower back or lower abdomen.
Important! Often the cause of complications is the frivolous behavior of the woman herself, who does not adhere to the doctor’s recommendations regarding the post-procedure period.
Biopsy during pregnancy: features
Having reasons for conducting a biopsy during pregnancy, it is worth taking into account both all of the above, as well as some nuances that are typical only for pregnant women. When deciding on a biopsy, doctors always weigh the duration of pregnancy and the degree of danger to the woman’s health. Whenever possible, the procedure is avoided:
- in and 3rd trimester;
- during pregnancy with complications (multiple pregnancy);
- if there are other factors that threaten the fetus.
However, there are situations during pregnancy that necessitate the procedure:
- if cervical erosion occurs, a biopsy is prescribed;
- critical change for the worse in some analyses.
For more careful monitoring of the condition of the pregnant woman and baby, the woman will most likely be hospitalized for the period before and after the procedure. Signs of complications in this case are:
- heavy bleeding;
- yellowish-green discharge;
- abdominal cramps that last more than a day.
So, a cervical biopsy is a complex and difficult procedure, but it is not something to be afraid of. With the help of regular visits to the gynecologist, she will become a faithful assistant in maintaining women's health, and not a harbinger of disaster. If you follow the rules, it is safe, fast and does not cause discomfort. With its help, you can find out about possible diseases in time - or make sure of your health.
Tests Health Uterus
Purpose of the study
A biopsy is performed if absolutely necessary.
Moreover, even if it was needed to clarify the diagnosis, but inflammation is currently detected in a female representative, the analysis is not carried out until complete recovery is achieved. Thus, sufficiently strong reasons and warning signs are necessary for the analysis to take place. These include:
- negative smear cytology results;
- the presence of any suspicious changes in the cervical area during colposcopy;
- erosion processes in this area;
- leukoplakia, or hyperkeratosis;
- polyps in the cervical area, as well as condylomas.
The most suitable period of the menstrual cycle for performing a biopsy should be considered the period from 7 to 13 days. For correct calculations, it is necessary to remember that the first day of the cycle is the first day of the onset of menstruation. It would be most correct to carry out this analysis immediately after the end of menstruation.