The amniotic sac in which your unborn baby grows and develops is called the amnion. From the very beginning of pregnancy, it provides the baby with conditions for intrauterine life. And one of the most important tasks of the amniotic sac is to produce a fluid called amniotic fluid. It fills the entire amnion cavity and performs a number of vital functions for the fetus. Water forms the first habitat of the fetus, so its importance cannot be overestimated. Thanks to the amniotic fluid, the baby feels comfortable (the temperature is always stable here - 37 degrees, quiet and cozy) and protected (the water prevents the entry of microorganisms from the outside world, as well as any other negative effects on the fetus from the outside).
Amniotic fluid is released continuously, but unevenly. As the period increases, its volume also increases, reaching its maximum at approximately 36 weeks of pregnancy, averaging 1000-1500 ml. Then, just before birth, the amount of amniotic fluid may decrease slightly, which is explained by the increased excretion of fluid from the mother’s body.
What is amniotic fluid?
The aqueous membrane (amnion or amniotic sac) is a closed sac.
Inside it is a fetus surrounded by amniotic fluid. The walls of the amnion are very thin, but strong and elastic: they stretch well and are very elastic. Normally, the aqueous membrane is transparent, smooth and has a shiny, pearlescent tint. Amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid) is produced by the walls of the amnion and fills its cavity. During the entire period of pregnancy, amniotic fluid constantly changes (a complete change occurs every three hours) its quantitative and qualitative composition in direct proportion to the duration of pregnancy and the growth of the baby. With each week, the volume of liquid steadily increases by an average of 40-50 ml. The maximum volume is observed by the 37-38th week of pregnancy and averages 1000-1500 ml. By the end of pregnancy, the amount of water may decrease to 800 ml as a result of increased fluid excretion from the woman’s body. The amount of water is determined by calculating the amniotic fluid index (AFI) during ultrasound.
The waters are transparent, do not have a specific odor, and in viscosity and consistency they really resemble water. Approximately 1/3 of the water consists of the child’s urine, his secretions from the lungs and through the skin, and also contains: glucose, fats, salts, urea, oxygen, carbon dioxide, vitamins, antigens corresponding to the fetal blood type and hormones. Epidermal scales (desquamated fetal skin cells), products of the activity of the sebaceous glands of the skin and vellus hair may be mixed with the waters. If the amniotic fluid has shades of green, this indicates intrauterine fetal hypoxia.
The IAF table contains data on the normal volume of amniotic fluid for each week of pregnancy and maximum permissible deviations from generally accepted indicators. If the AFI indicator goes beyond the upper limit of these norms, then, in accordance with the stage of pregnancy, the doctor speaks of polyhydramnios. If the index exceeds the norm slightly, then it is customary to talk about moderate polyhydramnios.
| Gestation period, weeks | Average normal value, mm | Probable fluctuations, mm |
| 16 | 121 | 73-201 |
| 17 | 127 | 77-211 |
| 18 | 133 | 80-220 |
| 19 | 137 | 83-225 |
| 20 | 141 | 86-230 |
| 21 | 143 | 88-233 |
| 22 | 145 | 89-235 |
| 23 | 146 | 90-237 |
| 24 | 147 | 90-238 |
| 25 | 147 | 89-240 |
| 26 | 147 | 89-242 |
| 27 | 156 | 85-245 |
| 28 | 146 | 86-249 |
| 29 | 145 | 84-254 |
| 30 | 145 | 82-258 |
| 31 | 144 | 79-263 |
| 32 | 144 | 77-269 |
| 33 | 143 | 74-274 |
| 34 | 142 | 72-274 |
| 35 | 140 | 70-279 |
| 36 | 138 | 68-279 |
| 37 | 135 | 66-275 |
| 38 | 132 | 65-269 |
| 39 | 127 | 64-255 |
| 40 | 123 | 63-240 |
| 41 | 116 | 63-216 |
| 42 | 110 | 63-192 |
Compound
97% is water in which nutrients are dissolved: proteins, fats, mineral salts (calcium, sodium, chlorine), hormones . In addition, skin and hair cells can be found in the amniotic fluid.
There is an opinion that the smell of amniotic fluid is similar to the smell of mother's milk , which allows the newborn to determine where the mother's breast is.
Until 14 weeks of pregnancy, fluid seeps into the baby’s body through the skin , and when the skin is enriched with keratin and thickened, from that moment the baby swallows amniotic fluid and excretes it in the urine . Over time, the volume of liquid processed reaches several liters per day.
What function do they perform?
During pregnancy, the water membrane protects the baby from mechanical damage (injuries, bruises, blows), creates a comfortable living environment, participates in metabolism, protects the umbilical cord from compression, prevents the formation of adhesions between the baby’s skin and the walls of the uterus, protects against infections from the genital tract . The baby constantly swallows liquid, training the digestive, excretory and respiratory systems.
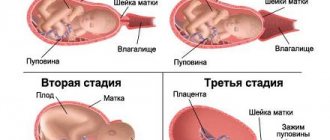
During labor, the amniotic sac presses on the cervix, causing it to dilate. During physiological childbirth, the amniotic sac ruptures in the first stage of labor with full or almost (5-6 cm) full dilatation of the cervix. Timely rupture of the membranes not only contributes to the normal process of effacement and dilatation of the cervix, but also maintains favorable conditions for the fetus during labor. As long as the membranes are intact, the baby is not in danger of infection. In addition, the contracting walls of the uterus do not directly envelop the fetus and do not disrupt the blood circulation between the mother and the fetus. The breaking of water after cervical dilatation of 3 cm or more rarely changes the normal course of labor. The absence of an amniotic sac at the onset of labor can lead to the development of labor weakness.
When water is scarce
If the amount of water at the end of pregnancy is less than 300-500 ml, doctors diagnose oligohydramnios. This is not a disease, but a consequence of certain complications.
Among the causes leading to oligohydramnios, the most common are gestosis, maternal hypertension, infectious and inflammatory diseases (toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, mycoplasma infection, etc.), malformations of the fetal excretory system (blockage of the urethra, ureters), fetoplacental insufficiency , chronic hypoxia.
The doctor can assume a decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid if the height of the uterine fundus and abdominal circumference lag behind the normative indicators for the expected period of pregnancy, as well as if the motor activity of the fetus decreases. During external examination, parts of the fetus are clearly identified, heart sounds are heard, and the uterus is dense. A more accurate determination of the severity of oligohydramnios is possible with ultrasound examination. The diagnosis of oligohydramnios is made by ultrasound. A Doppler study of blood flow in the “mother-placenta-fetus” system is also necessary, since with oligohydramnios there may be a disturbance in blood flow.
An extremely unfavorable prognostic sign is the detection of severe oligohydramnios in the second trimester of pregnancy, i.e. at 18-26 weeks. When oligohydramnios develops during these periods, pregnancy is terminated and intrauterine death of the fetus or newborn occurs in the first days of life. As the amount of amniotic fluid decreases, fetal growth retardation (hypotrophy), determined using ultrasound fetometry, increases. With I degree of malnutrition, there is a lag of fetometry indicators from the normative indicators by 2 weeks, with II - by 3-4 weeks, with III - by more than 4 weeks. Oligohydramnios can also lead to the development of intrauterine defects and intrauterine infection.
When oligohydramnios is moderate, the pregnancy is usually carried to term; emergency caesarean section is performed in exceptional cases. Low water during labor requires opening of the amniotic sac; due to insufficient water, a flat bladder is formed, which interferes with full labor.
Mechanism of occurrence
When a fertilized egg attaches to the uterus and begins to divide, four components of a complex mechanism appear: the membranes, the chorion (the future placenta), the umbilical cord and the embryo itself. The fluid inside these membranes is completely sterile, and by the end of the 2nd week of pregnancy, the fetal bladder occupies the entire uterine cavity.
directly formed due to the sweating of blood plasma from the mother's blood vessels . In late pregnancy, the baby's kidneys and lungs begin to take part in the production of amniotic fluid. By the end of the term, the amount of amniotic fluid reaches 1 - 1.5 liters, and every three hours it is completely renewed .
When there is a lot of water
The diagnosis of “polyhydramnios” is made if the amount of amniotic fluid during a full-term pregnancy exceeds 1.5–2 liters. It usually develops in the middle or second half of pregnancy.
The most common causes of polyhydramnios are: diabetes mellitus, the presence of an acute or chronic infectious process in the mother, Rh conflict, cardiovascular diseases, fetal development abnormalities (congenital malformations of the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract).
Polyhydramnios is divided into acute (a sharp increase in the amount of water, accompanied by shortness of breath, malaise, pain, heaviness in the abdomen, swelling) and chronic, when the amount of water increases gradually without causing significant ailments.
With the development of polyhydramnios, there is a significant increase in the size of the uterus: abdominal circumference and height of the uterine fundus. The uterus is tense, parts of the fetus are difficult to palpate, while the fetus easily changes its position, and its excessive motor activity may be observed. Fetal heart sounds are not heard clearly. Ultrasound plays an important role in the diagnosis of polyhydramnios. During the study, the size of the vertical pocket is determined (ultrasound criterion for assessing the amount of amniotic fluid): with a mild degree of polyhydramnios, its value is 8-11 cm, with a moderate degree - 12-15 cm, with severe polyhydramnios this figure reaches 16 cm or more.
Why is polyhydramnios dangerous? A child who feels spacious in the uterus may not descend into the pelvis for a long time or may take an incorrect position. An overstretched uterus contracts poorly, which causes weak labor (prolonged labor) and bleeding in the postpartum period. Due to polyhydramnios during childbirth, umbilical cord prolapse and placental abruption may occur. With this diagnosis, at the beginning of labor, the amniotic sac is punctured (a procedure called amniotomy) and amniotic fluid is slowly released through a needle or catheter so that the volume of the uterus decreases and its walls thicken, which will reduce the risk of serious complications. After the birth of a child, in order to prevent hypotonic uterine bleeding, drugs are prescribed that stimulate contraction of the uterine muscles.
With mild chronic polyhydramnios, pregnancy proceeds favorably, childbirth occurs at term, but in parallel, treatment is carried out for the disease that caused the polyhydramnios. With severe polyhydramnios, premature birth often occurs. With increasing circulatory problems in a pregnant woman (severe swelling, severe shortness of breath), sometimes there is a need for artificial termination of pregnancy.
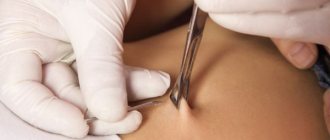
Amniocentesis
Since fetal cells are present in the amniotic fluid, analysis of the amniotic fluid allows us to identify a number of diseases in the child, including genetic abnormalities .
This study is called amniocentesis and involves puncture of the amniotic sac under ultrasound guidance . Based on the analysis data, you can determine:
- at 15–17 weeks, the chromosome set of the fetus is determined using amniocentesis;
- later – the stage of hemolytic disease (with Rhesus conflict);
- abnormal development of the kidneys and lungs;
- detect the infectious agent.
Amniocentesis is performed under local anesthesia ; cell examination takes from 2 to 6 weeks and, on average, the result is ready by 20–22 weeks.
A contraindication to amniocentesis is the threat of termination of pregnancy , since the procedure itself can provoke a miscarriage (in 1% of cases). Ultrasound examination and special genetic blood tests allow doctors only to suspect any diseases of the fetus, but the final diagnosis can be made only after amniocentesis.
And if the water leaks or pours out prematurely
If the membranes rupture before labor begins, this is called premature rupture of the membranes, or premature rupture of amniotic fluid. According to statistics, every tenth woman faces this, and more often primigravidas.
Symptoms of water rupture depend on where the rupture occurs. Most often, the bladder ruptures directly above the cervix; such a gap is called central. With it, water pours out in a stream, this happens unexpectedly and simultaneously. It is simply impossible to miss such a phenomenon!
If the rupture occurs high and the hole is covered by the wall of the uterus, such a rupture is called high lateral. In this case, water will constantly leak in small quantities, wetting the sanitary pad for 2-3 hours. In this case, there may be no pain at all. The danger is that this phenomenon can easily be confused with urinary incontinence or heavy vaginal discharge. You can find out what really happened yourself using the FRAUTEST amnio diagnostic test pad
. A positive test result allows you to figure out at home whether water is leaking or not and quickly decide what to do next.
There is no physical contact with diagnostic components in this test, and the risk of infection (if the bubble has truly lost its integrity) is minimal.
If you suspect leakage of amniotic fluid, you should immediately consult a doctor at the antenatal clinic or the emergency department of any maternity hospital. If a rupture of the membranes is detected, the woman must be hospitalized.
Causes of premature rupture
The reasons may be the following:
- overdistension of membranes (occurs in multiple pregnancies, large fetuses, polyhydramnios);
- pathological conditions of the cervix (flaccid, inelastic cervix, more often in women over 30 years of age, primiparas) due to prolonged inflammation, scar deformation after ruptures of previous births, scar on the cervix after cauterization of erosion before the first birth;
- incorrect position of the fetus (transverse, oblique and pelvic presentation of the fetus, large fetal head);
- incorrect size and shape of the pelvis (changes in the structure of the pelvic bones);
- changes in the membranes (increased permeability, low elasticity, disruption of fetal-placental blood flow, infection, post-maturity).
If the bladder bursts before 34 weeks and the baby's lungs have not yet matured, doctors do everything to prolong the pregnancy, often protecting the baby and mother with antibiotics from possible infection. At this time, the expectant mother will be prescribed medications with the help of which the baby’s lungs will mature and the cervix will prepare for childbirth. If the pregnancy is more than 34 weeks, the woman begins to prepare for childbirth.