Gastroduodenitis and pregnancy
November 23, 2020, 15:32 0 2.948
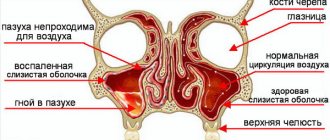
Gastroduodenitis is characterized by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the transport section of the stomach, from where the contents are pumped into the 12-variegated colon. The pathology develops against the background of increased secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, decreased production of gastric juice, and disruption of the endocrine system. The disease is accompanied by severe pain in the epigastric zone, severe belching with heartburn, bowel dysfunction, and frequent vomiting. Such symptoms are especially dangerous during pregnancy, as they can cause miscarriage.
Prevention
Measures to prevent gastroduodenitis come down to following the basic rules of a healthy lifestyle, proper, balanced nutrition. Do not overeat, do not eat too fatty, spicy or hot foods. Avoid stress. Take daily walks in the fresh air.
Such simple and well-known rules have an irreplaceable strengthening and healing effect on the body. Protective functions increase - immunity, which allows you to resist numerous diseases, including gastroduodenitis.
Gastroduodenitis and pregnancy are quite common nowadays. Gastroduodenitis is a disease characterized by inflammation of the mucous layer of the stomach and duodenum. Caused by an increase in the production of hydrochloric acid, a decrease in the amount of gastric juice, and pathological physiology of the endocrine system.
The pathology is accompanied by functional stomach disorders and motor-evacuation disorders. Today, this pathological disorder occupies the main place among extragenital diseases during pregnancy.
Reasons for the development of gastroduodenitis during pregnancy
If a woman suffers from a chronic form of gastroduodenitis, pregnancy acts as a provocateur for exacerbation of the disease. At this time, the body is especially weakened and susceptible to negative endogenous and exogenous factors. Primary or external causes:
- infection with the spiral-shaped bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- eating too hot, cold or spicy foods;
- special eating habits in pregnant women, for example, eating incompatible foods;
- chemical poisoning by pesticides;
- low mobility and physical activity, especially in the second half of pregnancy.
Secondary or internal causes of acute pathology are:
- excess acidity level;
- decreased secretion of beneficial mucus;
- hormonal dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to decreased secretion;
- chronic diseases of the biliary tract and liver;
- endocrine pathologies;
- fluctuations in hormonal levels due to bearing a child.
Return to contents
Causes of the disease
Predisposing factors for chronic gastritis are:
- stress caused by troubles at work or in the family and leading to disruption of the natural rhythm of life (lack of proper sleep due to night shift work);
- nutritional conditions (irregular, unbalanced meals “on the go”, “dry food”, “snacks”);
- infection of the body with bacteria Helicobacter pylori;
- intake of large quantities of poor quality food or strong alcoholic drinks;
- smoking;
- abuse of dishes with refined grains and refined oils, preservatives, emulsifiers, hormones and antibiotics (animal food).
More on the topic
How to treat indigestion during pregnancy: safe methods and tips
Abdominal pain during pregnancy
Riboxin during pregnancy
Treatment of heartburn during pregnancy
About the beneficial (and not so beneficial) properties of tomato juice in early pregnancy
Treatment with medications for gastroduodenitis during pregnancy
A medication course aimed at relieving gastroduodenitis during pregnancy should be selected taking into account the maximum benefit for the mother and child. It is prohibited to prescribe antibiotics during pregnancy, as such drugs have a negative effect on the development and growth of the fetus. First of all, the level of acidity in gastric juice is regulated, the main unpleasant symptoms of the disease are relieved. The following drugs are used for this:
- antacids, which increase pH and reduce heartburn;
- antispasmodics, which are intended to relieve pain during exacerbation;
- prokinetic drugs that help restore the motor function of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract, thereby relieving attacks of nausea.
If acidity is reduced with gastroduodenitis, pregnant women are prescribed:
- gastric enzymes, endowed with the ability to compensate for the lack of their own enzymes, the production of which is reduced due to the low productivity of the secretory glands located in the mucous epithelium in the stomach;
- pancreatic enzymes used to normalize digestion;
- probiotics with antagonistic properties to restore proper microflora in the gastrointestinal tract;
- combination drugs, characterized by an integrated approach to stabilizing digestion.
During the period of exacerbation, bed rest is mandatory.
Gastroduodenitis in children
Gastroduodenitis in children is the most common pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. This is a nonspecific inflammatory process of the stomach (distal section) and duodenum.
As a result, a structural restructuring of the mucous membrane, motor-evacuation and secretory disorders occur. Adolescents, as well as school and preschool children, are most susceptible to the development of gastroduodenitis.
Causes
One of the main exogenous factors that contributes to the development of gastroduodenitis in childhood is nutritional: regular violation of the diet and quality of nutrition, consumption of food that irritates the gastric mucosa (spicy and fatty foods, chips, crackers, nuts), monotonous diet, poor chewing of food , dry snacks, uneven intervals between meals and others. Often the cause of gastroduodenitis can be long-term use of certain medications (antibiotics, glucocorticoids, NSAIDs, etc.).
There can be a lot of endogenous development factors. An important role is played by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which persists in the gastric mucosa (60-70% of cases). Often, in parallel with helicobacteriosis, other pathogens can be found in children - herpes viruses (including the Epstein-Bar virus), enteroviruses. Duodenitis in most cases is associated with gastritis, which is caused by Helicobacter pylori.
Gastroduodenitis occurs in children who have a hereditary predisposition to this pathology and low compensatory and adaptive capabilities due to previous somatic and infectious diseases. Are at risk of developing gastroduodenitis
Source
Herbal treatment
Due to some prohibitions on medications prescribed to relieve inflammation in gastroduodenitis, the effect of the therapy used may be insufficient. Therefore, pregnant women are recommended to use traditional medicine methods that can relieve the patient from heartburn, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain.
Especially popular are home remedies based on medicinal flowers, roots and herbs, which contain a large number of useful microelements. But you should remember about the possibility of allergic reactions on the part of the sensitive body of a pregnant woman. Therefore, medicinal components and recipes should be selected in consultation with a gynecologist and a doctor treating gastrointestinal inflammation.
The first glass of mint tea should be drunk in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Mint tea. 1 tablespoon of mint per liter of boiling water is steamed in a thermos. The drink is infused for 10-12 hours. Ready-made tea should be drunk 4 times every 24 hours. Dosage: 200 ml before meals. The first glass should be drunk in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Healing infusion of celandine. It is prepared from 300 g of the plant in a liter of alcohol. The product should be infused in a dark place for 14 days. Treatment regimen: first dose - 5 drops of the drug;
- second - 6 drops;
- the following days it is added drop by drop;
- the dose is increased to 50 drops per day; Next, count down in reverse order, up to 5 drops.
Return to contents
Gastroduodenitis: symptoms and treatment
Like the names of all diseases, gastroduodenitis comes from the Latin words: stomach - gastro and duodenum - duodenum, and the ending -itis means inflammation of these organs. If we consider this disease in general terms, it is similar in many symptoms to gastritis, but the inflammatory process also spreads to the duodenum.
Causes of gastroduodenitis
2. Exogenous. They are based on various external factors, which under certain conditions can cause gastroduodenitis. Let us list the main exogenous causes of this disease:
Classification
A noticeable difference between these forms of gastroduodenitis is the pain syndrome. In the first case, intermittent and short-term pain is noted, and in the chronic course, the pain is less pronounced, but is almost constant.
1. Superficial. With this type, there is thickening of the folds of the mucous membranes of the stomach and duodenum, as well as swelling of the mucosa.
2. Hypertrophic. In addition to swelling, hyperemia and small hemorrhagic hemorrhages occur. The mucous membrane is covered with a fibrinous-mucosal coating.
3. Erosive. Swelling, hemorrhagic hemorrhages, and erosions on the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum are observed.
4. Mixed form. Small areas of atrophy may be observed, but the mucosa externally resembles the hypertrophic form.
Symptoms of gastroduodenitis
General symptoms may also be observed - irritability, increased fatigue, pale skin, dizziness, weight loss, sleep disturbances. During examination, the doctor may note tenderness of the abdomen upon palpation, a yellowish-white coating on the tongue with possible teeth marks. The tongue itself looks swollen.
If we talk about pain syndrome with gastroduodenitis
Source
Other treatments
Complex therapy of gastroduodenitis in pregnant women, as in other patients, includes:
- a strict diet developed individually;
- adherence to a meal plan at a specific time;
- drug treatment program;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- use of folk recipes according to a selected scheme.
In addition to herbal infusions, in the initial stages of the inflammatory process, pregnant women are recommended to use the following formulations:
- 500 g of viburnum berries in 3 liters of water, kept on fire until boiling. After which the product is infused for a day. The next day, crushed birch mushroom is added to the tincture. Two glasses are enough. The finished mixture is kept in the refrigerator for an additional 2 days. After filtering, 100 ml of aloe juice and 300 g of honey are added to the composition. The product should be drunk 200 g 3 times a day before meals.
- For chronic inflammation, medicinal tea is prescribed. To prepare it, rose petals, motherwort, chamomile flowers, sage, yarrow, thyme, taken in equal quantities, are used. The mixture is poured with 1.5 liters of boiling water. You should drink tea throughout the day.
- Blackcurrant juice, diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 1. You need to drink the juice a day in three small sips.
Gastroduodenitis: symptoms, treatment, diet
Gastroduodenitis is an inflammatory disease caused by a restructuring of the mucous membrane of the duodenum and the pyloric zone of the stomach, as well as disturbances in secretory and motor-evacuation functions.
Causes
The development of gastroduodenitis can be caused by functional disorders in the body and external agents.
prolonged stress and certain disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system often cause spasm of the vessels of the stomach and duodenum, which creates favorable conditions for the development of inflammation;
Infectious pathogens in the form of Helicobacter pylori are able to multiply in an acidic gastric environment, which leads to the development of an inflammatory process.
Systematic overeating. To prevent the occurrence of this condition, you need to eat slowly, since a feeling of complete satiety occurs 40 minutes after eating.
A violation of the diet, as a result of which the functional load on the stomach increases, which activates the effect of gastric juice on the mucous membrane.
Eating foods that cause increased production of gastric juice, which provokes inflammation (fatty, fried and spicy foods, smoked foods, spices, etc.)
Varieties
The course of gastroduodenitis can be acute or chronic. Acute gastroduodenitis lasts about three months, and chronic gastroduodenitis lasts at least six months.
Morphological changes in the mucous membrane of the duodenum and stomach make it possible to classify several types of chronic forms of the disease:
atrophic gastroduodenitis develops against the background of low acidity in people with a hereditary predisposition;
analysis for Torch infection during pregnancy is a blood test for ToRCH infection - a comprehensive detailed analysis that allows you to assess the immunity of the body and the mother's fetus to toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus and herpes, as well as to identify an acute infection.
Helicobacter gastroduodenitis is typical for people with high gastrointestinal acidity
Source
Diet therapy for pregnant women suffering from gastroduodenitis
The diet is developed taking into account the taste preferences of the pregnant woman and the recommendations of the attending physician. Along with observing the correct layout of dishes, you need to adhere to certain rules and diet:
- Meals should be fractional.
- It is recommended to increase the number of snacks to 7 times a day.
- It is important to provide a complete breakfast and dinner.
- Do not transfer overnight.
- In the first days after the attack has stopped, food should be semi-liquid and warm. A good start to diet therapy would be to consume slimy cereal soups, milk porridges, cottage cheese and milk.
- On the 4th day you are allowed to eat boiled chicken eggs, vegetables raw or as a stew, fruits and fruit purees.
- After a week, you can introduce boiled meat and fish, steamed cutlets, porridge, mashed potatoes, hard cheese and sour cream.
If acidity increases during a relapse of the disease, pregnant women should drink mineral water. “Borjomi”, “Smirnovskaya”, “Slavyanovskaya” are suitable for these purposes. For low acidity, “Essentuki”, “Mirgorodskaya”, “Arzni” are recommended. You need to drink 150 ml per day between three main meals. It is advisable to do this after 2 hours.
Recommendations for proper nutrition of pregnant women during inflammation of the duodenal region:
- ban on products that irritate the mucous membranes;
- food must be boiled or steamed;
- Be sure to consume large quantities of low-fat fermented milk products, cauliflower and berries.
source
Diet will help
With gastroduodenitis, proper nutrition is one of the most basic conditions for a quick recovery. At the time of treatment, to prevent further exacerbations, you should avoid:
- Alcohol;
- Smoking;
- Fatty, fried, spicy foods;
- Spices;
- Mayonnaise, ketchup, mustard;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Smoking;
- Cabbage;
- Plum, cherries;
- Sweets with cream;
- Coffee;
- Chocolate;
- Products containing flavorings, preservatives, taste enhancers.
Diet is the main point of treatment for gastritis during pregnancy. In the first week, it is best to eat only liquid foods - light soups with lean meat, milk porridges, oatmeal is especially effective. Fresh vegetables and fruits must be abandoned. After 7 days, you can add plant foods to your diet, preferably baked or boiled.
Avoid fried foods completely. Fish and lean meat are very good and healthy in this case. You can cook them by steaming or in the oven. You should not overuse spices - spicy and excessively salty foods are completely unacceptable in the diet. Pay attention to fermented milk products: homemade yoghurts, sour cream, kefir, fermented baked milk - all this is ideal for a pregnant woman, especially if she suffers from gastritis.
Caution should be exercised with whole milk - you can cook porridge with it, but it is not recommended to use it in its pure form.
It is very important not only to take what your doctor prescribes.
Home remedies, the main ingredients of which are medicinal plants and herbs, are very popular. Everyone knows that herbs contain many useful microelements that can cope with even the most serious ailments.
However, we should not forget that some plants contain undesirable components that can harm not only the woman, but also the child. That is why medicinal herbs should be used with extreme caution for the disease described above.
You should follow a diet for gastroduodenitis. All food consumed should be warm; cold and hot foods should not be consumed. Chew thoroughly, and it doesn’t matter what it is, carrots or soft cookies. Eat 5-6 times a day in small portions.
- pureed soups from vegetables and cereals, in meat, fish, and mushroom broths;
- lean meat, lean ham
- cutlets - stewed, steamed, fried without crust;
- boiled fish, soaked herring;
- low-fat fermented milk products;
- eggs;
- porridge (semolina, buckwheat, rice);
- flour dishes (stale white bread, gray bread, uneatable crackers;
- fruits, vegetables, boiled, raw, grated;
- vegetable fruit juices;
- tea, cocoa with water and milk.
After finishing the diet, you need to take a course of vitamins, register with your local doctor and undergo gentle treatment during the period of exacerbation - in the fall and spring.
General recommendations for a special diet for gastroduodenitis in children:
- food should not be too hot or too cold;
- Chew your food thoroughly, do not swallow hard pieces;
- eat little and often (five to six times a day).
Recommended dishes:
- soups from cereals and vegetables, pureed;
- boiled lean meat in pieces, boiled chicken;
- steamed, stewed cutlets;
- lean ham;
- boiled lean fish;
- kefir, curdled milk, non-sour sour cream, fresh non-sour cottage cheese, mild grated cheese;
- steam omelette;
- porridge, well boiled or pureed (buckwheat, semolina, rice);
- flour dishes (except baked goods), stale white, gray bread, uneatable crackers;
- vegetables, fruits, boiled, raw, grated;
- fruit and vegetable juices (do not overuse);
- tea, coffee (do not overuse).
This article has been read 218 times.
PREGNANCY AND CHRONIC DUODENITIS
Chronic duodenitis is a chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the duodenum, accompanied by structural restructuring of the glandular apparatus, the development of metaplasia and atrophy.
ICD-10 CODE K29.8 Duodenitis.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
In the population, during endoscopic examination, duodenitis is detected in 19.4% of the adult population, and in relation to all gastrointestinal diseases it is up to 30%. Women get sick 3 times less often than men.
PREVENTION OF EXCERNSATIONS OF DUODENITIS DURING PREGNANCY
Rational regular nutrition, the fight against alcoholism, timely treatment of other diseases against which secondary duodenitis occurs.
CLASSIFICATION
Duodenitis is distinguished between acute and chronic, widespread and limited (mainly to the duodenal bulb - bulbitis).
Chronic duodenitis can be: · superficial; · atrophic; interstitial; · hyperplastic or erosive-ulcerative.
ETIOLOGY (CAUSES) OF DUODENITIS
Irregular diet with frequent consumption of spicy, irritating, too hot food, alcoholism.
Secondary chronic duodenitis is observed in chronic gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, chronic pancreatitis, giardiasis, food allergies, and uremia.
Causes of duodenitis: · poor diet (addiction to spicy, hot and rough foods, excessive alcohol consumption, irregular diet, dry food); · stress; · bacterium Helicobacter pylori; · long-term use of medications (acetylsalicylic acid, some antibiotics); · smoking; · intestinal infections; Chronic infections in the oral cavity and pharynx (caries, inflammation of the tonsils); · diseases of the gallbladder, liver, pancreas.
PATHOGENESIS
The pathogenetic basis of chronic duodenitis is inflammation, accompanied by a structural restructuring of the glandular apparatus with the development of atrophic changes.
In addition to the direct effect of the irritating agent on the mucous membrane of the duodenum, the proteolytic effect of active gastric juice on it (with trophic disorders, dyskinesias) is important in the pathogenesis of chronic duodenitis.
Among patients with dyspeptic syndrome, chronic duodenitis with morphological confirmation of the diagnosis is found in 17–25% of subjects, more often in people under 40 years of age.
PATHOGENESIS OF GESTATION COMPLICATIONS
In the uncomplicated course of chronic duodenitis, the condition of pregnant women is not significantly disturbed and the disease does not have a noticeable effect on the course of pregnancy and its outcome.
CLINICAL PICTURE (SYMPTOMS) OF DUODENITIS IN PREGNANT WOMEN
Characterized by pain in the epigastric region (constant, dull or ulcer-like), a feeling of fullness or distension in the upper abdomen after eating, decreased appetite, nausea, and sometimes vomiting. Patients note hunger and night pain (eating reduces them). In addition, pregnant women during the period of exacerbation of the disease complain of belching air and heartburn. Chronic duodenitis is characterized by a cyclical exacerbation (spring–autumn).
COMPLICATIONS OF GESTATION
More often, exacerbation of chronic duodenitis is noted in the first trimester of pregnancy or 4–5 weeks before childbirth. Women suffering from chronic duodenitis may develop early toxicosis of pregnancy.
Chronic gastritis
Symptoms of chronic gastritis
The most numerous type of gastritis. The clinical picture is varied and includes a large number of symptoms, but the two most important can be identified:
- Pain in the upper abdomen, around the navel or in the right hypochondrium. Aching, less often cramping. Most often it worsens during or immediately after eating.
- Digestive system disorders, such as: heartburn, nausea, vomiting, loose stools.
One of the factors that may indicate an exacerbation of gastritis during pregnancy is severe toxicosis in the early stages of the first trimester. This sign is not a guarantee that chronic gastritis will worsen during pregnancy, but if relatives have this disease, the woman should consult a gastroenterologist.
Course of the disease
At the very beginning of the disease, gastric juice is produced in normal quantities, the patient has no complaints and does not need treatment. However, with the further development of gastritis, the secretory function of the stomach is disrupted. At this stage, symptoms appear, which is a reason to consult a doctor.
Most often, the digestive organs located next to the stomach are involved in the pathological process - the duodenum, liver, gallbladder, pancreas. The disease is characterized by periodic exacerbations and periods of remission. Exacerbation of gastritis during pregnancy occurs especially often, due to the hormonal characteristics of the body.
Lack of treatment for gastritis in pregnant women leads to a deterioration in the emotional state and stress, which negatively affects the health of the unborn child. Damage to the gastrointestinal tract reduces the amount of nutrients that the child receives from the mother, which is extremely dangerous for his health, especially in the early stages of embryonic development.
Diagnostic procedures
In most cases, an examination by a specialist is sufficient to confirm the diagnosis. Sometimes doctors may order additional examinations, such as ultrasound, examination of gastric juice and endoscopic examination.
An ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs establishes the condition of the liver, gallbladder and pancreas and shows whether they are involved in the pathological process, which happens quite often during pregnancy. Collection of gastric juice and its further analysis are necessary to measure the secretory activity of the stomach and prescribe the correct treatment.
Endoscopy allows you to assess the degree of damage to the mucous membrane and ensure the absence of damage and gastric ulcers. However, this examination process causes significant discomfort to patients, so it is prescribed to pregnant women only in extreme cases, for example, when the prescribed treatment is low in effectiveness.
All these procedures are additional. Most often, when making a diagnosis, the doctor limits himself to studying the patient’s complaints and medical history. Gastritis during pregnancy requires certain treatment protocols. In the future, the patient is prescribed periodic tests for blood in the stool, tests for the content of hemoglobin and formed elements in the blood.
What will the doctor prescribe?
Treatment of gastritis during pregnancy has its own characteristics, since not all medications can be used without risk to the child’s health. Only a specialist can prescribe medications and set a diet for gastritis. In this case, the doctor analyzes the general condition of the patient, the period of pregnancy, as well as possible factors that caused the disease.
The following drugs are most often used in modern medical practice:
- Antacids: the most famous brand in Russia is Phosphalugel. You can also take analogues recommended by your doctor. Antacids are used to protect the gastric mucosa and relieve pain.
It is important to know: only a doctor can prescribe medications. Pharmacists and other pharmacy chain employees do not have sufficient knowledge to give you advice on which drug to take for gastritis. The pharmacist does not have an anamnesis or the ability to adequately assess the patient’s condition.
- Enzymes: for example, Mezim - enzyme-based preparations to improve digestive function.
- Prebiotics and probiotics: in most cases, these are dietary supplements or dietary supplements. The following drugs are safe for pregnant women: Gastrofarm, Linex, Hilak Forte and Laktovit. All of them have a beneficial effect on the intestinal microflora.
- Patients with gastritis with reduced secretory function are also prescribed medicinal herbs that suppress inflammation of the gastric mucosa and stimulate its secretory function: these are herbal medicines that are sold in pharmacies without a prescription. Examples include mint, St. John's wort or wormwood. You should consult a gynecologist or gastroenterologist about which drugs from this series are useful in a particular case.
Antibiotics, especially tetracyclines, are not used during pregnancy, since they have an extremely negative effect on the development of the fetus, but only the attending physician decides how to treat the patient in this particular case.
Important! Note to the expectant mother: it is best for the pregnancy to be managed by one doctor - from the first to the third trimester. The doctor will know the medical history, monitor the course of pregnancy and gastritis will most likely be identified and treated on time.
Diet is the main treatment for gastritis during pregnancy. During an exacerbation of the disease, it is recommended to eat small amounts, often and in fractions.
During the first week, a classic diet for gastritis is followed - eating only liquid or pureed food:
- pea, potato and milk soups;
- soups from ground products;
- oatmeal, which is based on water or highly diluted milk;
- It is permissible to eat meat that does not contain fat and is steamed or boiled without salt or spices.
Important! The following are strictly excluded:
- lemonades, including Coca-Cola, Pepsi and similar sodas;
- cakes, pastries, muffins and other sweet products;
- meat broths;
- vegetable and fruit salads, and fresh vegetables and fruits.
After a period of exacerbation, you can use:
- soups with milk, viscous jelly;
- steamed omelettes and eggs “in a bag”;
- steamed food from meat and porridge;
- White bread crackers can be included in the diet in limited quantities;
- biscuits;
- You can eat fruits and vegetables by cooking them in the oven or boiling them.
Then you can gradually return to a normal diet, but it is worth remembering that the disease can worsen again at any time. Therefore, you should exclude from your diet foods that strongly irritate the gastric mucosa. If you have any doubts about the diet, you should consult your doctor. He is the one who will tell you what you can eat and what you should avoid.
Treatment of gastroduodenitis during pregnancy
Gastroduodenitis during pregnancy disrupts the digestion process and causes severe discomfort to the expectant mother. Poor health can negatively affect the development of the fetus. Epigastric pain during pregnancy requires medical supervision. How to treat gastroduodenitis during pregnancy? What complications can arise from this disease? Let's look at the answers to the most popular questions later in the article.
Gastritis during pregnancy: from conception to childbirth
This disease (both acute and chronic) can develop during pregnancy at any time: in the first, second and third trimester. If in the initial stages gastritis during pregnancy is easy to identify on your own, then aggravated gastritis in the third trimester is quite difficult to diagnose. In the initial stages of pregnancy, women often confuse gastritis during pregnancy with ordinary toxicosis.
Important! Note to expectant mothers: in order to get rid of toxicosis, avoid sharp, unpleasant odors; try to follow the regime and diet. If toxicosis does not go away, be sure to contact the antenatal clinic, tell your doctor about the problems, who will explain to you what to do.
Gastritis during late pregnancy can easily be confused with mechanical problems of the body, when a large, already developed fetus puts pressure on a complex of body systems. The stomach, pancreas and liver may suffer from this, which is similar in symptoms to those symptoms when gastritis has worsened.
Women of any age should remember that pregnancy is not a disease. However, bearing a child is usually accompanied by hormonal and physical changes and the mother’s body is susceptible to various diseases, including gastritis of various types. In this regard, in case of any manifestations of symptoms of the disease, it is important to consult your doctor in a timely manner.
What is gastroduodenitis and why is it dangerous for pregnant women?
Gastroduodenitis is an inflammatory process that affects the gastric mucosa.
As a rule, the disease is localized in the transport department of the digestive organ. Pathology occurs against the background of hypersecretion of hydrochloric acid.
Gastroduodenitis during pregnancy has an extremely negative effect on a woman’s condition. Many expectant mothers complain of pain and disorders of the digestive tract.
In turn, this can provoke such violations as:
- decreased blood pressure levels;
- increased fatigue and severe weakness;
- dizziness and loss of consciousness;
- nausea, vomiting, dyspeptic disorders;
- psycho-emotional disorders, anxiety and irritability.
The disease occurs in 50% of pregnant women.
Modern medical practice offers effective methods for treating and preventing gastroduodenitis during pregnancy.
What can cause exacerbation of gastritis?
Many reasons can provoke a recurrence of gastritis in a pregnant woman. But the following are especially common:
- unstable psycho-emotional state;
- disruption of the usual daily routine;
- working at night;
- frequent lack of sleep;
- power supply errors;
- infections;
- allergic reaction to food;
- chronic diseases of internal organs (pancreas, gall bladder and liver);
- metabolic disorders;
- taking medications;
- smoking;
- drinking large amounts of alcohol.
Causes and symptoms
The following factors can provoke gastroduodenitis during pregnancy:
- excessive secretion of gastric juice, which provokes an increase in the acidity of the environment;
- changes in hormone balance;
- improper functioning of the endocrine system organs;
- incorrect temperature of food consumed;
- dysbacteriosis, excessive proliferation of E. coli;
- hereditary predisposition;
- taking certain medications;
- state of chronic stress.
There are many reasons that provoke pathology.
As a rule, the disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- spasmodic pain in the abdominal cavity;
- nausea, which is often accompanied by vomiting;
- feeling of heartburn;
- frequent belching;
- stool disorders;
- appetite disorders.
When diagnosing manifestations, you must consult a doctor for examination.
Acute gastritis
Unlike chronic gastritis, it develops rapidly - in a few hours or days. Symptoms appear for no reason, most often as a result of poor diet, taking anti-inflammatory drugs, and frequent stress.
Symptoms and treatment
Acute gastritis is usually divided into the following types:
- catarrhal - superficial irritation of the gastric mucosa. Most often, inflammation develops within a few hours and goes away without treatment. Clinical manifestations typical of catarrhal gastritis are increased body temperature, weakness, loose stools.
- erosive - occurs with the appearance of small ulcers on the mucous membrane. In this case, acute pain appears in the upper abdomen, as well as around the navel. Possible vomiting with blood.
- hemorrhagic - accompanied by loose stools, profusely black in color, which indicates bleeding in the stomach.
- phlegmonous - a rather rare form of gastritis associated with purulent damage to the walls of the stomach. May develop in people with weakened immune systems. This variety is very dangerous, as inaction can lead to human death. Symptoms are typical for gastritis, but the increase in body temperature occurs to higher numbers.
If you have any of these signs, you should immediately consult a doctor.
When treating acute gastritis, all attention is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease and preventing negative consequences. Fasting is indicated on the first day, and subsequently a gentle diet is prescribed. Diagnosis and treatment of aggravated gastritis can only be carried out in a medical institution, under the supervision of a specialist.
Diagnostics
After the first consultation with a doctor, the pregnant woman receives directions for a comprehensive examination.
It includes the following procedures and tests:
- endoscopic examination of the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- histological examination;
- analysis of the chemical composition of gastric juice;
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis.
For pregnant women, analysis of stomach juice is prescribed only if absolutely necessary. This is due to the fact that the procedure requires complex preparation and a long period of fasting.
Based on the data obtained, the gastroenterologist will be able to establish an accurate diagnosis and select treatment.
Symptoms
In case of chronic gastroduodenitis during the period of remission, the symptoms are smoothed out and do not cause pain, but abdominal discomfort, weak condition, and irritation of the nervous system are constantly present. During the period of exacerbation, the manifestations of gastroduodenitis are clearly felt. The situation is a little more complicated with young children who cannot yet explain their condition and well-being; parents have to guess by the baby’s behavior.
Symptoms in adults
How bad a person will feel depends on the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the body. With gastroduodenitis at the initial stage, inflammation covers only the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum; in the absence of qualified therapy, organ tissues are involved in the pathological process. In the second case, the symptoms will be more severe.
Typical symptoms for gastroduodenitis are as follows:
- General malaise;
- Decreased ability to work, mental activity;
- Headache;
- Dizziness;
- Weakness;
- Increased fatigue;
- Stomach ache;
- Increased acidity with heartburn, belching;
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth, odor;
- Hiccups, belching sour, bitter;
- Nausea, rarely with vomiting;
- Coated tongue;
- Pain, discomfort in the abdomen;
- Increased gas formation;
- Bloating, rumbling;
- Constipation or diarrhea;
- Loss of appetite;
- Heaviness in the stomach;
- Weakening libido;
- Painful sensations during sex in women, weak erections in men.
In the first days of an exacerbation, a person cannot accurately determine what is hurting him or what medications to take. When the discomfort is accompanied by painful sensations in the abdomen and stomach, it becomes clear that there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms in children
Symptoms of gastroduodenitis can be completely different: pain in the epigastric region, nausea, a feeling of fullness in the stomach, lethargy, unpleasant taste in the mouth, weakness, frequent headaches, sleep disturbances, heartburn. Symptoms of vitamin deficiencies.
The tongue becomes covered with a yellow coating, and teeth marks appear on the sides. In the acute form of gastroduodenitis, the symptoms will be pronounced and short-term, but in the chronic form they will be aching and constant.
The stool is disrupted, diarrhea and constipation alternate.
Diagnosis of gastroduodenitis
Only a gastroenterologist can diagnose gastroduodenitis and make an accurate diagnosis after conducting research and examination: x-ray, ultrasound, esophagogastroduodenoscopy, with taking a biopsy from the gastric mucosa. Gastric secretion tests and pH measurements of the duodenum and stomach are also performed. This will allow you to identify the form of gastroduodenitis, with low or high acidity, and select the correct treatment.
Chronic gastroduodenitis develops gradually over a long period of time, characterized by periods of exacerbation and progression. The development of the chronic form is influenced by heredity, infection, poor nutrition, and consumption of junk food.
Treatment
Drug therapy
Treatment of gastroduodenitis during pregnancy often requires taking special medications.
Antibiotics should not be used during this period. They can disrupt the intrauterine development of the child and provoke defects.
Expectant mothers are prescribed medications that reduce the concentration of hydrochloric acid and reduce pain.
- antacids;
- antispasmodics;
- prokinetic drugs;
- enzymatic agents;
- probiotics;
- complex means.
Antacids - reduce the acidity of gastric juice by neutralizing excess hydrochloric acid.
Antispasmodics reduce pain.
Prokinetic drugs activate proper peristalsis of the digestive tract.
Enzymatic preparations and probiotics speed up the process of breakdown and digestion of food.
Treatment with traditional medicine
In addition to the use of synthetic drugs, therapy for gastroduodenitis during pregnancy involves the use of folk recipes.
The most popular are the following:
- mint infusion;
- tincture of celandine;
- infusion of plantain, nettle, chamomile and St. John's wort;
- decoction of calamus rhizome and orange peel;
- viburnum decoction with the addition of crushed chaga.
Traditional medicine recipes, like medications, should be taken with caution. This is especially true during the perinatal period.
Many plants can cause allergic reactions and uterine contractions. Therefore, before using any decoctions and infusions, you should consult a doctor.
Nutrition rules
The main treatment for gastroduodenitis during pregnancy is to follow dietary and therapeutic nutrition recommendations.
The diet involves following the following rules:
- it is important to follow the principles of fractional nutrition - eat often in small portions;
- There must be snacks between main meals;
- in the morning there should be a full breakfast;
- you can’t refuse dinner;
- the preferred consistency of dishes is liquid or viscous;
- cooking methods - boiling, steaming, stewing, baking;
- You can’t eat spicy and salty foods;
- Fried foods are prohibited.
Between meals with gastroduodenitis you need to drink mineral water. Your doctor will help you choose the ionic composition.
It is recommended to exclude from the diet foods that stimulate an increase in the acidity of gastric juice.
How to get rid of heartburn during pregnancy
During pregnancy, this unpleasant sensation occurs often. The most common way to get rid of heartburn is baking soda. However, doctors do not recommend it, because it “puts out” acidity for a short time and does not have a healing effect. Usually after drinking soda, heartburn recurs.
A more harmless way is seeds. Although you shouldn’t get carried away with them either.
And yet, antacids, such as Rennie or Maalox, are considered indispensable. They act quickly and effectively, enveloping the gastric mucosa, reducing acidity and relieving heartburn in a couple of minutes. However, drugs do not allow beneficial substances to be absorbed into the blood; it is also better not to get carried away with them. And in general, use only as prescribed by a doctor.
If you strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations, listen to your own body and monitor your health, then your pregnancy will go well. Discomfort with gastritis during pregnancy can be significantly reduced with a special diet, and after the birth of the child, you can begin full-fledged therapy using medications.
Preventive measures
The main preventive measures for gastroduodenitis during pregnancy are to follow the rules of a healthy diet and lifestyle:
- nutrition should be balanced and include the correct ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates;
- it is important to maintain adequate physical activity, regularly walk in the fresh air, and do exercises;
- It is recommended to maintain a drinking regime;
- reduce consumption of fatty, spicy and smoked foods;
- among cooking methods, give preference to boiling, stewing, baking and steaming;
- reduce the amount of salt consumed;
- enrich your diet with natural fiber, including fresh vegetables and fruits.
The combination of gastroduodenitis and pregnancy is a common occurrence in medical practice.
If alarming symptoms appear, you should consult a specialist for advice.
After passing a comprehensive examination, it will be possible to select treatment that is permitted during the period of bearing a child.
Treatment methods
First of all, pay special attention to your daily diet and follow your doctor’s recommendations.
In medical practice, there are several methodologies, which will be presented below in the form of small paragraphs.
Physiotherapy
A safe method is magnetic therapy. Acupuncture and electrophoresis cannot be classified as methods that will not harm the baby.
It is not recommended to use for late toxicosis. If accompanied by vomiting and renal pathologies occurring in the chronic stage are observed.
Medications
Not all medications are approved for women in an “interesting situation.”
So, what can pregnant women with gastritis do to moderate its manifestation:
- "Raglan";
- "Dimethicone";
- "Cerucal";
- "Narine";
- "Bifidum".
Avoid advertised drugs: Gastal, Maalox and the like, as they contain aluminum.
Diet food
The following products are allowed: milk, eggs, vegetables, meatballs, puree soup.
Steam meat cutlets and vegetable stew.
Meat of chicken, turkey and other poultry, only in boiled form.
The diet contains a complete absence of pickles, smoked foods and other harmful dishes.
Doctors also recommend drinking medicinal mineral water.