When does the second trimester begin?
The second trimester of pregnancy includes 4-6 months, starting from the 14th to 26th obstetric week. This period is characterized by maximum calm and security. According to statistics, the 2nd trimester of pregnancy is the time when miscarriages are least likely to occur. But an ectopic pregnancy can continue to develop.
It is worth noting that the expectant mother’s well-being is improving: she is less and less bothered by nausea and dizziness, her tummy has become rounder and more noticeable, but it still does not cause trouble. During this period, doctors advise spending more time outdoors, visiting yoga and the pool. You may need to think about a bandage that you can wear as early as the 20th week of pregnancy. The bandage is an excellent prevention of stretch marks and miscarriage.
Fetal development
Starting from 4-5 months, the fetus changes greatly in appearance. This can be noticed if you do not miss an ultrasound during the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. At 4 months the baby weighs only 20 grams, and by the sixth month it already weighs up to a kilogram. Now he does not look like a fetus, he is an almost formed child. Every month of the second trimester it changes more and more.
Starting from 13-16 weeks of pregnancy, the baby begins to intensively build up bone tissue. His skeleton becomes strong and durable. In most places, connective tissue turns into bone. The internal organs of the abdominal cavity continue to form. This is even noticeable to the doctor during an ultrasound examination. The kidneys take the right position in the body and begin to work. Now the baby is able to excrete urine after swallowing amniotic fluid. The organs of the gastrointestinal tract begin to function, and the adrenal glands are already capable of producing hormones. The cerebral cortex continues to develop.
At 5 months, the expectant mother begins to notice fetal movements. If this is the first pregnancy, then this usually occurs at 19-20 weeks, if the second or more, then at 16-18. The baby’s endocrine system begins to work harder, this contributes to the proper development of his hormonal levels. The baby's skin is coated with a special lubricant that will help him pass through the birth canal more easily. The baby's spleen begins to produce blood cells.
At 6 months of pregnancy, the fetus continues its intensive development. He is gaining strength and sleeping a lot. While awake, the baby actively pushes, which can cause concern for the mother. He sleeps from 16 to 20 hours a day. His lung tissue is still underdeveloped, but the baby is already trying to make breathing movements, so he is preparing for his birth.
The brain increases in size, its weight can already reach 100 grams. The cortex is actively developing, right now the child is developing his mental abilities, creative inclinations, etc. Scientists believe that if a mother is often in a bad mood at 6 months, this can lead to undesirable consequences. For example, in the future the baby will have a tendency towards depression and even suicide.
Development, weight and height of the fetus in the second trimester
Every week the height and weight of the fetus increases, and the baby learns new skills and new functions are formed. At this time, the urinary system starts working. The baby inhales and exhales for the first time, the lungs begin to produce surfactant (a liquid that lubricates the lungs from the inside). There is a gradual preparation of the gastrointestinal tract for the intake of food from the outside - the baby swallows the amniotic fluid, assimilating everything necessary from it. These waters are processed and stored in the intestines in the form of meconium (original feces) until childbirth.
The formation of brown subcutaneous fat begins, which is designed to retain heat. Vernix lubrication begins to accumulate on the surface of the skin, which protects the skin from damage due to constant contact with the amniotic fluid.
The size of the fetus is now more difficult to determine. Body parameters such as height and weight are associated with similar characteristics of the parents (features of body constitution), the course of pregnancy, and hereditary prerequisites. The approximate weight of the fetus at the end of the second trimester varies between 700-900 grams, height from crown to toe - 330-350 mm.
Mother's condition
As a rule, until 3 weeks of pregnancy (the first week of missed menstruation), a woman has no idea about her situation. Her condition is comparable to the sensations before the onset of the expected menstruation. However, menstruation does not come, and unusual new symptoms keep appearing and growing:
- Food cravings;
- Aversion to certain aromas and smells;
- Breast engorgement;
- Drowsiness and mood lability.
Toxicosis can cause the greatest discomfort in the first trimester of pregnancy
. Nausea and vomiting in the morning are not very pleasant.
Information Sometimes these manifestations of toxicosis can occur more than 3-4 times a day. Then the woman is recommended to be under medical supervision to monitor the condition until recovery. Physiologically, toxicosis recedes by 12-13 weeks, when the placentation process ends.
Starting from the very beginning of the 1st trimester of pregnancy, the first changes occur in the uterus, preparing this organ for bearing a fetus. During the process of its growth, due to the thickening and lengthening of the uterine ligaments, a woman may feel a slight stretching on the sides of the lower abdomen. By the end of the first trimester, the uterus protrudes above the symphysis pubis. In some expectant mothers, if you look closely, you can see a rounded tummy.
Second trimester of pregnancy: pregnant woman’s well-being
It is believed that the 2nd trimester of pregnancy is characterized by a more stable emotional state than the first. The hormonal changes of the first months are over, and now the hormone levels have come to some balance, as well as the emotions of the woman expecting a baby. The surrounding circumstances no longer cause an immediate response, you are less nervous about trifles. Perhaps, like most other women, you began to feel happier by the fourth month. There is an explanation for this - the risk of miscarriage has decreased, and along with it the fear of losing the baby has disappeared. In addition, nausea and constant fatigue, frequent companions of toxicosis in the first trimester, no longer accompany you. What a relief! Often, expectant mothers even experience unexpected bursts of strength, energy, and joy. Especially because the baby began to be active and move inside your body.
The 2nd trimester of pregnancy is characterized by various changes in the pregnant woman’s body. For example, many women indicate changes in their skin - pigmentation increases, the skin becomes oilier, and sweats more often. These processes are associated with pregnancy hormones. In addition, the skin begins to tighten due to an increase in body volume. The subcutaneous glands are activated, causing the woman to sweat more often and produce more sebum and melanin. This causes the appearance of a dark line from the navel to the center of the pubic bone. Darker-skinned women note that during pregnancy it was clearly visible, but disappeared some time after childbirth.
In the second trimester of pregnancy, the belly is not yet too large to interfere with everyday activities, but is already quite noticeable. It's likely that your clothes no longer fit well on your figure, so it's time to go to a specialized store for pregnant women and buy some beautiful and comfortable new clothes.
At this time, it is worth establishing a daily routine in order to experience a minimum of inconvenience. First, take enough time to rest. Try to get yourself at least nine hours of sleep per night.
Let it not come as a surprise to you that your usual sleeping position has become uncomfortable. If before you could sleep in any position, then in the second trimester you will have to master the habit of sleeping on your side. It is better to lie on your left side, because... in this position, the uterus will not compress the inferior vena cava. It is one of the most important blood vessels that provides blood supply to the lower part of the body. This vein is located to the right of the spinal column. Accordingly, sleeping on the left side will not threaten to compress it and limit the blood supply to the fetus.
What is happening at this time in the body of the expectant mother, how is the baby developing and how to behave so that the pregnancy proceeds without problems?
The 2nd trimester is the period from 13 to 28 weeks of pregnancy. The period of 13 weeks is considered the boundary between trimesters because by this time the complex processes of formation of the main organs and systems of the fetus are completed, which takes on the appearance of a small person and begins to grow and develop rapidly.
The second trimester of pregnancy ends at 28 weeks, since at this time the fetus reaches such a stage of development that, with appropriate care, it is capable of life outside the womb. The average weight of a baby born at 28 weeks is 1000 g, height – 35 cm. Let us recall that the gestational age is calculated in obstetric months, each of which includes exactly 4 weeks, so pregnancy lasts 10 obstetric months, or 40 weeks, which corresponds to 9 calendar months.
This period is a fairly calm time for a pregnant woman, because such early troubles as toxicosis, sudden mood swings, etc. have already passed, and childbirth is still far away. It is in the 2nd trimester that the expectant mother has the opportunity to fully enjoy her “interesting position.”
How the fetus develops
4 months pregnant.
By the 13th week of pregnancy, the fetus is actively developing muscles and ligaments, as well as 20 baby teeth. The baby is actively moving in the uterus, but so far, at 13 to 16 weeks, the expectant mother does not feel this “internal movement.”
The first hairs begin to grow on the head of the fetus, and its entire body is covered with vellus hairs called lanugo. Usually, by the time of full-term pregnancy, lanugo disappears completely or remains in small quantities on the shoulders and ears. The skin of the fetus during this period is still very thin, blood vessels are visible through it, which gives it a bright red color, and subcutaneous fat is practically absent, so the baby’s skin is wrinkled.
During this period, the fetus is already able to empty the bladder: approximately every 45 minutes it urinates into the amniotic fluid, making its “contribution” to its formation.
By the end of the 16th week of pregnancy, the fetus reaches a height of 15–16 cm, a weight of 135 g and, floating freely in the amniotic fluid, can easily change position in the uterus.
5th month of pregnancy.
By 17–20 weeks, the uterus reaches such a size that pregnancy becomes obvious to others, because at 20 weeks the fundus of the uterus is already 2 cm above the navel.
At 5 months, the fetus has already formed the rudiments of permanent teeth, which are located above the milk teeth. The baby develops eyelashes and eyebrows, which are still colorless, since melanin, the pigment that gives them color, will begin to be synthesized later. The fingers and toes are fully formed, and an individual pattern appears on them - fingerprints. The sebaceous glands of the skin begin to work, and a whitish lubricant is formed from vellus hair and epithelial cells of the skin, which obstetricians call cheese-like for its characteristic appearance. At this stage, it covers the entire body of the fetus and performs a protective function, since the baby is in the aquatic environment for quite a long time before birth.
The muscles of the fetus' body reach such a degree of development that its movements become orderly and controlled: it can suck a finger, touch its body and face. The child is already showing movements of the facial muscles - he frowns, opens and closes his mouth, opens his eyes, but does not see yet.
In the fifth month of pregnancy, the baby’s intestines are already sufficiently formed; they contain villi through which nutrients are absorbed. The pancreas secretes insulin, a hormone that helps process and absorb glucose. When amniotic fluid is swallowed, which occurs normally, the process of formation of original feces - meconium - occurs in the child’s intestines; it goes away after birth. By the end of the 20th week of pregnancy, the fetal growth is 20–21 cm, and the weight is 300–350 g. The baby has already grown so much that the doctor can listen to its heartbeat through the anterior abdominal wall with an obstetric stethoscope. If the expectant mother has a pronounced subcutaneous fat layer, then the baby’s heartbeat can be heard from a later date – from 22–24 weeks. The normal heart rate of the fetus is 120–160 beats per minute, that is, one beat of the mother’s heart corresponds to two beats of the baby’s heart.
6 months pregnant.
At 21–24 weeks, the rapid growth and development of the fetus continues, movements become more and more active. He develops his own regime of alternating periods of rest and activity, which does not always coincide with the mother’s regime. The intensity of fetal movements is an excellent marker that allows a woman to monitor the intrauterine state of the baby, since changes in the nature of movements (excessively violent or, on the contrary, sluggish and infrequent movements) may indicate any problems during pregnancy.
By the end of 6 months, the baby’s growth slows down somewhat, but active weight gain begins. Brown fat, which has a high energy capacity, actively accumulates under the skin of the fetus, since its combustion produces a large amount of thermal energy, which plays an important role in maintaining a constant body temperature after the birth of the child.
During the second trimester of pregnancy, the fetal brain intensively develops, nerve cells - neurons - improve, and the degree of development of the central nervous system is such that the baby hears sounds coming from outside. Too loud and sharp sounds can frighten the baby, and soft, gentle music sometimes has a calming effect on him.
The fetus's way of understanding the world is through touch: it touches the umbilical cord, its arms and legs, and the walls of the uterus. While in the womb, the child may hiccup: at this time, the woman feels small internal tremors that occur at regular intervals. Baby hiccups are not a sign of pathology and are observed during the normal course of pregnancy.
At the 6th month, the child’s bone marrow is already functioning: it produces erythrocytes - red blood cells containing fetal hemoglobin, which is able to saturate the cells with oxygen to a greater extent in comparison with ordinary hemoglobin, which is produced in the human body after birth. This adaptive mechanism creates reliable protection against hypoxia - insufficient oxygen supply under the influence of various unfavorable environmental factors and pregnancy complications. Before the bone marrow began to work, the synthesis of blood cells was carried out in the liver and spleen. The bone marrow also produces white blood cells—leukocytes—responsible for fighting infection.
By the 24th week of pregnancy, the internal organs of the fetus are sufficiently formed, but the lungs remain significantly immature, in which the synthesis of surfactant has already begun - a substance that does not allow them to collapse on exhalation. However, its quantity is not yet sufficient for the full functioning of the lungs in the event of a premature birth of a child, so in this case he will not be able to breathe on his own - he will need artificial ventilation, intensive care and the administration of a medicine containing a synthesized surfactant. At this stage, the baby’s breathing occurs through the placenta, in which gas exchange occurs between the body of the mother and the fetus.
While in the womb, the baby begins to make the first breathing movements; this does not mean that he is breathing - such movements are necessary for complete blood supply to the chest organs and the development of the respiratory muscles.
At the end of the second trimester of pregnancy, the fetus reaches an average weight of 900 g and a height of 34 cm.
Feelings of a pregnant woman
From the beginning of the 2nd trimester, the expectant mother’s well-being improves significantly. The troubles of early toxicosis recede: as a rule, by 14–16 weeks of pregnancy, nausea, vomiting, and the general weakness associated with them are a thing of the past, as the processes of rapid hormonal changes characteristic of the beginning of pregnancy are stabilized and the placenta begins to function.
In the 2nd trimester, the expectant mother’s body experiences an intensive increase in circulating blood volume (CBV): by the end of pregnancy, there is 1500 ml more blood in the body than at the beginning. This is necessary for the full functioning of the so-called “third circle of blood circulation” - the uteroplacental one, which forms during the progression of pregnancy.
The increase in circulating blood volume is an important adaptive mechanism. Firstly, it provides intensive blood supply to the placenta and the developing fetus, and secondly, it prepares the pregnant woman’s body for the upcoming blood loss during childbirth, which is inevitable after the placenta is separated.
It has been established that the greatest increase in blood volume is observed precisely in the second trimester, therefore during this period the load on the cardiovascular system increases, which needs to “pump” a larger volume of blood. The pulse rate increases (the norm for pregnant women is 80–90 beats per minute), slightly, by about 10–15 mmHg. Art., blood pressure rises.
After 20 weeks of pregnancy, the fundus of the uterus begins to rise higher and higher, and therefore the tummy begins to protrude forward and round, stretching the skin of the anterior abdominal wall. Due to the individual structure of the skin, it does not always have time to adapt to the rapid stretching of the growing uterus, which leads to the formation of stretch marks - stretch marks. During pregnancy, they are red or even purple in color due to translucent blood vessels, but over time they fade and become less noticeable.
Undoubtedly, the most memorable and exciting moment of the second trimester is the appearance of fetal movements felt by the expectant mother: pregnant women clearly feel how a new life is growing and developing inside. Many mothers look forward to this unforgettable moment, listening to their feelings for a long time. Women describe the first movements of the fetus as “the swimming of a fish”, “the fluttering of a butterfly”. Sometimes expectant mothers experience sensations similar to active intestinal motility. As pregnancy progresses, fetal movements become more obvious and distinct, and it becomes impossible to confuse them with anything else. Since women who are carrying a baby more than once are well familiar with these sensations, they begin to feel them 2-3 weeks earlier than those expecting their first baby. As a rule, primiparous women first feel fetal movements at 20 weeks, multiparous women at 18 weeks. Also, a little earlier (at 17–18 weeks), first-time mothers of asthenic build, with unexpressed subcutaneous fat, can feel the baby’s movements for the first time.
By the end of the 2nd trimester, many pregnant women notice the appearance of yellowish discharge from the nipples, which often causes concern. There is nothing wrong with this - this is how colostrum is released. You should not squeeze it out of the mammary glands, since mechanical stimulation of the nipples provokes an increase in the tone of the uterus.
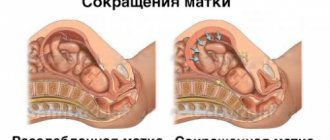
In the 2nd half of pregnancy, in response to fetal movements, the uterus may become toned for a short time: in this way, it begins to “train” before childbirth. If the uterus relaxes on its own, the duration of its tone is several seconds, and it is not accompanied by pain, then this phenomenon can be considered as a variant of the norm.
Possible problems
At this stage of pregnancy, the uterus is growing rapidly. Therefore, typical complications of this period can be associated not only with pregnancy, but also with problems in the functioning of internal organs due to the large size of the uterus.
Threat of miscarriage.
One of the most common complications of both the first and second trimester is the threat of termination of pregnancy. It is always a consequence of some kind of problem either on the part of the mother (somatic diseases, excessive mental or physical stress, the presence of an infectious process, etc.) or on the part of the fetus - this complication can be caused, for example, by placental insufficiency.
Manifestations of the threat of miscarriage are painful contractions of the uterus. They are felt as an aching, nagging pain, a periodically occurring feeling of “heaviness” in the lower abdomen lasting more than 2 minutes, with a frequency of more than 7–10 times a day. If these symptoms appear, you should contact your doctor as soon as possible for timely diagnosis and treatment. The time factor in the development of this complication is very important.
Firstly, the earlier treatment is started, the more effective it will be: in this case, the woman will not experience significant dilatation of the cervix.
Secondly, with increased tone of the uterus, the placental vessels are in a state of spasm - narrowing, which leads to a decrease in the supply of oxygen and vital nutrients to the fetus and becomes the direct cause of the development of oxygen starvation - fetal hypoxia, and with a long-term threat of miscarriage - even intrauterine delay. fetal growth. Treatment of threatened miscarriage includes eliminating the causative factor that caused this complication, eliminating all psycho-emotional and physical stress, as well as taking medications that reduce the tone of the uterus; these include GINIPRAL, magnesium preparations - MAGNESIUM SULFICATE, MAGNE B6, MAGNEROT, antispasmodics.
Heartburn. The main hormone of pregnancy, progesterone, reduces the tone of the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, which manifests itself in the form of heartburn, which quite often overshadows the second half of pregnancy.
Heartburn is an unpleasant burning sensation or, less commonly, a feeling of heaviness, fullness, or a lump behind the sternum, which is caused by reflux and irritation of the esophageal mucosa with acidic gastric contents as a result of relaxation of the esophageal sphincter - a muscular “lock” that does not allow stomach contents to be thrown back into the esophagus. In the vast majority of cases, this problem can be overcome by split meals - at least 5-6 times a day in small portions - and the exclusion of foods that provoke heartburn from the diet: their list is individual for each pregnant woman. Among medications, antacids are used - drugs that neutralize hydrochloric acid, which is produced by the cells of the gastric mucosa - GAVISCON, MAALOX, RENNY, etc.
Anemia. This complication is associated with a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells - erythrocytes. As pregnancy progresses, iron reserves are actively consumed not only for the needs of the mother, but also for the full development of the fetus. Therefore, in the presence of chronic diseases that prevent the absorption of iron or lead to its increased consumption: gastritis, gastric ulcers, liver diseases, hemorrhoids, as well as heavy menstruation or an unbalanced diet, which leads to pregnancy, anemia is one of the most common complications . This diagnosis is made when the hemoglobin level decreases below 110 g?/? l; in 90?% of cases, anemia in pregnant women is iron deficiency. With anemia, the delivery of oxygen to cells and tissues deteriorates, which leads to a complicated course of pregnancy: the threat of miscarriage, placental insufficiency. Childbirth can be complicated by birth abnormalities and obstetric hemorrhages. To treat anemia in pregnant women, iron preparations are prescribed - SORBIFER, MALTOFER, FENULS, etc.
Cramps. These unpleasant and often painful spastic muscle contractions most often occur in the area of the legs, but can also be observed in the area of the arms, neck, etc. Cramps appear in the second trimester of pregnancy, since it is during this period that intensive growth of the fetus occurs, and therefore occurs active consumption of calcium, magnesium, potassium. Due to the fact that the expectant mother’s body does not always have time to replenish the deficiency of these microelements, convulsions occur. Other possible reasons for their appearance are a decrease in blood sugar levels, which can be observed with an improper diet, as well as the presence of varicose veins of the lower extremities due to impaired blood outflow from the legs and the development of tissue hypoxia. If a cramp occurs, you need to pull your leg with your foot towards you to ensure tension in the muscle, and then massage the spasmed muscle in the direction from the periphery to the center.
In case of periodic occurrence of seizures, it is necessary to conduct an additional examination in order to identify diseases that may be their cause. If serious causes of cramps are excluded, it is recommended to rest with elevated legs to improve blood flow, and take foot baths with sea salt to activate blood circulation. In such cases, multivitamin preparations with microelements are used; if necessary, in addition to multivitamins, calcium, potassium and magnesium preparations can be prescribed - CALCIUM D3 NYCOMED, MAGNE B6, MAGNELIS, PANANGIN, ASPARKAM.
Edema. In pregnant women, edema appears quite often; it is caused by the accumulation of fluid in the intercellular space and, as a result, an increase in tissue volume. Most often, they first appear on the legs, then on the arms, stomach, and face.
The reasons for the development of edema in expectant mothers are as follows:
- The pregnancy hormone progesterone promotes fluid retention in the body.
- The outflow of blood from the lower extremities is hampered due to compression of a large vessel - the inferior vena cava - by the pregnant uterus.
- Edema during pregnancy can be a symptom of serious kidney disease, the cardiovascular system, and a complication such as gestosis, in which, in addition to edema, protein appears in the urine and high blood pressure.
- If edema occurs, further examination is required to diagnose its possible causes. A slight fluid retention in pregnant women in the absence of underlying pathology does not pose a serious danger. In this case, to reduce swelling, the doctor will recommend wearing special tights with a compression effect to prevent the development of venous insufficiency of the lower extremities. To optimize kidney function, the doctor will prescribe renal herbal preparations, herbal medicines - CANEPHRON, PHYTOLYSIN. Treatment methods will depend on the specific situation, the severity of edema, as well as the presence of concomitant pathology.
Behavior rules
In the 2nd trimester, the expectant mother can fully enjoy her “interesting position”, since the troubles of the early stages of pregnancy have passed, and the tummy is not yet so large as to limit the woman’s activity to one degree or another. In this regard, you can gratefully accept the care and attention of your loved ones, but you should not give up moderate physical activity, household chores, and walks in the fresh air.
If you are going to attend a prenatal course or school for a new mother, now is the time to take care of her choice: if you want to undergo thorough preparation, then you need to attend classes starting from 20-22 weeks or even earlier - this will depend on the type of courses chosen.
Don’t forget about choosing the right clothes, since today there are a huge number of models for pregnant women. Clothes should not squeeze the stomach; the fabric should contain predominantly natural fibers. If you wish, you can choose clothing models that will be useful for the postpartum period. It is also important to choose the right underwear, which must be “breathable”, perform a good supporting function, but at the same time not squeeze the body and not make breathing difficult.
The right choice of shoes is a matter of not only convenience, but also the safety of the expectant mother and baby, since due to the softening of the ligaments, the mobility of the joints, including the knees and ankles, increases, which increases the risk of twisting the leg or falling. You will have to forget about high heels and platform shoes for a while. The heel height should not exceed 4 cm; it’s time to replenish your wardrobe with ballet shoes or moccasins, which will serve you well during walks with your baby.
Do not forget to regularly visit the antenatal clinic: in the 2nd trimester you will have to do this more often than in the first – once every 2 weeks. This is dictated by the increasing load on a woman’s body, which necessitates more careful monitoring of the health of the expectant mother and fetus. Before each visit, it is necessary to take a general urine test - this fairly simple research method will help to timely diagnose such serious abnormalities as pyelonephritis, gestosis, and gestational diabetes. In the case of a normal pregnancy, blood tests are taken less frequently: in the second trimester, this study is carried out at 18 - 20 weeks. Of course, if indications arise: complications of pregnancy, exacerbation or initial detection of any diseases, a blood test can be taken additionally and repeatedly.
In the 2nd trimester, a triple test is performed - a screening study (screening means “sifting”, “selection”). This analysis allows us to determine the contingent of expectant mothers who need an in-depth examination in terms of identifying fetal malformations. The triple test involves examining three components, which include:
- alpha-fetoprotein, produced in the liver and gastrointestinal tract of the fetus; a change in its concentration indicates malformations of the nervous system, chromosomal abnormalities, anomalies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- estriol is a hormone produced with the active participation of the fetus and therefore allows us to judge its condition;
- human chorionic gonadotropin, synthesized in the placenta.
The optimal period for conducting a triple test is 16–18 weeks. It is worth remembering that the presence of deviations in the triple test results does not mean that the child will necessarily be born with congenital anomalies.
Changing the analysis parameters is possible if there is a threat of miscarriage, gestosis, or intrauterine growth retardation. However, in order to be on the safe side, if there are deviations in the triple test, it is necessary to undergo additional research to clarify the condition of the fetus: for this, a consultation with a geneticist and an unscheduled ultrasound are prescribed. If there are indications and the patient’s consent, invasive diagnostic methods are used that are highly informative - sampling amniotic fluid (amniocentesis) or fetal umbilical cord blood (cordocentesis) to study the chromosomal set of fetal cells.
At 24–26 weeks, the doctor will prescribe a second scheduled ultrasound, which is performed on all expectant mothers, even in the case of a normal pregnancy. During an ultrasound, the size of the fetus will be measured to ensure that its size corresponds to the gestational age. The location and structure of the placenta, the structure of the internal organs of the fetus will also be studied in order to exclude developmental defects, and the sex of the baby will be accurately determined if its position in the uterus allows this.
Since during this period the fetus’s musculoskeletal system is actively developing, the expectant mother’s need for calcium increases. To prevent calcium deficiency in the body, on the recommendation of a doctor, take special medications - CALCIUM D3 NYCOMED, KALCEMIN. They can be prescribed in addition to multivitamin complexes. It is also necessary to consume foods rich in calcium: milk, cottage cheese, cheese, fish.
After 24 weeks of pregnancy, it's time to think about buying a maternity bandage. This device will help to avoid many troubles, as it will relieve the growing load on the spine. The bandage also prevents the appearance of stretch marks on the abdomen, well supports the uterus in an optimal position, which reduces compression of the bladder and large vessels of the abdominal cavity. Due to the fact that there is now a large assortment of bandages on sale, the choice is a matter of your taste and body type.
Basic tests in the second trimester
The 2nd trimester of pregnancy is marked by a routine ultrasound. It is carried out at 20-24 weeks, it all depends on the indications. Ultrasound examination is carried out traditionally - on a full bladder. This allows you to assess the condition of the fetus and amniotic fluid. If problems are detected early, the risks of complications are significantly reduced.
What tests should I take? In the second trimester, the doctor may prescribe additional tests to monitor the health of the expectant mother and her baby.
- List of laboratory tests that may be prescribed:
- clinical blood test to determine hemoglobin level;
- a general urinalysis to evaluate kidney function;
- gynecological smear;
- analysis for TORCH infections (if necessary).
Among other tests, the second trimester may be marked by the need to conduct a “triple test”: hCG, estriol, alpha-fetoprotein, which can determine defects in fetal development, chromosomal abnormalities, and problems in the formation of the spinal cord. Basically, these tests are taken by those women who have previously been diagnosed with a frozen pregnancy. These tests are best carried out between 16-18 weeks.
Do not lose your vigilance, monitor your health and feelings, as one of the biggest risks is the child freezing. If you do not feel the baby moving inside you, you should immediately consult a doctor. The expectant mother feels movements at about 18 weeks. Some women can feel their baby earlier, especially for multiparous women. Frozen pregnancy in the second trimester most often occurs at 16-18 weeks.
What week does the 2nd trimester begin?
1-3 weeks. The countdown for the start of the baby's waiting period begins on the first day of the last menstruation. A little later, the egg is fertilized and the tiny embryo is attached to the walls of the uterus. You don't even know what's going on inside you while you're still waiting for your next period.
4-6 weeks. A woman’s body produces the hCG hormone; during this period, most expectant mothers find out about their position using a pregnancy test. The tiny embryo begins to form a heart. Some women begin to experience malaise and nausea in the morning.
7-10 weeks. The future baby is growing and developing rapidly, his weight is already about 4 grams. Mommy may gain a little weight, but no external changes have yet been observed. Most girls fully suffer from toxicosis.
11-13 weeks. Time to undergo the first screening test, which includes ultrasound diagnostics and a biochemical blood test to determine the likelihood of possible chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus.
Toxicosis is most likely already receding. The baby's cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, spine and face have developed.
By the end of the first trimester, its height reaches 10 cm, and its body weight is about 20 grams.
2nd trimester of pregnancy by week
14-17 weeks. The baby is actively moving in the mother’s tummy, but most pregnant women do not feel this yet. The height of the fetus reaches 15 cm, and the weight is about 140 grams. The expectant mother herself is also actively gaining weight, and by this time her gain can reach 5 kg.
18-20 weeks. During this period, most women become familiar with the feeling of their baby moving. The tummy already stands out so much that it is impossible to hide it from prying eyes. The baby is developing by leaps and bounds, his weight reaches 300 grams, and his height is 25 cm.
21-23 weeks. At this time you will have to undergo a second screening test. Very often, it is at the second ultrasound that the doctor can already determine the sex of the baby, whose weight reaches 500 grams.
24-27 weeks. The uterus becomes quite large, and the expectant mother may experience discomfort - a feeling of heartburn and heaviness in the stomach, cramps in the legs, etc. The baby has occupied the entire cavity of the uterus, his weight has already reached 950 grams, and his height is 34 cm. His brain is fully formed .
Fetal size and weight in the second trimester
Starting from the 13th week of pregnancy, the fetus begins to actively develop. His skeleton and internal organs are formed. If in the first trimester the formation of all organs and systems occurs, then starting from the second trimester, its organs and systems begin to work independently.
For example, the fetal heart begins to beat 2 times faster and pumps about 22 liters of blood. The formation of the brain also occurs, convolutions appear, the pituitary gland begins to work, the intestines, bladder, kidneys and other organs are formed.
Only the respiratory system rests.
At this stage of pregnancy, the growth and size of the fetus increases. If in the 1st trimester he weighed about 20 g, and the body length was 7 cm, then in the 2nd trimester, towards the end, the baby weighs from 850 g to 1000 g. The fetal growth increases to 35 cm in full height. Thus, the fetus from a small embryo turns into a fetus weighing up to 1 kg.
In the fourth month of pregnancy, the fetus is developing rapidly. The following changes occur in his tiny body:
- The skeleton is strengthened, the bones grow rapidly.
- The abdominal organs develop.
- The kidneys begin to produce urine.
- The stomach, gallbladder and intestines function.
- The cerebral cortex is formed.
- The first hormones are produced in the adrenal glands.
- The formation of baby teeth is completed.
- The proportions of the baby's body change.
- The gonads develop.
- Toenails appear.
- In girls, the uterus and fallopian tubes form, in boys, the genitals.
- Facial muscles are formed.
Starting from the 18th week of pregnancy, the fetus has formed auditory ossicles, which allows it to hear its mother.
During this period, he is quite active, moves a lot, often changes his position, which allows the mother to feel the baby’s first movements. From the 19th week, the fetus can blink and squint, open its mouth.
His taste buds begin to form, which allows him to taste the food his mother eats.
By the end of the 2nd trimester, the mental abilities of the fetus are formed, all parts of the cerebral cortex are well developed. The placenta at this stage is also fully formed.
It provides the fetus with all nutrients, protects against negative effects, and provides access to oxygen.
In the second trimester, the fetus is fully formed, increasing in size every day and by the end of the 27th week reaches almost 1 kg.
Condition of a pregnant woman in the second trimester
Unlike the first trimester, in the second, the woman feels much better. She is no longer tormented by toxicosis, there are no big risks for terminating the pregnancy. At this stage, the expectant mother begins to feel the first movements of the fetus, which become more pronounced and noticeable every day.
In the second trimester, hormonal levels begin to normalize, general well-being improves, and mood and appetite increase. During this period, many mothers are full of energy, start visiting the pool, doing yoga, and some decide to travel. The woman's belly is hardly noticeable, but begins to acquire roundness.
Despite the improvement in well-being, there are still some nuances that bother a woman and can cause anxiety.
Nausea in the second trimester of pregnancy
Normally, with the onset of the second trimester, toxicosis recedes and is replaced by a good appetite. However, due to the individual characteristics of women, many women still continue to complain of slight nausea, which is mainly present in the morning or as a reaction to unpleasant or pungent odors.
If you have minor nausea, there is no need to worry; it will go away by the 18th week. In the absence of any pathologies during pregnancy, doctors recommend drinking water with lemon or tea immediately after waking up for morning sickness.
The cause of this condition may also be the mother’s poor diet, eating fatty foods, overeating or fasting.
In cases where nausea is constant and the urge to vomit is present, you should immediately consult a doctor, as this may be a sign of gestosis or another pathology dangerous to the development and life of the child and the woman herself.
Discharge in the second trimester of pregnancy
In the second trimester of pregnancy, vaginal discharge can be both normal and a sign of internal diseases. It is very important to pay attention to the nature of the discharge.
Normally, discharge in the 2nd trimester has a milky tint. What is the result of hormonal changes in a woman’s body. The discharge itself has a slight odor, and its quantity may increase slightly as the period increases. The following vaginal discharge is a cause for concern:
- Curdled discharge accompanied by itching and burning in the vaginal area is a sign of thrush (candidiasis).
- Spotting is a sign of cervical erosion, the threat of miscarriage, premature birth.
- A yellowish or greenish discharge is a sign of a vaginal infection.
- Clear discharge with an unpleasant odor is bacterial vaginosis.
The appearance of such discharge in any trimester of pregnancy should alert a woman and become a reason to consult a doctor, who, after the results of the examination, will be able to identify the cause and, if necessary, prescribe appropriate treatment.
Pain in the second trimester of pregnancy
Starting from the second trimester, a woman may periodically experience pain in the lower back or pelvis. Doctors explain such painful sensations as an increase in the uterus and its pressure on neighboring organs.
But in cases of pathologies or possible risks, pain may be the first signal for immediate consultation with a doctor. A pregnant woman should be alerted to nagging pain in the lower abdomen, pain in the sacrum or hips.
If there is a threat of miscarriage, in addition to pain, there will also be bloody discharge from the vagina.
In the second trimester, a pregnant woman often suffers from heartburn, which also appears as a result of an enlarged uterus and its pressure on the stomach. Heartburn is not a serious symptom. It bothers almost 80% of pregnant women.
Due to the same enlargement of the uterus, the expectant mother may be bothered by constipation and there is a risk of developing hemorrhoids. In such cases, doctors recommend adjusting your diet, consuming as much fermented milk products as possible or those that contain fiber.
Painful sensations can also appear as a result of cramps - muscle spasms due to involuntary contraction. Cramps may be a sign of impaired mineral metabolism in the body.
It is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, in the absence of contraindications, to do gymnastics for pregnant women, and also to pay attention to your diet, which should be rich in vitamins, minerals and other beneficial substances.
Colds in the second trimester of pregnancy
Source: https://zdorovo.live/beremennost/s-kakoj-nedeli-nachinaetsya-2-trimestr.html
Weight gain in the second trimester
Observations of pregnant women show that in the second trimester, expectant mothers gain weight most actively. However, the baby is also growing fastest right now. The nutrition of a pregnant woman at this time is reflected in the weight of the fetus. Between 15 and 25 weeks, most pregnant women quickly gain 2 to 5 kg due to the increase in blood volume needed to nourish the baby.
It turns out that until the second trimester the child does not require such intensive nutrition, but already the second trimester of pregnancy is characterized by increased appetite. There is no point in limiting your desire to eat, especially if the food is not only tasty, but also nutritious and rich in vitamins. Try to keep your diet balanced and varied - after all, this is the basis of your baby’s nutrition, the key to his full and timely development. If you have exceeded the permissible weight gain limits by a couple of kilograms, you can arrange a fasting day.
Compliance with the principles of proper nutrition can prevent intrauterine growth retardation of the baby, since most parameters of fetal development (body weight, height, development of internal organs) depend on the content of nutrients in the blood of a pregnant woman and on the nature of the blood supply to the placenta and uterus.
Changes in the body of the expectant mother
In order to ensure the process of growth and development of the fetus, the pregnant woman’s body works in an enhanced mode. The load on all systems increases: endocrine, digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular, urinary, etc.
During the second trimester of pregnancy, the following changes occur in the female body:
- The belly is gradually increasing. The uterus rises even higher, at the 20th week it is already at the level of the navel. This is the best time to arrange a photo session and take photos as a keepsake.
- After the 20th week, the uterus may periodically become toned, and the woman may feel slight contractions, the so-called Braxton-Hicks training contractions. Thus, the uterus performs a kind of exercise aimed at preparing for the upcoming birth.
- Under the influence of certain hormones, the mammary glands continue to increase in size. The skin around the nipples darkens a little, and colostrum may be released from the nipples themselves.
- Due to the rapid development of the fetus and an increase in the body's need for nutrients, iron deficiency anemia may occur, a condition that in some cases requires drug correction. But you should not prescribe iron-containing medications yourself, because moderate anemia in pregnant women is a completely normal phenomenon that can be corrected with a balanced diet. But foods rich in iron (apples, buckwheat porridge) can be consumed without special restrictions.
- Since the enlarged uterus puts pressure on the intestines, a pregnant woman may experience constipation. You can get rid of this problem by eating enough foods containing fiber: fruits, vegetables, cereals.
- Many women may experience heartburn. It occurs most often in the second trimester and can continue until the moment of birth.
- The amount of vaginal discharge in a woman may increase. If this is not accompanied by itching, burning and other unpleasant symptoms, and the discharge has a whitish tint, then there is no need to worry. Otherwise, you should consult a doctor, because this condition can be dangerous.
- During the second trimester, some women may experience swelling. Swelling occurs more often in the third trimester, closer to the time of birth, so the appearance of alarming symptoms in the middle of pregnancy should alert the expectant mother.
- Women prone to varicose veins may notice in mid-pregnancy that the veins in their legs have become bulging and nodular vascular formations have appeared. In order to prevent the occurrence of vein diseases, it is recommended to move more and change body position as often as possible.
- Skin pigmentation may occur in certain areas, mainly in the abdomen, sometimes on the face. After giving birth, your skin color will return to normal, so don't worry about it.
Second trimester of pregnancy: nutrition for a pregnant woman
Diet plays a fundamental role in the health of the expectant mother and baby. A balanced diet will provide the pregnant woman’s body with the vitamins and microelements she needs.
The daily menu should include fish, beef, fermented milk and dairy products, eggs, buckwheat, tomato juice, apples.
For a while, you should give up spicy foods, marinades, store-bought snacks, sweets, and also completely eliminate processed foods and alcohol.
There is also no need to give up multivitamin preparations, which will complement your diet and have a positive effect on your immunity and well-being. Multivitamin complexes should be selected by a doctor, taking into account your situation; moreover, you need to drink them at certain intervals. Vitamins deserve special attention. A, C, E, D, as well as trace elements - calcium and magnesium. Don't forget about folic acid, which promotes the active formation of the baby's nervous system and reduces the risk of developing hypertension.
Threats and dangers
Throughout the first trimester, the fetal organs are at the stage of formation and development. Therefore, any negative factors (smoking, alcohol, medications) can affect full development. It is worth abandoning all manifestations of adverse effects on the fetus.
When pregnancy occurs, the woman’s body activates the process of suppressing cellular immunity in order to prevent rejection of the fertilized egg. But until this mechanism is fully operational, a certain period of time will pass, so in the early stages in the 1st trimester there is a high probability of early miscarriage
.
Important Symptoms of a miscarriage are bloody discharge and nagging pain in the lower abdomen. If this condition occurs, the woman should immediately seek medical help.
Second trimester of pregnancy: discharge
At this time, the amount of discharge becomes greater. The color of the discharge is milky, and the smell is slightly sour. This is largely due to hormonal changes in the body, so an increase in discharge is a natural occurrence. In this case, it is worth taking into account the additional sensations that accompany the discharge: if there is itching or burning, this indicates the presence of a disease. Most often we are talking about thrush. This disease should be treated only under the supervision of a doctor who will select the right and gentle medications. But ignoring thrush can lead to infection of the baby.
Bloody discharge deserves special attention. Of course, they can be caused by erosion, but it also happens that such a symptom indicates a threat of losing a child or giving birth to a baby prematurely.
If vaginal discharge has a strong unpleasant odor and a greenish or yellow-green tint, it is likely an infection, which should also be treated as soon as possible.
Other causes of discharge include bacterial vaginosis, which affects expectant mothers. Vaginosis is characterized by the presence of copious discharge that is clear in color and has no particular odor. It may be caused by some irritant, for example, panty liners.
Self-medication is contraindicated; it can harm you and your child. Only after examination and diagnosis can you begin treatment under the supervision of a doctor.
Tests and examinations in the 1st trimester of pregnancy
The most important moments of the first trimester are the diagnosis of pregnancy using reliable criteria and the first screening.
There are tests and clinical manifestations that can only indirectly indicate pregnancy. Among them:
- pregnancy test;
- cyanosis of the cervix upon visual examination (can also be 1-2 days before the onset of menstruation);
- change in a woman's condition.
A pregnancy test can give a false positive result. This is possible due to the oncological process of the uterus, adrenal glands or the onset of biochemical pregnancy. It is spontaneously interrupted before the implantation stage, after activation of the failed genome of the embryo.
A reliable sign of pregnancy is the presence of a fertilized egg in the uterus, which is determined by ultrasound from the 3rd week of obstetric pregnancy. This indicates that the first critical stage has been passed and the embryo has settled in the uterine cavity.
After establishing the fact of pregnancy, a woman is prescribed a number of examinations:
- General analysis of urine and blood.
- Biochemical tests.
- Coagulogram.
- Determination of blood group and Rh factor.
- Tests for infections (HIV, viral hepatitis, syphilis).
- Vaginal smear to detect pathogenic flora (chlamydia, Candida fungi, mycoplasma and ureaplasma).
- Tests for the group of TORCH infections - herpes virus types 1 and 2, cytomegalovirus (herpes type 5), toxoplasmosis, rubella.
The first screening is carried out for the early detection of severe anomalies and malformations, as well as genetic abnormalities in the fetus. Duration: from 10 to 14 weeks of pregnancy. The examination consists of 2 components: a blood test for hormone levels (beta subunits of hCG and PAPP) and an ultrasound, during which the doctor:
- determines the fetal heart rate;
- determines the main dimensions: coccygeal-parietal, biparietal, etc.;
- assesses the condition of the fetal facial skull for the presence of facial clefts;
- determines the thickness of the collar space, which may be an indicator of genetic abnormalities;
- the length of the femur determines the exact duration of pregnancy (along with other signs) and the presence of genetic pathologies;
- establishes the exact gestational age, determines the correspondence of the level of fetal development to the gestational age;
- assesses the state of organs (for example, the pairing and symmetry of the cerebral hemispheres).
The conclusion of a screening ultrasound is usually issued on A4 sheets, where all the relevant parameters are written down.
Colds and acute respiratory viral infections in the second trimester
During pregnancy, a woman is susceptible to colds because the body's immune strength is reduced. A peculiarity of the course of colds is their relative safety for the baby, since they occur with a minimum of complications. Colds and acute respiratory viral infections should be treated only after consultation with a specialist, since not all drugs are equally safe during this period. Are there risks? Unfortunately, complications can be of the following nature:
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- fetal hypoxia;
- disorders in the development of the nervous system;
- pathologies in the development of the endocrine system;
- disturbances in the formation of eggs (if a woman is expecting a girl).
Bed rest will make it possible to get in shape faster, and the risk of complications will be much lower.
Separately, it is necessary to say about temperature. The temperature of 37 during pregnancy in the second trimester does not go down. All that the expectant mother can do is drink more fluids to improve her condition. But a significant increase in temperature must be reduced with safe drugs based on paracetamol. Nurofen, Aspirin and Analgin cannot be used by pregnant women.
It is worth noting that fever in the second trimester can occur for other reasons. If you do not have a cough, runny nose, or sore throat, and your temperature has risen, this is probably a low-grade fever. In this case, the temperature reaches no higher than 37.2-37.5. As for the more serious causes of fever, we should not forget about diseases such as herpes, pyelonephritis, and tuberculosis. An experienced doctor will be able to determine the true cause of the increase in temperature in the second trimester as soon as possible.
Registration before 12 weeks: why is it so important?
The first three months are the most crucial period, on which the course of the entire pregnancy and the health of the baby largely depend. The fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus (implantation), the placenta begins to form, and the baby’s organs and tissues are formed.
First trimester: baby development week by week
* 5-6 weeks : the length of the embryo is 5 mm, it already has a heartbeat, arms and legs are defined. * 7-8 weeks : the fetus’s eyes are wide open and fingers are already visible, the umbilical cord is gradually forming and the amniotic sac appears. * 9-10 weeks : the baby’s brain and heart are fully formed. * 12 weeks : the fetus is a small, full-fledged person, which is already formed externally and internally, reacts to external stimuli and strokes itself with its hands.
Later during pregnancy, the organs and tissues of the fetus mature.
The impact of even a minor adverse factor can lead to disruption of the normal course of these processes at any stage. For example, lack of folic acid or magnesium, stressful situations, increased uterine tone and others.
Agree that knowing the “enemy” by sight makes it easier to resist, and the development of any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. Therefore, do not delay your visit to the antenatal clinic.
Pain in the second trimester
Pain in the second trimester of pregnancy can also become one of the unpleasant companions of the expectant mother. It is worth noting that most often women complain of pain in the pelvis and lower back. This is due, first of all, to an increase in the load on the back, as the tummy gradually increases. But there should not be any unpleasant sensations in the abdominal area, since such a symptom may portend a pregnancy failure. It is especially worth seeking help from a specialist if abdominal pain is accompanied by bleeding.
Features of the course and signs of pregnancy in the second trimester
During the second trimester of pregnancy, certain physiological processes occur in a woman’s body. Due to increased estrogen levels, melanin production increases. Therefore, the expectant mother may have darker nipples and areolas. A dark stripe often appears on the skin of the abdomen. This is the midline, which doctors call Linea nigra. But don’t be afraid, hyperpigmentation disappears after childbirth.
During this period, the woman’s body begins to actively prepare the mammary glands for feeding the child. Under the influence of hormones, blood circulation in them increases, they begin to grow, sometimes increasing by 1-2 sizes.
In the fourth month (around 16 weeks), some pregnant women undergo an invasive procedure called amniocentesis, which involves removing amniotic fluid, for medical reasons. Their analysis will help identify various genetic pathologies in the early stages.
In the fifth month of pregnancy (19th week), significant changes in the body begin to occur. Due to an increase in cardiac output, a woman’s pulse quickens, the volume of circulating blood increases by about 0.5 liters, and the hemoglobin level may fall.
From the 21st week, when the child’s musculoskeletal system begins to actively develop, the need for vitamins and minerals increases sharply. It is during this period that the expectant mother needs to take care of their sufficient intake into the body. All reserves will go to the baby, and due to a shortage, a woman may experience calf cramps, teeth become brittle, the level of iron in the blood drops, and as a result, anemia develops.
Between the 24th and 28th weeks, a complex blood test is performed to determine your glucose tolerance. It allows you to detect gestational diabetes in pregnant women. This condition is temporary and goes away after the birth of the child, but during pregnancy it can negatively affect the fetus.
At 25–26 weeks, placental lactogen, a special peptide hormone, stimulates the production of the first colostrum. The mammary glands continue to enlarge. It's time to start preparing them for lactation. To do this, you need to wash your breasts with warm water and lightly rub the skin with a hard towel. But this is done carefully, since excessive massage can provoke unwanted uterine tone.