About the amniotic sac
During intrauterine development, the fetus is surrounded by a dense amniotic sac, which has an elastic consistency. Inside it there is amniotic fluid, which protects the child from negative environmental factors: microorganisms that can live in the organs of the female reproductive system, pressure and noise. In addition, the optimal temperature of the amniotic fluid (37°C) promotes normal fetal maturation.
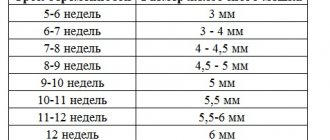
When labor begins, contractions lead to a gradual increase in pressure on the membranes of the amniotic sac. At the same time, the amniotic fluid shifts to its lower pole, forming a “water cushion”. The latter begins to put pressure on the cervix, promoting its opening without damaging the fetal head. At the moment when the cervix dilates 4-6 cm, the bladder ruptures, accompanied by the release of amniotic fluid. This usually occurs when it is introduced to the level of the internal os of the cervix.
After rupture, the opening of the birth canal is caused by the fetal head. The release of prostaglandins when the integrity of the amniotic membranes is disrupted stimulates contractions and leads to delivery.
Why amniotomy is needed
“Why open the amniotic sac at all if the waters break on their own, what if this stimulation disrupts the natural course of labor?” - many women in labor express similar concerns. But the fact is that when childbirth occurs naturally and without complications, the need for amniotomy does not arise. Simply put, if you can do without puncturing the amniotic sac, then doctors are happy to do so.
The procedure may be required when the condition of the child or mother requires urgent delivery, or when labor is weak. Also, a puncture is a solution in some cases when the natural sequence of the birth process is disrupted. The membranes may be so strong that they do not tear and a puncture is required; another common reason for amniotomy during childbirth is the so-called “flat bladder”, when there is no fluid in its lower part and the membranes tighten around the baby’s head and interfere with its advancement and opening cervix.
However, it is not at all harmful to remember the indications for which this procedure is performed, so that if it is necessary, you can clearly understand what is happening.
Expert commentary
Indications for amniotomy:
- induction of labor during post-term pregnancy;
- weakness of labor;
- , ;
- “flat” amniotic sac (the membranes are stretched on the fetal head, preventing its movement through the birth canal);
- complete opening of the uterine pharynx, if the fetal bladder has not opened on its own (dense membranes);
- in case of multiple pregnancy, after the birth of the first fetus, an amniotomy of the second amniotic sac is performed;
- suspicion of fetal hypoxia and premature placental abruption;
- the condition of the pregnant woman does not allow further prolongation of pregnancy;
- It is advisable to perform an amniotomy before labor anesthesia using the prolonged method.
From the moment the integrity of the bladder is broken, there is no turning back - the clock counts, because the anhydrous period cannot last indefinitely (usually doctors recommend limiting the time period from the moment the bladder opens to the onset of labor to 10-12 hours, but this issue is resolved in each case individually).
Expert commentary
Amniotomy is a fairly common procedure. The urgency of its implementation is determined only by the doctor. It all depends on the condition of the mother and the fetus. The procedure does not have any negative consequences if it is carried out according to indications and all conditions for its implementation are met. The main requirements are the biological readiness of the patient’s body for childbirth (mature cervix) and the qualifications of the doctor, allowing him to carry out this manipulation.
general information
Amniotomy is the mechanical opening of the fetal bladder, as a result of which amniotic fluid flows out. The procedure can be performed with special surgical instruments or using the fingers of a gynecologist. During amniotomy, the woman does not feel pain, since the membranes of the amniotic sac are not innervated.
The manipulation is performed in accordance with strict indications. This reduces the risk of complications and also speeds up the delivery process. At the same time, gynecologists note that rupture of the membranes due to external influence disrupts the process of childbirth, which can negatively affect the entire birth process. In this regard, its use in obstetric practice is limited.
During the procedure, doctors achieve the following effects:
- increasing the intensity of contractions and decreasing the duration of the intervals between them;
- labor intensifies as uterine contractions become stronger;
- the cervix opens faster;
- if a pregnant woman is diagnosed with placenta previa, amniotomy can stop birth hemorrhage;
- As a result of amnion rupture, blood pressure levels decrease.
There are no negative consequences of the amniotomy for the child. If the technique is incorrect, the arms and legs may fall out or bleeding from superficial vessels may occur. However, if the manipulation is performed as planned, subject to a number of conditions, the risks are minimal.
Amniotomy - what is it?
In the mother's uterus, the baby grows and develops in the amniotic sac filled with amniotic fluid. The rupture of the membranes triggers the production of the hormone prostaglandin in the mother's body, which stimulates the birth process. Normally, the lining of the bladder bursts on its own under the pressure of the uterus during labor. If for some reason this does not happen naturally or it is necessary to induce labor, then an artificial rupture of the membrane, or amniotomy, is performed. Amniotomy is an obstetrician's manipulation aimed at opening the amniotic sac.
Beginning of labor
The onset of labor after amniotomy is observed in 95% of pregnant women. Obstetricians note that the mechanisms of this are not entirely clear. It is believed that there are several mechanisms by which rupture of the membranes stimulates labor.
The first theory is due to the fact that when the amniotic membranes are opened, a large number of prostaglandins are released. These are biologically active substances, the important effect of which is to enhance contractions of the smooth muscles of the uterus. As a result, contractions begin, which gradually become more pronounced and regular.
Rupture of the membranes leads to mechanical irritation of the birth canal. This is due to a sharp decrease in the volume of the uterus and the subsequent contraction of the muscular membrane. An additional effect is exerted by the pressure of the fetal head on the cervix.
Contraindication to amnitomy
A competent doctor always knows what to do in a given situation, but the expectant mother should also know everything about the upcoming birth. Puncture of the bladder is impossible if:
- Disagreement of the mother in labor. Specialists cannot carry out any intervention without the patient’s permission. The woman in labor has the right to refuse the procedure, but the responsibility rests entirely on her shoulders. The refusal is documented.
- . If a pregnant woman is expecting two or more children.
- Impossibility of natural childbirth. Sometimes the cervix does not open, being in a sacral state. In this case, rupture of the bladder is impossible, and there is every reason for a cesarean section.
- Incorrect position of the fetus. If the child is positioned non-standardly, the procedure is not used.
- Fetal weight less than 3 kg.
Requirements for the procedure
In addition to the indications for amniotomy, obstetricians take into account a number of conditions relating to the condition of the woman and the fetus. These include:
- the presence of an obstetrician-gynecologist and an equipped office in a hospital setting;
- the child should only be in a cephalic position;
- singleton pregnancy;
- pregnancy period is at least 38 weeks;
- fruit weight is not less than 3000 g;
- the position of the head is correct, while it is inserted into the entrance of the small pelvis;
- readiness of the birth canal for delivery;
- when assessing maturity on the Bishop scale, 6 or more points are scored;
- the pelvis is of normal size;
- There are no scar changes in the uterus after any surgical interventions.
In cases where any condition is not met, specialists refuse to perform an amniotomy. This can lead to the development of complications on the part of the mother or fetus, including their death.
Risks of amniotomy
Risks are practically reduced to zero. If many decades ago cases of fetal infection were often recorded, now this is very rare, since amniotomy is performed under sterile conditions using disposable equipment. It is extremely rare that bleeding may begin - in such cases, specialists decide to perform a CS.
Doctors do not perform amniotomy if the woman is fundamentally against this procedure. This usually happens if the pregnant woman does not know enough about the procedure and thinks that it will entail serious consequences. The doctor’s main task in this matter is to explain in detail why in a particular situation it is very important to perform an amniotomy and why refusing it can be dangerous. Only after detailed explanations should a woman make a decision.
Since the procedure is performed manually, its results largely depend on the doctor. Therefore, you need to contact only specialized clinics, where doctors with extensive experience in performing amniotomy and managing complicated pregnancies and childbirth work.
Types of manipulation
There are several options for the procedure. The main difference is the time of opening of the amniotic sac.
If an amniotomy is performed before labor begins, it is called premature. It is performed when necessary to induce contractions and the onset of labor. A similar situation arises when a pregnant woman has obstetric pathologies: gestosis, preeclampsia and eclampsia. In addition, premature manipulation is carried out in case of decompensated somatic diseases: diabetes mellitus, etc.
Early amniotomy is performed after contractions begin, but before the cervix dilates more than 7 cm. The purpose of the intervention is to speed up labor. Their prolonged course can lead to fatigue of the woman in labor and deterioration in the condition of the fetus. In this regard, if contractions are irregular 2 hours after the manipulation, additional drug stimulation of labor is necessary.
Timely amniotomy is performed when contractions are regular and the cervical dilatation reaches 10 cm. In this case, preservation of the bladder membranes can lead to compression of the baby’s head when it is inserted into the birth canal.
Delayed amniotomy is a section of the amnion at the moment when the child begins to descend into the pelvic cavity. Otherwise, the fetus is born inside the amniotic sac. This is fraught with various complications: postpartum hemorrhage in a woman or asphyxia of a child.
Types of amniotomy
About 7% of women undergo this procedure before giving birth. What is amniotomy, and what are its types? It is divided depending on the period of birth:
- Premature amniotomy for stimulation. It is carried out to induce contractions.
- Early amniotomy. It goes away when the cervix dilates up to 7 cm.
- Timely amniotomy. It is performed with the cervix open 8-10 cm.
- A delayed amniotomy occurs when the cervix is fully dilated. If this is not done, the baby will be “born in a shirt,” which can cause bleeding in the mother and breathing problems in the newborn.
When carrying out the procedure, some features must be taken into account.
Main indications
Depending on the purpose of the manipulation, it can be performed to stimulate labor or during delivery according to indications. In the first case, amniotomy is indicated for the following conditions:
- Against the background of severe gestosis. The pathology is characterized by increased blood pressure and edema, which indirectly worsens blood circulation in the placenta and leads to fetal hypoxia. In such a condition, emergency induction of labor with amniotomy is indicated.
- High level of blood pressure, since against the background of contractions with an unruptured amniotic sac, it further increases. When it ruptures, the compression of the vessels of the uterus and small pelvis is reduced.
- Post-term pregnancy.
- Premature placental abruption in its normal location.
- Decompensated diseases of a pregnant woman that disrupt the normal course of gestation: diabetes mellitus, renal or heart failure, hypertension, etc. Their progression may be associated with the risk of developing life-threatening complications in the mother and child.
- Intrauterine fetal death.
- Absence of contractions at the onset of labor. This situation can be complicated by hypoxia of the child and general fatigue of the woman. The maximum time from amniotomy to delivery is from 12 to 20 hours.
- Detection of Rh conflict. In the absence of delivery, the child's condition as a result of hemolytic disease can quickly deteriorate. Amniotomy is performed only if the pathology of the fetus progresses and this is established using ultrasound or blood tests of the pregnant woman.
All indications for carrying out the procedure before contractions are related to the need for emergency delivery. These conditions, in the absence of regular labor, threaten the life of the fetus and mother. It is important to understand how long after amniotomy contractions begin. On average, they occur 12 hours after dissection of the amniotic sac. Otherwise, drug stimulation is started.
The main medical reason for opening the amnion during childbirth is the weakness of labor. Amniotomy allows you to enhance labor in 9 out of 10 women in labor without the use of Oxytocin and other medications. The indications are as follows:
- Preservation of the intact amnion and the absence of rupture of amniotic fluid when the cervix is dilated to 8 cm. Preserving the integrity of the amniotic sac in this case is impractical.
- In some cases, the amniotic sac has a dense membrane that protects it from rupture even when the cervix is fully dilated. The fetus inside it experiences hypoxia. Lack of oxygen can cause the development of perinatal hypoxia and various damage to internal organs.
- Placenta previa to the cervix. This condition is a risk factor for bleeding. Opening the amniotic sac allows the fetal head to pass through the exit of the uterus without obstruction and normal delivery to continue.
- With polyhydramnios, since excess amniotic fluid can lead to excessive stretching of the uterine wall and loss of its ability to contract normally. This is a risk factor for the development of labor weakness.
- Oligohydramnios can cause compression of the fetal head by the amniotic membranes with the development of hypoxia. If there is a small amount of amniotic fluid, an early amniotomy is performed when the cervix is dilated to 2-4 cm.
Also indicated are gestosis, post-term pregnancy, arterial hypertension. In the absence of direct indications, dissection of the amniotic sac should be performed only after cervical dilation is greater than 6 cm.
Amniotomy during childbirth: what is it?
Amniotomy is a procedure in which an obstetrician-gynecologist punctures a pregnant woman's amniotic sac to stimulate labor.
It is quite normal when a woman in labor worries on the eve of an amniotomy and asks the obstetrician-gynecologist questions: “Amniotomy during childbirth: what is it? And why do they give it to me?” Let's answer these questions in detail.
The cervix dilates halfway around the middle of the 1st labor period. At some point, the pressure on the amniotic sac becomes so strong that it bursts. As a result, the anterior waters (located in the amniotic sac in front of the baby's head) are poured out. There are no nerve endings in the amniotic sac, so its rupture and discharge of water occur absolutely painlessly.
Spontaneous discharge of water during labor occurs in most women, but a small number of women (approximately 7%) need help - they undergo an opening of the amniotic sac (amniotomy). In this case, the obstetrician-gynecologist quickly makes this puncture, after which the anterior waters pour out, and soon the woman begins to feel contractions. The reason for the onset or intensification of contractions is the intense production of prostaglandin, a hormone that promotes contraction of the smooth muscles of the uterus.
The amniotomy procedure is quite simple and therefore does not require anesthesia or the participation of a surgeon. There is no need to be afraid of amniotomy: it is performed only by a professional obstetrician-gynecologist for medical reasons. However, the manipulation is carried out strictly in a hospital setting, because at this time the cervix is almost ready for childbirth.
Indications for amniotomy
- gestosis (preeclampsia in pregnant women), in which the mother’s blood pressure increases, swelling appears, and the protein content in the urine increases;
- post-term pregnancy (if labor does not begin at 41-42 weeks) may cause an amniotomy without contractions);
- sluggish labor;
- the occurrence of Rh conflict in mother and child;
- very high density bladder shell;
- the amniotic sac is flat due to a lack of anterior water and cannot burst on its own;
- polyhydramnios;
- multiple pregnancy (with sluggish labor);
- placental insufficiency.
Types of amniotomy
- Prenatal amniotomy (induction of labor with amniotomy): performed to start the labor process when contractions have not yet begun. The reason for this is either postterm pregnancy or fetal pathologies that require faster delivery.
- Early amniotomy: performed when labor has already begun at the initial stage (when the cervix is less than 7 cm dilated), if contractions are weak. In this case, the expectant mother is concerned with the question: “If I have an amniotomy during childbirth, how long will it take for contractions to become regular?” The timing of the arrival of regular and active contractions can vary from 30-40 minutes to 12 hours.
- Timely amniotomy: performed when the uterus is almost completely open (8-10 cm), but the bladder has not burst.
- Late amniotomy: performed at the final stage of labor, when there are attempts and the baby’s head is located in the mother’s pelvis, but the baby cannot rupture the membrane on its own due to its excessive density. It is unsafe to perform an amniotomy at a late stage, since there is a risk of hitting the baby's head. However, the obstetrician takes such a risk to prevent hypoxia in the baby. An experienced doctor will be able to avoid risk by choosing the safest moment to puncture the membrane, namely, when the amniotic sac is clearly visible at the time of contraction.
Contraindications
A common situation in which the procedure is not performed is an exacerbation of genital infections. Preserving the integrity of the amniotic sac during childbirth helps prevent infection of the baby as it passes through the birth canal. Manipulation is also not carried out if the fetus is in an incorrect position: pelvic or leg, as well as in an oblique or transverse position. The presentation of the umbilical cord or placenta during opening of the amnion can lead to compression of the baby's head and acute hypoxia.
Situations in which vaginal delivery is impossible are also a contraindication:
- complete placenta previa diagnosed by ultrasound during pregnancy;
- undergone operations on the uterus (caesarean section, surgical removal of fibroids, etc.) in the last three years, due to the risk of divergence of an incompetent scar;
- identification of 2 or more scars on the uterus;
- malignant neoplasms of the pelvic organs;
- anatomical features of the pelvis that prevent normal delivery: deformation of bone structures, pronounced narrowing, etc.;
- fetal body weight more than 4500 g;
- scars in the vaginal or cervical area;
- third degree perineal rupture associated with previous childbirth;
- pathology on the part of the fetus: delay in its development or pronounced extension of the head of the third degree;
- other reasons that prevent natural childbirth.
Indications for the procedure
There are situations when amniotomy is necessary to save the fetus and the woman in labor. These include:
- Preeclampsia. About 80% of women experience puffiness and swelling during pregnancy. Preeclampsia is accompanied by high blood pressure. A lot of protein appears in the urine. This is an important indication for piercing the bladder. Although it should be noted that gestosis in later months is much less common. It usually appears in the early stages.
- Post-term pregnancy. On average, a normal pregnancy lasts 38-40 weeks. If the 41-42nd week has passed, there is a reason to think about opening the bubble. With a long gestation period of 42-43 weeks, the placenta begins to age and ceases to perform its functions, and this is very unhealthy for the baby. If the cervix is ready, that is, it is soft, short and allows a finger to pass through, do not hesitate to pierce the bladder, since a lack of oxygen in the fetus can lead to asphyxia.
- Generic weakness. This is when contractions are present, but they are weak and unproductive. Sometimes women in labor themselves cannot stand it and ask to speed up the process through this procedure.
- . In this case, the uterus does not work at 100% due to the large amount of amniotic fluid. It contracts incorrectly and contractions are weak.
- Refusal of amniotomy can provoke placental abruption, which will lead to bleeding and all sorts of complications. Of course, expectant mothers can understand, most want to give birth naturally, but the interests of the child should come first.
Preparing and performing the manipulation
Before prescribing an amniotomy, the necessary studies are carried out: a gynecological examination, anamnesis, and, if necessary, additional examination methods are prescribed. If any contraindications to the procedure are identified, the optimal tactics for labor management are selected - cesarean section, etc. Due to the need to use antispasmodics, it is important to exclude cases of allergic reactions in the woman in labor to such medications.
The algorithm for performing amniotomy involves preparing the woman in labor. 30 minutes before the procedure, antispasmodic medications (Drotaverine, Papaverine) are used in tablet form or as an intravenous injection. The drugs allow you to relax the smooth muscle muscles of the cervix, which facilitates the manipulation.
The procedure is carried out in compliance with sterility. After treating the hands, the obstetrician puts on gloves and inserts the fingers of one hand into the vagina. A special hook-shaped jaw is taken in the second hand. They need to hook the outer membrane of the amnion and, pulling it towards themselves, tear it.
The jaw is inserted along the arm to prevent damage to the structures of the vagina and cervix. The rupture should be made at a certain time - at the maximum of contraction, when the membranes of the amniotic sac are tense and bulge towards the perineum. After the puncture, the instrument is removed, and a finger is inserted into the hole formed in the amnion. It gently widens the hole through which the amniotic fluid comes out.
It is impossible to abruptly release amniotic fluid, as this can lead to prolapse of the legs or arms of the fetus, as well as to hypoxia. The liquid is removed gradually over several minutes. After the amniotic fluid is removed, the process of delivery continues naturally.
Amniotomy technique
The operation is performed without the involvement of a surgeon or anesthesia. It is performed by an obstetrician during a vaginal examination of a pregnant woman. Both regular and planned amniotomy are performed in exactly the same way. It does not cause any discomfort, so women in labor should not be afraid of it. Before starting manipulations, the doctor must obtain the consent of the pregnant woman and inform her about all possible consequences.
The procedure is carried out with a special plastic hook:
- Shortly before the operation, the woman is given a medicine such as No-shpa. After this, all manipulations are carried out on a gynecological chair.
- Before starting the procedure, the specialist checks the condition of the fetus.
- A specialist wearing sterile gloves inserts his fingers into the vagina, expanding it. With the second hand, using an instrument, pry up the amniotic sac and pull it until the amniotic fluid is released.
- When is examination performed after amniotomy? After the procedure, the woman remains at rest for another 30 minutes. Doctors monitor the baby's heartbeat at this time to understand his reaction to the amniotomy.
During the operation, the woman does not feel pain because there are no pain receptors in the amniotic sac.
A sudden burst of water is prohibited, as this can lead to prolapse of the umbilical cord or parts of the baby before labor begins.
Rehabilitation period
Opening the amniotic sac is stressful for the body. In this regard, after the procedure, the patient must remain in a lying position under the supervision of a physician. Specialists monitor the condition of the fetus using cardiac monitoring. After a short period of time, true contractions appear, which mark the beginning of labor.
During the appearance of attempts, the woman is placed on a chair and the birth takes place. On average, 10-20 hours pass from the moment of dissection of the amniotic membrane to delivery. After giving birth, the woman in labor is transferred to a ward, where she is under the supervision of medical personnel.
Amniotomy does not require any specialized rehabilitation measures. Additional medications may be used for medical reasons.
Complications and consequences
When performed correctly, amniotomy is a safe procedure. But, in rare cases, childbirth after puncture of the bladder can be complicated. Among the undesirable consequences of amniotomy are:
- Prolapse of the umbilical cord or fetal limbs into the vagina of the woman in labor.
- Injury to the vessels of the umbilical cord during its membrane attachment, which may be accompanied by massive blood loss.
- Deterioration of uteroplacental blood flow after manipulation.
- Changes in fetal heart rate.
There is also a risk that opening the amniotic sac will not give the desired result and labor will not become active enough. In this case, the use of drugs that stimulate contractions or a cesarean section will be required, since a prolonged stay of the child without water threatens his life and health.
Any intervention in the body has its consequences and they are not always positive. But compliance with all conditions for amniotomy allows you to reduce the risk of complications to a minimum. Therefore, if there are indications, you should not refuse to open the amniotic sac and other necessary manipulations during childbirth.
Author: Yana Semich, Anna Sozinova specially for Mama66.ru
Possible complications
If the indications and contraindications for the procedure, as well as the technique for performing amniotomy, are observed, negative consequences for the woman and fetus do not develop. However, in some cases, the following complications may occur:
- as a result of sudden removal of amniotic fluid, there is a risk of developing acute hypoxia associated with changes in environmental conditions;
- weakness or incoordination of labor, rapid labor is less common, which can cause birth trauma;
- infection of the child during passage through the birth canal;
- intrauterine hemorrhage resulting from damage to large vessels that can pass through the membrane of the fetal bladder;
- loss of the child’s arms, legs or individual umbilical cord loops.
If complications arise, the obstetrician chooses tactics to eliminate them and continue labor. According to statistics, such conditions occur in 1 woman out of 1000.
Indications for manipulation
Amniotomy is performed in the following cases:
- post-term pregnancy
- if labor does not occur on its own after 42 weeks of pregnancy. This condition threatens the baby with hypoxia and birth injuries, complications for the mother during labor in the form of ruptures and bleeding; - Preeclampsia
is a malfunction in the body of a pregnant woman, in which vasospasm and circulatory disturbance occur. The disease is characterized by high blood pressure and swelling. A severe form of gestosis can lead to the death of the fetus and even the death of the mother if treatment is not started in a timely manner and the onset of labor is not promoted; - Rh conflict
- occurs when a woman with negative Rh blood carries a child with a positive Rh factor. In this case, the mother’s immune system perceives the fetal red blood cells entering her blood as foreign and begins to actively produce antibodies aimed at destroying them. At some point, the baby’s body cannot cope with replenishing the loss of red blood cells, and severe oxygen starvation occurs. To save the fetus from death, it is necessary to induce the birth process through amniotomy; - pathological preliminary period
- characterized by irregular contractions, prolonged pain in the lower abdomen. One way to induce effective labor is amniotomy; - weak labor
is a condition in which the dilation of the cervix slows down and contractions weaken. If the amniotic sac does not open independently, then amniotomy in this case is an effective means of inducing active labor; - flat bladder
- this condition is observed, as a rule, with oligohydramnios. Normally, there should be approximately 200 ml of amniotic fluid in front of the fetal head. When there is little anterior water, the membranes of the amniotic sac are stretched on the baby's head. For labor to be effective, artificial opening of the bladder will be required; - polyhydramnios
- due to the high content of amniotic fluid, the walls of the uterus are stretched and weakly contract. To activate the birth process, they resort to the amniotomy procedure; - low location of the placenta
- after the discharge of amniotic fluid, the fetus descends into the pelvic inlet and presses the placenta, preventing its premature detachment. Manipulation in this case will avoid bleeding.
Indications for amniotomy.
The main indication for amniotomy is stimulation of labor. As already mentioned, after the cervix is dilated by 4-5 centimeters, an intact amniotic sac no longer helps, but can also inhibit labor. Often after an amniotomy, contractions intensify and the total duration of labor can be reduced to one hour.
Amniotomy can also be used as a method of induction, that is, inducing labor if it does not begin on time. True, this method is rarely used independently, since the more time that passes after the opening of the amniotic sac before the birth of the child, the greater the risk of infection, and it is difficult to predict when labor will begin. Therefore, amniotomy is mainly combined with other induction methods, for example, with the administration of oxytocin.
After puncturing the amniotic sac, you can monitor the baby’s heart rate by placing an electrode on his head (direct CTG), which is sometimes required for a more accurate assessment of the baby’s condition.
Also, amniotomy allows you to examine the amniotic fluid, which helps to understand how the child feels. For example, if the waters are contaminated with meconium (original feces), then fetal hypoxia can be assumed.
Amniotomy: essence and purpose
Amniotomy is the opening of the fetal bladder to stimulate labor.
The essence of amniotomy is that the opening of the amniotic sac, which surrounds the baby in the uterus and keeps water from pouring out, does not occur naturally, but through medical intervention.
There are several ways to carry out this manipulation:
- cut;
- tear with fingers;
- inject with a special medical object.
When the membranes rupture, a hormone called prostaglandin is released, which helps stimulate the cervix and uterus to give birth naturally. There is also an opinion that during the procedure the birth canal is irritated, which speeds up the process of the birth of a child.
Indications
The main indication for prescribing an amniotomy is when the pregnancy is truly post-term (this is when obstetricians do not observe natural labor at 42 weeks).
Waiting here is simply unacceptable - it is dangerous for both mother and baby, as it entails:
- deterioration of placenta functions;
- development of fetal hypoxia;
- complications during childbirth (ruptures, poor health of both).
Severe gestosis (late toxicosis) is the second reason why an amniotomy should be performed. In the case of a full-term pregnancy and there is no threat to the baby, the doctor can make a positive decision only taking into account the consent of the woman in labor.
When the birth canal is not ready and the condition of the mother and child worsens, a caesarean section is performed.
Amniotomy: consequences.
If an amniotomy is performed too early, the likelihood of infection in the mother or baby increases. Once the integrity of the bladder is broken, bacteria can enter the uterus and there is a risk of developing an infection.
A rare consequence of amniotomy is umbilical cord prolapse. If the fetal head is not pressed against the entrance to the pelvis, then the breaking of water can cause the umbilical cord to prolapse into the birth canal, which leads to impaired circulation of the fetus and requires an immediate cesarean section.
In most cases, puncture of the amniotic sac does not lead to negative consequences for either the mother or the child. Sometimes artificial rupture of the fetal membranes is simply necessary, because the membranes can remain intact until the very attempts, which is fraught with a protracted course of the second stage of labor and fetal hypoxia. Nevertheless, amniotomy is a medical intervention and it should not be performed on all women in labor, but according to indications.
Video: Amniotomy
Approximately 7-10% of women in the maternity hospital undergo an amniotomy. Pregnant women who hear about this manipulation for the first time are frightened by it. Natural questions arise: amniotomy, what is it? Is it dangerous for the child? Not knowing why this procedure is performed, many expectant mothers are negative in advance. Information about the indications, contraindications and possible consequences of amniotomy will help you understand whether your fears are justified.
Amniotomy is an obstetric operation (translated as amnion - water membrane, tomie - dissection), the essence of which is to open the amniotic sac. The amniotic sac and the amniotic fluid that fills it play an important role in the normal intrauterine development of the child. During pregnancy, they protect the fetus from external mechanical influences and microbes.
After opening or natural rupture of the amnion, the uterus receives a signal to expel the fetus. As a result, contractions begin and the baby is born.
The manipulation of opening the amniotic sac is carried out with a special tool in the form of a hook at the moment when the bubble is most pronounced, so as not to damage the soft tissues of the baby’s head. Amniotomy is a completely painless operation, since there are no nerve endings on the membranes.
How is amniotomy performed?
The amniotomy procedure is performed by an obstetrician-gynecologist in a maternity hospital. A special medical instrument is used, which is called a “branch” and has the shape of a hook. The doctor makes a hole in the membrane with an instrument and then uses his fingers to widen the hole. At the same time, the specialist controls the volume of amniotic fluid leakage.
After this, the woman needs to lie down for half an hour. During this period, doctors monitor the condition of the woman and her fetus: they monitor the heartbeat, record the appearance of contractions, and analyze general indicators. Depending on how the expectant mother’s body responded to the procedure, doctors draw up a plan for further actions.
When is it needed?
Basically, an amniotomy is performed during childbirth if the fetal sac has not ruptured on its own. But there are situations in which urgent delivery is necessary. In this case, puncture of the amniotic sac is performed even in the absence of contractions. Indications for it are:
- Post-term pregnancy.
A normal pregnancy lasts up to 40 weeks, but if the period is 41 weeks or more, the question arises about the need to induce labor. During a post-term pregnancy, the placenta “grows old” and can no longer perform its functions in full. Accordingly, this affects the child - he begins to experience a lack of oxygen. If there is a “mature” cervix (the cervix is soft, shortened, and allows one finger to pass), the woman’s consent and there are no indications for a cesarean section at the moment, a bladder puncture is performed to induce labor. In this case, the fetal head is pressed against the entrance to the pelvis, and the volume of the uterus decreases slightly, which contributes to the occurrence of contractions. - Pathological preliminary period.
The pathological preliminary period is characterized by long, several days of preparatory contractions, which do not develop into normal labor and tire the woman. During this period, the child experiences intrauterine hypoxia, which resolves the issue in favor of prenatal amniotomy. - Rhesus conflict pregnancy.
When the mother's blood is negative and the fetus's is positive, a conflict arises regarding the Rh factor. At the same time, antibodies accumulate in the blood of the pregnant woman, which destroy the red blood cells of the fetus. If the antibody titer increases and signs of hemolytic disease of the fetus appear, urgent delivery is necessary. In this case, the amniotic sac is also punctured without contractions. - Preeclampsia.
This is a serious disease of pregnant women, characterized by the occurrence of edema, the appearance of protein in the urine and increased blood pressure. In severe cases, preeclampsia and eclampsia are added. Preeclampsia negatively affects the condition of the woman and the fetus, which is an indication for amniotomy.
If labor has already begun, with certain characteristics of the expectant mother’s body, you will also have to resort to opening the fetal sac. Indications for which amniotomy is performed during childbirth:
- Flat amniotic sac.
The amount of anterior water is approximately 200 ml. A flat amniotic sac is practically the absence of anterior waters (5-6 ml), and the membranes are stretched on the baby’s head, which prevents normal labor and can lead to a slowdown and cessation of contractions. - Weakness of generic forces.
In the case of weak, short and unproductive contractions, the dilation of the cervix and the advancement of the fetal head are suspended. Since amniotic fluid contains prostaglandins that stimulate cervical dilatation, early amniotomy is performed to enhance labor. After the procedure, the woman in labor is observed for 2 hours and, if there is no effect, the issue of birth stimulation with oxytocin is decided. - Low location of the placenta.
With this position of the placenta, as a result of contractions, its detachment and bleeding may begin. After amniotomy, the fetal head is pressed against the pelvic inlet, thereby preventing bleeding. - Polyhydramnios.
The uterus, overstretched by a large amount of water, cannot contract correctly, which leads to weakness of labor. The need for early amniotomy is also explained by the fact that its implementation reduces the risk of prolapse of umbilical cord loops or small parts of the fetus during spontaneous rupture of water. - High blood pressure.
Preeclampsia, hypertension, heart and kidney diseases are accompanied by high blood pressure, which negatively affects the course of labor and the condition of the fetus. When the amniotic sac is opened, the uterus, having decreased in volume, frees nearby vessels and the pressure decreases. - Increased density of the amniotic sac.
Sometimes the membranes are so strong that they cannot open on their own even with the cervix fully dilated. If an amniotomy is not performed, the baby may be born in the amniotic sac with water and all membranes (in the shirt), where it can suffocate. This situation can also lead to premature placental abruption and bleeding.
Mandatory conditions for conducting
Even if there are medical indications, it is not always possible to perform an amniotomy. In order to perform the manipulation, certain conditions must be present:
- there should be only one fruit;
- the position of the child in the uterus is cephalic;
- pregnancy is 38 weeks or more;
- fetal weight no more than 3 kg;
- women meet established standards;
- missing;
- the birth canal is ready for the advancement of the baby (examination confirms shortening of the cervix).
Technique of the operation
Half an hour before amniotomy, antispasmodics (No-spa) are usually administered.
The bladder is opened using a special hook during a vaginal examination. The puncture is absolutely painless, it is advisable to perform it outside of a contraction, when the bladder is not tense.
During amniotomy, only the anterior waters are released; they are located in front of the baby's head. The water is released slowly to prevent prolapse of parts of the fetal body or the umbilical cord.
After opening the bladder, the woman in labor needs to lie down for at least half an hour. It is necessary to monitor the fetal heartbeat (CTG).
Indications for amniotomy
The procedure is performed to solve medical problems such as artificial induction of labor or assistance in childbirth.
In what cases is amniotomy prescribed even before the natural process of birth of the baby begins:
- post-term pregnancy confirmed by diagnostic studies;
- gestosis in late pregnancy;
- the presence of Rh conflict;
- detection of serious pathologies in the expectant mother from the heart muscle, kidneys, lungs, metabolic and autoimmune processes;
- abruption of a normally located placenta in late pregnancy;
- fetal diagnosis;
- prolonged failure of labor;
- prolapse of the membranes (protrusion into the cervix);
- over 28 weeks.
That is, the amniotomy procedure is carried out when it is necessary, for medical reasons, to urgently induce labor artificially. Usually, within 12 hours after the manipulation, the woman begins to experience contractions. If labor has not begun after the specified time, doctors decide on the need to use medications or perform a cesarean section.
An amniotomy is often performed during childbirth. The doctor will recommend such manipulation in the following cases:
- the fetal bladder did not rupture on its own when the cervix was 8 cm dilated;
- multiple pregnancy;
- lack of amniotic fluid (oligohydramnios);
- excess intrauterine fluid (polyhydramnios);
- long;
- placental presentation;
- weak labor, lack of contractions or pushing;
- post-term pregnancy;
- high blood pressure in a woman.
Childbirth after amniotomy
How long after amniotomy can you give birth or in what week can it be performed? These are the questions that inexperienced women in labor ask doctors.
As a rule, according to women’s reviews, it is this process that significantly shortens the period of labor, since:
- Contractions become more pronounced and painful;
- Soon the attempts begin;
- It is possible to give birth literally in 10-30 minutes.
In special cases, labor may occur within 6-8 hours. Unfortunately, no process goes without complications. For example, with amniotomy there may be complications that are caused by a violation of the integrity of the blood vessels.
In other words, among the complications we can note the formation
:
- Bleeding that develops under the condition that at the time of opening the bladder, a large blood vessel located on the surface of the fetal membrane was touched;
- A dropped loop of the umbilical cord or small parts of the fetal body, due to improper release of water;
- Deterioration of the fetus' condition;
- Weakening or, conversely, strong acceleration of labor;
- Fetal infection.
Such moments are quite rare in medical practice, but they are not excluded and therefore you need to trust your health only to trusted specialists.
What it is
Amniotomy or puncture of the amniotic bladder is a procedure for artificially breaking the integrity of the fetal membrane during childbirth.
As a rule, this process occurs independently during the normal course of labor. The outpouring of water is accompanied by complete dilatation of the uterine cervix. This serves as a signal that the baby is beginning to move along the birth canal.
However, in some cases the bubble does not burst on its own. In this case, medical attention is required.
Using a special tool that resembles a hook, the bubble is pierced.
The procedure does not cause pain to the woman. For a child, amniotomy is usually also safe.
Types of punctures:
- prenatal;
- early amniotomy;
- timely;
- belated.