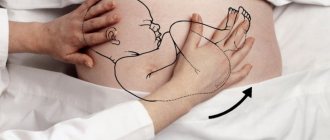
Indications for the use of an obstetric pessary
Modern medicine makes every effort to maintain pregnancy to full term and uses various methods to do this to prevent the onset of early labor.
The use of a uterine pessary, also called a relief ring, makes it possible to exclude early dilatation of the cervix and prevent the threat of miscarriage.
Such a remedy is a mechanical way to prevent the threat of interruption, and is installed strictly as prescribed by the observing gynecologist for possible pathological abnormalities:
- When diagnosing or preventing the development of isthmic-cervical insufficiency
- To reduce the load and maintain the uterus in the required position
- If damage occurs or sutures come apart in the cervical area
The pessary is indicated for use starting from the second half of pregnancy and is removed 7-10 days before the estimated time of birth, in the absence of complications.
The need to use a pessary is determined by the gynecologist observing the pregnancy.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency
ICI is a common pathology in which the initial opening of the cervical canal occurs.
- This complication is dangerous because it leads to weakening of the support of the amniotic sac.
- A gradual increase in fetal weight increases intrauterine pressure, which leads to squeezing out the membranes into the canal, dilation of the cervix and the onset of labor before the due date.
- When the canal is open, the risk of external infections increases, which can trigger the onset of inflammatory processes and the threat of miscarriage.
The reasons for the development of ICI can be various factors:
- Physiological structure of the cervix.
- The presence of damage to the cervix after previous childbirth, abortion or surgery.
Determination of the position of the fetus and the condition of the uterus is determined using ultrasound
Contraindications
Unfortunately, there are pregnant women for whom the installation of an obstetric ring is contraindicated. The device cannot be used in the following cases:
- if an allergy to the material of the device is detected;
- when pathologies are detected in the fetus that require abortion;
- with a neck diameter less than 50 mm;
- if prolapse of the membranes has occurred;
- with constant bleeding, increased tone of the uterus, dilatation of the cervix;
- in case of infectious and inflammatory processes in the vagina at the time of installation.
Obstetric pessary – what is it?
Early cervical dilatation in the past meant termination of pregnancy and could lead to fetal death. For a long time, the method of suturing the cervix was used to preserve the fetus, but the disadvantages of this method were the risk of infection during surgery and the use of general anesthesia.
The obstetric pessary began to be used in gynecological practice relatively recently, but this method has already successfully proven itself and is actively used to preserve and normalize pregnancy. The effectiveness of the method is up to 80-85%.
- The pessary is designed in accordance with the anatomical features of the woman’s body structure. The pessary is a silicone or plastic elastic ring made of hypoallergenic material. It is preferable to use silicone products. They have a softer structure, so they are not felt when worn. The edges and surfaces of the product are made absolutely smooth, so they do not damage the internal tissues. In addition, there are other forms, the use of which can be recommended for various pathologies of pregnancy.
- A uterine pessary is a disposable product in sterile packaging that has a certain period of use. Before purchasing from a pharmacy, you should obtain detailed medical advice and pay attention to the expiration date and integrity of the packaging.
- The shape and material from which the ring is made may vary depending on the manufacturer. Products vary in size. The price of a product from Russian manufacturers ranges from 500 to 1000 rubles. Analogs from foreign manufacturers will cost more.
The convenience and effectiveness of this product will depend on the correct shape and size.
Obstetric pessary
Content
- 1 History of pessaries
- 2 Types of pessaries 2.1 Obstetric pessaries 2.1.1 Types of obstetric pessaries 2.1.1.1 Domed obstetric pessary
- 2.1.1.2 Obstetric ring pessary
- 2.1.1.3 Obstetric relief pessary
- 2.2.1 Types of urogynecological pessaries
How the pessary works
The need to use a pessary is due to its action:
- The membranes protruding into the open canal cease to affect the cervix.
- The opening of the cervix closes because the structure of the ring helps to compress and hold its walls.
- A mucus plug forms, creating a barrier to infection.
The uterine pessary is successfully used to treat pathologies and to prevent miscarriage in the following cases:
- Women who have already suffered miscarriages.
- For expectant mothers with high fetal weight or multiple pregnancies.
- Pregnant women whose occupation involves intense physical activity.
- The pessary is not only a mechanical support for the uterus, but also a psychological protection for the expectant mother, who for some reason doubts the successful gestation and delivery.
The pessary is installed by a supervising physician.
Reasons for installation
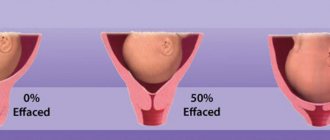
During the normal course of gestation, the cervix is closed almost until the end of the gestation period. A few weeks before giving birth, the cervix dilates 1-2 centimeters. It holds the unborn baby, amniotic fluid and amniotic fluid in the uterus.
With ICI, the cervix dilates earlier than expected. Gynecologists attribute 9 etiological factors to the most common causes of complications:
- History of cervix ruptures.
- Surgical interventions on the neck.
- History of abortion.
- Carrying twins or triplets—multiple pregnancies increase pressure on the cervix.
- Congenital anatomical defect of internal organs.
- The source of the infectious process is in the genital tract.
- Constant physical activity during the gestation period.
- Increased amount of amniotic fluid.
- Increased secretion of male sex hormones.
The installation of a pessary is recommended for women with a cervical length of less than 3 centimeters. Also, medical manipulation is indicated for expectant mothers with a softened and smoothed uterine os.
An additional indication for the introduction of an obstetric device is low placentation. The pathology is accompanied by a high risk of spontaneous abortion. The pessary prevents miscarriage and premature birth.
How is a pessary installed?
- A pessary can only be installed by a supervising doctor in a hospital setting or in a antenatal clinic.
- The installation procedure is painless and is performed in a gynecological chair, without the use of any type of anesthesia. Some women report short-term discomfort.
- One of the conditions for successful installation is a healthy vaginal microflora, so before the procedure it is recommended to undergo appropriate tests and, if necessary, undergo treatment.
- Before inserting the ring, the bladder must be completely emptied.
- To avoid contraction of the uterine muscles and the appearance of pain, it is recommended to take an antispasmodic agent, for example, No-spa, in the dosage prescribed by the doctor 30 minutes before the start of the procedure.
- For better passage, the product is treated with gel or Vaseline immediately before use, and then inserted through the vagina and secured to the cervix.
- If the size is optimally selected and placed correctly, the ring will not be felt when worn before childbirth.
A support ring is recommended for multiple pregnancies
Recommendations after installing the pessary
To avoid complications, additional preventive medications may be prescribed:
- Antifungal suppositories for vaginal sanitation
- Hormonal agents
If no deviations are observed during the period of using the support ring, the following recommendations must be followed:
- It is necessary to be under constant medical supervision to monitor the condition of the cervix and the position of the ring.
- Since the ring is a foreign body, you will need to undergo regular tests to prevent the development of infectious diseases. Typically, examination and analysis of microflora is carried out every 2-3 weeks, ultrasound - every 4 weeks.
- While wearing a pessary, complete sexual rest is prescribed, so in order to successfully preserve the fetus, it is necessary to abstain from sexual contact.
- Physical activity and long trips should also be minimized or eliminated, and try to avoid stressful situations and hypothermia.
- Removal of the pessary is carried out on an outpatient basis or in a hospital at 37-39 weeks, when the fetus is considered to be at term and the risk of early labor is excluded.
- Natural childbirth in the presence of a pessary is impossible, therefore, at the onset of labor, its urgent removal is necessary.
After installing the ring, you must follow the recommendations
Contraindications to further use of the pessary
Despite the effectiveness and safety of this product, there are a number of indications in which the ring must be urgently removed:
- The appearance of bloody or mucous discharge.
- The presence of serious pathologies of the fetus or a danger to the health of the mother, in which termination of pregnancy is necessary.
- The release of membranes.
- Leakage of amniotic fluid.
- Acute infectious inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system.
- Pain or the development of mechanical colpitis - such symptoms indicate improper installation or displacement of the ring.
- Suspicion of a frozen pregnancy.
You cannot remove the pessary yourself. In case of any discomfort, pain or other complications, you should consult a doctor immediately.
If you experience pain, discharge or suspect the onset of labor, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Possible complications
What might cause you anxiety while wearing a pessary? And when do you not need to wait for the next visit to the antenatal clinic, but should you go there immediately?
If you have not previously observed any discharge, but after installing the unloading ring they appear, this is not yet a reason to sound the alarm. An increase in the amount of leucorrhoea soon after the procedure is a natural reaction of the vaginal mucosa to the appearance of a foreign body in it.
You should rush to see a doctor if:
- brownish or bloody discharge is observed, which appeared already in the process of wearing the ring (ichor can be released immediately after the procedure, but in scanty quantities and not for long);
- the discharge has a yellowish or greenish color (they indicate the development of a bacterial infection in the vagina);
- the discharge is abundant, liquid, transparent and has a slight sweetish odor (which may be a sign of a violation of the integrity of the amniotic sac).
Mucous discharge may appear even after the ring is removed, and in quite large quantities. This is cervical mucus that has accumulated while wearing a pessary. This phenomenon does not require any intervention from doctors. After some time, everything will return to normal on its own.
Displacement of the pessary during wearing often causes inflammation of the vaginal mucosa - colpitis. This disease is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and itching in the vagina. If you notice similar symptoms in yourself, immediately go to the doctor and start treatment.
Can a pessary fall out? In the literal sense of the word - no. It may move into the vagina. This happens extremely rarely, but it does happen. A woman will immediately feel it. The ring will put pressure on the front wall of the vagina (this is especially felt when changing body position and sitting).
If the pessary becomes dislodged, you should consult a doctor.
There may be several reasons for the displacement of the pessary:
- The device is not selected correctly.
- The ring was installed unprofessionally.
- The expectant mother did not follow the instructions for wearing the obstetric discharge ring.
Statistics show that the occurrence of complications after the installation of a gynecological ring is a fairly rare occurrence. However, there are still cases recorded when, as a result of a doctor’s violation of the technique of performing this manipulation, the patient experiences certain complications. For example, if the uterine ring is poorly fixed, it may move or even fly off, which can give impetus to the development of colpitis.
Removal of the pessary ahead of schedule may be associated with damage to the integrity of the membranes before the expected end of gestation, as well as in the event of premature labor. In addition, endometritis can cause spontaneous removal of the pessary.
In addition to these complications, the negative consequences of improper installation of the gynecological ring can be:
- ulcerative lesion of the vaginal wall;
- bleeding from the genital tract;
- deformation of the vaginal walls. In difficult cases, a fistula may form between the vagina and rectum;
- constipation;
- an unnatural protrusion of the rectum from the vaginal wall.
Reviews from women
Oksana, 24 years old I was fitted with a pessary at 26 weeks. The threat was due to low presentation, the uterus was in constant tone, dilatation was 10 mm. It didn’t hurt at all - almost like a simple examination by a gynecologist. The main thing is to relax and not be afraid - everything took a couple of minutes. After installation, walking became somehow calmer. They removed it at 37 weeks, also painlessly. 12 hours after removal, contractions began.
Daria, 28 years old I was diagnosed at 23 weeks, my cervix was 29 mm and they said that the baby was very low. At first it was scary, because I had read that it was painful to install and many then suffer from thrush. My procedure went quickly, I wouldn’t say it was painful, but rather unpleasant. The main thing is that the doctor is experienced and the size is appropriate. There was a threat throughout the pregnancy, and I finally gave birth at 36 weeks. They removed the ring already in the maternity hospital, when they brought me in with contractions.
Karina, 31 years old I was fitted with a pessary at 30 weeks, from the German company Dr-Arabin, the cervix was 21 mm, but the pharynx was closed. The procedure is unpleasant, but quick. Then you don’t feel at all whether he is there or not. Ginipral was prescribed for 3 days, Utrozhestan until 32 weeks, 1 tablet per day. The doctor advised complete rest.