No woman is immune from complications during pregnancy. Pathologies that occur early and do not manifest themselves externally throughout pregnancy include single and multiple amniotic cords. With the onset of pregnancy, the amniotic sac (amnion) begins to develop in the uterus, which produces amniotic fluid. Amniotic cords are formations that look like threads, constrictions or fusions. They are formed from fibers of the inner epithelial tissue of the amnion. The cords can be stretched between its walls in the anteroposterior or anterolateral projection, attached to it at one end, or freely floating in the amniotic fluid.
Amniotic band syndrome is a term used in cases where such formations wrap around and compress the fetus itself, the umbilical cord or certain parts of the placenta so much that this can negatively affect the formation of organs and systems, cause the occurrence of anatomical defects and disruptive defects, terminate pregnancy or cause fetal death.
Causes
Accurate statistics on the detection of amniotic band syndrome are not yet available. The number of women giving birth with this pathology varies from 1 in 1,200 to 1 in 15,000 cases. Moreover, in 7-8 cases out of 10 identified, the cords resolve or rupture on their own, and do not lead to the development of congenital anomalies.
Medical scientists still cannot accurately name the mechanism and causes of amniotic cords. Therefore, research continues to confirm the following assumptions of gynecologists:
- Amniotic bands can be the result of minor tears in the inner lining of the membranes that occur between 4 and 18 weeks of pregnancy. The fibrous threads of the internal epithelium that are torn off from the amnion “stick” to the fetus, and as it grows, they are pulled or pressed into the places to which they are stuck.
- It is likely that the cause of the strands lies in intravascular pathologies, which negatively affect the blood supply to the amniotic bladder and lead to duplicative detachments.
- Anatomical constriction syndrome may be caused by diseases and conditions that a woman had before pregnancy or developed with its onset:
- acute or chronic endometritis;
- infectious diseases of the embryo;
- oligohydramnios and chronic leakage of amniotic fluid;
- pathology of the cervix or isthmus of the uterus;
- genital injuries;
- violation of sterility during invasive gynecological examination;
- teratogenic effects on the embryo of alcohol, drugs, medications, radiation.
chorioamnionitis;
Nevertheless, it has been established that in the vast majority of cases, the appearance of both single and multiple amniotic cords is not a consequence of a genetic mutation and is not inherited. Their occurrence also does not depend on the woman’s age, her experience of childbirth, and the likelihood of their development in subsequent pregnancies is difficult to predict.
What to do if a septum is discovered during pregnancy?
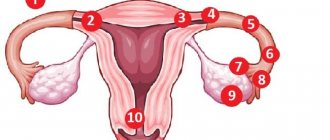
The septum is easy to detect on an ultrasound examination - triangular tissue divides the uterus in two. A complete septum is a lot of problems, so many experts recommend removing it before conception. If it is incomplete, then it is sometimes left, since 50% of women can normally carry and give birth to a baby without pathologies.
If the septum is found during pregnancy. Most gynecologists try not to touch anything and actively monitor the development of the embryo.
The doctor regularly examines the patient, carefully listens to the fetal heartbeat and feels the size of the uterus. A special role is given to ultrasound, which, perhaps, puts all the dots. The pregnant woman herself is shown:
- lead a healthy lifestyle (never smoke, drink alcohol or take drugs);
- refuse harmful production and use of any chemicals in everyday life;
- consume as many vitamins as possible, eat well and properly;
- do not overwork, avoid heavy physical labor;
- walk more in the fresh air;
- If you experience the slightest discomfort, go to the hospital immediately.
You should listen to all the recommendations of the gynecologist, because the outcome of pregnancy depends on how accurately the woman follows everything.
But this continues as long as everything matches the deadlines and there are no deviations. In case of a hopeless situation, endoscopic surgical treatment is offered. This restores fertility and minimizes all risks of complications. The procedure is low-traumatic and subsequent pregnancy will not be problematic. Sometimes such a diagnosis serves as a reason for a caesarean section.
If the pregnancy had to be terminated or a spontaneous miscarriage occurs, doctors wait 2-3 months until the body recovers, and only then begin to act. Before surgical treatment, hormonal medications are prescribed, which the woman must take for about three months. After them, the endometrium becomes thinner. If there is no time to wait, then the operation is performed in the 1st phase of the cycle and hormonal therapy is optional.
To clarify the anomaly and to observe it in the future, laparoscopy, hysteroscopy or fibrohysteroscopy are used.
If the patient is given the opportunity to choose a corrective surgical intervention, then it is better to choose a technique that preserves the muscular layers of the uterus. This will improve the functionality of the organ during childbirth and during pregnancy. Previously, the Jones operation, according to Strassmann, Tompkins, was always traditionally used. There are many disadvantages to such surgical interventions, namely: the abdomen was cut, protectors were introduced into the uterine cavity, the woman had to stay in the hospital for a long time, after which adhesions and synechiae formed. After such treatment, spontaneous delivery was rare, because the uterus could simply rupture, so a cesarean section was performed two to three weeks later. It is possible to carry out the operation now with ordinary surgical intervention, but after that the wound takes a very long time to heal. The recovery period can last up to 12 months, as there are serious injuries. The duration of the operation itself is much more significant, and there is blood loss.
It is still preferable to remove the defect using hysteroresectoscopy under general anesthesia. If necessary, laparoscopic observation is carried out. This method does not damage the muscles of the organ and during childbirth the contractility of the middle layer is preserved. After the manipulation there is no extensive bleeding or adhesions. After treatment, the chances of becoming a mother increase several times, and you can give birth on your own.
If the operation is performed in a resestoscope, then a double loop, special ultra-flexible and thin scissors or a spherical electrode are used. Thin partitions are removed using scissors. It is difficult to cut through large septa; it is advisable to use a resestoscopy loop. The branches conduct electricity to the organ, the loop cuts through the septum. First, this happens from below, then the movement goes to the bottom, and this is how a smooth surface is formed.
During resection, the cervix dilates. To do this, Hegar dilators are used, then a resectoscopic sleeve is inserted into the uterine cavity. If there is local or diffuse bleeding, hemostasis is performed.
The pipe mouths must be visualized at all times. To see the thickness of the organ wall, a specialist uses a luminous ball. If there is a sanitary groove on the organ, then everything is done extremely carefully. To stretch the uterine cavity, a special liquid is injected through a hysteroscopic pump. The most commonly used solutions are Mannitol and Reopolyglucin.
Diagnostics
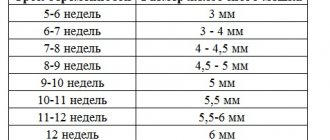
Differentiation of amniotic band syndrome occurs after an ultrasound examination reveals amniotic folds and bands that are not connected to the fetus, or by defects such as abnormal development of the limbs, head or body. Structural abnormalities can be seen on a monitor screen or on a printed photo only during an instrumental examination after the 12th week of pregnancy.
Diagnosis of amniotic septa is difficult. If their existence is suspected or there is a hint of pathology in fetal development, additional studies are prescribed: CT, MRI, transvaginal volumetric echography with colorectal dosage or 3D ultrasound. If the diagnosis is confirmed, then further regular instrumental monitoring is mandatory.
Should I worry if an amniotic cord is detected in the uterine cavity during pregnancy that is not in contact with the baby? When an amniotic cord is detected that is not connected to the fetus, but which is stretched between the front and side walls of the bladder, such an anomaly is recorded in the pregnant woman’s chart, since the pathology can affect the functioning of the amniotic sac, cause oligohydramnios, and subsequently affect labor.
If multiple amniotic cords are detected, which can or have already led to the development of defects in the fetus, the tactics of pregnancy management or the question of its termination is within the competence of a council consisting of a gynecologist, geneticist, diagnostician and neonatologist surgeon. The expectant mother is required to be informed about the likely physical and mental state of the unborn child, as well as about the possibilities of orthopedic care and prosthetics.
The influence of pathology on the course of labor
An intrauterine septum can cause:
- Premature birth. They begin due to the pressure of the septum on the fetus, which has already become quite large.
- Deterioration of the contractility of the uterus: the muscles of the second half of the uterus (on the side where the fetus did not develop) did not stretch as much as it grew. As a result, incoordination or weakness of labor develops. Less commonly, the intrauterine membrane becomes the cause of a life-threatening condition for the mother in labor, when after the end of labor the uterus relaxes, which causes heavy bleeding, which can only be stopped by removing it.
Such complications are more typical for a complete intrauterine membrane.
How to remove amniotic cord in the uterine cavity during pregnancy
Pharmacological drugs and non-invasive methods that would help resolve amniotic cords have not yet been invented, but medicine does not stand still. Recently, it has become possible to get rid of such formations using fetal surgery.
Operations for intrauterine excision of abnormal formations are still classified as experimental and are carried out only in clinical centers in Cincinnati, San Francisco and Melbourne. Surgeons selectively operate in cases where there is a threat of fetal death - with a pronounced constriction of the umbilical cord, compression in the head, neck, torso or in the area of the hip joints.
Prevention
At the moment, there is no prevention of amniotic band syndrome. However, when a child is born with a neural tube defect, its origin should be differentiated. The risk of pathology during the second pregnancy is 5%, and during the third it increases to 10%. In this case, pregnancy planning and the following prevention are recommended - daily intake of 400 mcg of folic acid for 3-4 months.
At the same time, geneticists warn that a sporadic risk of developing multiple amniotic cords exists in women with the genetic pathology Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, and in Meckel Syndrome with an autosomal recessive type of inheritance, the prognosis for the recurrence of the complication reaches 25%.
All other women who had a pregnancy with amniotic band syndrome, despite the statistical 2% risk of developing a similar complication in subsequent pregnancies, are recommended to be monitored at a medical genetic center. It has all the conditions for accurate diagnosis in the early stages and competent monitoring of the development of pathology, which will allow the woman and the council of doctors to make a timely decision on artificial termination of pregnancy, in cases where the fetus is incurable or non-viable.
Possible consequences
Single or multiple amniotic cords may, but not necessarily, lead to fusion of the walls, decreased elasticity and inhibition of growth of the amniotic sac, oligohydramnios, as well as to the following conditions and destructive changes in the fetus:
- fetal hypoxia;
- swelling of the head, limbs or parts thereof;
- circular constrictions of limbs and fingers;
- tissue necrosis;
- atrophy, paresis, muscle paralysis;
- amputation of body parts or a separate organ;
- torsions, false or true knots, umbilical cord rupture;
- pseudarthrosis, fused toes, clubfoot, defects or absence of nails;
- defects of the nasal septum, lip or palate;
- strabismus, drooping upper eyelid, delayed development of the eyeball and lacrimal gland;
- cleft of the anterior abdominal wall;
- infantile hemangioma;
- miscarriage, death of the fetus inside the womb or directly during childbirth.
According to statistics, in most cases this syndrome leads to flat feet and deformities of the fingers and hands.
FAQ
We will try to clearly and briefly answer the most popular questions found on the Internet.
How to recognize: twins or fusions?
In the early stages of pregnancy, when it is impossible to determine how many fetuses are developing - one or several, with identical twins with one placenta, but individual amniotic sacs, their membranes may look so thin due to ultrasound effects that in the photo echo studies will resemble an amniotic cord . Therefore, a misdiagnosis is possible – a single pregnancy with amniotic band syndrome.
The ability to differentiate one fetus with amniotic band syndrome from monochorionic diamniotic twins is possible only at a later date, when the beats of both hearts are visible. But if on ultrasound the thickness of the membrane is visualized as more than 1.9 mm, then these are definitely twins with two placentas.
Until when is it dangerous?
Amniotic band syndrome poses a threat until the last day of pregnancy, including the moment of birth itself. But the type of defect depends on the immediate time of occurrence of these strands, according to some authors. For example, if the amniotic cord formed on the 42nd day of pregnancy, then polydactyly of the foot occurs, if after the 9th week, then a cleft palate, and if after the 10th week, prolapse of the intestine.
Folk remedies that can resolve the cord?
What needs to be done to resolve the amniotic cord? Dissolving single or multiple amniotic cords is a task that is absolutely impossible to solve even with the help of official medicine and pharmacological drugs, not to mention folk methods and remedies. Taking witchcraft potions or performing dubious procedures can cause irreparable harm to both the unborn child and the woman herself.
Will the Ilizarov apparatus help in treating the consequences?
The question of the advisability and timing of using the Ilizarov apparatus to correct a congenital defect in a child is decided by an orthopedist on an individual basis.
How does pathology affect the development of a child after birth?
In cases where the amniotic cords did not influence the formation of the fetal brain, the child’s mental development will be normal. Nevertheless, it is very important to create and maintain an appropriate atmosphere in the family and among those close to you, which will help to form confident, adequate self-esteem and a positive outlook on life.
And in conclusion, let us reassure expectant mothers - although amniotic band syndrome is common today, in most cases future boys and girls cope with these “difficulties” on their own, quite quickly and successfully.
Treatment
Pathology is treated only after its long-term presence. The woman constantly goes for examinations for control. If the septum compresses a vital organ for the baby, then radical treatment is prescribed. Modern medicine is improving and it is now possible to cut amniotic cords in utero. In some cases, a caesarean section is performed.
After the birth of a baby who has intrauterine anomalies that appeared due to the above-mentioned partitions, appropriate measures are taken.
- If the child has severe indentations of the arms or legs and this interferes with normal blood circulation, the scar tissue is excised. The operation must be done within the first 12 months.
- If there are fused fingers, they are separated.
- If clubfoot or strabismus is detected, appropriate therapy is prescribed.
- If a limb was amputated in utero, a special prosthesis can be made.
- Cleft palate and cleft lip are eliminated through surgical interventions. Keep in mind that one operation will not help, you may need from 2 to 6. The latter must be carried out before the child turns six years old.