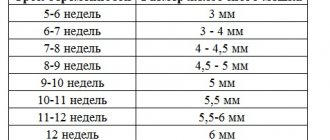
WMD during pregnancy by week - table
Assessment of UHM indicators (the abbreviation stands for uterine fundal height) is one of the most important diagnostic measures during pregnancy.
Firstly, the indicator under consideration allows us to determine the age of the developing baby, secondly, to assess the condition of the fetus, and thirdly, to assume the presence of various types of deviations in the child’s development. In sexually mature women, the uterus in normal condition has a length of up to 8 cm, of which about 2.5 cm is at the cervix. As the child develops, the size of the uterus also changes, and by week 40 it can reach about 40 cm. The weight of this organ also increases - before conception it is approximately 50 g, and by the third trimester it increases up to 4 kg.
Basic information about WYD
The condition of the uterus changes significantly throughout pregnancy. So, in the initial stages, this organ can be felt through the vagina. Already by the 12th week, the uterus is in the area of the pubic symphysis, and from the next week it extends beyond the pelvis and can already be felt with your fingers when palpating the abdominal wall.
To determine the indicator in question, with the patient in a supine position, the length of the gap between the highest point of the uterus and the pubic symphysis is recorded with an ordinary measuring tape. The results of each such test are saved in a notebook, which allows you to evaluate the dynamics of changes in the state of the organ.
In general, the size of the uterus in centimeters usually corresponds to the week of pregnancy: at 8-9 weeks - about 8-9 cm, at 40 - about 40 cm.
If during a certain week the AMR indicator does not coincide with the average normal values, deviating upward, the specialist can assume a multiple pregnancy. If there are deviations in the direction of decrease, delayed development of the fetus and various types of pathologies can be diagnosed, for example, oligohydramnios or incorrect position (transverse, oblique), etc.
It is important that the VDM values are recorded regularly and at approximately the same frequency, because one-time measurements are not informative and sufficient for correct diagnosis of pregnancy.
Important! The given indicators for the height of the uterine fundus are the statistical average. This value may vary depending on different circumstances, for example, in large mothers, the uterus is larger than in miniature representatives of the fair sex, therefore, their UGM indicators will also differ.
Deviations of VDM from the norm
The average normal indicators of VDM by week are given in the following table.
In general, the GMR indicator may change under the influence of the following factors:
- size of the developing fetus;
- individual anatomical features of the maternal body;
- baby's position;
- number of developing babies;
- volume of amniotic (amniotic, intrauterine) fluid.
Under certain circumstances, the VDM value may deviate from the average norm. Information on this matter is consecrated in the table.
Table. Reasons for deviation of VDM from the norm
Along with the AMF indicator, specialists usually simultaneously determine the content of amniotic fluid, on which the processes of fetal development largely depend. The amount of intrauterine water depends on a number of indicators, for example, the total thickness of subcutaneous fat, the individual characteristics of the female body, etc.
By the end of pregnancy, using the mentioned indicators, you can determine the approximate weight of the baby. To do this, you need to subtract from the GMR the value obtained by measuring the volume of the maternal abdomen.
Table. Composition of amniotic water by streamester
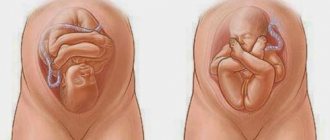
Features of changes in the uterus during pregnancy
The size, shape and other characteristics of the organ in question differ according to the stage of pregnancy.
On average, by the 8-9th week the dimensions of the female uterus are similar to the size of a goose egg. At this stage, it is usually impossible to feel it when palpating the abdominal wall, because the organ resides in the pelvic area, and only by 3-4 months does it rise slightly higher than the pubis. There is an increase in the activity of the placental system function. The size of the corpus luteum decreases until it completely disappears. The embryo develops blood vessels and begins to make its first movements.
By the 10-13th weeks of the term, the female uterus grows to an average of 11 cm. The body of the expectant mother is cleansed of various types of toxins and other harmful substances, which leads to a noticeable increase in the severity of toxicosis.
By the 14th-16th weeks, the organ grows to an average of 14 cm. At this stage, the fetus completes the creation of organs.
At the 16th week, the position of the uterine fundus is noted in the space between the woman’s pubis and her navel.
During the 17-18th week, the formation of the placental system is completed. The child's immune system, cerebellum, and limbs are already present. The uterus grows to approximately 18-19 cm.
Starting from the 20th week, the dimensions of the organ in question begin to align with the gestational age. Already from the 21st week, the gap between the fundus and the pubis is approximately 21 cm. Further, with each subsequent week, this figure increases by approximately 1 cm. The fundus of the uterus during this period is located 2 fingers lower than the navel.
During the 22-24th weeks, the dimensions of the organ increase to an average of 23 cm. The embryo, actively developing inside the mother, already has its own bones and muscles and weighs about 0.6 kg. At the 24th week, the bottom is located in the navel area, and its standing height is about 24 cm. The formation of the child’s respiratory system begins.
During the 28th week of the term, the UMR indicator is approximately 28 cm. The bottom itself is located a couple of centimeters higher than the navel.
In the third trimester, at 29-30 weeks, the size of the organ is about 31 cm.
During the 32nd week, the female uterus is located approximately in the center between the pregnant woman’s navel and the xiphoid process of her sternum. The VDM, in this case, is about 32 cm. By the 36th week, the organ in question is located on the line through which the costal arches are connected.
Already from the 38th week of the term, the organ gradually descends. The bottom, at the same time, puts pressure on the female diaphragm and her stomach. Food begins to be digested noticeably slower, and unpleasant heartburn occurs. The average weight of the fetus by this period can reach 2.5 kg.
At the 40th week, as noted, the UMR can be 40 cm, but on average it is less - at the level of 32 cm. The fundus of the uterus during this period lies between the navel and the ribs. The fetus is fully formed, developed and full term. During this period, the body of the expectant mother is actively preparing for an early birth, if it has not yet occurred.
Fundal height of the uterus by week
Throughout pregnancy, gynecologists measure standing height and uterine size week by week. This helps them not only determine the duration of pregnancy, but also make a conclusion about its course - whether there are developmental abnormalities in the fetus or whether the development is normal. Therefore, you should not be surprised that your leading doctor pays special attention to this organ during each examination. Remember, he is not worried about himself, but about you and your baby. Are you wondering how your pregnancy is going, but you can’t decipher the numbers? In today’s article we will tell you in detail what the height of the uterine fundus depends on by week, and also introduce you to the table in which the norms are set.
Preparing and conducting analysis
VDM during pregnancy by week (the growth chart does not always correspond to the woman’s parameters) first involves measuring the circumference of the pregnant woman’s abdomen. For this you need a measuring tape. Before taking measurements, the woman's bladder must be emptied.
Algorithm for measuring the abdomen:
- The woman lies down on the couch with her legs straightened.
- In the second half of pregnancy, the circumference is measured from the front at the level of the navel, and from the back - at the level of the lumbar region.
Algorithm for measuring VDM:
- The woman is asked to lie on the couch, with her legs bent at the hip and knee joints.
- The measurement is carried out using the first obstetric measurement method using the Leopold Levitsky method (performed by a gynecologist).
- Lying down, the woman stretches her legs horizontally.
- Using a centimeter tape, the distance between the upper edge of the symphysis (pubic symphysis) and the protruding part of the uterine fundus is measured (done by a midwife).
Fundal height of the uterus by week, how to determine:
- at the beginning (in the first weeks), the gynecologist can determine its size only through a gynecological examination - through the vagina, palpating it;
- at 11 and 12 weeks, the VSD of the uterus reaches the pubic symphysis;
- from the 14th week it can already be felt through the abdominal wall, because its dimensions already extend beyond the pelvic region;
- A fairly common method for determining height measurements and assessing the fundus of the uterus is measurement using a centimeter tape. The expectant mother is in a supine position, and her leading gynecologist measures the distance from the symphysis pubis to the fundus of the uterus;
- The obtained data is recorded in a log in order to monitor further developments.
- size of the height of the uterine fundus by week (measurements from the 8th week of pregnancy): 8-9 weeks - about 8-9 centimeters, 10, 11, 12 and 13 weeks of pregnancy - from 10 to 11 cm, at 14-15 weeks - from 12 to 13 cm, at 16-17 weeks - from 14 to 19 cm, at 18, 19, 20 and 21 weeks - from 18 to 24 cm, at 39-40 - from 35 to 40 cm (more details see below for meanings).
- The VSD (fundal height) of the uterus corresponds to approximately one week of pregnancy.
By the way, if during an examination the gynecologist notices deviations from the norm in a larger direction, this may mean that the patient is carrying twins or triplets. To a lesser extent - a woman experiences oligohydramnios, a transverse or oblique position of the fetus, or slow development of the baby. The height of the uterine fundus must be measured constantly in order to monitor the dynamics of the results.
Important!
The given average statistical dimensions of the height of the uterus may not correspond to reality, because Before pregnancy, each woman's uterus has an individual size.
Note :
Sometimes too slow or too fast growth of the uterus is an individual characteristic of a pregnant woman.
Size table ! Week of pregnancy
Uterine changes
4 weeks The size of the uterus is comparable to a chicken egg.
8 weeks The uterus has expanded to the size of a goose egg.
12 weeks The fundus of the uterus reaches the upper edge
pubic symphysis
Over
12 weeks The uterus can now be felt through the anterior
abdominal wall.
16 weeks The fundus of the uterus is located midway between the pubis
and navel.
Height of the fundus of the uterus during pregnancy, table and description
The initial measurement begins at 8-9 weeks, when the uterus changes its shape and becomes like a goose egg. It is from this period that it can be felt, because it extends beyond the pelvis and has a new position - just above the pubis. In addition, it is at this time that the corpus luteum begins to disappear gradually, and the placenta begins to work actively. The baby, despite his small size, is already moving, and blood vessels are beginning to form in his body. At 10-13 weeks, the length of the pregnant woman’s uterus reaches approximately 10-11 cm. The body tries to cleanse itself, due to this toxicosis increases. The height of the uterine fundus at 14-16 weeks already reaches approximately 15 cm. By this period, all organs of the fetus are already formed. The uterus changes its position and is already in the gap - from the pubic part to the navel. At 17-18 weeks, the UMR of the uterus = 19 cm. For this period, the mother has already formed the placenta, and her baby has the immune system, all limbs and the cerebellum. Half term is 20 weeks. The height of the uterine fundus by week corresponds (approximately) to the period of pregnancy of a pregnant woman. The uterus is located 1.5 fingers below the navel. The weight of the fetus at 22-24 weeks is 550-610 grams. His lungs begin their formation, and his muscles and bones begin to develop. The size of the uterus reaches 23 cm. The height of the uterine fundus at week 28 = 28 cm. The VSD is already located above the navel, about 1.5-2 fingers. The beginning of the third trimester is 29-30 weeks. The UMR of the uterus is slightly longer than the term, approximately 31 cm. At this moment, many women complain of high blood pressure and this is not surprising, because The uterus has greatly increased in size. 9 months of pregnancy and 32 weeks, the length of the uterus is 32 centimeters. At week 36, the fundus of the uterus rises again and reaches the line of the costal arches. Pregnancy is approaching its logical onset; you only have to wait 2-3 weeks before meeting your baby. At week 38, the baby’s weight reaches 2200 kg, although in some cases it may not be much more. A woman experiences heartburn due to the fact that the uterus puts pressure on the digestive organs, because its length is 32 cm. Preparation for childbirth is the 40th week. IMD - 34 cm. Such a pregnancy is usually called full-term. The woman needs to prepare for childbirth and for the first meeting with the baby.
Why can the height of the uterine fundus differ from the average from week to week? Several factors can have an impact:
- child's weight;
- the structure of the expectant mother (height, weight);
- fetal position;
- a pregnant woman is bearing 2 or more children;
- amount of amniotic fluid.
Why is the fundus of the uterus during pregnancy lower than the statistical norm? Factors:
- Mom’s figure is curvy and her pelvis is wide;
- little amniotic fluid;
- the gestational age does not correspond to the actual one;
- possible delay in fetal development.
Reasons for rejection
GMD during pregnancy by week (table attached) should approximately equal in centimeters to the number of weeks during which the woman is pregnant. For example, after 20 weeks the height should be approximately 17–23 cm.
The size of the uterus is determined by the doctor during an examination of the woman.
Possible reasons for the rapid increase:
- Post-term pregnancy. An ultrasound will help determine a more accurate date of birth.
- Weak, stretched abdominal muscles, which is typical for women who have had pregnancies in the past.
- Excess weight of a pregnant woman.
- Obesity often makes it difficult to obtain accurate measurements.
- Fibroids.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- A large amount of amniotic fluid. Unusual position of the child in the womb.
- A woman's pelvis is too narrow.
- Increasing weight of the child, when by the end of pregnancy it greatly exceeds 4.5 kg. The risk group includes women who have given birth many times, have gestational diabetes or type 1-2 diabetes, and obesity.
- A healthy child without any abnormalities, but with a lot of weight and length.
Deviation of the size of the VDM towards a decrease of 3 cm or more from the norm occurs for the following reasons:
- A woman of small stature, strong muscles.
- Too little amniotic fluid.
- The child is healthy, but has low weight and short length.
- Incorrect determination of gestational age. This occurs in women who have irregular menstrual cycles.
- A wide pelvis that allows the uterus to be positioned widely between the pelvic bones.
- Transverse presentation of the fetus.
- Delayed development of the baby in the womb.
- Impaired development of the placenta or umbilical cord.
The main guidelines that the doctor relies on during the examination:
| Gestational age | The point of the upper edge of the uterus |
| 12–13 weeks | Pubic symphysis |
| 20–21 weeks | Navel |
| 35–40 weeks | Xiphoid process of the sternum |
| 36–40 weeks | Height regression: 36–32 cm |
If changes increase or decrease by more than 3 cm, the doctor will prescribe an additional ultrasound to determine the cause of the abnormal growth or its slowdown.
How are measurements taken?
Information AMR is measured at every visit to a pregnant woman's antenatal clinic, starting from 16 weeks of pregnancy.
To do this, the woman lies down on the couch with her legs straightened and, preferably, with an empty bladder, and the doctor uses a centimeter tape to measure the height of the uterine fundus. The study takes only one minute, but allows you to judge the nature of fetal growth, its position and the amount of amniotic fluid.
There are generally accepted values of GMR corresponding to a specific stage of pregnancy, however, it must be taken into account that this is still an individual indicator and its value can vary within 3 cm. You should pay attention to the rate of increase in GMR relative to the previous value. Starting from 24 weeks of pregnancy, the height of the uterine fundus usually coincides with the gestational age. And a few days before childbirth, when the fetal head is installed in the pelvic cavity, the fundus of the uterus drops by 2 - 3 cm.
Method for measuring the uterus during pregnancy
The measurement is carried out using the “Leopold technique” - a special obstetric technique.
- The measurement is carried out with an empty bladder.
- The woman lies on her back on the couch.
- Raising your hand from the pubic area along the midline of the abdomen, you feel the area where the dense tissue becomes soft and loose - this is the border of the uterus, called the bottom.
- Using a soft ruler, measure the distance from the pubic bone to the bottom.
With physiologically correct development, the distance in centimeters coincides with the period established in weeks. Possible error: 1 – 2 cm. This calculation is applicable up to 37 – 38 weeks. Later, the uterus settles into the pelvic cavity in preparation for childbirth.
Is it possible to take measurements at an early stage?
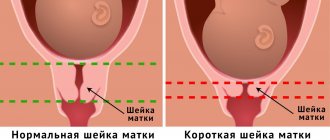
Table of norms for the cervix
Not only the uterine cavity, but also the cervix undergoes changes. From the moment of conception, it lengthens, softens, and changes color. Its length reaches 4.0–4.5 cm. Subsequently, a gradual shortening of the canal is noted.
The following parameters indicate the successful development of pregnancy.
Important! Rapid shortening of the cervix is a threat to full pregnancy. Such progress is especially dangerous at a period before.
Table of norms of UMR - fundal height of the uterus
Fundal height of the uterus is measured weekly, starting at 14 weeks. The data is recorded in the patient’s individual table to monitor the dynamics. A physiologically normal pregnancy corresponds to the following indicators.
Possible reasons for non-compliance with the VDM
VDM is below normal
If the height of the uterine fundus is lower than normal, this may mean:
- Error in determining the duration of pregnancy;
- Wide, capacious pelvis in tall, large women;
- Intrauterine growth retardation;
- Oligohydramnios – decreased amount of amniotic fluid;
VDM is higher than normal
If AMD is higher than normal, this may indicate:
- Large fruit;
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Narrow pelvis;
- Incorrect fetal positions;
- Polyhydramnios is an increase in the amount of amniotic fluid.
Also, to monitor the condition of the fetus, its growth rate and the amount of amniotic fluid, the abdominal circumference (AC)
at the level of the navel. This indicator very much depends on the individual characteristics of the woman and the thickness of the subcutaneous fat, so the dynamics of the increase in circumference are taken into account. Using these two indicators at the end of pregnancy, you can calculate the expected weight of the fetus. To do this, you need to multiply the VDM value by the coolant. So, for example, if the VDM is exactly 36 cm, and the coolant is 95 cm, then we get the possible weight of the child - 3420 grams.
Information If the indicators of the height of the uterine fundus do not correspond to the term by more than 3 cm, then the doctor prescribes additional examinations for the pregnant woman. An ultrasound of the fetus, Doppler ultrasound and cardiotocography are performed and, based on the results obtained, treatment is prescribed and the tactics for the upcoming birth are determined.
Why the uterus does not meet its term
The height of the uterine fundus does not always correspond to the indicated period. Deviations can be significant, although the date of conception is set correctly. Why does this situation arise?
Placental insufficiency leads to a delay in the formation of the embryo, as a result – to reduced dynamics. This condition is caused by the presence of long-term debilitating toxicosis, severe.
The opposite situation is the increased size of the uterus in relation to gestational age. A common diagnosis is an increased amount of amniotic fluid. It occurs as a result of infection with an intrauterine infection (herpes, and others). It has been noted that polyhydramnios occurs in women with a history of surgical or spontaneous abortion.
During a dynamically developing pregnancy, the upper border of the uterus fits within the allotted weekly norms reflected in the table. But if deviations occur, do not panic; non-compliance with accepted indicators does not indicate fetal pathology. There are many reasons why the size of the uterus exceeds or falls short of normal. It is necessary to conduct an examination and adjust the timing and condition.
Current video
Comments (3)
Sometimes it seems to me that it would be nice for our gynecologists to read at least articles like this. My uterine fundus height during pregnancy was higher than normal, but the doctor didn’t care. She said everything was fine. Already at the maternity hospital they said that there was a lot of water and this caused the child to have problems. Now I understand that every centimeter is important to ensure that everything goes well with the child.
And I was lucky in this, I was observed by a qualified doctor. Throughout my entire pregnancy, the height of the uterine fundus coincided with the gestational age, that is, at 24 weeks the UMR was equal to 24 cm, at 28 weeks - 28 cm, although at one time, according to the results of an ultrasound at 28 weeks, I was even diagnosed with oligohydramnios, although this is not measured by centimeters had no effect. It’s good that I completed the course of treatment on time and everything returned to normal.
Unfortunately, I was very unlucky with the doctor. It turned out that during the examination they said that everything was fine with me, but in reality it turned out to be wrong, the number of weeks did not coincide with the centimeters. Although the doctor confidently asserted that everything was fine. It turned out that I I’m not the only one, the girls in the ward said the same thing, in general, a negligent attitude towards young mothers. Thank God, everything worked out and I gave birth to a healthy baby normally.
Decoding the results
AMR during pregnancy, measured every 2–3 weeks, must correspond to the parameters indicated in a special table. A woman at 30 weeks should have a UMR of 28 to 31 cm.
The ratio of real height to the numbers in the table tells about the current state of the child, as shown by the VDM:
- Was the child's date of birth calculated correctly?
- An increased size of the VDM may indicate the presence of fibroids, which affected rapid growth. The formation is often benign and does not affect pregnancy or the health of the baby, but it can enlarge the uterus.
- Perhaps the expectant mother is carrying twins, or even triplets, under her heart.
- Breech presentation. It occurs in 4% of all full-term babies.
- The child turned out to be larger than the required size, therefore, there is a risk of developing gestational diabetes in the woman.
- If the baby's growth is underestimated and does not correspond to the indicators, then a small amount of amniotic fluid may be to blame.
Parameters for some weeks may not coincide with the official table. The doctor will compare all the data, ask for an additional ultrasound examination, which is more accurate, and then make a final decision.
What should be the height of the uterine fundus by week?
The height of the uterine fundus should increase over the weeks of pregnancy. This is very important, since in this way the doctor, without performing an ultrasound, can say with a high degree of probability whether the fetus is developing, whether the pregnancy has frozen, whether the child is lagging behind in development, whether the amount of amniotic fluid is normal, etc.
The height of the uterine fundus by week of pregnancy is reflected in the graph, which is printed in the dispensary card of each expectant mother. This chart is created by a doctor or nurse who fills out the chart.
Many women have a rough understanding of the issue of fundal height by week of pregnancy: we also have a table of average values on our website. You should know that the average values approximately coincide with the duration of pregnancy. For example, at 30 weeks the height of the uterus will also be 30. Errors of 2-3 cm are allowed in one direction or the other. But because of them, especially if the abdominal circumference also does not increase enough over the weeks, many doctors prefer to play it safe and admit women to the hospital for treatment in order to improve blood flow in the placenta and umbilical cord. Although in reality these measures are ineffective.
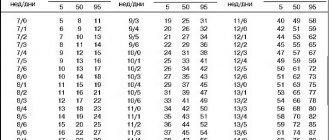
Table of uterine fundus height (UFH) and abdominal circumference by week of pregnancy (WG)
:
You will need :
Tape measure.
Empty your bladder. This is necessary to accurately measure the height of the uterine fundus.
Lie on the bed with your legs straight.
Determine where the uterus ends. To do this, place your hands on the midline of the abdomen in the area of the pubic bone. Gradually move your fingers upward, trying to feel the place where the denser part of the abdomen turns into a soft one. This will be the bottom of the uterus.
Take a measuring tape and measure the resulting distance. Normally, the height of the uterine fundus corresponds to the obstetric period in weeks, plus or minus 2 centimeters. And only towards the end of pregnancy, a couple of weeks before birth, the baby descends into the small pelvis, and the height of the uterine fundus becomes several centimeters lower.
Too large a discrepancy between measurements and obstetric term may indicate either that the gestational age is set incorrectly, or possible problems, for example, delayed fetal development, oligohydramnios/polyhydramnios, etc. It is recommended to monitor the dynamics of uterine growth and, for your own peace of mind, do an ultrasound to make sure that the child is developing normally.