Causes and Effects
The diagnosis of “anembryonia” is made by doctors quite often. According to statistics: out of 1000 women who become pregnant, 100 do not have an embryo - only an empty fetal face. This diagnosis is also called anembryonia.
It is given to a woman if the fertilized egg develops and grows, but there is no embryo in it. This occurs due to the cessation of cell division, as a result of which the embryo stops growing. In this case, the doctor announces the woman’s diagnosis: an empty fertilized sac without an embryo.
There is also another case when a pregnant woman can be diagnosed with anembryonia; in this case, the embryo not only stops developing, but its absence is observed altogether. There is also one pathology associated with this diagnosis: when the embryo grows, but the fertilized egg does not, and in the case of this pathology, an anembryonic pregnancy can also be diagnosed.
In this case, the doctor may advise ending the pregnancy, since subsequently the pregnancy may become frozen and the embryo will no longer continue to develop, but the development of the fertilized egg may even out, and the pregnancy will continue quietly without being called frozen, and the embryo will grow. This situation is very uncertain, and you should not rely on the opinion of one specialist.
Ultrasound diagnostics
Only in the sixth week of pregnancy can an empty ovum be diagnosed using ultrasound. It is carried out in any case to determine the location of the fetus, as well as to exclude ectopic pregnancy. A woman can hear such a terrible diagnosis as anembryonia even if she feels well and has no symptoms. The first trimester of pregnancy is the most important time for the formation of the fetus; at this stage, the expectant mother should especially carefully monitor her health, since the threat of miscarriage is very high.
This video shows an ultrasound of an empty ovum:
If a woman is found to have an empty fertilized egg without an embryo, she will need to undergo medical correction (cleansing the uterus).
Signs of complications
Another pregnancy is called frozen if the fetus does not continue to develop and dies. An empty fertilized egg can also be called a frozen pregnancy. Pregnancy can become frozen in the first 12 weeks, while the fetus is growing. It is also worth clarifying about another complication - an ectopic or false pregnancy. This occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterine cavity, or rather, implantation occurs inside the fallopian tube. The diagnosis of VB (inside the pipe) is dangerous for the health of the woman and child and requires urgent medical intervention, otherwise, without treatment, this complication can lead to death if the pipe ruptures. The incidence of ectopic pregnancy is only 2%, but almost all of them develop an embryo inside the fallopian tube. The reasons may be:
- Hormonal imbalances or lack of any hormones;
- Tumors of the uterus or its appendages;
- The genital organs develop incorrectly;
- Surgical operations that take place in the abdominal cavity;
- Disturbances in the transport function of the fallopian tube.
The first signs of fetal development inside the ectopic tube: drowsiness, nausea, weakness, pain in the lower abdomen, bleeding.
The development of an ectopic pregnancy is determined before 4-6 weeks of pregnancy, otherwise it can lead to a bad end.
To eliminate this complication of VB, an operation is performed in which the fertilized egg located inside the ectopic tube is removed, and if the tube ruptures, the tube itself is removed. A false fertilized egg in the uterus can serve as an indirect sign of an ectopic pregnancy; this is clearly visible if the so-called false fertilized egg is smaller than normal in size. A false gestational sac in the uterus simulates an intrauterine pregnancy while another gestational sac may begin to develop inside the fallopian tube or inside the cervix, promoting an ectopic pregnancy. A false fertilized egg is an accumulation of blood inside the uterus or an accumulation of secretion from the tubular glands.
How the embryo is formed
By 7-14 days after conception, the embryo in the amniotic sac should already descend into the uterine cavity. At this point, the fragmentation of the cells of the fertilized egg ends. The “reserve” of material has already been created, the process of implantation begins - the introduction of the fetal sac into the previously prepared uterine wall. In parallel, the development of the embryo itself continues.
Implantation is the “immersion” of the fetal sac into the functional part of the endometrium. This takes about a week, after which the mucous membrane above the fetal sac is restored. To make things easier to understand, you can compare the process to a stone falling into water. First, it comes into contact with the surface, then it disappears into the water surface, and after a minute it is impossible to determine the place of its fall. This is approximately the same as a fertilized egg.
As the vesicle with the embryo penetrates the endometrium, the glands of the inner layer of the uterus thicken and begin to produce a special secretion. Subsequently, they form the decidua - it is located between the embryo, the fetal sac and the body of the uterus from the inside.
In parallel with the development of the outer membranes of the embryo, the cells inside are transformed. By 7-14 days, tissue is separated from the total mass, from which all the rudiments of organs are subsequently formed. From a smaller group, the yolk sac is formed, which plays an important role until seven to eight obstetric weeks of pregnancy.
The following happens to the fetus at 2 weeks of pregnancy:
- the fertilized egg descends into the uterus;
- it is introduced into the endometrium;
- the yolk sac and part of the cells of the embryo itself are formed.
All these changes can be monitored by ultrasound using a vaginal sensor. The discovery of a fertilized egg in the cavity is direct evidence that more than a week has passed since fertilization. But it is necessary to understand that ovulation and conception in most women occurs “not according to the rules” on the 14th day, especially if the cycle is long, short or irregular. Therefore, for some, the picture described above is visible even before the delay, while for others, only two weeks from the date of the expected start of new menstruation.
It is the first four weeks of development that are critical - at this time, the laying of the main cells from which organs are subsequently formed occurs. The impact of unfavorable factors during this period leads to “global” anomalies. For example, the absence of a limb, the brain, large abdominal hernias. Therefore, it is important to protect a woman at the planning stage from negative influences, since it is impossible to predict when conception will occur.
Signs of pathology
Now let's figure out what can cause the development of anembryonia. The causes of anembryonia are not completely known: pregnancy without an embryo or a fertilized egg without an embryo, but there are some conditions that can lead to the death of the embryo in its early stages of development.
For example, bad habits lead to anembryonia: nicotine addiction, excessive alcohol consumption, drug addiction and substance abuse. Harmful substances reach the fetus and have a detrimental effect on it, as a result of which the embryo may stop growing. This pathology can also be caused by genetic abnormalities: initial disturbances during fertilization affect the development of the embryo in the early stages. Also, the cause of this pathology can be fertilization of the egg with the sperm of a blood relative. Another reason is hormonal disorders: there is a deficiency or, conversely, an excess of any hormones in a woman.
Diagnosis of “absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg”: signs of pathology. The absence of an embryo inside the fertilized egg may not in any way affect the external and internal sensations of a woman either in the first week or in subsequent weeks. A woman may experience nausea, a desire to eat something special, and other signs of pregnancy without feeling any discomfort. Therefore, a woman may be completely unaware of the diagnosis of anembryonia, without feeling it. But some representatives of the fair sex may feel unwell, excluding signs of pregnancy: pain in the lower abdomen, red or brown discharge may be observed, which indicates anembryonia. This happens because the body begins to reject an empty fertilized egg or an egg with an embryo, which will not be able to further develop and live.
If a woman is concerned about the above symptoms, then she needs to see a doctor and explain everything to him. An ultrasound examination is performed, during which the doctor observes the absence of an embryo or the suspension of its development. And if a woman has no symptoms, she will learn about anembryonia at the next examination with an ultrasound machine, when the doctor notices a discrepancy in the development of the fertilized egg and the embryo.
The size of the ovum and anomalies in its development
Wednesday, April 8, 2020 – 13:47
The fertilized egg is the embryo along with the embryonic membranes. The period of formation of the fertilized egg is the first stage in the development of pregnancy.
After the fusion of germ cells, the egg is at the stage of active division. First it is divided in half, then into four and so on. The number of cells and the size of the embryo gradually increases. It moves along the fallopian tube into the uterus to attach there.
Implantation occurs approximately seven days after fertilization. Until this time, the embryo receives nutrients from the egg, and after attachment - from the mucous membrane of the uterus.
This feeding continues until the placenta is formed.
The placenta is formed from the outer layers of the fertilized egg, densely covered with villi. They are the ones who remove the mucous uterine layer at the implantation site and are introduced into the prepared area.
The presence of a fertilized egg is the first sign of a normally started pregnancy. It can be seen on an ultrasound monitor 14 days after the delay, and the embryo can be seen only after five weeks.
The size of the fertilized egg according to weeks
If the fertilized egg is only four millimeters in size, this indicates a very early stage of pregnancy - up to six weeks. Most often, this size of the fertilized egg indicates a period of four weeks. At five weeks it is equal to six millimeters, and at five weeks and three days it is seven.
We can say with certainty that the fertilized egg grows by one millimeter every day for up to 15-17 weeks. Then it increases by two and a half millimeters daily.
It happens that an ultrasound of a pregnant woman gives an inaccurate gestational age. This often happens, since in the first weeks it is difficult to establish a specific date based on the size of the fertilized egg. In the future, it is recommended to repeat the ultrasound examination, starting from the sixth or eighth week of pregnancy.
Deformations of the fertilized egg
A small fertilized egg in the early stages is not a reason to worry, since usually everything returns to normal after some time. It is important to initially monitor the process using ultrasound. It’s another matter when the fertilized egg has irregular outlines.
This phenomenon is a pathology and most often indicates abnormal development of the fetus. Normally, the egg should have an oval or round shape. If it is flattened on the sides, then this is the first sign of uterine hypertonicity. The patient needs to be under the supervision of a doctor for some time. If no dangerous symptoms develop in the future, then the threat is eliminated.
If a pregnant woman experiences pain or vaginal discharge appears, immediate action must be taken. Bed rest and absolute rest are prescribed. Medications to reduce uterine tone and hormonal medications are required. It is possible that the woman will have to spend the entire remaining period before giving birth in the hospital.
Detachment of the ovum
Detachment of the ovum is the early rejection of the egg from the wall of the uterus. If spontaneous abortion is diagnosed in time, there is a good chance of maintaining the pregnancy.
Detachment of the ovum manifests itself in aching pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, bleeding or dark red discharge.
Causes of pathology:
- disturbances in the functioning of the ovaries;
- inflammatory processes;
- exacerbation of infectious processes;
- presence of tumors;
- underdevelopment of the genital organs;
- strong physical activity;
- severe toxicosis;
- stress.
If you notice the first signs of detachment, you should immediately call emergency help. Before the specialists arrive, the woman needs to lie on her back and raise her legs up, placing them on some kind of support (on the wall, the back of the sofa).
Absence of embryo in fertilized egg
In the earliest stages of pregnancy, the embryo in the fertilized egg is not yet visible, and this is the norm. However, starting from the fifth week, it should already be noticeable on the device monitor. If it is not possible to visualize the embryo, then a repeat ultrasound examination is scheduled after two weeks.
If upon repeated examination of the embryo and no heartbeat is observed, then an anembryonic pregnancy is diagnosed. In this case, curettage is performed.
It is important to know that despite the absence of an embryo, pregnancy is confirmed during testing. Pregnancy tests also show a positive result. The fact is that in the female body all the processes corresponding to bearing a child have already been launched and certain hormones are being produced.
It is impossible to name the exact causes of this pathology. Most often, its occurrence is associated with genetic factors. In addition, anembryonia can be caused by the use of certain medications that are prohibited for use during pregnancy.
Anembryony does not indicate the impossibility of successfully conceiving a child in the future. It is quite possible that the next pregnancy will be favorable. However, planning should begin no earlier than six months later.
It is important for the patient to provide not only physical rehabilitation, but also psychological one. The loss of an unformed child is a difficult ordeal.
Polyhydramnios
Polyhydramnios can also be attributed to anomalies in the development of the fertilized egg. This pathology is very dangerous and can lead to diseases in the fetus. Excessive amounts of fluid can provoke premature birth, entanglement of the fetus in the umbilical cord, or become an indication for a cesarean section.
During childbirth, complications may also occur, for example, the development of hypoxia in the child.
Causes of polyhydramnios:
- diabetes;
- past flu, acute respiratory infections;
- Rhesus conflict;
- kidney diseases;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- multiple pregnancy;
- Fruit size is too large.
To exclude polyhydramnios, an ultrasound examination, cardiotocography, and blood testing are performed. If the diagnosis is confirmed, then various medications are usually prescribed: diuretics, vitamins, drugs to increase metabolic processes.
Signs of polyhydramnios: pain and pulling sensations in the lower abdomen, rapid fatigue and loss of tone, rapid heartbeat, swelling of the arms and legs, shortness of breath, gurgling in the abdomen, nausea and vomiting.
You should go to the hospital immediately if you notice any signs of polyhydramnios.
Source: https://www.probirka.org/eko/embrio/8341-razmeri-plodnogo-yaytsa-i-anomalii-v-ego-razvitii.html
Treatment options
With this pathology: pregnancy without an embryo - anembryonics, medical intervention is necessary. There are two ways to treat this pathology:
- Treatment with medications. This pathology treatment can be offered if the woman is in position for no more than 6 weeks. This method is a medical abortion and it happens like this: to do this, you need to take the necessary medicine under the supervision of a doctor and wait until the contents of the uterus begin to be rejected and come out. After this, the woman will have to stay under the supervision of a doctor in the hospital for several days until the bleeding finally stops. To complete the treatment, the doctor performs an ultrasound examination and determines the cleanliness of the uterine cavity;
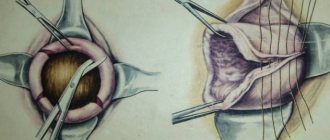
- Surgical intervention. This method is chosen by doctors more often, since it allows you to thoroughly clean the uterus of an empty fetus without giving rise to the development of any complications, and the operation can be performed at any week of pregnancy. During this operation, the woman is put into a state of deep sleep and does not feel any pain. The operation itself can last for 5-20 minutes. The operation goes like this: an empty fertilized egg is cleaned out of the uterine cavity by a gynecologist using special tools. In this case, the woman does not need to stay in the hospital and can leave the hospital after a few hours. After the operation, the woman will only be bothered by slight bleeding, after which she needs to visit an ultrasound room and make sure that there are no remnants of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity.
To find out the causes of this pathology, the doctor sends the material obtained after the operation for histological examination. During the study, the following questions are clarified: whether the embryo was in the fertilized egg or at what period it stopped developing, and also what was the reason.
To recover, the woman is prescribed anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs. It is also necessary to take sedatives, because the loss of a child, despite the term, is always the greatest stress for any woman.
If a woman wants to try to get pregnant again, it is recommended to do this no earlier than six months after the operation, and it is necessary to eliminate the reasons that caused the arrest of embryo development.
In this situation, you should be attentive to your lifestyle, habits and especially your well-being. You need to find out about all the possible reasons that can lead to this pathology or any other pathology in order to prevent the development of false, ectopic and other types of pregnancy. And if you experience any unpleasant sensations, contact a specialist.
Treatment of anembryonia
This diagnosis can be made to a woman when the fertilized egg develops and grows over weeks, but does not have an embryo.
Under the influence of certain factors, cell division stops at a certain level, and the embryo stops growing. In this case, its size is so small that even an ultrasound machine cannot detect it. Then the doctor announces this terrible diagnosis to the woman: a fertilized egg without an embryo.
There are also cases when the embryo not only stopped developing at the very initial stages, but was completely absent. Then the pregnant woman is also diagnosed with anembryonia. With this type of pathology, the fertilized egg may not meet its due date for weeks or may develop and enlarge without contents.
There are two ways to correct this pathology.
Drug treatment
If the pregnancy has not reached six weeks, the patient may be offered a medical abortion. In this case, the woman drinks the necessary medicine under the supervision of a doctor and waits for cramping pain to begin. The contents of the uterus are rejected and come out.
The patient should remain under the doctor's supervision for several more days until the bleeding is completely completed. Next, the woman is examined by a doctor using an ultrasound sensor and determines the cleanliness of the uterine muscle.
Surgical intervention
In most cases, doctors choose this particular method of treatment, since during it it is possible to thoroughly clean the internal cavity of the uterus without developing complications.
The doctor puts the patient to sleep using general anesthesia and begins the procedure. This manipulation lasts from five to twenty minutes. Using special instruments, the gynecologist scrapes out the upper uterine layer with the pathological fertilized egg. Within a few hours after such a manipulation, the woman can be discharged.
After the bleeding is completed, an ultrasound should be performed to ensure that there are no parts of the fertilized egg left in the uterus.
If a fertilized egg without an embryo lingers in the uterine cavity, then there is a real threat to the woman’s health and her life. Therefore, the pathology requires active treatment tactics. After a diagnosis of a non-developing pregnancy is made, it is terminated in one of the following ways:
- Vacuum aspiration.
- Scraping (curettage).
- Medical abortion.
After the fertilized egg has been eliminated, the woman is prescribed anti-inflammatory therapy, immunostimulating and restorative drugs. If a complication in the form of bleeding develops, then hemostatic agents and plasma substitutes are used. Endocrine disorders require appropriate hormone therapy, and autoimmune disorders require the use of glucocorticoids. To normalize the psychophysiological state, sedatives are indicated.
Subsequent pregnancy is recommended only after eliminating all factors involved in the development of pathology. The woman is advised to undergo medical genetic counseling and a careful approach to conception planning. It doesn’t hurt to lead a healthy lifestyle and be emotionally attuned to a favorable pregnancy.
Anembryonia is a fairly common obstetric pathology, which becomes known from ultrasound results. Laboratory methods are also of no small importance in diagnosis, allowing one to identify systemic disorders and suggest whether a subsequent pregnancy can end successfully. And to implement a positive scenario, it is necessary to adhere to medical recommendations in everything.
We suggest you read: What to eat when breastfeeding
Empty fertilized egg. Causes of the anomaly
There are quite a few reasons that can cause this pathology, among them:
- Genetic disorders;
- Infectious diseases;
- Toxicological effects;
- Unfavorable environmental conditions;
- Lack of vitamins, microelements and much more.
Thus, it is almost impossible to identify the exact reason why an empty ovum developed in a particular case. Please note that the risk of an anomaly can be minimized only in the case of a planned pregnancy, when even before the baby is conceived, future parents refrain from stress, bad habits and lead a healthy lifestyle. Otherwise, when an unplanned pregnancy occurs, the risk of an empty sac can be eliminated by following the recommendations of your doctor and regularly taking folic acid, which is so necessary for the body of the mother and fetus.
When pregnancy occurs, an empty ovum can be diagnosed as early as the fifth or sixth week, if precise, high-tech equipment is used, which is equipped in modern reproductive medicine centers. Otherwise, the first “alarm bells” may ring much later, when spotting and gradual rejection of the fetus begin. If we talk about statistical data, now, in the conditions of the modern environmental situation, one out of eight pregnancies is accompanied by an empty fertilized egg, the reasons for this vary greatly depending on the characteristics of the body. However, if this is not the first time this has happened to you, then you urgently need to undergo additional genetic research to identify the cause of the disease and its further elimination.
Diagnosis of the death of the fertilized egg
It is quite difficult to detect the early death of the fertilized egg and its retention in the uterine cavity; in the absence of characteristic manifestations, this requires dynamic observation. If severe symptoms appear: bloody vaginal discharge, heavy bleeding, acute pain, the patient is urgently hospitalized.
The main sign of a non-developing pregnancy is: cessation of uterine growth, determined by repeated studies. It is recommended to test the blood levels of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), the level of which constantly increases during normal pregnancy. Echo signs of a non-developing pregnancy during ultrasound may include the following indicators:
- lack of fetal heartbeat;
- the fertilized egg is wrinkled;
- no fertilized egg was found;
- “sleeping” uterine cavity.
If the fertilized egg has died, there is a disappearance of subjective symptoms of pregnancy: cessation of nausea, shrinkage of the mammary glands, lack of pigmentation of the areolas.
Fetal death in the second half of pregnancy is characterized by cessation of the heartbeat and movement of the fetus, delayed growth of the uterus, and also, in some cases, a crunching sound when palpating the skull due to separation and mobility of the bones.
Timely diagnosis will help to detect this pathology in time, which requires immediate hospitalization for further observation and prevention of complications.
The diagnosis of an empty fertilized sac without an embryo is not uncommon; it is made in 5-10% of cases. The most unpleasant thing is that the chances of identifying its causes are minimal. For a planned pregnancy to be successful, experts recommend taking multivitamin complexes and leading a healthy lifestyle.
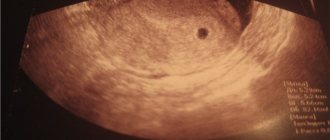
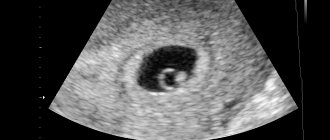
This is what an empty fertilized egg looks like on an ultrasound.
How to diagnose an empty ovum: hCG and its effectiveness
When there is an empty ovum, the hCG analysis will not be able to diagnose this. When pregnancy occurs, at first even the body itself does not suspect the presence of a disorder and fetal fading; the symptoms observed are the same as during the normal course of a child’s development:
- Fast fatiguability;
- Nausea, dizziness;
- Delayed menstrual cycle;
- Increased breast sensitivity, etc.
Of course, an empty fertilized egg cannot be left until the baby is born, so it is necessary to clean the uterus by performing curettage under general anesthesia. Of course, this is a complex medical operation, which previously quite often ended in heavy blood loss and infections. However, now medicine has stepped forward, so such manipulations should not cause concern.
After the operation, a repeat ultrasound is performed, and appropriate tests are performed on the removed tissue, which make it possible to identify the actual cause of the pathology. Pregnancy after an empty ovum should be planned no earlier than 6-12 months later; this period is enough for the body to rehabilitate, and future parents have enough time to prepare and plan the birth of the baby properly.
Question: The embryo is growing, but the fertilized egg is lagging behind in development - what does this mean?
The gestation period is 9 obstetric weeks. The ultrasound revealed the following indicators: CTE - 17 mm, internal diameter of the PU - 20 mm, heart rate 173 u/m, internal diameter of the yolk sac - 3.3 mm, corpus luteum 15x14 mm. Local tone of the anterior wall of the uterus. The ultrasound doctor said that the fertilized egg is lagging behind in development and the embryo is too crowded in it, what does this mean? What is the threat? And how to fix the situation?
In this situation, there is no need to panic - slight variability in size is acceptable. In such a situation, dynamic observation is required, and you also need to personally visit a gynecologist, who will prescribe adequate treatment for you, taking into account the existing tone of the uterus. You can get more detailed information on the issue you are interested in in the thematic section of our website by clicking on the following link: Ultrasound in obstetrics and gynecology. You can also get additional information in the following section of our website: Pregnancy calendar
Unfortunately, the situation described above ended in a frozen pregnancy. They did a “cleansing”, then endometritis developed, and they injected me with antibiotics. Severe depression. The husband offers to change the situation and go to the sea. Is it possible to go to the sea two weeks after curettage? Swimming and sunbathing are probably not allowed, I suppose, but at least just stay on the shore for another week? Thank you for your reply!
We regret what happened and recommend that you try not to become depressed. In this case, a change of environment will only benefit you, but, of course, you should refrain from sunbathing and swimming, given endometritis, so it is better to replace a trip to the sea with a trip to the mountains, where you can relax and take your mind off heavy thoughts.
Hello. Help me please!
A week before, on June 30, I was admitted to the hospital with scarlet, creamy discharge. They sent me straight away for an ultrasound. According to an ultrasound on June 30: the pregnancy is alive, but the ovum was delayed (the fetus was 7 weeks 5 days, PT - 5 weeks).
I can't find the cause of this problem anywhere. Please explain why this could happen? I don't want this to happen again in the future.
At the hospital they took a hormone test. Progesterone was less than normal (they didn’t talk about hCG. In the hospital they don’t talk about test results at all).
Pregnancy occurred due to the abolition of Midian contraceptives. The gynecologist prescribed contraception to restore the cycle. My periods disappeared for 8 months due to weight loss. I took birth control for 7 months.
So I think that the pregnancy froze, because the ovaries first “slept” after losing weight (8 months of no menstruation), and then after taking approx. They simply could not cope with the production of hormones to maintain pregnancy, as they did not function for a long time.
Another possibility is that this outcome was caused by taking antibiotics at the time of conception. This was at the beginning of May. We went on vacation to Thailand, where I fell and seriously injured my elbow, they put a stitch on it, which festered. They prescribed strong (according to the doctor) antibiotics to cure this wound. I finished antibiotics on May 9th. The estimated date of conception according to ultrasound is May 8. I don’t remember the name of the antibiotics, as they were given out locally in the Thai hospital.
Or are there other reasons for the lag (hypoplasia) of the fertilized egg?
Please advise what to do with new planning and how to avoid such an outcome?
Thanks in advance for your help.
The cause of a non-developing pregnancy could be a hormonal imbalance in the body. After discontinuation of hormonal contraceptives, as a rule, it is recommended to plan pregnancy no earlier than 3-6 months, which is required to restore the natural menstrual cycle. Taking antibiotics, especially in the early stages of pregnancy, also negatively affects the development of the fetus and can cause missed abortion.
We invite you to read: The fertilized egg grows during a frozen pregnancy
You can get more detailed information on the issue you are interested in in the thematic sections of our website by clicking on the following links: Pregnancy planning, Hormonal tests - types, principles of conduct, diagnosed diseases. You can also get additional information in the following section of our website: Hormonal disorders in men and women - causes, symptoms, treatment methods and in the series of articles: Endocrinologist
Thanks for your reply.
When prescribing a contraceptive drug (Midiana or Yarina, from which I chose Midiana), the gynecologist said that you can immediately become pregnant during withdrawal.
In the hospital, upon discharge (after curettage), I asked the doctor whether the missed pregnancy could have been due to pregnancy during the withdrawal of contraceptives, to which the doctor answered me in the negative. She said that infertile women are prescribed a course of OK to get pregnant within 3 months during withdrawal.
We will plan after 6 months. I would like to ask you, is it necessary to take OK after curettage? The gynecologist simply prescribed OK again from the date of the start of menstruation. I wouldn't want to take them again (due to concerns).
To restore my cycle, my endocrinologist prescribed cyclic vitamin therapy (phase 1: B vitamins, folic acid, vitamin E; phase 2: vitamin C (ascorutin), folic acid, vitamin E). You can just do it for 6 months. before planning to take these vitamins.
After curettage (scraping) of the uterine cavity, hormonal contraceptives are not prescribed to all women, but only in cases where there are menstrual irregularities. As a rule, it is initially necessary to take a blood test for sex hormones, evaluate hormonal levels, and only after this the issue of prescribing birth control pills is decided. A course of vitamin therapy is effective, we recommend taking it.
You can get more detailed information on the issue you are interested in in the corresponding section of our website by clicking on the following link: Menstrual cycle and menstruation and in the series of articles: Menstrual disorders. You can also obtain additional information in the following section of our website: Hormonal disorders in men and women and in the section: Hormonal tests: types, principles of conduct, diagnosed diseases
Symptoms of an empty ovum
The anomaly of anembryonia or an empty fertilized egg, the causes of which are still not fully understood, is accompanied by symptoms similar to the course of a normal intrauterine pregnancy. Later, when a frozen pregnancy enters the last stage of spontaneous abortion, first minor and then severe bleeding may occur.
This phenomenon indicates that the body has arbitrarily decided to get rid of pregnancy, and the empty fertilized egg is rejected. In this case, it is necessary to urgently contact a specialist, but you should not panic, because it is much better if the woman’s body itself rejects the empty body than if it needs to be stimulated to do so with medication or surgery. However, what actions should a woman take if she suspects she has an empty fertilized egg? HCG, ultrasound and going to the doctor to find out the reasons and take all the necessary tests - this is what you should do.
Pregnant women should listen especially sensitively to their body and, in case of the slightest suspicion, immediately contact competent and experienced doctors who will provide individual, comprehensive treatment. This is the only way to expect a normal pregnancy after an empty ovum in the future.
Fertilized egg is overdue
A fertilized egg in the uterus is the first and most important sign of a normal intrauterine pregnancy.
You can see it with an ultrasound as early as the second week of delayed menstruation. In the first weeks of development, doctors pay special attention to its size, shape, location, and whether there are detachments.
What does the fertilized egg look like in the first weeks of pregnancy, and what problems may arise in its earliest stages?
It is known that in the first trimester of pregnancy there is the greatest threat of spontaneous abortion. Most often, the reasons for this are disturbances in the genetics of the unborn child, progesterone deficiency and pathologies of the uterus and endometrium. And if in the first case the doctors are unable to help save the child, other situations can be completely resolved in favor of the mother and child.
If the shape of the fertilized egg is not oval or round, but has uneven corners, doctors may suspect uterine tone. In most cases, the condition is harmless, but only if it is not combined with pain, dilatation of the cervix, brown or bloody vaginal discharge.
You can relieve the tone of the uterus, thereby returning the “correct” shape to the fertilized egg, if you relax the muscles of the reproductive organ. This happens spontaneously, usually the tone does not last longer than a couple of minutes. As a last resort, you can take an antispasmodic if the tension of the uterus becomes painful.
But a single “deformation” is not a sign of a threat to pregnancy.
An ultrasound examination necessarily measures the diameter of the fetal egg week by week - its size in millimeters. On the one hand, this makes it possible to determine the gestational age with an accuracy of one day, while the obstetric period (which is calculated using the Naegele formula, depending on the first day of the last menstruation) is not always accurate.
The exact period can only be calculated using the “classic” 28-30 day cycle. On the other hand, it allows us to judge the child’s development at the earliest stages. This is important, for example, during IVF, when there is a high increase in spontaneous abortion. With artificial insemination, the doctor knows exactly the gestational age.
And knowing that, for example, the diameter of the ovum at 5 weeks is approximately 6 mm, will allow you to understand whether the unborn baby is developing, while a heartbeat is not yet visible on ultrasound. If nothing changes for several days, you can suspect a frozen pregnancy.
The size of the fetal egg of 50 mm approximately corresponds to a period of 10 weeks; after this period, the size of the head and limbs of the fetus itself are taken into account, for which there are also their own standards.
It is a very unpleasant situation if an ultrasound reveals a fertilized egg without an embryo, that is, anembryony. With a short pregnancy (1-2 weeks late) this is the norm.
But if the embryo is not visible even later, such a pregnancy cannot be maintained; doctors recommend medical termination.
Anembryonia is often caused by accidental genetic “breakdowns” (more common in women over 35 years old), taking various medications prohibited for pregnant women, and other teratogenic effects.
Interesting: 27 weeks twins pregnancy
Detachment of the ovum is not as hopeless as anembryonia, although it often has clear signs of miscarriage - uterine bleeding. This pathology is very common.
With this complication of pregnancy, the woman is recommended to have bed rest and take progesterone medications. And if the detachment is small in area, usually everything works out without consequences for the child.
Treatment is carried out exclusively in a hospital.
If the doctor suspects you have one of the above pathologies, try not to worry and pull yourself together. Do you have doubts about the diagnosis? Get examined by another doctor. Just do not ignore medical recommendations and treatment.
Waiting for the stork
What could it be.
Source: https://rojaismelo.ru/retsepty-dlya-detej/plodnoe-yajtso-bolshe-sroka
Anembryonia - what is it?
When, during an ultrasound about pregnancy, the doctor says that the fertilized egg is empty, what does this mean, the woman may not fully understand. Many expectant mothers have doubts at first, wondering: could the fertilized egg be empty or is this a medical error? A similar pathology occurs. It is characterized by the absence of an embryo inside the formed shells. At the same time, the rudiments of the future baby are very small.
Anembryonia is often considered a type of frozen or undeveloped pregnancy. A similar diagnosis is made before the 6th week of gestation. Anembryonia is common during IVF, when after fertilization the egg does not develop further. It is worth noting that with this type of pathology, diagnostic errors are often possible.
When the timing of pregnancy is not accurately determined, at the time of examination the embryo may be of insufficient size, so it is undetectable using standard ultrasound sensors. The doctor mistakenly diagnoses anembryonia. To exclude errors, if pathology is suspected, the examination is repeated after a few weeks.
Why is the embryo not visible on ultrasound?
It happens that a woman who saw the long-awaited two lines on the test comes to the doctor and hears: “The fertilized egg is empty, the embryo is not visible on the ultrasound.” This phenomenon is called anembryonic pregnancy.
If a pregnant woman is diagnosed with anembryonia, this means that with an increase in the level of hCG in the blood, there is no embryo in the fertilized egg. It is difficult to say exactly what week specialists will be able to see the embryo on an ultrasound. This period ranges from 5 to 9 weeks, depending on certain factors:
- Features of the body of each specific woman.
- The correctness of calculating the period from the date of conception.
- What kind of pregnancy is it? With each subsequent pregnancy, the likelihood of detecting an embryo earlier increases significantly.
On average, it has been determined that visualization of the embryo is possible at 7 weeks from the date of conception, with an active and ongoing increase in the level of hCG in the blood. However, even if at this time specialists did not see the embryo in the fertilized egg, you need to panic only if the growth of the hCG level has stopped or has started to decline. This picture indicates that the pregnancy is frozen. However, it doesn’t hurt to make sure of this once again, so it’s worth double-checking everything with another doctor or doing a transvaginal ultrasound.
A woman should consult a doctor if, several weeks after the growth of hCG levels has stopped, the embryo is not visible in the fertilized egg, even when examined transvaginally, while the pregnancy is approaching nine weeks. Stopping the growth of the embryo and the beginning of its decomposition may be accompanied by the following accompanying symptoms:
- Unreasonable jump in body temperature.
- The appearance of nausea and vomiting.
- Constant weakness, muscle pain.
- Lower abdominal pain.
- The appearance of discharge with blood impurities or bleeding.
You should not delay your visit to the doctor and put off the curettage procedure. The decomposition of the embryo can threaten a woman with serious health problems.
Empty fertilized egg or absence of embryo - reasons
Why anembryonia occurs, doctors still cannot name the reasons for this disorder. Most doctors are inclined to the theory of genetic disorders. Chromosomal abnormalities in the genetic material of one of the parents often cause fetal death: at one stage the embryo stops growing and developing.
When a woman is diagnosed with an empty fertilized egg, doctors associate the causes of this phenomenon with the following factors:
- Acute viral or bacterial infections in the early stages of pregnancy. Under their influence, the fetal development process is disrupted.
- The effect of radiation or toxic substances on the mother's body.
- Hormonal imbalances in the body of the expectant mother (lack of progesterone).
- Bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
- Taking a certain number of medications with a pronounced embryotoxic effect.
- Excessive physical activity, stressful situations, worries.
Anembryonia - symptoms
Signs of anembryonia in the early stages are not specific. This explains the frequent accidental detection of pathology during a routine ultrasound scan during pregnancy. The signs that appear during pathology have a continuous connection with the process of implantation or the threat of miscarriage.
Among the symptoms that require examination, doctors identify the following possible signs of anembryonia:
- cramping pain in the lower abdomen;
- bloody discharge from the vaginal cavity;
- symptoms of toxicosis (nausea, increased fatigue, headache, fainting);
- increase in the size of the uterus;
- absence of regular periods;
- increase in body temperature to 37–37.5 degrees.
HCG for anembryonia
In order to determine the possible presence of pathology and consult a doctor in a timely manner, women often ask their gynecologist whether hCG increases with anembryonia. Human chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone that is synthesized by the chorion - the membranes that form at the beginning of gestation.
Anembryonia is also accompanied by their formation, so hCG in this type of disorder is present in the bloodstream. However, with dynamic monitoring of the concentration of this compound in the bloodstream, a pathological pattern can be noticed. HCG levels do not rise every two days, as in normal physiological pregnancy.
How to confirm
At a period of 10-14 days, pregnancy can be confirmed with high reliability. The main research is as follows.
hCG
From the tenth day after conception, the level of hCG in the blood is sufficient to be determined by laboratory methods. To do this, you need to take a blood test from a vein. Interpretation of the result in the table.
Table - blood hCG in early pregnancy
| Level | Interpretation | Possible reason |
| Up to 50 mIU/ml | Short | - Ectopic pregnancy; - undeveloped pregnancy; - deadlines do not match |
| 50-150 mIU/ml | HCG norm at 2 weeks of pregnancy | |
| Over 150 mIU/ml | High | — Multiple pregnancy; - hydatidiform mole (tumor) |
At such a short period of time, it is most informative to take hCG over time - after five to ten days or even daily, depending on the clinical situation. A systematic increase in its amount in the blood indicates the normal course of pregnancy.
Human chorionic gonadotropin test
In the short term, the test will not always show a reliable result. To increase information content, the following conditions must be met:
- take it only in the morning - at this time the concentration of hCG in the urine is maximum;
- strictly follow the instructions - stand for three to five minutes in a horizontal position, use a jar, and do not try to get under the stream of urine.
Ultrasonography
An ultrasound at 2 weeks of pregnancy should show a fertilized egg in the uterus. Sometimes at this time the heartbeat of the embryo is already detected, often not very clearly. Good prognostic signs are the following:
- embryo in the uterus;
- fertilized egg 10 mm or more in diameter;
- the yolk sac is determined;
- there is a corpus luteum on the ovary.
However, the absence of a fertilized egg in the visualization area or a discrepancy between its size and timing does not indicate a 100% pathological course of pregnancy. In this case, it is recommended to repeat the study over time after 7-14 days in the absence of other complaints.
Inspection
When examined by a gynecologist, the doctor may already suspect pregnancy. The main features are as follows:
- uterus - still remains of normal size, but its body is “softened”;
- the cervix and vaginal mucosa are cyanotic (bluish color) due to the gestagenic background;
- on the right or left - an enlarged ovary may be detected due to the corpus luteum.
However, an examination at this time only provides additional information. Similar symptoms can be detected in a woman even before menstruation. Therefore, an assessment of the clinical situation is carried out in combination with ultrasound and a blood test for hCG.
The sensations at 2 weeks of pregnancy no longer fail a woman. She notes that the chest or lower abdomen hurts, a delay in menstruation is detected, and symptoms of toxicosis appear. The baby is far from moving; the fetus still looks like a small vial of liquid. If severe pain or bleeding occurs, consult a doctor. Only a specialist can understand what is happening to the expectant mother and whether there is a threat of termination of pregnancy.
Anembryonia - what to do?
An empty ovum can only be detected using an ultrasound, so if there is a suspicion of pathology, it is necessary to undergo an examination. An accurate diagnosis is possible only after the 8th week of gestation - at this time an ultrasound is performed. In the case when the study for pathology was carried out earlier than the specified period, ultrasound is repeated every 5–7 days.
To completely exclude possible pathology, a pregnant woman needs to:
- visit a gynecologist.
- undergo an ultrasound.
Anembryonia – ultrasound
The diagnosis of anembryonia can be made only on the basis of data obtained during ultrasound. This method is the most reliable for such pathology. The timing of the procedure is important. The embryo reaches diagnostic parameters only by the 8th week of gestation, so conducting research to exclude anembryonia before this period is pointless.
It is worth noting that not only the absence of the embryo itself in the fertilized egg may indicate the development of pathology. Additional signs of violation include:
- irregular shape of the fertilized egg;
- small dynamics of increase in the diameter of the fertilized egg;
- insufficient severity of the decidual reaction;
- absence of heartbeats in the 7th week of gestation and later.
Cleaning for anembryonia
When a woman is diagnosed with anembryonic pregnancy, the only treatment method is artificial termination of gestation. In this case, the doctor takes into account the timing, severity of the clinical picture, and the woman’s condition. The procedure for termination of gestation is carried out in a hospital setting. For some time (from several hours to several days), the patient is under the supervision of specialists. The length of stay in a medical institution is determined by the condition and method of cleaning the uterine cavity. It is carried out by:
- Medical abortion
- expulsion of the embryo from the uterine cavity by taking hormonal drugs that provoke endometrial rejection and increase uterine contractility. - Vacuum aspiration
- carried out using a device operating on the principle of a vacuum cleaner. - Curettage
– removal of the implanted fertilized egg along with the endometrial layer using a carriage.
Two fertilized eggs, one empty - what to do?
In the case when a woman is diagnosed with two fertilized eggs, one empty, doctors take a wait-and-see approach. This kind of multiple pregnancy is often recorded after an IVF protocol. Of several fertilized eggs, only one takes root; the rest develop anembryony. The development of a healthy fertilized egg is assessed over time. In the case of normal viability indicators, it is left, and the rest are removed by vacuum cleaning.
Fertilized egg without an embryo: what to do and why does this happen?
The diagnosis of an empty fertilized sac without an embryo is not uncommon; it is made in 5-10% of cases. The most unpleasant thing is that the chances of identifying its causes are minimal. For a planned pregnancy to be successful, experts recommend taking multivitamin complexes and leading a healthy lifestyle.
This is what an empty fertilized egg looks like on an ultrasound.
Why is this happening?
An empty fertilized egg is essentially a pregnancy that has not begun to develop. The development process stopped even before the stage of embryo formation. There are many reasons for this violation. Any negative changes in a woman’s body can provoke it. When diagnosing anembryonia, the necessary measures should be taken immediately, as this entails the inevitable death of the fetus.
Among the main reasons for an empty ovum are:
- Genetic disorders.
- Infectious diseases.
- External factors (state of the environment).
- Wrong diet.
- Lack of vitamins.
That is, in each specific situation, it is extremely difficult to determine the reason for the formation of an empty fertilized egg. Genetic disorders begin at the initial stage of cell division and entail subsequent errors. This may be the formation of extra chromosomes or, conversely, an incomplete set of them. In this case, the egg does not transform into an embryo; the woman’s body understands this and begins to reject it.
According to statistics, out of 100 women, 5-10 do not have an embryo in the ovum.
How does anembryonia manifest?
At the initial stage, an empty pregnancy will not be noticeable. It cannot be determined even with the help of a gynecological examination. Violations become visible already at the most extreme stage, when the body begins to reject the fetus. At this stage, there is pain in the lower abdomen, brown vaginal discharge and a pungent odor - and these are already signs of a fertilized egg without an embryo that the body has begun to reject.
How does hCG change when the ovum is empty?
Monitoring the dynamics of hCG is one of the ways to determine an empty ovum. HCG values will change, but significantly less than during normal pregnancy. It is also possible that the hCG values stay the same - this is the main sign of the existence of problems with fetal development.
Be sure to watch this useful video:
The symptoms of an empty pregnancy are no different from a normal one: a delay in menstruation, manifestations of toxicosis, and a constant feeling of fatigue.
In the early stages, it is extremely difficult to identify an empty fertilized egg. Since the size of the embryo is very small and it can simply not be noticed. Only after 5 weeks does it become possible to determine the absence of a fetus.
Ultrasound diagnostics
Only in the sixth week of pregnancy can an empty ovum be diagnosed using ultrasound. It is carried out in any case to determine the location of the fetus, as well as to exclude ectopic pregnancy. A woman can hear such a terrible diagnosis as anembryonia even if she feels well and has no symptoms. The first trimester of pregnancy is the most important time for the formation of the fetus; at this stage, the expectant mother should especially carefully monitor her health, since the threat of miscarriage is very high.
This video shows an ultrasound of an empty ovum:
If a woman is found to have an empty fertilized egg without an embryo, she will need to undergo medical correction (cleansing the uterus).
What to do with anembryonia?
If such a disappointing diagnosis was made, it will be necessary to make a correction. Medical correction is possible using two methods.
Surgical method
This is the most common correction option. This method allows you to clean the uterine cavity without consequences. During surgery, general anesthesia is used. The operation takes place very quickly, from 10 to 25 minutes. The doctor must scrape out the uterine layer and the empty fertilized egg. After just a couple of hours, the woman can go home.
Medical abortion
Abortion using special drugs can be used if the pregnancy is less than 6 weeks. The woman takes the medicine and waits for contractions to begin. It hurts. The entire procedure takes place in a hospital under the supervision of a doctor. After all the excess has come out of the uterus, the woman must spend a couple of days in the hospital until the bleeding stops.
To clarify the cause of the disruption of pregnancy, the material obtained from the uterus during the cleaning process is sent for histological examination. Such a study should find out the reasons for the cessation of embryo development and when exactly it stopped its development.
After an abortion you need to do an ultrasound.
When completing either of the two methods of abortion, an ultrasound scan must be performed. In this way, you can make sure that the uterus is clean and there are no particles of the fertilized egg left in it.
Prevention
It is better to prevent a problem than to solve its consequences. If an empty fertilized egg is detected, then extreme measures are taken. But if you follow some recommendations when planning a pregnancy, you can reduce the likelihood of developing pathologies.
You can reduce the risk of an empty sac forming in the following ways:
- both spouses undergo a full medical examination (do tests, ultrasound, consult with a gynecologist and therapist to rule out chronic diseases, it is also recommended to visit specialists);
- on the recommendation of a specialist, start taking multivitamins, including folic acid. A course of vitamins should be started 2-3 months before conception;
- When preparing for pregnancy, you should give up bad habits: drinking alcohol, smoking. Review your diet and diet: fill it with foods rich in vitamins and minerals.
Brief summary
It is worth agreeing in advance with an obstetrician-gynecologist who will advise you throughout your pregnancy. It is important to understand that an isolated case of an empty ovum is not a death sentence. This absolutely does not mean that one of the partners has disorders in the reproductive system. The main thing is not to get upset and continue trying to get pregnant (after anembryony, you can start procreation in six months), then everything will definitely work out.
Don't forget to write comments. Tell us about your experience, ask questions. Share this article on your social networks. Don't forget to rate it. Thanks for visiting.
ecobesplodie.ru
Pregnancy after anembryony
In most cases, the pathology does not affect reproductive function. Women who have experienced anembryonia once subsequently successfully carry and give birth to healthy children. At the same time, it is important to have a clear idea of when you can become pregnant after anembryonia. Each case is individual, so after suffering a pathology, before planning your next pregnancy, you must consult a doctor. At the same time, gynecologists do not recommend attempting to conceive again 3–6 months after diagnosing anembryonia.
Empty fertilized sac or no embryo
Obstetric pathology is an important aspect of modern medicine. And among all diseases, miscarriage holds a special place. For women who hoped for a successful conception and further development of the child, this becomes a heavy blow. A similar situation can occur in the early stages, when a non-developing pregnancy of the anembryonic type occurs, which indicates the absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg. Why this happens and what actions should be taken are questions that the doctor will answer. And a woman should follow his recommendations.
Causes and mechanisms
The causes of undeveloped pregnancy are diverse and complex. It is difficult to single out one factor that has the greatest impact on a woman’s body before and after conception. Most often we are talking about an association of several reasons. Of these, the following are important:
The sensitivity of the embryo to external unfavorable factors is greatest in the early stages. There are critical periods during pregnancy when the risk of pathology is significantly higher. This is mainly observed 7–12 days after conception, during implantation of the fertilized egg into the uterine mucosa, and from 3 to 8 weeks of gestation, which is associated with active processes of embryogenesis.
Among the mechanisms of development of anembryonia, the main role belongs to disruption of the life support processes of the embryo, which leads to its death. This occurs against the background of cessation of chorionic blood flow, involution of the villous membrane and exudative-fibrous reaction of the endometrium. The latter, instead of decidual transformation, acquires signs of glandular-cystic hyperplasia. If the pregnancy is not rejected, the fertilized egg without an embryo can persist in the uterus for a long time, increasing the risk of complications.
Anembryonia is a type of non-developing pregnancy. And its causes include external and internal factors that have an adverse effect on the fetus in the early stages of gestation.
A fertilized egg without an embryo does not have clear symptoms. But despite this, certain features can be identified in the clinical picture that make it possible to suspect obstetric pathology. As a rule, we are talking about the following manifestations:
- The size of the uterus does not correspond to the gestational age.
- Signs of pregnancy gradually disappear.
- Uterine tone is reduced.
- Scanty bleeding from the vagina appears.
During a dynamic gynecological examination, the size of the uterus does not grow, as is normal, but, on the contrary, decreases. Cyanosis of the mucous membrane of the cervix and vagina disappears. Rectal temperature also decreases.
If a non-developing embryo lingers in the uterine cavity for a long time, then complications arise. First of all, we are talking about a blood clotting disorder (coagulopathy or DIC syndrome). In this case, increased bleeding occurs from various parts of the body and internal organs, which is difficult to stop. The second danger is infection of the mummified ovum and the development of endometritis.
What is a fertilized egg?
The sac is the structure surrounding the embryo (the fetus in its earliest stages of development).
Inside it, in addition to the embryo, there is amniotic fluid, which is a natural environment and protection for the developing fetus. It is this structure that is an indicator of the presence of pregnancy and its viability in the first weeks. After a missed period, a woman can take a pregnancy test, but the result of this test is not 100% proof that she is pregnant. A delay in menstruation is also not a reliable sign, as it can occur due to a number of other reasons, for example, inflammatory processes and other pathological processes in the organs of the reproductive system (after the delay, the fertilized egg was not detected).
It is possible to detect a fertilized egg in the early stages using a diagnostic method such as ultrasound, which gynecologists have recently given their preference to.
Visualization of the fertilized egg most often occurs at about five weeks of pregnancy, but its presence does not always guarantee the development of a healthy pregnancy.
In the middle of the fifth week, a specialist can examine the yolk sac inside the fertilized egg, which is the first source of nutrition for the developing fetus. If the fetal egg and yolk sac become visible in the ultrasound image, this is also not a guarantee of a healthy pregnancy, however, the absence of the latter may indicate serious pathologies in the development of the embryo.
Characteristics of the ovum that indicate problems in the development of pregnancy may include the following indicators:
- the fertilized egg does not grow as it should during a normal pregnancy (its growth until the 9th week of pregnancy should be about 1 mm per day);
- fertilized egg of irregular shape;
- absence of a yolk sac.