03/01/2018 Category: Diseases and complications Author: Marina Kravchenko
Many pregnant women wonder whether this frequent routine examination by a gynecologist and ultrasound examination is really necessary, which, according to some beliefs, harms the unborn baby. Maybe if nothing bothers you, then these tests and measurements are not needed? But many problems are outwardly asymptomatic, and can affect a newborn in a completely unpredictable way and cripple him not only physically, but also mentally for his entire life span. Low hydramnios also applies to this problem.
- What is oligohydramnios, classification
Video: Dr. Komarovsky’s commentary on ultrasound during pregnancy
- Video: comments by Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology B.M. Petrikovsky regarding oligohydramnios
What is amniotic fluid, why is it needed, the volume is normal
The medical term for this concept is amniotic fluid. It is located inside the membranes (vesicle) and surrounds the fetus. From this environment, the embryo (human embryo) receives nutrients in the early stages of development; it also performs a protective function and ensures the baby’s comfort.
This is a clear or slightly cloudy liquid that contains proteins, fats, glucose, hormones, salts, vitamins, as well as fetal waste products.
The protective functions of amniotic fluid include:
- mechanical (the aquatic environment absorbs shocks and pressure from the outside);
- infectious (due to tightness and the presence of immunoglobulins in it);
- noise (muffles external sounds).
To ensure favorable living conditions for its inhabitants, the environment creates:
- constant pressure mode;
- constant temperature;
- freedom and convenience of movement.
The amount of these waters is important for determining the condition and development of the fetus. To measure them, the amniotic fluid index (AFI) is used.
The amniotic fluid index depends on the stage of pregnancy, and starting from 16 weeks, its value gradually increases, reaching a peak at 32 weeks, and then AFI values decrease.
Sozinova A.V., practicing obstetrician-gynecologist. More than 12 years of experience in the specialty.
https://diagnos.ru/procedures/analysis/iazh
IAH standards:
- 16 weeks - 73–201 mm (average 121 mm);
- 17 weeks - 77–211 mm (average 127 mm);
- 18 weeks - 80–220 mm (average 133 mm);
- 19 weeks - 83–230 mm (average 137 mm);
- 20 weeks - 86–230 mm (average 141 mm);
- 21 weeks - 88–233 mm (average 143 mm);
- 22 weeks - 89–235 mm (average 145 mm);
- 23 weeks - 90–237 mm (average 146 mm);
- 24 weeks - 90–238 mm (average 147 mm);
- 25 weeks - 89–240 mm (average 147 mm);
- 26 weeks - 89–242 mm (average 147 mm);
- 27 weeks - 85–245 mm (average 156 mm);
- 28 weeks - 86–249 mm (average 146 mm);
- 29 weeks - 84–254 mm (average 145 mm);
- 30 weeks - 82–258 mm (average 145 mm);
- 31 weeks - 79–263 mm (average 144 mm);
- 32 weeks - 77–269 mm (average 144 mm);
- 33 weeks - 74–274 mm (average 143 mm);
- 34 weeks - 72–278 mm (average 142 mm);
- 35 weeks - 70–279 mm (average 140 mm);
- 36 weeks - 68–279 mm (average 138 mm);
- 37 weeks - 66–275 mm (average 135 mm);
- 38 weeks - 65–269 mm (average 132 mm);
- 39 weeks - 64–255 mm (average 127 mm);
- 40 weeks - 63–240 mm (average 123 mm);
- 41 weeks - 63–216 mm (average 116 mm);
- 42 weeks - 63–192 mm (average 110 mm).
How does oligohydramnios affect a pregnant woman?
Oligohydramnios, especially if severe, poses a particular threat to both the fetus and the expectant mother. If there is insufficient amniotic fluid in early pregnancy and in the 2nd trimester, spontaneous miscarriages often occur. Low hydramnios is also dangerous in the later stages of pregnancy, since in this case it is fraught with premature birth.
Contractions during childbirth with oligohydramnios are quite painful and practically ineffective, moreover, in this case there is a slow dilatation of the cervix. Such weak labor activity is prolonged, and when the amniotic sac is opened, a small amount of thick fluid stained with fetal feces is observed.
The danger of low water
Now about the consequences. First of all, oligohydramnios threatens abortion. In this regard, severe oligohydramnios is most dangerous in the second trimester of pregnancy, since at 18-26 weeks the unborn child is not yet ready for independent life outside the mother’s womb.
As the period increases, the risk of fetal death decreases. Thus, oligohydramnios at 37 weeks can result in premature birth, but this is no longer critical for the child, because at this stage the pregnancy is already considered full-term.
In 80% of women with oligohydramnios during childbirth, labor is weak.
Features of the 33rd week of pregnancy
33 weeks pregnant
With the onset of the third trimester of pregnancy, expectant mothers begin to worry, because now their baby can appear at any time, especially from the 33rd week. This week is characterized by peak belly growth.
At the 33rd week of pregnancy, the baby develops facial features: ears, legs, eyebrows, hands, nails, and hair begins to grow. All systems, with the exception of the respiratory, immune and nervous systems, are practically formed. The baby's weight at 33 weeks is on average 2 kg, and his height reaches 43-44 cm. At this time, leakage of amniotic fluid is possible, which may indicate oligohydramnios.
Is moderate oligohydramnios dangerous at 29 weeks of pregnancy?
Oligohydramnios is a low volume of amniotic fluid - 0.5 liters or less. This pathology is associated with disorders related to the formation and absorption of fluid. Currently, moderate oligohydramnios during pregnancy is observed in 0.3 - 0.5% of pregnant women.
It should be clarified that oligohydramnios is not a pathology characteristic only of a certain category of pregnant women. It can equally appear in firstborns, as well as in women giving birth to their second or third baby.
To avoid an unpleasant situation, you should know why oligohydramnios occurs in a pregnant woman. The reasons lie, as a rule, in the presence of hypertension or gestosis. Typically, the degree of pathology directly depends on the severity of the disease and its duration.
If the urethra is blocked, for example, there is insufficient production of amniotic fluid.
Chronic oxygen deficiency of the fetus is one of the provoking factors of oligohydramnios. Against the background of hypoxia, blood flow is redistributed to vital organs. At the same time, the supply of oxygen to the kidneys and lungs, those organs that, at the end of the pregnancy, are primarily responsible for the production of amniotic fluid, is significantly reduced.
A presumptive diagnosis occurs if there is a difference in the height of the uterine fundus and the size of the abdomen from existing standards. Low fetal activity can also be an indicator of oligohydramnios.
It is important to perform Doppler measurements in the uterine arteries of the pregnant woman, in the middle cerebral artery of the infant and in the umbilical cord artery. The preliminary diagnosis is confirmed using ultrasound
Ultrasound examination allows you to determine the volume of water and calculate the amniotic fluid index (AFI). When diagnosed with “moderate oligohydramnios,” the index is 2–5 centimeters. Normally, the figure should be 5–8 centimeters. If the IAF does not reach 2 centimeters, we are talking about a pathology such as severe oligohydramnios
The preliminary diagnosis is confirmed using ultrasound. Ultrasound examination allows you to determine the volume of water and calculate the amniotic fluid index (AFI). When diagnosed with “moderate oligohydramnios,” the index is 2–5 centimeters. Normally, the figure should be 5–8 centimeters. If the IAF does not reach 2 centimeters, we are talking about a pathology such as severe oligohydramnios.
A pregnant woman should be aware of the dangers of oligohydramnios in severe and moderate degrees. Of course, the greatest risk is posed by a severe form of pathology detected at 18–26 weeks.
However, such an early termination of pregnancy leaves virtually no chance for a baby who is not prepared for existence outside the womb.
It is possible to develop intrauterine developmental defects, for example, fusion of the aqueous membrane and the skin of the fetus, which leads to obstacles in the normal physical development of the baby. If there is a threat to the woman's health, it is recommended to perform a cesarean section at any stage of pregnancy.
Moderate oligohydramnios at 29 weeks can lead to the birth of a baby with varying degrees of malnutrition. Hypotrophy is the discrepancy between gestational age and fetal size.
As a rule, the outcome of pregnancy is favorable and the child is in satisfactory condition.
Sometimes outpatient treatment is prescribed with the necessary vitamin and mineral complexes. Severe pathology requires treatment in a hospital setting using pharmacological drugs. First of all, doctors treat the disease that led to the pathology.
Simultaneously with treatment, constant monitoring is carried out, monitoring the child’s development using ultrasound, Dopplerography, and CTG. The woman herself may not feel any changes in her condition.
Rarely, there is pain in the abdominal area, which may become stronger with fetal activity.
Preventive measures will help reduce the risk of developing oligohydramnios at week 29. These include proper nutrition, adherence to the recommended daily routine, lack of heavy physical activity, visiting a gynecologist, and frequent walks.
Low water
Moderate oligohydramnios during pregnancy is quite rare; statistically, no more than 5% of pregnant women have this diagnosis by the end of pregnancy.
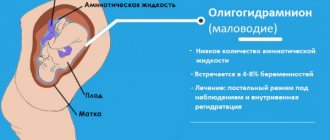
Oligohydramnios in pregnant women is an insufficient amount of amniotic fluid.
Amniotic fluid is the water world that surrounds the baby throughout pregnancy. For the first time, amniotic fluid appears already in the third week of pregnancy, and at first its quantity in relation to the size of the fetus itself is very large; in fact, the child has complete freedom.
As the gestational age increases, the amount of amniotic fluid increases more slowly than the child grows, and his freedom is increasingly limited. By 37-38 weeks of pregnancy, the normal amount of amniotic fluid reaches one and a half liters, and by the time of birth it becomes slightly less.
The importance of amniotic fluid for a child’s development cannot be underestimated. They not only serve him as protection, food and environment. Amniotic fluid contains vitamins, microelements and protein necessary for the fetus. Constantly being renewed as a result of both the vital activity of the child himself, who swallows them and urinates in them, and as a result of their constant production and resorption by the membranes, amniotic fluid creates a comfortable sterile environment in which the baby is completely safe.
During childbirth, the amniotic sac serves as a wedge necessary for the soft and rapid opening of the cervix.
The composition of amniotic fluid remains relatively constant, and complete renewal of the aquatic environment occurs every three hours.
If the processes of production and resorption of amniotic fluid are disrupted, their quantity may either exceed the norm or be less than the norm. It just so happened that these conditions in obstetrics are called polyhydramnios, oligohydramnios.
It is important to say that oligohydramnios itself is not some kind of disease, it is just a symptom, and the consequences of oligohydramnios are primarily the consequences of the cause that caused it. Moderate oligohydramnios at the end of pregnancy may be of a physiological nature and pose no danger, while at the same time, oligohydramnios that began early and subsequently become severe in the middle of pregnancy can end sadly.
Causes of oligohydramnios during pregnancy
Oligohydramnios during pregnancy can occur for many reasons and at different stages.
— A tendency toward oligohydramnios, which appears from the very first months of pregnancy, may indicate the presence of severe congenital kidney pathology in the child. Such oligohydramnios, the causes of which lie in the pathology of the fetus itself, unfortunately does not have a favorable prognosis. Very often such a pregnancy has to be terminated (the child cannot live without kidneys).
— Another known cause of oligohydramnios is high blood pressure in the mother. It usually develops at the end of pregnancy, and the mechanism of its occurrence is due to dysfunction of the placenta due to impaired blood flow due to the mother's high blood pressure.
- Slight oligohydramnios is normal during post-term pregnancy, and this is associated with the aging of the placenta.
— Quite often, relative oligohydramnios occurs in one of the fetuses in twins, which is associated with the syndrome of shunting (discharge) of blood in the placenta from one fetus to the other. As a rule, violations in most cases are minor and do not threaten the child.
— The cause of oligohydramnios in pregnant women can also be the presence of a chronic long-standing sexually transmitted infection, untreated and hidden.
— In some cases, the causes of oligohydramnios in pregnant women remain unknown; perhaps there is a dysfunction of the amniotic fluid-producing epithelium of the fetal bladder. It is not always possible to determine what causes oligohydramnios, but the search for causes should always be very careful, because polyhydramnios is only a symptom, and its actual cause can be dangerous for the child and mother.
Symptoms of oligohydramnios
Oligohydramnios during pregnancy, the symptoms of which can be noticed by the woman herself, is very severe. It is necessary that there is very little amniotic fluid so that the pregnant woman can independently suspect that something is going wrong. If oligohydramnios is moderate, the woman does not worry at all, and only with a pronounced decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid do scant signs appear that make it possible to assume this problem.
If a woman has severe oligohydramnios, there is not enough amniotic fluid to allow the baby to move freely in the uterus. This makes fetal movements painful for the mother, and women notice that the baby kicks a lot. Moderate oligohydramnios, which is common in pregnant women, has virtually no symptoms and is diagnosed only by ultrasound examination.
An obstetrician-gynecologist in a antenatal clinic may notice indirect signs of oligohydramnios, such as a discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the gestational age, and ease of palpation of parts of the fetal body. If the uterine fundus is lower by more than 2 cm from the normal norm for pregnancy, the cause may be not only polyhydramnios, but also fetal malnutrition, and even its incorrect position in the uterus.
There is no way to determine oligohydramnios without special examination methods.
There are also other signs of oligohydramnios, for example, some pregnant women report abdominal pain. But they are not specific and cannot indicate exactly oligohydramnios with a full guarantee.
Why is oligohydramnios dangerous during pregnancy?
Is polyhydramnios dangerous? It is impossible to answer this question unequivocally, since everything depends on the duration of pregnancy, the severity of the pathology and the cause that caused it. For example, oligohydramnios in the early stages may be evidence of a severe pathology of fetal development, and of course, such a pregnancy will be terminated. However, this is not always the case, and in some cases the reason is different, the fetus is healthy, moderate polyhydramnios is subsequently compensated with proper treatment and a healthy child is born.
What does oligohydramnios mean for a baby in mid-pregnancy? At 17-27 weeks, the fetus needs enough space in the uterus to develop properly, but oligohydramnios in the second trimester means this space is limited. If the mother has severe oligohydramnios, the fetus is literally squeezed from all sides by the walls of the uterus, and this can cause severe deviations in its development, for example, clubfoot, skull deformities, and congenital dislocation of the hips. The consequences of oligohydramnios during pregnancy subsequently require active treatment of the child by an orthopedist; as a rule, these deformities can be eliminated.
What does oligohydramnios lead to in later stages?
First of all, it affects the course of childbirth. In oligohydramnios, the amniotic sac is flat and does not serve as a wedge to open the cervix. Childbirth with oligohydramnios is often delayed, accompanied by weakness of labor forces, and almost half of women have contraindications to natural childbirth and are prescribed a caesarean section. For example, oligohydramnios and breech presentation are a combination that tends to tip the scales in favor of surgery. Moderate oligohydramnios before childbirth is detected in many women with postterm pregnancy, which complicates their already difficult childbirth.
In the early postpartum period, those who give birth with oligohydramnios have a higher risk of postpartum hemorrhage.
Overall, don't take low water levels as a complete disaster. Most women with moderate polyhydramnios have healthy children. There is only a high frequency of fetal malnutrition, which is understandable, since both oligohydramnios and malnutrition develop for the same reason, due to feto-placental insufficiency.
Diagnosis of oligohydramnios
The diagnosis of oligohydramnios can only be made based on the results of an ultrasound examination. This diagnosis cannot be confirmed by any other methods. For diagnosis, the calculation of the so-called IAF, the amniotic fluid index, is used. It is calculated by measuring in at least 4 places the free space between the fetus and the wall of the uterus, summing the resulting numbers and dividing them by 4. If a woman has a normal amount of amniotic fluid, the IAF is from 5 to 8 cm; if there is moderate oligohydramnios, the index is from 5 up to 2 cm. If the amniotic fluid index is less than 2 cm, oligohydramnios is pronounced.
Treatment of oligohydramnios during pregnancy
Treatment of oligohydramnios is not an easy task, if not impossible. Doctors choose how to treat oligohydramnios during pregnancy based on the cause that caused it, the duration of pregnancy and the severity of the pathology.
If fetal malformations and oligohydramnios, incompatible with life, are detected in the early stages of pregnancy, treatment is reduced to terminating this vicious pregnancy.
If ultrasound reveals aging of the placenta and oligohydramnios, treatment of feto-placental insufficiency is carried out. Actovegin, chimes for oligohydramnios are prescribed very often and even on an outpatient basis. Treatment for moderate oligohydramnios usually does not require hospitalization.
Severe oligohydramnios in pregnant women, which is treated in a hospital, when combined with fetal hypoxia, often becomes a reason for cesarean section even in premature pregnancy due to severe fetal suffering. At the end of pregnancy, doctors decide what to do about oligohydramnios based on the condition of the fetus. If the pregnancy is full-term and the child is not suffering, there is no need to treat this pathology; the pregnant woman is simply given birth.
In any case, if you are diagnosed with oligohydramnios, treatment should be carried out as prescribed by your doctor. During the treatment process, constant monitoring of the fetal condition is carried out using CTG, Doppler, ultrasound, so that if it worsens, there is time to take measures to preserve its and your health.
Since oligohydramnios is practically untreatable, nutrition and folk remedies cannot help here at all. If oligohydramnios is treated with folk remedies, it is aimed at treating the cause, for example, reducing blood pressure in a pregnant woman.
Prevention of polyhydramnios is a planned pregnancy against the background of complete health; there is no other recipe.
Knowing what the dangers of oligohydramnios are and that you most likely will not be able to get rid of it, do not forget that this is a rare pathology, and yet in most cases everything ends well. Listen to your doctor and try to worry less, even if such a diagnosis is made.
Introducing our partner - online store BAG IN THE MATERNITY HOUSE
On the store’s website you can order a ready-made set of things for the maternity hospital or you can independently equip the bag with everything you need for you and your baby. All things in the maternity hospital are certified and approved by the SES for use in a maternity hospital, packed in a special branded transparent bag, which both the ambulance and any maternity hospital will allow you to take with you. Check out several hundred real reviews about how we help expectant mothers.
Free delivery by courier in Moscow and St. Petersburg on the day of order.
Sending orders to other regions by Russian Post and various transport companies.
Causes
Doctors identify several clinical situations that can lead to the appearance of oligohydramnios at this stage of pregnancy. If the expectant mother suffered any infectious disease during the previous trimesters, this may lead to the appearance of oligohydramnios.
This pathological condition also occurs in women who suffer from high blood pressure. The severity of its manifestation is largely due to the frequency of attacks of severe increases in blood pressure.
One of the causative factors for the appearance of oligohydramnios is the presence of various kidney pathologies in the baby. It must be said that in the presence of diseases of the urinary organs, the mother can also develop similar disorders. In this case, mandatory drug correction and the prescription of a treatment complex are required.
The risk of developing oligohydramnios at this stage of pregnancy increases significantly in expectant mothers carrying twins or triplets.
The larger the children, the more clearly this pathology can manifest itself. For the growth and full intrauterine development of several babies, a lot of different nutrients, as well as oxygen, are required.
Doctors note that this pathology can manifest itself in any woman; it can develop both during the first pregnancy and during subsequent ones. If a woman is at increased risk for the development of this pathology, then her health should be monitored more carefully. Also, the appearance of oligohydramnios is practically not affected by the age of the expectant mother.
The amount of amniotic fluid can be determined using an ultrasound examination. Such an examination, as a rule, is carried out routinely for all expectant mothers at the 32nd week of the baby’s intrauterine development. To assess the baby's condition, doctors use a special amniotic fluid index. Its norm is 5-8 cm3.
The severity of various disorders may vary. It is usually moderate to severe. These conditions can be differentiated by the amniotic fluid index used. If its values are in the range from 2 to 5, then the resulting violations can be called moderate. A drop in the index below two cm3 indicates that the degree of severity can be considered quite pronounced.
Oligohydramnios as a symptom
As already mentioned, pathological oligohydramnios is not an independent disease, but is associated with serious changes. It may indicate:
- chromosomal breakdowns;
- intrauterine growth retardation;
- congenital defects (impaired kidney development in the form of polycystic disease, underdevelopment of the kidneys or their complete absence, narrowing or absence of the urethra, blocking the lumen of the ureters);
- disruption of placental development.
There is also idiopathic oligohydramnios during pregnancy - a low amount of fluid for unknown reasons. It does not affect pregnancy and the health of the fetus, is mild, goes away on its own until the end of pregnancy or persists until delivery.
You need to know that oligohydramnios cannot cause genetic disorders or structural defects of internal organs. On the contrary, chromosomal changes or developmental defects provoke the appearance of oligohydramnios. Therefore, if the diagnosis of oligohydramnios sounds next to genetic changes or “deformities,” this means their simultaneous presence.
The development of oligohydramnios can lead to:
- infections in the mother (40% cause oligohydramnios);
- post-term pregnancy (the mother’s body does not produce amniotic fluid longer than required, and its amount in the body is depleted after 9 months);
- hypertonic disease;
- diabetes;
- multiple pregnancy.
During multiple pregnancies, sometimes additional vessels form in the placenta, and blood is redistributed in favor of one of the two fetuses. It absorbs more fluid and, accordingly, produces more urine. The second fetus develops hypoxia, it lags behind in development, and oligohydramnios occurs.
Oligohydramnios during pregnancy may have iatrogenic causes. The formation of amniotic fluid is disrupted by taking certain medications, most often angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Drug names: captopril, enalapril, ramipril and other drugs with similar names. They are contraindicated during gestation. But not all women carefully read the instructions. The doctor does not stop these medications because he does not know that the patient is taking them.
The amount of water is significantly reduced as a result of smoking. Not all women find enough willpower to give up nicotine for this period. Not every expectant mother who smokes develops moderate oligohydramnios during pregnancy. But the risk increases significantly. On average, the volume of amniotic fluid in a woman who smokes is less than in one who leads a healthy lifestyle.
Low AFI level oligohydramnios
In obstetrics, the case when the level of amniotic fluid does not reach normal levels is called oligohydramnios. The causes of this condition are varied, here are the most common:
- Amnionic hydrorhea. When amniotic fluid begins to leak much earlier than PDR (leakage of amniotic fluid). This complication occurs due to rupture of the membranes. The causes of this condition have not yet been studied; experts believe that rupture may occur due to the thinness of the membranes, which occurs as a result of viral infection or their aging. A very small amount of water flows out through the gap that appears as a result of the rupture, but this happens constantly. In this case, the woman needs bed rest - in this case, the amniotic fluid has time to renew itself and the child is not in danger.
- Anomalies in the development of membranes - there are quite a lot of them. The cause of any of these disorders may be poor ecology, genetic factors, and others.
- Infection of the membranes. This situation occurs most often. Infection of the fetal bladder with viruses (this can be measles, ARVI, chicken pox, influenza, and many others) occurs because the placental barrier is not able to protect the fetus from this type of infection. Sometimes infection occurs due to STDs (sexually transmitted diseases). Toxins that are produced as a result of the activity of viruses poison the fetal membranes and disrupt its functioning.
- True post-term pregnancy. In this case, the fetal membranes and placenta no longer perform their full functions, and this leads to the fact that the child begins to lack nutrients and his general condition worsens. Blood circulation in the amniotic membranes worsens, resulting in a decrease in the production of amniotic fluid.
Causes, diagnosis and results of oligohydramnios during pregnancy
Oligohydramnios during pregnancy, what are the risks and what to do when diagnosing it?
Sometimes, while carrying a child, the doctor diagnoses the expectant mother with “oligohydramnios.” This means that there is a small amount of fluid around the child. During pregnancy, the amount and condition of amniotic fluid is important, since the general condition of the pregnant woman and the fetus may depend on it. It is usually impossible to estimate the exact amount of amniotic fluid. At each examination, the doctor measures the abdominal circumference of the expectant mother, checks the height of the uterine fundus in order to promptly identify symptoms of oligohydramnios
during pregnancy (and also polyhydramnios) and check how normal the rate of development of the child is (if there is a developmental delay). Diagnostics using ultrasound can provide a clearer result of the study. A specialist with extensive experience is able to find the approximate amount of water, using the amniotic fluid index as a basis. Such an examination can detect a tendency towards the development of oligohydramnios in the early stages of pregnancy.
The doctor always approaches the treatment of the patient personally. If a small amount of amniotic fluid is found, a secondary examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist is needed. This is, for example, if moderate oligohydramnios is diagnosed during pregnancy - the most appropriate situation in this case, which is often considered a normal option.
Why does the amniotic sac become “empty”? The main sources of amniotic fluid formation are considered to be: the plasma of the expectant mother, the kidneys of the developing fetus and the membranes.
3 years ago
It follows that the potential causes of oligohydramnios during pregnancy are:
- pathology of the vascular-cardiac system of the expectant mother;
- severe congenital diseases of the excretory system and kidneys in the fetus;
- early rupture of amniotic fluid (leakage);
- oddities in the development of membranes (in most cases detected before 20 weeks of pregnancy);
- nephropathy (preeclampsia).
After determining the cause of the pathology, one can judge the subsequent tactics of therapy or diagnosis. Decide whether to try treatment for oligohydramnios
during pregnancy in a certain patient or observation will be sufficient.
Treatment of severe oligohydramnios
Treatment of severe oligohydramnios will require a more serious approach. The pregnant woman is hospitalized so that she is under the constant supervision of doctors. Drug treatment will be used, and if necessary, doctors will induce labor or perform a caesarean section.
Perhaps it is worth reassuring impressionable expectant mothers: the majority of pregnant women diagnosed with moderate oligohydramnios, if they follow medical recommendations, give birth to absolutely healthy, normal children.
Take care of yourself and be healthy!
How dangerous is oligohydramnios for a baby?
Amniotic fluid is the place of growth and development of the fetus. Their deficiency negatively affects the growth and development of the child in the womb. In the early stages of pregnancy, this condition can lead to clubfoot in the baby, congenital dislocations of the hips, and various deformities of the skull. In the later stages, such pathology is dangerous as a complication of labor.
With oligohydramnios, the amniotic sac does not dilate the cervix or only causes it to dilate slightly. This is why childbirth most often occurs by caesarean section.
Ignoring treatment for oligohydramnios during pregnancy can lead to a number of negative consequences. Severe oligohydramnios is dangerous due to complications in a child such as:
- deformation of the fetal skeletal system (injury to large joints and spine);
- abnormal development of limbs;
- asphyxia leading to disruption of the central nervous system;
- fusion of the surface of the fetus with the amnion with the subsequent appearance of malformations;
- growth retardation;
- body weight deficiency;
- excessively dry skin and the appearance of wrinkles on it;
- the birth of a child with low weight and insufficient vitality.
Important: in most cases, during pregnancy with moderate oligohydramnios, healthy children are born. There may be only slight malnutrition of the fetus of varying degrees of severity, which is quite natural, since malnutrition and oligohydramnios are a consequence of fetoplacental insufficiency. At the same time, in the future, such children often get sick and are very excitable.
Diagnosis of oligohydramnios
The amniotic fluid that washes the amniotic sac performs very important functions:
- this is the natural and necessary habitat of the fetus;
- protecting the baby, as well as the umbilical cord and placenta from injury;
- regulates metabolism between mother and fetus;
- helps the baby move freely and take the correct position in the last stages of pregnancy;
- reduces discomfort for the mother during active movements of the child;
- prevents fusion of the skin with the amniotic sac;
- promotes dilatation of the cervix before childbirth.
Amniotic fluid begins to be produced at 8 weeks after conception, constantly changing in volume. At any moment they may be less than normal, but then the amount naturally reaches the required level. Normalization often occurs within a month. This is functional oligohydramnios, that is, a temporary reaction to external causes that does not threaten the child and does not affect the course of pregnancy.
If the lack of water is observed for a long time, for example, at 32, 36 and 39 weeks, we are talking about a dangerous pathological process that requires serious therapy. Fortunately, this is extremely rare - only in 0.3-0.5% of cases and is always accompanied by severe developmental disorders of the baby and placenta, which are determined by ultrasound. In the absence of such defects, treatment of oligohydramnios is limited to taking vitamin support complexes.
Causes of oligohydramnios
Factors that influence the occurrence of oligohydramnios in women are not fully understood. According to medical practice, in most cases the development of a pathological condition at different stages of pregnancy is influenced by the following reasons:
- High blood pressure during pregnancy. Increased blood pressure can occur in every expectant mother, but during pregnancy this phenomenon is minor. With a strong increase in blood pressure, oligohydramnios may develop, especially in late pregnancy. The mechanism of formation of this pathology is due to a malfunction of the placenta due to impaired blood flow due to increased blood pressure in the mother. In this case, the severity of oligohydramnios depends on pressure indicators. Oligohydramnios on the background of hypertension can lead to delays in fetal development (lag in size compared to the norm).
- Multiple pregnancy, during which the distribution of blood flow in the common placenta occurs unevenly. This results in one of the fruits receiving more oxygen and nutrients, while the other receives almost nothing. Often this pathology is observed in one of the fetuses in twins due to the syndrome of shunting (discharge) of blood in the placenta from one fetus to the other. Most often, such violations are minor and do not pose a threat to the child.
- Severe congenital pathologies and defects in fetal development, including renal pathologies and genetic abnormalities of facial development. As a rule, such a pregnancy is terminated.
- Insufficient development of the epithelium of the fetal bladder or reduced secretory function of the aqueous membrane.
- Previous but not fully cured bacterial infections. In this case, pathogenic flora can be present both in the birth canal and in the amniotic fluid, which is determined using special tests.
- Metabolic disorders, in particular obesity.
- Post-term pregnancy - in this case, aging and abruption of the placenta occurs, which leads to a deterioration in the performance of its functions. Most often, in such a situation, artificial birth is caused.
- Leakage of amniotic fluid due to membrane damage.
Pregnant woman has a stomach ache
Oligohydramnios does not cause any specific deviations in the well-being of the expectant mother. Symptoms of severe oligohydramnios are:
- nausea;
- weakness;
- dry mouth;
- aching pain during fetal movements - from the 20th week of pregnancy, the baby’s activity in the womb increases significantly, and if there is a lack of amniotic fluid, its shock-absorbing function is lost, which leads to severe pain. For this reason, only a specialist can diagnose pathology using a gynecological examination and ultrasound;
- a lag in the size of the uterus from the norm at a given stage of pregnancy;
- discrepancy in abdominal circumference at a given stage of pregnancy;
- limited fetal mobility;
- sleep disturbance;
- loss of appetite.
Moderate oligohydramnios during pregnancy at 32 weeks
Modern pregnant women know firsthand what oligohydramnios is. Oligohydramnios is a pathological disease associated with a lack of amniotic fluid. Amniotic fluid is produced by the epithelial cells of the amniotic sac, which contains the fetus.
At the beginning of pregnancy, the water is clear in color. Towards the end, they become cloudy, filled with waste products of the fetus, epithelial cells, vellus hairs, vernix lubrication and other things.
The normal amount of amniotic fluid ranges from 600 ml to 1.5 liters, depending on the individual characteristics of the female body and the unborn child. If there is a deviation from the norm, an ultrasound examination reveals insufficiency of amniotic fluid and diagnoses oligohydramnios, which is also divided into moderate or severe, depending on the degree of deviation from the norm, and later (after 32-33 weeks) or early in pregnancy.
Oligohydramnios, detected after the 26th week, is considered late. Moderate is observed with a slight deviation from the norm and does not require increased attention, often corrected by simple actions in the diet.
Need to drink more fluid
Severe oligohydramnios should be under the supervision of a doctor, who will prescribe a number of actions aimed at possible correction of the condition. Oligohydramnios is diagnosed in every fifth pregnant woman. The reasons for its formation are poorly understood.
Symptoms also differ in individual cases: pronounced or absent altogether. If the pathology is obvious, the following signs are observed:
- aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- painful movements of the child;
- increased or, conversely, noticeably decreased activity of the baby;
- discrepancy between the size of the abdomen and the period of pregnancy (a very relative criterion);
- the height of the uterine fundus differs from normal values;
- fetal developmental delay;
- weakness and nausea, etc.
Symptoms depend on the stage of pregnancy, individually in each case. The above listed signs (even at 32 weeks) are not a cause for concern and stress, but a reason to discuss this with your supervising doctor. Often what is normal for one is pathological for another.
Symptoms of oligohydramnios, diagnosis
With oligohydramnios, there is a lag in such an indicator as the height of the uterine fundus (UFH), and one of the obvious signs is the small volume of the mother’s abdomen, which is uncharacteristic for the established period of pregnancy. These data are analyzed by a gynecologist during each routine examination of a pregnant woman. A decrease in fetal activity may also signal a decrease in amniotic fluid.
Laboratory tests are also carried out: blood is taken for analysis, and amniocentesis is performed for certain indications.
Using a syringe and under ultrasound control, a small amount of amniotic fluid is drawn out, followed by karyotyping
Oligohydramnios should be differentiated from an error in determining the gestational age.
Severe oligohydramnios
This diagnosis indicates serious problems with the placenta or malformations of the child. It is placed when the length of the vertical pocket is no more than 2 cm and the following AFI indicators:
- at week 16 – 62 mm;
- 17 – 65 mm;
- 18 – 68 mm;
- 19 – 71 mm;
- 20 – 73 mm;
- 21 – 75 mm;
- 22-26 weeks – 76 mm;
- 27 – 72 mm;
- 28 – 73 mm;
- 29 – 71 mm;
- 30 – 70 mm;
- 31 – 67 mm;
- 32 – 65 mm;
- 33 – 63 mm;
- 34 – 61 mm;
- 35 – 59 mm;
- 36 – 58 mm;
- 37 – 56 mm;
- 38 – 55 mm;
- 39-42 – 54 mm.
With severe oligohydramnios, additional examinations are required to determine possible abnormalities in the fetus and the condition of the placenta.
When water deficiency is detected against the background of chronic diseases in the mother or placental disorders are detected, the pregnancy is maintained. In this case, a number of measures are carried out, including supportive treatment, monitoring the condition of the fetus and creating favorable conditions for its growth. In most cases, after such therapy, the child is born completely healthy, but with a lack of weight, which returns to normal after a few months.
If severe developmental abnormalities, genetic or chromosomal abnormalities are found in the fetus, it is recommended to terminate the pregnancy. At the same time, the woman has the right to keep the child. In this case, doctors are obliged to accept her decision and carry out all the measures necessary to maintain his life.
Expectant mothers should know that there are some factors that can trigger the development of oligohydramnios. Among them, the most frequently noted are:
- Untreated and previously suffered bacterial and viral infections.
- Chronic diseases in the mother.
- Infections of the genital organs.
- Obesity in pregnant women and, accordingly, metabolic disorders.
- Hypertension.
- Smoking and other bad habits.
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Late toxicosis.
- Postmaturity of the fetus.
- Pathology of the placenta, damage to the epithelium that protects the membrane with amniotic fluid.
- Hereditary pathologies, anomalies, delay in fetal development.
- Congenital defects of the kidneys and urinary tract of the baby.
To be fair, it is worth noting that these signs are generalized. For example, hypertension is recorded in many pregnant women (about 90%), but only 4% of them develop oligohydramnios.
With a moderate form of oligohydramnios, it is quite difficult to determine its presence. The woman feels well, there are no obvious signs of impairment.
Severe oligohydramnios is characterized by the following symptoms:
- insufficient abdominal size;
- sharp pain that occurs during fetal movement;
- constant nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- poor health with general weakness, nausea, not associated with toxicosis;
- dry mouth.
Only a doctor can determine the problem, so the best solution in this case would be a timely visit to the antenatal clinic.
During the initial examination, the volume of the abdomen and the fundus of the uterus are measured. If the indicators do not correspond to the norm or the signs of oligohydramnios are very pronounced, the pregnant woman is sent for an instrumental examination, where an accurate diagnosis is made.
Deviations from the data given in the table indicate a small amount of amniotic fluid:
What is the difference between moderate and severe oligohydramnios?
Moderate oligohydramnios during pregnancy is determined only by ultrasound and is characterized by a decrease in water volume to 500 ml (AFI 5–8 cm) and the absence of other pronounced symptoms. “Severe oligohydramnios” is a diagnosis that is made if the amniotic fluid volume is less than 500 ml (AFI
Expectant mothers should not panic when they hear or read about oligohydramnios in their medical records, because modern medicine has many methods for getting rid of this condition. First of all, the woman and baby need timely diagnosis, constant monitoring and adequately selected treatment.
The doctor determines the treatment tactics after receiving the results of the study and determining the causes of the development of oligohydramnios:
- post-term pregnancy requires amniotomy and stimulation of labor;
- oligohydramnios, which appears due to leakage of amniotic fluid (amnionic hydrorrhea), requires treatment in a hospital with mandatory bed rest, constant monitoring of the condition of the fetus and the use of vitamins and medications that reduce the tone of the uterus and prevent infection of the membranes;
- infection with the virus requires home treatment with the use of antiviral restorative medications, drugs that improve blood circulation;
- anomaly in the development of fetal membranes suggests the need for therapy to maintain pregnancy and prevent possible infection of the fetus.
Drug therapy
Treatment of oligohydramnios during pregnancy is carried out using various combinations of the same drugs, depending on the identified cause of oligohydramnios. The most commonly used drugs are:
- vitamin complexes, in which water-soluble vitamins B and C predominate;
- angioprotector "Trental", which enhances blood microcirculation and increases its rheological properties;
- antihypoxant "Actovegin" in the form of tablets, ointments or solutions in ampoules, which improves cellular nutrition and accelerates regeneration and metabolism;
- antiplatelet and immunomodulator “Curantil” (tablets), which supports the functionality and youth of the placenta by improving blood circulation in small vessels (we recommend reading: how to drink Curantil during pregnancy?).
Folk remedies
The effectiveness in solving the problem of reducing amniotic fluid was shown by the folk methods used by our ancestors:
- A decoction of 1 teaspoon of young birch buds and leaves has a diuretic effect. It should be taken three times a day.
- Juice from chokeberry berries or 50 grams of the berries themselves before meals. Helps lower blood pressure and replenish vitamin C deficiency.
- Infusion of lingonberry leaves - 1 tablespoon is added to a glass of boiling water and infused for 30 minutes. It is necessary to take ¼ cup before meals to have an anti-inflammatory and diuretic effect.
- Infusion of valerian or motherwort to relieve stress, excess nervousness and normalize sleep.
- A decoction of a mixture of crushed strawberry leaves, yarrow, birch buds, bean leaves and peppermint, rose hips, nettle leaves and string. All ingredients are mixed in equal proportions and poured with a liter of boiling water. This decoction is taken half a glass 3 times a day to relieve the inflammatory process.
The expectant mother needs to remember that before trying this or that ancient method on herself, she needs to consult with the supervising doctor and get his approval. A herbal remedy can weaken or, conversely, enhance the effect of a particular drug.
How to treat
You cannot detect oligohydramnios on your own. This pathology is determined by an obstetrician-gynecologist during a clinical examination. To do this, the specialist uses several basic signs. One of them is the discrepancy between the height of the location of the main reproductive organ and the gestation period of the baby.
If during such an examination the doctor suspects any abnormalities, he will definitely recommend that the expectant mother undergo an ultrasound examination. In this case, you can quite accurately determine the amount of amniotic fluid.
The selection of therapy is carried out individually. This is largely due to the reason that caused the development of this condition. The final period of pregnancy is very important. To assess the need for hospitalization in a hospital, it is necessary to establish the severity of the disorders that have arisen.
With moderate or slight oligohydramnios, the expectant mother will have to attend a day hospital. During these visits she will receive the necessary therapy. Also, to improve your well-being, you may need to use tablets at home. The doctor will prescribe them for the expectant mother.
To improve your well-being, it is very important to maintain the correct daily routine. A mandatory condition of treatment is limiting physical activity.
The expectant mother should get more rest. Regular walks in the fresh air at a moderate pace will be an excellent alternative to exercise.
The choice of delivery tactics is very important in case of oligohydramnios.
In most cases, doctors recommend a cesarean section in this case. This obstetric care tactic is more gentle and reduces the risk of possible injuries and damage during childbirth.
The prescription of multivitamin complexes is a very important condition for therapy. Regular consumption of all vital vitamins and microelements helps improve the overall well-being of the expectant mother.
These medications are prescribed by a doctor. The combination of multivitamin complexes with other methods of therapy helps to achieve fairly good results. In this case, the treatment regimen is drawn up by an obstetrician-gynecologist together with a therapist.
Severe violations require mandatory referral of the expectant mother to a hospital. The risk of premature birth in this case is very high. During such hospitalization, the expectant mother will be given a complex of necessary therapy.
We recommend watching the following video, in which you will learn useful information about oligohydramnios during pregnancy.
Treatment and prevention
Oligohydramnios in the third trimester
If a diagnosis such as oligohydramnios is made at the 33rd week of pregnancy, the woman is prescribed various examinations and laboratory tests. Having passed this path, the expectant mother, together with the doctor, will find out whether there are any pathologies or developmental anomalies in the fetus.
Unfortunately, if defects are diagnosed in a child, it is proposed to terminate the pregnancy. But what if the woman wants to keep the child? Then the treatment will be the same as in the absence of pathologies.
Treatment methods depend directly on the origin of the disease. But in the third trimester, oligohydramnios is considered a late form, so hospitalization in a hospital is necessary. Under the supervision of doctors, ultrasound, CTG, Doppler examinations, as well as laboratory tests will be carried out regularly.
Basically, the doctor prescribes a set of drugs for general improvement:
- Medicines to improve the functioning of the placenta
- Vitamins
- Medicines to normalize metabolism
- Remedies that eliminate the disease - the cause of oligohydramnios
If treatment does not bring the expected results or the disease is diagnosed in a severe form, then a decision is made about a caesarean section.
In order to reduce the risk of oligohydramnios in the third trimester, it is recommended:
- Proper nutrition
- Balanced drinking regime
- Dream
- Hiking
- Taking tests
- Regular scheduled examination by a gynecologist
- Abstinence from physical activity
- Special gymnastics for pregnant women
- Light physical activity
- Chronic Disease Control
- Vaccination
- Planning a pregnancy
It is also worth saying that there are no specific indications for the prevention of oligohydramnios, but the above points will help to significantly reduce the occurrence of this disease.
The best prevention is pregnancy planning. This method involves eliminating all diseases, vaccination, laboratory tests, and an individual consultation with a gynecologist before conception. With this approach, the likelihood of any disease is significantly reduced, which means a new healthy life will be born.
Video about the third trimester of pregnancy:
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
What is the danger
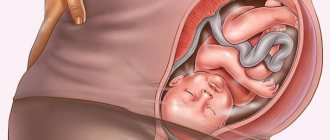
This condition while expecting a child is fraught with various complications. If there is very little amniotic fluid, then the walls of the uterus begin to tightly adjoin the fetal sac, which leads to strong pressure on the child - he bends in an uncomfortable position. This can lead to the following consequences: curvature of the spine, clubfoot, accretion of the skin to the fetal membrane. The skin of the fetus becomes wrinkled and dry.
With prolonged and severe oligohydramnios, close contact of the amniotic sac with the baby’s skin can lead to the formation of Simonart’s ligaments. They wrap around the fetus, interfere with its activity, and in some cases can even lead to serious injury. When they wrap around the umbilical cord, this leads to disruption of blood flow in the vessels, as a result, the child may experience delayed physical development, and in especially dangerous cases, fetal death.
Severe polyhydramnios is physically felt even by a pregnant woman. This is constant pain in the lower abdomen in the second and third trimester. When the child moves, the mother experiences pain. This is especially felt at 36-42 weeks of pregnancy, when the fetus is already quite large.
If there is very little amniotic fluid, labor is often accompanied by slow dilatation of the cervix and weakness of labor develops. The contractions are painful, but their effectiveness is very small. Bleeding may occur after childbirth.
Causes and consequences
Despite the fact that the nature of oligohydramnios is poorly understood, doctors identify some signs:
- gestosis in late pregnancy;
- placental insufficiency (circulatory and metabolic disorders);
- congenital pathologies (for example, reduced function of amniotic fluid production by amnion cells);
- pathologies of the kidneys and genitourinary system;
- past infectious diseases during pregnancy;
- poor nutrition, lack of vitamins, microelements, violation of the drinking regime;
- blood pressure problems (hypertension, hypotension);
- severe and frequent stress during childbearing;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- true post-maturity;
- hydrorrhea, leakage of amniotic fluid;
- multiple pregnancy;
- abnormal fetal development (can be congenital or acquired);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system, metabolic problems in the expectant mother, etc.
Unfree stay in the womb
The situation with oligohydramnios either does not require treatment (usually up to 32 weeks), but is only observed or corrected. However, in case of inappropriate attention to oligohydramnios, the following consequences may develop:
- violation of the free presence of the fetus in the womb and, as a result, entanglements, excessive pressure (dislocations, curvature of the spine), injury to the surface of the child’s skin (dryness, adherence to the amniotic sac), etc.;
- weakness of labor due to the lack of necessary pressure on the cervix, resulting in either slow dilatation or the need for additional stimulation of labor;
- the possibility of delayed fetal development cannot be ruled out.
What is the threat and how dangerous?
Technology in the field of perinatal medicine is developing and oligohydramnios is being diagnosed more and more often. The diagnosis is not always correct; for this reason, pregnant women are prescribed a number of examinations and diagnostics. If reliable, the severity of the pathology is determined and, in accordance with this, treatment is prescribed or, at the discretion of the doctor, medication is limited.
More often, oligohydramnios is not dangerous and occurs without any special symptoms or with minor complications, when it practically does not bother the woman or child.
However, in some cases, severe symptoms are possible, causing not only inconvenience and physical discomfort for both the baby and the mother, but also causing serious problems during pregnancy. In severely advanced cases, the pathology threatens to impair the development of the fetus and can even lead to its death. Therefore, you should not self-medicate, but seek help from specialists.
At 31-32 weeks pregnant, the amniotic fluid level is important. Since the baby is practically formed and occupies all the space in the womb. In order for his existence to be comfortable, the amount of amniotic fluid must be sufficient.
Everything will be fine
How much amniotic fluid should be normal?
The amount of amniotic fluid is determined in pregnant women during ultrasound diagnostics in the second trimester. In the protocol for the ultrasound procedure after 20 and 33 weeks, the volume of water is designated as IAF - this is the amniotic fluid index.
Normally, fluid volume should increase in accordance with the weeks of pregnancy:
The normal volume of amniotic fluid for the entire period of gestation should remain in the range from 600 ml to 1500 ml to ensure normal growth of the baby and ensure sufficient safety. In the last weeks of pregnancy (from 35–36 to 41 weeks), their number decreases to 800–900 ml before birth.
Norms of amniotic fluid
The volume of water is calculated by the amniotic fluid index and the length of the vertical pouch (the area between the fetus and the anterior abdominal wall, which should reach 5-8 cm). In our country, the following IAH standards have been adopted:
- 16 week – 73 – 201 mm;
- 17 week – 77 – 211 mm;
- 18th – 80 – 220 mm;
- 19th – 83 – 230 mm;
- 20th – 86 – 230 mm;
- 21st – 88 – 233 mm;
- 22nd – 89 – 235 mm;
- 23rd – 90 – 237 mm;
- 24th – 90 – 238 mm;
- 25th – 89 – 240 mm;
- 26th – 89 – 242 mm;
- 27th – 85 – 245 mm;
- 28th – 86 – 249 mm;
- 29th – 84 – 254 mm;
- 30th – 82 – 258 mm;
- 31st – 79 – 263 mm;
- 32nd – 77 – 269 mm;
- 33rd – 74 – 274 mm;
- 34th – 72 – 278 mm;
- 35th – 70 – 279 mm;
- 36th – 68 – 279 mm;
- 37th – 66 – 275 mm;
- 38th – 65 – 269 mm;
- 39th – 64 – 255 mm;
- 40th – 63 – 240 mm;
- 41st – 63 – 216 mm;
- 42 week – 63 – 192 mm.
What is oligohydramnios in pregnant women: why is it dangerous?
Oligohydramnios means a condition in a pregnant woman in which the amount of amniotic fluid in the bladder decreases. This pathology is a rare case; it indicates certain deviations in the course of pregnancy.
Why amniotic fluid is needed:
- Protection of the placenta and umbilical cord from the baby’s movements;
- Protecting the child from trauma;
- Prevents the baby's skin from fusing with the amniotic sac;
- Ensuring the exchange of useful substances between mother and fetus.
The longer the pregnancy, the more amniotic fluid is in the bladder. By the end of the period, the volume of water reaches 1-1.5 liters. With oligohydramnios, this indicator is at around 0.5 l.
A lack of amniotic fluid can cause serious consequences for the baby.
There are two types of oligohydramnios: moderate, in which the woman’s well-being does not change, and severe form, when nagging pain appears in the lower abdomen, the child’s movements bring discomfort and the uterus decreases in size.
Consequences of oligohydramnios:
- The fetus cannot move normally in a small amount of amniotic fluid, which leads to the development of physical pathologies;
- The likelihood of pressure from the mother’s organs on the baby increases, which can become a reason for the improper development of his own organs;
- During childbirth, the cervix dilates very poorly, which leads to painful delivery, as well as bleeding.
- Premature birth – 50% chance;
- Lack of oxygen and nutrients.
In severe cases of oligohydramnios, the gynecologist may decide to deliver by obstetric surgery. Natural childbirth can lead to serious complications for both mother and baby.
Moderate oligohydramnios
Often, in conclusion, ultrasound indicates moderate oligohydramnios, when the AF index is 10-15 percent higher than the lower limit, in other words, is within the normal range, and the length of the upper pocket is 2-5 cm. They do this, so to speak, to be on the safe side.
During a normal pregnancy, the gynecologist may prescribe vitamins and medications to improve blood flow.
In some cases, a pregnant woman is referred for Doppler testing and CTG. If their results turn out to be satisfactory, and ultrasound diagnostics did not reveal any defects, then this is considered a physiological feature of the woman, and not oligohydramnios.
Most often, a repeat ultrasound a month later shows that the level of amniotic fluid has returned to normal.
What is oligohydramnios, classification
In a situation where the AFI is below normal, we are dealing with oligohydramnios. Statistics show that such cases are 0.3–5.5% (according to various authors).
The amount of water is determined by the ultrasound specialist in two ways: subjective and objective
Video: Dr. Komarovsky’s commentary on ultrasound during pregnancy
There are two types of oligohydramnios:
- Moderate (slight deviation from the norm).
- Pronounced (2-3 times less than normal).
It can also be:
- Acute (appeared suddenly due to a new causative factor).
- Chronic (develops slowly and the causative factor cannot be quickly eliminated).
What is prescribed for oligohydramnios?
If the doctor determines moderate oligohydramnios at 30, 32, 33, 34 weeks of pregnancy, then treatment will not require hospitalization. The woman will be advised to get more rest and fill her diet with green vegetables and fruits. The pregnant woman will be prescribed special vitamins. You should refrain from heavy physical activity. The woman will be under special supervision by the gynecologist. Treatment will also be aimed at eliminating the cause of oligohydramnios.
Vitamin therapy, as reviews from pregnant women say, has results. Signs of this phenomenon, which caused severe stomach and headache pain and pain in the heart, did not appear. The diagnosis of oligohydramnios in many women was removed, and no negative consequences for the fetus were identified.
If home treatment does not help and there are signs of decreased amniotic fluid, the woman will be treated in a hospital. For placental insufficiency, which causes poor oxygen supply to the fetus, Actovegin is prescribed. Treatment with the drug improves blood circulation, gas exchange in the mother-fetus chain, restores the function of cell membranes, and improves metabolic processes in the placenta. Reviews from young mothers about this drug are positive. For many, blood pressure normalized during pregnancy, fetal movements became calmer, and children were born without pathologies. Treatment with Actovegin did not affect their health.
Treatment with Curantil is added to this drug. It normalizes blood pressure, relieves swelling, increases immunity, stimulates the production of interferon in the body, and will help improve blood supply to the placenta and fetus. Reviews indicate that the effect of the drug did not cause any changes in the development of the fetus. A pregnant woman should not self-medicate with medications. Only the doctor selects the dosage.
If treatment at 36, 38, 39, 40 weeks does not help, and there is a danger to the life of the fetus, then the gynecologist may decide to perform a premature birth. By 38, 39, 40 weeks, all fetal systems are fully defined, and their qualitative development occurs. The child is born without pathologies.
As reviews from young mothers say, not everyone carried children until 40 weeks of pregnancy. Many children were born at 38, 39 weeks and were quite healthy.
Medical definition
According to the classic definition, a similar conclusion is given to women at 40-41 weeks of pregnancy if the volume of amniotic fluid has decreased to 500 ml or less. This formulation takes into account deviations from the norm only before childbirth. But meanwhile, oligohydramnios can be diagnosed at 20 weeks, 30, and 37; the closer the birth is, the more the placenta “ages” (37, 38, 39 weeks).
Throughout the 9 months of a child's development, the volume of amniotic fluid constantly changes. Its specific values for each week of gestation have become known as a result of numerous studies. At any moment, a situation may arise when the amount of amniotic fluid turns out to be abnormally low. Doctors diagnose and prescribe treatment for oligohydramnios during pregnancy, recording a special indicator - the amniotic fluid index (AFI), which for each week has an average value and normal range, for each week it is different (starting from the 16th week onwards - 20, 30, 34 , 35, 36, 37, 38, 39), and additionally, each ultrasound machine has its own table of these indicators.
Considering the degree of severity, moderate and severe oligohydramnios during pregnancy are distinguished. The first type of disease is much easier to deal with. The condition will return to normal if the expectant mother stops being nervous, starts eating rationally, and pays more attention to her health - just do this and things will get better, and this also applies to the period of 37 - 39 weeks. And the second case is a serious problem for a woman. To eliminate it, you will have to go to the hospital and undergo a course of therapy.
Oligohydramnios in pregnant women is a dynamic condition. Its tendency is unpredictable - it can suddenly appear and disappear at any time. We are talking about a functional deviation if it was present at the 20th week of pregnancy, and disappeared at the 32nd week, and in the last weeks - 37-39 and then the decrease in water levels is considered normal. These are temporary disorders that are not considered a pathology.
A persistent abnormal condition for many weeks, that is, severe oligohydramnios, is a sign of severe abnormalities in the development of the child and the course of pregnancy. According to statistics, the incidence of serious pathology is 0.2-0.3% of all cases. In each of them, abnormalities in the development of the fetus and placenta are visible on ultrasound.
Prevention of oligohydramnios is carried out not during pregnancy - at 34 or 35 weeks, for example, but during the period of planning the birth of a child.
Health care
Treatment for oligohydramnios will depend on its type and the cause of its development. If moderate oligohydramnios is the norm, then the treatment will be as follows: the expectant mother will be advised to rest more, watch her diet, take vitamins and periodically consult with a gynecologist. If this is not done, or when the measures taken do not help, the situation worsens, the woman will have to go to the pregnancy pathology department.
When diagnosing a decrease in water, the patient is sent to the hospital for additional studies. It is necessary to undergo an ultrasound, cardiotocography, donate blood and urine to the laboratory. A smear on the fluid will help you find out about leakage of amniotic fluid.
In late pregnancy (37 or more than 38 weeks), an amnioscope can be passed through the cervical canal. The gynecologist will conduct accurate studies of the fluid that will not harm the baby in any way.
If fetal malformations are detected, the woman will be offered to terminate the pregnancy. In case of refusal, treatment will be carried out without changing the technique. The expectant mother will receive the same assistance as if the child has no abnormalities.
If significant abnormalities are observed at 20 weeks, the patient will be asked to consider abortion. This decision has its own reason - the inability to predict the outcome of pregnancy. True, in most cases, by the time the child is born, the situation changes, and people spend their whole lives regretting that they succumbed to the doctor’s persuasion.
The treatment method for oligohydramnios depends on several factors:
- the reason due to which it developed;
- severity of oligohydramnios;
- gestational age.
The most common drug prescribed to pregnant women is Actovegin, due to its ability to maintain the normal condition of the child in many critical situations. The consequences of oligohydramnios are higher in terms of threat to the fetus, depending on when it appeared; the earlier, the more critical. What does this mean? For example, oligohydramnios at the 20th week and at the 30th week differs in that in the first case there is an increased risk of developmental delay and the appearance of deformities. And at 32 weeks and above, oligohydramnios in most cases occurs due to water leakage. Revealed oligohydramnios during the third semester (27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40 weeks) is the basis for the woman being sent to the antenatal department and prescribed a number of procedures: the introduction of vitamins B, C and others, as well as taking Curantil medications, which have a better effect on the blood circulation process in the placenta. Or Actovegin, which ensures the delivery of oxygen to the fetus. The development of oligohydramnios in the first trimester (from 20 to 27 weeks) is unpredictable; even doctors do not undertake to predict the outcome of such a pregnancy and recommend terminating the pregnancy.
IAF is calculated using ultrasound - in a subjective or objective way; the resulting data is compared with a table of amniotic fluid norms for all weeks. For example, at week 16, the normal range of AFI is 73-201 mm. Week 20: 86 – 230 mm; Week 30: 82 – 258; 31: 79–263; 32: 77 – 269; 33: 74 – 274; 34: 72 – 278; 35: 70 – 279; 36: 68 – 279; 37: 66 – 275; 38: 65 – 269; 39: 64 – 255; 40: 63 – 240. Accordingly, the obtained indicators in different weeks, after comparison, indicate polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios.
Meanwhile, there is also an average indicator, which is considered the norm. 20 week – 141 mm; 30 – 145; 31-32 – 144; 33 – 143; 34 – 142; 35 – 140; 36 – 138; 37 – 135; 38 – 132; 39 – 127; 40 – 123.
With a one-time ultrasound examination, a diagnosis of oligohydramnios is not immediately made, since amniotic fluid changes throughout the entire period of pregnancy, its quantitative composition depends on the week of pregnancy and the growth of the child. In addition, each ultrasound machine has its own table.
Not every woman can boast of excellent health, so during pregnancy it is impossible to avoid taking various medications, for example, the same vitamins. Doctors often prescribe Actovegin, which promotes the normal development of the child. Moreover, it can be prescribed at any time, and sometimes Actovegin can be prescribed even during pregnancy planning, for example, in case of impaired blood supply.
The dosage form of the drug is selected by the doctor depending on the woman’s condition and the severity of the disease. Actovegin is available in tablets, ointments, ampoules, creams, and gels. During pregnancy, Actovegin should not be taken based on one’s own considerations and after reading reviews, even knowing the standard dosage prescribed by a doctor - Actovegin is not an ordinary analgin that can be taken without a doctor’s instructions. All medications always have side effects and there is a risk of an allergic reaction.
Only the attending physician individually calculates the dosage, time and method of using a medicine such as Actovegin. After all, the doctor, based on the condition of the pregnant woman, can prescribe Actovegin in tablets, or can prescribe a course of treatment in the form of injections, and in critical situations, Actovegin can be administered parenterally.
Moderate oligohydramnios is not the worst threat when carrying a little person. The most important thing is to stop being nervous, monitor your health and respond to problems in a timely manner.
A gynecologist rarely detects oligohydramnios during pregnancy at 32 weeks. The reasons for this phenomenon are often unknown. Before making a diagnosis and starting treatment, the pregnant woman will be given an ultrasound and a full examination. Screening is carried out more than once, because the amount and composition of amniotic fluid changes every week. The doctor may diagnose moderate or severe oligohydramnios. If a moderate decrease in amniotic fluid is detected, the pregnant woman will be treated at home. If the reasons for the decrease in water volume are associated with any diseases, then hospital treatment will be required.
Insufficient amniotic fluid can affect the development of the fetus. Amniotic fluid contains minerals, proteins, carbohydrates, fats, oxygen, hormones, and enzymes. This is a comfortable living environment for a child. The liquid maintains a constant temperature of +37 C o, preventing stress on the spine, internal organs and organs of movement of the fetus.
When is the diagnosis made?
Reviews from pregnant women indicate that doctors have not fully studied the reasons for the decrease in amniotic fluid. This phenomenon often occurs at 30, 32, 33, 34, 36 weeks of pregnancy. Sometimes oligohydramnios is detected in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. What causes a decrease in the level of amniotic fluid? Doctors identify some reasons for the decrease in amniotic fluid.
- The closer to childbirth, the older the placenta becomes, so the walls of the amniotic sac may become thinner and tear. Most often this happens at 38, 39, 40 weeks of pregnancy or when it is postterm. Amniotic fluid may leak.
- The causes of oligohydramnios are often associated with metabolic disorders in the body of a woman or fetus.
- Genetic abnormalities in child development.
- Infectious diseases in which dehydration of the body is established. Mom may feel dry mouth and limb cramps.
- Chronic diseases: diabetes, heart disease, respiratory diseases.
- Gestosis, late toxicosis.
- The causes of oligohydramnios may be hidden in the incorrect diet of a pregnant woman. When she weighs herself, she is found to be overweight.
- The fetus can also be overweight, which is determined by ultrasound and certain calculations by the gynecologist. Because of this, the placenta may be injured.
- Multiple pregnancy, excessive fetal activity.
To find the causes and establish a diagnosis of oligohydramnios, a woman undergoes an ultrasound scan for several months in a row and is prescribed urine and blood tests. The water level is determined in (mm).
- At 30, 32, 33 weeks of pregnancy, the fluid level is the same 144.
- By week 34 it decreases to 142.
- 36 138
- 38 — 132
- 39 — 127
- 40 — 123
Oligohydramnios will be diagnosed if the thickness of the layer of amniotic fluid is reduced by more than 70 mm or more than 500 ml.
What is the danger?
Oligohydramnios can have negative consequences for both the expectant mother and the child. A pregnant woman has pain and pulling in her lower abdomen. At 30, 32, 33 weeks of pregnancy, the fetus begins to actively move. By 34, 36 weeks the number of his movements can reach 600 per day. Every movement causes severe, persistent pain in the pregnant woman.
By 38, 39, 40 weeks, oligohydramnios can cause nonproductive contractions. The cervix is unable to open quickly. Without enough amniotic fluid, childbirth is very painful with heavy bleeding. The doctor may decide to perform a caesarean section. This will save the woman from excruciating pain and the child from injury.
Oligohydramnios is also dangerous for the fetus. It affects the child’s intrauterine development and may have consequences after birth.
- The position of the fetus in the amniotic sac will change, which will affect the improper formation of the skeleton.
- The walls of the uterus will shrink and put pressure on the baby: there is a danger that the fetal skin will adhere to the fetal membrane.
- The child's skin develops dryness. Skin folds that straighten out by 30, 32 weeks will remain wrinkled.
- The child will not gain sufficient weight and height: by the 32nd week, the average fetal growth is 1700 g, height is 40 cm.
- The consequences of oligohydramnios will affect the baby’s respiratory system. 30, 32 weeks are the development of the respiratory system: hypoxia will not allow the alveoli to form correctly in the lungs.
- At 33, 34, 36 weeks of pregnancy, the fetus is actively gaining weight, the kidneys begin to work, and the reproductive system develops. Oligohydramnios threatens the appearance of pathologies in the development of the genitourinary system.
- At 38, 39, 40 weeks the baby is ready to be born. The danger of oligohydramnios is that Simonart's ligaments appear. These are threads that grow between the fruit and the shell. They can wrap around the child’s entire body or individual parts of his body. The ligaments prevent the child from moving, the consequences can be irreparable: there is a high risk of injury to the child.
- Sinomartic ligaments at 38, 39, 40 weeks disrupt the blood circulation of the fetus. If the threads are wrapped around the baby’s arm or leg, then this threatens atrophy.
- Oligohydramnios can cause the umbilical cord to be improperly positioned. In this case, the fetus will not receive sufficient nutrition and oxygen, which will affect its development. The umbilical cord can wrap around the baby's body and lead to his death.
The consequences of oligohydramnios affect both the health of the expectant mother and the full development of the fetus. The life of the child sometimes depends on the amount of amniotic fluid.