Treatment
During the consultation, the medical specialist will prescribe for the patient an algorithm of actions that will help the patient cure the inflamed eyelid.
Treatment of upper eyelid disease includes:
- Carrying out daily eye hygiene. These procedures include: Careful and thorough removal of crusts;
- Rinsing the eyes with special herbal infusions or special solutions.
Each type of inflammation of the upper eyelid has its own characteristics during treatment:
Scaly blepheritis
If a medical specialist discovers scaly blepheritis in a patient, then treatment of such a disease will be carried out according to the following scheme:
- Washing of sore eyelids;
- Apply at least 4 times a day with medicinal ointments, for example, Tetracycline.
Ulcerative inflammation
For ulcerative inflammation of the upper eyelids, the patient needs to undergo the following treatment:
- Use a special medicinal ointment to remove dried crusts;
- The cleaned surface must be lubricated with brilliant green;
- Apply disinfectants to your eyes.
Meibomian blepharitis
The following methods are used to treat meibomian blepharitis:
Inflamed eyelids are lubricated with the following preparations: Brilliant green solution; Antiseptic ointment; Disinfectants.
In the case when this type of disease appears due to infection, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics to the patient;
A competent specialist will numb the inflamed area and perform a special eyelid massage.
The patient should pay attention to the fact that this procedure should only be performed by a medical professional. Because doing a massage on your own can only make your condition worse.
Demodectic inflammation
In case of demodicosis inflammation of the upper eyelid, the patient must follow the following recommendations:
- The patient needs to carry out hygiene procedures every day using degreasing medications. Such drugs can be tinctures of calendula or chamomile, which the patient can purchase at any pharmacy;
- In order to speed up the recovery of the inflamed upper eyelid, the patient can use a special pharmaceutical solution for the procedures, a prescription for the preparation of which will be issued at an appointment with an ophthalmologist. This medicine is made by employees of the prescription pharmacy department. To prepare the remedy, alcohol (70 degrees) and ether are used in equal quantities. In the case when the patient does not have the opportunity to purchase this medicine, the patient can wipe the inflamed eyelids with medical gauze, which is soaked in a solution of salicylic acid.
- A patient with inflammation of the upper eyelid after being bitten by an infected tick should keep in mind that such a disease is contagious. To ensure that the patient’s loved ones do not also become infected, the patient must use only his own personal towel and sleep on his own personal set of bed linen. Do not forget that the treatment of this disease can take more than 1 month, so it is better to use disposable napkins and towels for hygiene procedures.
Medicines
After examining the patient’s upper eyelid and establishing the cause of the pathology, the ophthalmologist will prescribe the following types of medications for health-improving procedures:
- Eye ointments, which include: Yellow mercury;
- Gentamicin;
- Tetracycline.
- Eye drops. Medicines of this medicinal category to reduce the inflammatory process of the upper eyelid in a patient include: Sulfacyl sodium;
- Prednisolone.
- The medications that the patient will need to take orally are: Biseptol;
- Ampiox.
Diagnostics
In case of inflammation of the upper eyelid, the patient needs to consult an ophthalmologist. Based on the clinical picture, the doctor will determine the cause and type of inflammation, but the patient often incorrectly assesses the complexity of treating the disease. Uncontrolled, and even more so independent treatment can lead to serious complications. That is why it is necessary to strictly follow the recommendations of a medical specialist.
We also recommend that you familiarize yourself with the reasons for a sharp deterioration in vision in this article.
If inflammation of the eyelid occurs, the patient needs to see an ophthalmologist, undergo an examination, and also take samples of discharge for analysis (if your form of the disease has them). If you suspect certain types of infection or specific reactions of the body to certain substances, the doctor may additionally recommend consultations with an allergist, venereologist, or immunologist. After passing through all these specialists and taking a comprehensive history, the patient will certainly be prescribed adequate effective treatment.
To make a diagnosis, consultation with an ophthalmologist is necessary. In some cases, an accurate diagnosis can be made after a visual examination, interviewing the patient, and taking an anamnesis.
To clarify, the ophthalmologist usually prescribes the following diagnostic measures:
- Visometry. Visual acuity is checked without and with correction. If there is blepharitis (especially in children), farsightedness or astigmatism is determined using visometry.
- Biomicroscopy. Slit lamp examination. Swelling, redness of the edges of the eyelids, purulent discharge, and skin scales are detected.
- Microscopic examination of eyelash roots. Several eyelashes are taken from the patient and examined under a microscope to identify tick-borne infestations.
- Sowing tank A smear is taken from the eyelids and conjunctiva to determine the infectious agent that caused blepharitis. This is necessary for selecting an antibacterial drug.
There are many eyelid diseases that have a similar clinical picture. To make a correct diagnosis, proper selection of research methods is of great importance.
- Visual examination followed by determination of visual acuity and measurement of intraocular pressure;
- Diagnostics of refraction;
- Study of the functions of the muscles of the visual apparatus;
- Ophthalmoscopy and exophthalmometry;
- Clinical analysis of urine and blood;
- Microscopic analysis and keratometry of the cornea;
- Fundus angiography;
- Additional auxiliary tests are x-ray, MRI and CT scan of the brain.
Diagnosis of eye blepharitis is based on the clinical picture of the disease. It consists of the patient’s complaints (history), examination data, identification of concomitant diseases and laboratory tests.
Initially, the ophthalmologist determines the patient's visual acuity. To identify myopia, astigmatism, presbyopia, hypermetropia, the doctor examines the state of accommodation and refraction of the eyes.
Then biomicroscopy is performed. This is a visual examination to determine the structure and condition of the tear film, conjunctiva, eyelashes, cornea and eyelid margins. The examination uses a slit lamp (ophthalmic microscope).
1. If necessary, additional analysis is done at the diagnostic center. It reveals the microbial, cellular composition of scrapings from the conjunctiva, the separated base of the eyelashes and the secretion of the glands located there.
2. Demodectic blepharitis is diagnosed by microscopic examination of removed eyelashes. Five of them are taken from both eyes. The diagnosis is confirmed if the laboratory technician detects 6 or more motile Demodex, their larvae at the ciliary roots. If there are fewer ticks, then the person is a carrier, but not sick.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=okSoNGtr0QM
3. If infectious blepharitis is suspected, a bacteriological culture of a smear from the conjunctiva is performed.
4. If the cause of the disease is allergic reactions, the patient visits an allergist. He prescribes allergy tests.
5. If a worm infection is suspected, the doctor will prescribe a fecal test for their eggs.
6. Chronic blepharitis with thickening of the bases of the eyelashes gives reason to suspect carcinoma, basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma. To confirm or refute the prognosis, a histological biopsy is performed.
7. Differential examination of anterior blepharitis is carried out if the patient has eyelid cancer or keratoconjunctivitis.
Careful eyelid care is the basis of treatment for blepharitis, regardless of the cause of the disease.
Blepharitis
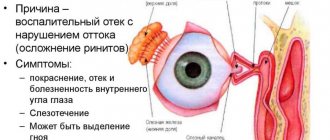
Inflammation of the eyelid margin can be caused by a variety of reasons, including:
- Meibomian gland dysfunction;
- bacterial infection. Bacteria live along the edges of the eyelids and at the base of the eyelashes, the excessive growth of which can cause activation of the pathological process;
- allergic reaction in response to exposure to a drug, microbes, cosmetics, dust, pollen, wool, food;
- autoimmune processes;
- fungal infection;
- long stay in dusty rooms;
- farsightedness and myopia;
- digestive problems;
- parasites. Blepharitis can be caused by Demodex mites. Usually, not only the organs of vision are involved in the process, but also the skin of the face. Acne, redness appears, and the oiliness of the skin increases;
- dry eye syndrome.
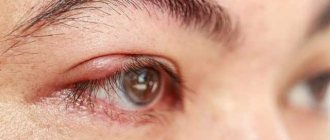
The disease causes itching and pain, swelling, redness, a feeling of heaviness in the eyelids, and lacrimation. Active loss of eyelashes, the appearance of scales, and pathological discharge may also be observed.
Symptoms of the disease may differ depending on the type of inflammatory process. Thus, with the demodectic form, intense itching is observed, which intensifies in warmth. There is a foamy discharge at the edges of the eyelids. The eyes quickly get tired and red. With the seborrheic type, scales appear on the eyelid that look like dandruff. There is a burning sensation, itching, and a feeling of the presence of sand. The ulcerative type is characterized by the appearance of purulent secretion on the edges of the eyelids. In the morning, the eyes stick together due to pathological secretions, so they are difficult to open.
Experts distinguish inflammation of the upper and lower eyelids. In the first case, swelling, redness, burning, severe itching, and narrowing of the palpebral fissure appear. Scales and ulcers appear on the side of the eyelash edge. In some cases, the process may affect general well-being, causing weakness and fever.
Inflammation of the upper eyelid can be caused by a large number of reasons:
- demodicosis;
- allergy;
- injuries;
- decreased immunity;
- infectious diseases;
- endocrine disorders.
Inflammation of the lower eyelid usually has less severe symptoms. Most often there is slight swelling and redness. The pathology is sometimes accompanied by photophobia and increased eye fatigue. Scales and ulcers form very rarely. If this is still present, then there is a discharge of pus or loss of eyelashes. Blepharitis can be caused by poor diet, poor hygiene, reaction to cosmetics, burns, injuries, and ophthalmological disorders.
There can be many reasons for inflammation of the eyelid above the eye. A survey will help you figure this out.
Symptoms
One of the main causes of inflammation of the lower eyelid is blepharitis. The insidiousness of this pathology lies in the fact that it can last for quite a long time, and then even recur. Blepharitis can occur in two forms:
- an inflammatory process develops that affects the tissue of the ciliary area;
- posterior marginal blepharitis, which affects the glands located inside the eyelid.
The danger of posterior marginal blepharitis is that it can gradually affect the conjunctiva and corneal layer of the eyeball.
When the area under the eyes becomes inflamed, the following symptoms may occur:
- severe swelling of the lower eyelid;
- discharge of an oily fluid when touching the affected part of the eye;
- red coloration of the skin on the inflamed eyelid;
- visual heaviness of the eyelid;
- increased lacrimation;
- eyelash growth is too slow;
- burning and itching sensation in the area of the inflamed eyelid;
- pronounced peeling of the epidermis in the affected area.
When the lower eyelid is affected, the production of moisturizing lubricant is disrupted, and the sebaceous glands are responsible for this process. The liquid secretion becomes thick enough and does not manage to get under the eyelids. All this leads to the fact that it accumulates along their edges and dries out, forming scales before our eyes. Over time, they fall off and in their place ulcers form, which are accompanied by infection. There is severe swelling of the edges of the eyelids, red discoloration, itching and pain.
With a constant inflammatory process in the eyelids, the normal growth of eyelashes may be disrupted and they may even fall out. Mostly, this symptom indicates that the inflammatory process of the lower eyelid has become chronic.
Along with the listed symptoms, with severe inflammation of the lower eyelid, there is a significant deterioration in vision, as well as severe pain in the eye area. In some cases, eyelash loss and severe swelling occur. In addition, there may be a deterioration in the patient’s general well-being, increased fatigue and lethargy, which interferes with maintaining a normal lifestyle.
Blepharitis: symptoms
Blepharitis is characterized by inflammation of the upper eyelid and the corner of the eyelid. It has already been mentioned that the symptoms of blepharitis depend on the type of disease. Only a doctor can determine the type of blepharitis after a thorough laboratory examination.
There are general symptoms that are characteristic of any type of blepharitis, which should alert the patient and guide the doctor.
The main symptoms are swelling of the edge of the eyelid and redness of this area. In this case, the patient feels unpleasant sensations: itching, burning.
Often ulcers appear that either look like small scales or constantly bleed and dry out. A sticky secretion may be released from the eyelash follicles. If blepharitis is allergic, the eye becomes very watery.
The eyes get tired quickly, especially if a person constantly needs to be attentive. It's hard to work on a computer. The patient reacts difficultly to light; in special cases, this symptom turns into photophobia. The pain also intensifies when exposed to wind or dust.
If the disease affects the eyelash follicles, the eyelashes may fall out, become discolored, and then change the direction of growth.
In a child, blepharitis manifests itself with the same symptoms. The child scratches his eyes, reacts painfully to light, and may wake up from dried discharge. In the morning, my eyes hurt more because of this.
Blepharitis in children: features and methods of treatment
Blepharitis in children occurs when the skin and loose tissues of the eyelids have a low fat content. A common cause of pathology is infection of the eyelids with Staphylococcus aureus against the background of the general weakening of the child.
Street games, interacting with animals, exchanging toys, etc. make children's hands dirty. They do not like to wash them, but they often rub their eyes as a result of which viruses, microbes, worm eggs, sand, dust and other pathogenic agents get into them.
Children can get all types of blepharitis. Pathology can develop unnoticed for a long time. Because of this, therapy is started when the disease takes an acute form.
Often, blepharitis in children develops in a sluggish form, and some of its traditional signs are not observed. There is a risk of complications: phlegmon, meibomitis, keratitis, conjunctivitis, etc. Due to unwashed hands, children can become infected with multiple infections, which provoke combined forms of blepharitis.
- immunodeficiency;
- hypothermia;
- nervous and physical stress;
- current or resolved infectious diseases;
- allergies;
- chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- infection with worms;
- diabetes;
- metabolic disorders;
- foreign objects in the eyes;
- infectious foci in the nose, mouth, tonsils, etc.;
- hormonal changes in the body during puberty;
- poor eye hygiene;
- congenital visual pathologies: strabismus, astigmatism, myopia;
- food allergies: diffuse neurodermatitis, diathesis, sensitivity to milk, etc.;
- vitamin deficiency, protein deficiency, anemia due to impaired absorption in the gastrointestinal tract or infection with worms.
- swelling, inflammation, redness and itching of the eyelids;
- narrowed palpebral fissure;
- the appearance of crusts on the base of the eyelashes and their loss;
- redness of the proteins and dilated blood vessels on them;
- burning, stinging, sensation of a foreign object and film in the eyes;
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=
The photo shows the symptoms of blepharitis in children.
For the treatment of childhood blepharitis, eye drops are used: Miramistin, Sulfacyl, Picloxidine. Antibacterial ointments are also used: Ophthalmotrim, Oriprim, Colbiotsin.
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment include: magnetic therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, electrophoresis with antibiotics and vitamins, ultra high-frequency therapy.
Herbal remedies for local treatment include tinctures of calendula and chamomile. They have an anti-inflammatory effect.
In addition to therapeutic measures, the child’s diet is adjusted; in case of allergic blepharitis, it should be hypoallergenic.
Treatment tactics depend on the correct diagnosis of the patient. To do this, you should visit an ophthalmologist. Based on complaints and examination results, the doctor will determine a strategy for managing the patient.
Some forms of eye pathologies require hospital treatment. These are purulent processes, abscess, phlegmon, tuberculosis, penetrating injuries and infections caused by them.
If a fungal or allergic nature of the disease is suspected, the ophthalmologist will refer you to culture the discharge from the eye or to an appointment with an allergist to identify the allergen.
Infectious diseases of the eye system require topical antibacterial drops, and in some cases, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs orally or by injection.
The herpes virus requires the use of antiviral drugs, and fungal infection requires antimycotics.
Barley
Barley is an acute purulent inflammation of the eyelids. The disease is accompanied by pain, redness, and swelling. The pathology tends to worsen in the autumn-winter period. Experts distinguish two main forms of the disease:
- external – damage to the hair follicle;
- internal – inflammation of the meibomian gland.
Often, the pathological process develops in response to a staphylococcal infection entering the hair follicle of the eyelash. Infectious agents can enter the body along with dirt and dust.
The disease occurs in four main stages. At the infiltration stage, itching, swelling, pain, and redness appear. After a few days, the inflammatory process ends with self-healing or the formation of a capsule within which pus forms.
Important! A stye may appear on the inside or outside of the eyelid. It looks like a whitish formation on the edge of the eyelids
The cyst breaks out either independently or is done by a qualified specialist. After the pus drains, the capsule decreases in size, but a purulent secretion may still come out of it for several days. And at the last stage, a crust forms, under which healing processes take place.
It looks like a whitish formation on the edge of the eyelids. The cyst breaks out either independently or is done by a qualified specialist. After the pus drains, the capsule decreases in size, but a purulent secretion may still come out of it for several days. And at the last stage, a crust forms, under which healing processes occur.
Localization of inflammation in the eyes
The eye has a very complex structure. It consists of several parts and fabrics, each of which has its own functions. Inflammation of the organs of vision is understood as the totality of their various inflammatory pathologies. They affect one or another part of the organ of vision. When the eyeball is inflamed, a pronounced vascular pattern is observed. The reason is plethora. A chronic pathological process may affect the eyelids, lacrimal glands or corners of the eyes. In general, inflammation affects:
- conjunctiva;
- eye socket;
- cornea;
- iris;
- tear ducts;
- vessels.
It is worth distinguishing between inflammation itself and redness of the eye, which is caused by physical factors. These include dust, lenses, sand, bright light, wind, smoke and even headaches. Redness as a result of these factors is comparable to simple irritation, which most often goes away on its own. It can become a true inflammation only as a result of the addition of an infection caused by viruses, bacteria or fungi.
Inflammation of the lower eyelid
One of the common diseases that causes inflammation of the lower eyelid is stye. It often results from a bacterial infection. The developing inflammatory process is complemented by swelling, painful discomfort and accumulation of pus in the affected area.
The inflamed area must be treated with medicinal ointment (tetracycline, erythromycin).
The products are used before bedtime, and the following rules must be followed:
- Before applying the ointment, hands are thoroughly washed with soap.
- During the procedure, you should use a cotton swab.
- You should act carefully so as not to damage the mucous membrane of the eye.
In the treatment of stye, you cannot do without eye drops, which have a number of useful properties:
- anti-inflammatory;
- antibacterial;
- disinfectant;
- painkillers.
To eliminate the problem, it is recommended to use Floxal, Tobrex, Levomycetin. Before instilling the product, you need to hold the bottle in your hands for a while. The procedure is performed with clean hands. For preventive purposes, it is also worth treating the healthy eye.
If the disease is severe, drugs in the form of ointments and drops will not be enough. In this case, the specialist will prescribe tablets with an antibacterial effect.
Prevention
Hygienic procedures are very important for the effective treatment of inflammation of the upper eyelid. The final result directly depends on a responsible attitude to treatment.
The basic rule of eye care is to wash the eyes daily. To do this, use sterile dressings and only boiled water. You can use boiled infusion of calendula or chamomile. Infusions of these herbs have a local anti-inflammatory effect. The solution should be at room temperature so as not to damage the delicate skin of the eyelid. It is necessary to rinse both eyes, even if only the eyelid of one eye is inflamed. Use individual swabs or bandages for each eye.
To avoid re-infection, maintain cleanliness and sterility during morning and evening toilets, and do not touch your eyes with unwashed hands.
The most important condition for successful prevention of blepharitis and further inflammation of the eyelids is eye hygiene and cleansing. These procedures are performed in the same way as in the treatment of blepharitis.
You should not touch or rub your eyelids, especially if your hands are dirty. This can cause additional infection and damage the base of the eyelashes. This will lead to a severe form of blepharitis, which will be very difficult to cure. A chronic, incurable form of the disease is also possible. With it, long periods of recession are possible, but not a complete cure.
When preventing blepharitis, it is important to regularly clean and disinfect your eyes. For this purpose, a solution of Furacilin or infusions of calendula and chamomile are used. The eyelids are wiped from the outer corner moving towards the inner edge of the eye. Sterile cotton wool swabs are used for the procedure.
The patient's lifestyle and diet should be healthy. It is important that the food consumed contains enough microelements and vitamins.
If pathologies of the respiratory tract, oral cavity, or gastrointestinal tract appear, they must be treated in a timely manner. Interaction with allergenic agents, including seasonal ones, which cause inflammation of the eyelids in the patient, must be avoided. If this does happen, you should urgently contact an ophthalmologist.
If infection with intestinal parasites, including worms, occurs, it is necessary to urgently carry out therapy to get rid of them.
It is better for women to refrain from using cosmetics. It will irritate the eyelids and mucous membranes of the eyes. This will worsen the course of the disease and delay its recession.
There are several ways to prevent the development of eyelid diseases:
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- Refusal to use low-quality cosmetics;
- Strengthening the immune system, especially during infectious diseases and during exacerbation of allergies;
- Timely treatment of diseases, reducing contact with a sick family member in the presence of contagious eye diseases;
- Caring for glasses or lenses, competent selection of vision correction products;
- Maintaining a daily routine and even distribution of physical activity.
Treatment
It is possible to cope with the inflammatory process in the eyes using various methods and means that should be selected by a specialist. The choice of treatment method depends on the nature of the pathology and the cause that provoked the appearance of unpleasant symptoms. Only a specialist can determine how to treat inflammation of the lower eyelid.
Folk remedies
Along with drug therapy at home, you can use traditional medicine recipes. A good effect is achieved by using decoctions and lotions of medicinal herbs, which you can prepare yourself.
It is possible to stop the inflammatory process in the eye using the following alternative medicine recipes:
- Chamomile decoction. To prepare the medicine, you need to pour a tablespoon of dry raw materials into a bowl and brew a glass of boiling water. The prepared product should be used warm to wash the affected eye membranes and eyelids. It is recommended to carry out this procedure several times during the day until the unpleasant symptoms are completely eliminated.
- Clover juice. Clover juice has a good effect in the fight against inflammatory diseases of the organs of vision. To prepare the solution, you need to take a handful of flowers and squeeze the juice out of them using gauze. This remedy must be used to treat the inflamed eyelid throughout the day.
- Cumin seeds. It is possible to quickly cope with the inflammatory process in the eyes and alleviate the patient’s condition with the help of a remedy made from caraway seeds. To prepare it, brew a teaspoon of raw material with 200 ml of boiling water and leave to steep for an hour. After a while, the product should be filtered through gauze, moistened with a cotton pad and applied to the inflamed eye. It is recommended to carry out this procedure several times during the day.
A simple and proven remedy is to brew black tea, which is best used without impurities, additives and sugar. The prepared tea must be fresh, because after 5 hours it forms toxic substances that are harmful to the body. It is necessary to moisten a gauze bandage in the tea leaves and apply it to the inflamed eyelid for 10 minutes. It is best to do this procedure several times a day until the unpleasant symptoms are completely eliminated.
Eye drops and ointments
For inflammation of the lower eyelid, drug treatment consists of daily washing and treating the affected organ of vision with solutions with an antiseptic effect and a suspension that slightly dries the inflamed area.
The patient’s condition can be alleviated using the following medications:
- Alomide;
- Lecrolin;
- Hydrocortisone;
- Maxitrol;
- Dexamethasone.
If the cause of the inflammatory process is demodicosis, then medications are selected that have a detrimental effect on mites. Basically, medications are selected in the form of an ointment, which should be applied to the affected area before going to bed. The medication contains components that disrupt the normal functioning of ticks and shorten their natural cycle.
With the allergic nature of the inflammatory process, the main goal of treatment is to eliminate the allergen that caused the disease. If this is not possible, corticosteroid ointments and anti-allergic drugs are selected. To eliminate the pathological irritant, the use of antibacterial drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs is indicated. A good effect in the treatment of eye pathologies is achieved by antiseptic treatment, which is carried out with a soft sterile swab. Typically, this procedure is resorted to if purulent exudate accumulates under the eyelid and papules form.
In addition to drug treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed. It is possible to eliminate the inflammatory process with the help of electrical stimulation and antiseptic applications. The choice of one or another physiotherapy procedure depends on the general condition of the patient, age and the reasons that caused the disease.
What should not be done if the eyes are purulent?
First aid for suppuration from the eyes can be provided to a patient at home, but it must be remembered that some procedures are strictly prohibited so as not to worsen the patient’s condition.
Eyes fester
If purulent discharge and other symptoms of ophthalmic diseases appear, you should not:
- warm the affected area, as this creates a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms (in some cases, dry heat is indicated for the treatment of such diseases, but only after a doctor’s prescription);
- drip vegetable and essential oils into the eye, as well as other viscous substances that block the access of oxygen to the tissues;
- apply bandages to sore eyes or cover them with patches;
- use alcohol, vodka, vinegar or other substances that can cause burns to treat affected areas;
- squeeze out or open ulcers and abscesses yourself.
Do not treat affected areas with vinegar
In addition, if the eyes are suppurated, it is recommended to stop wearing contact lenses and decorative cosmetics and reduce eye strain.
Congenital pathologies
The formation of the eyelids begins at a six-month-old embryo and ends only at the age of ten. Unfortunately, certain diseases suffered by a pregnant woman or genetic disorders can cause a defect in the formation of these supporting structures of the eye.
Cryptophthalmos in combination with ablepharia is a malformation of the eyeball and the division of the skin flap over it into the upper and lower eyelids. In this case, there are no eyelashes and eyebrows, glands, cartilage and the inner layer of the conjunctiva. It is impossible to cure this disease. For cosmetic purposes, an operation is performed to separate the eyelids and form the palpebral fissure. An underdeveloped eyeball must be removed, as it can become a source of tumor formation.
Coloboma - from the Latin "mutilation" - is a painless defect that looks like a cut on the edge of the eyelid. It can be barely noticeable, or it can cover a significant part of the eyelid. The notch has the shape of a triangle, the base of which is directed towards the ciliated edge. With a large defect, connective tissue threads stretch from the apex of the triangle to the cornea, making it difficult to move the eye.
Severe coloboma
As a rule, impaired formation of the visual organs is combined with other similar defects - cleft lip or cleft palate. But often a defect can also occur in an adult in already formed eyelids after injury, tumor, or surgery. As with a birth defect, there are no eyelashes or glands in this area.
Ankyloblepharon is a disease of the eyelids, which is characterized by complete or partial fusion of the edges of the upper and lower eyelids.
The pathology may be congenital, or may appear as a result of a facial burn or injury. Surgical separation of adhesions or scar tissue restores the normal anatomy of the organ.
Microblepharon is characterized by a decrease in the size of the eyelid, more in the vertical direction. The size of the skin fold does not allow it to cover the eyeball, so when the eyes are closed, a visible gap or “hare's eye” remains. Treatment is carried out using eyelid surgery.
Blepharophimosis. This is a decrease in the horizontal size of the palpebral fissure due to short eyelids or their fusion at the outer corners. This condition creates pressure on the eyeball and disrupts its blood supply. When blepharophimosis is detected, they try to perform surgery to enlarge the palpebral fissure as early as possible.
Epicanthus. This appearance of the eyelid can hardly be called a pathology, since this is a normal condition for people of the Mongoloid race, although unusual for Europeans. The epicanthus looks like a fold of skin covering the lacrimal sac at the inner corner of the eye. It can increase due to the large amount of subcutaneous fatty tissue, so with age, when this layer becomes thinner, the epicanthus can also decrease.
Molluscus contagiosum.
This disease is transmitted by contact, therefore a child in a children's group who is diagnosed with molluscum contagiosum is subject to quarantine until cured.
The disease is characterized by the appearance of yellowish-white nodules up to 2 mm in size with an oval edge and a small depression in the center. They are most often located in the area of the inner corner of the lower eyelid, closer to the eyelash edge, and sometimes several nodules form right on the edge of the eyelid. When the process is localized at the edge of the eyelids, maceration of the nodules occurs and a pasty mass is released into the conjunctival cavity.
Treatment includes the following activities:
- squeezing out the contents of the nodule followed by cauterization with a 1% alcohol solution of brilliant green, Lugol's solution, 5% silver nitrate solution, 5% tincture of iodine, lapis pencil, etc. The manipulation is carried out on an outpatient basis.
Therapy with folk remedies
For eye inflammation, treatment with folk remedies can only be used if there is no large accumulation of pus and mucus. In this case, it is necessary to consult with specialists before using traditional medicine. So, the most popular and effective means:
Warm baths. You need to lower your face into warm water for 15–20 seconds, while keeping your eyes open. The procedure must be repeated 5-6 times throughout the day. Infusion of cucumber peel. The peel of 1 medium peeled cucumber must be chopped and poured with half a glass of boiling water, add 0.5 tsp. soda, mix thoroughly and leave to infuse for an hour or an hour and a half. The finished infusion should be filtered and applied to the eyes in the form of lotions. Onion decoction. 1 onion needs to be boiled, and then add 1 tsp to the resulting broth. honey or a little boric acid. The resulting product should be used to rinse your eyes several times a day. Chamomile. Dried chamomile inflorescences in the amount of 3–4 tbsp. l. you need to pour a glass of boiling water, wrap it in something warm and leave for two hours. After the prescribed period, the infusion must be filtered and rinsed with it every 2-3 hours throughout the day. Brewing black tea. Rinsing tired or sore eyes with strong black tea has been practiced for a very long time.
However, before using this procedure, it is important to remember that the tea must be freshly brewed and in no case old, since black tea leaves brewed about 3-5 days ago contain a large amount of toxic substances that can cause harm to the patient instead of benefit. . Black tea compresses and rinses can be done several times throughout the day.
The compress should only be warm, not hot or cold. You need to brew regular black tea without adding any herbs, fruits, flavorings or sugar; the tea leaves should not come into contact with the mucous membranes of the eyes. Kalanchoe juice. Fresh leaves and stems of Kalanchoe must be thoroughly washed and the juice squeezed out of them. They need to apply eye lotions several times a day. Decoction of marshmallow root. 2 tbsp. l. marshmallow root, which can be purchased at a pharmacy, pour half a liter of boiling water and boil for half an hour. After the prescribed period, cool the broth, strain and apply it to the eyes. A decoction of millet cereals. For blepharitis, the use of a remedy such as a decoction of millet is very effective. In order to prepare it, you need to thoroughly rinse 2-3 tbsp. l. millet cereals, pour a glass of water over them and simmer over low heat for 30 minutes. The finished broth must be cooled, strained and washed with it in the eyes half an hour or an hour before bedtime. At night, you can put a sterile swab or a piece of gauze soaked in the broth on your eyelids. Apple and honey. Apple juice with honey has no less effective properties. To prepare it, you need to make a small depression in the upper part of a thoroughly washed apple and fill it with 1 tsp. honey After honey is completely dissolved in apple juice, you can drop 3-4 drops into your eyes several times a day. This remedy can be used not only in the treatment of eyelid inflammation in adults, but also in children. Infusion of marshmallow leaves and flowers. 2 tbsp. l. Dried marshmallow leaves and flowers must be crushed, then pour 2 cups of boiling water and leave for half an hour. Strain the finished infusion and apply to the eyelids as a lotion. Caraway infusion. 1 tbsp. l. Caraway fruits need to be crushed, pour a glass of boiling water and leave to infuse for 30–40 minutes. Strain the finished infusion and apply lotions and compresses to the eyes.
Why do the eyes of an adult fester?
Normally, in an adult, the mucous membrane of the eye produces a film of mucus, which performs a protective function. A small amount of white mucus the morning after sleep is normal. But you should be wary if purulent discharge appears instead of mucus. They can signal problems in the human body.
So why do a person’s eyes begin to fester? This manifestation may indicate various diseases of the visual system. Only an ophthalmologist can make the correct diagnosis. The most common reasons for such discharge are:
We will consider all these diseases below and tell you what to do in such cases.
Causes of inflammation of the upper eyelid
If the upper eyelid has become noticeably larger than it was before, it looks swollen and has become painful, then you need to figure out what could be the reason.
A common cause of inflammation of the upper eyelid is an unhealthy lifestyle. Namely:
- lack of sleep
- poor nutrition
- abuse of bad habits
- excess ultraviolet rays
- Swelling of the upper eyelid can be caused by the following reasons:
- infectious diseases
- traumatic factors
- allergic reactions
- inherited diseases
Inflammatory swelling occurs as a consequence of an infectious disease. Also, swelling of the eyelid can appear during a cold or flu.
In most cases, the cause is damage to the edge of the eyelid by demodex mites. These mites do not appear from the outside, but live in human hair follicles, skin and sebaceous glands. The process of tick reproduction can become more active when immunity decreases. The mite spreads to the skin of the eyelids and eyelashes.
The eyelid may become inflamed as a result of an allergic reaction. Most often, this is how the skin reacts to dust, pollen, and decorative cosmetics.
Inflammation of the upper eyelid can occur against the background of internal diseases of the body that affect metabolism, including:
- diabetes
- gastritis
- cholecystitis
If a person has vision problems, but does not fight this problem, does not treat his eyes and does not wear glasses, then the eye muscles are constantly under tension. In this case, it is easiest to cause an infection, since a person often rubs his tired eyes with dirty hands.
The infection can also be introduced from other foci through the general bloodstream or lymph flow. Usually these are diseased organs that are located near the eyes: the oral or nasal cavity.
Causes of eye suppuration
Normally, the mucous membrane of the human eye produces a secretion that protects the eyeball from damage, so a small amount of white mucus is considered normal. With the development of pathological processes in the body, in particular in the tissues of the eyes, the discharge becomes abundant and thick, acquiring a yellowish or greenish tint.
There are many reasons for eye swelling
The causes of suppuration are most often infectious diseases of the eyes, less often - diseases of the nasal sinuses. Anatomically, the eyes are located next to the nose, so inflammation (especially in the absence of appropriate treatment) can move from one tissue to another.
- Conjunctivitis. A disease of the conjunctiva caused by bacteria, viruses or allergens. Discharge of pus from the eyes is characteristic of bacterial and allergic forms of conjunctivitis, and the nature of the discharge depends on the cause of the development of the pathology. When pathogenic microorganisms enter the eye, the discharge is abundant and thick, yellowish-green in color, and when exposed to allergens, it is watery and yellow.
- Dacryocystitis. Inflammation or blockage of the lacrimal sac causes a yellow discharge that appears after pressing on the inner corner of the eye.
- Blepharitis. Damage to the hair follicles of the eyelashes, caused by the ingress of pathogenic microorganisms, as well as the activity of microscopic parasites living in the upper layers of the epithelium. With blepharitis, suppuration is observed, as a rule, in the morning; the secretion has a yellow-green tint and a foamy consistency.
- Keratitis. The inflammatory process occurs in the cornea of the eye due to the influence of negative factors, external or internal (trauma, burns, metabolic disorders, allergic reaction, etc.). Pus that sticks together on the eyelids in the morning is one of the first signs of keratitis.
- Barley. A pathology that affects the sebaceous glands located along the edges of the eyelids and also causes abundant discharge of pus - most often this symptom is observed when an abscess is opened or when the pathological process is advanced.
- Trachoma. An infectious process caused by chlamydia. In the first stages of the disease, the discharge may be mucous with small purulent patches, but as the pathology develops, an abundant thick secretion of a yellowish or greenish color appears.
- Dry eye syndrome. If the secretion of tear fluid or its qualitative composition is impaired, the eyes become susceptible to the effects of negative factors. When an infection or mechanical irritation occurs, an inflammatory process begins, which is characterized by the appearance of mucopurulent discharge.
- Foreign body getting into the eye. If, due to mechanical damage to the eye or a foreign body entering it, bacteria or viruses enter the injured tissue, a pathological process begins, accompanied by the release of pus.
In addition to the above diseases, the release of pus can be observed during abscesses, phlegmon and other processes associated with the entry of viruses and bacteria into tissues, as well as with basic non-compliance with hygiene rules, the use of low-quality cosmetics, and failure to care for contact lenses. In addition, a similar symptom is observed after medical procedures and surgical procedures related to the diagnosis and treatment of ophthalmological diseases.
Orbital phlegmon
Causes of swelling of the lower and upper eyelids
The causes of eyelid edema may vary. Exogenous factors that cause inflammation or an allergic reaction. If there is severe pain or fever, you should consult a doctor. Swelling in the upper eyelid area may indicate a serious pathology that requires immediate medical attention.
External factors
The upper and lower eyelids may swell under the influence of provoking factors:
- allergy;
- head injuries due to impact, concussion;
- upper eyelid blepharoplasty;
- unfavorable external environment;
- improper drinking regime;
- poisoning;
- drinking alcohol;
- excessive salt intake;
- cosmetic procedures - Botox injections, tattooing, eyelash extensions.
In medicine, it is customary to divide the course of allergies into two types: rapid and slow.
The condition is characterized by severe itching, lacrimation, and swelling. It is determined by damage to one or two eyes at the same time.
A dangerous reaction of the first type is Quincke's edema. It can develop within the first 6 hours after contact with the pathogen. Symptoms: absence of itching, change in skin color. The process can develop in the eye area and in other areas with well-developed subcutaneous tissue - cheeks, corners of the mouth, neck. Quincke's edema typically spreads to the upper eyelids and to mucous membranes of different locations. Cases of asphyxia have been observed. The condition requires emergency medical attention to avoid consequences.
The second type of allergic reactions develops 12 hours after contact with the irritant. Manifests itself in the form of skin eczema, toxicderma.
Eczema occurs against the background of dermatitis due to repeated cases of contact with the allergen.
Papules affecting the eyelid may open on their own. Serous exudate flows out and a crust forms on the surface of the affected area. In case of purulent discharge, treatment with antiseptic agents is necessary. To avoid complications, you should consult a doctor.
Blepharoplasty is an operation to remove excess skin. Swelling in the postoperative period reaches its maximum by the end of the second day. On the 3-4th day, excess water begins to drain away. After a month, when the microvasculature is restored, the swelling may completely disappear.
Internal factors
Internal factors include diseases and pathologies of individual systems:
- violation of the outflow of lymph and venous blood;
- viral diseases - ARVI;
- pathologies of organs - kidneys, liver, heart;
- inflammation of the sinuses – sinusitis, sinusitis;
- myxedema;
- stye, causing swelling in the upper eyelid;
- blepharitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- lacrimal sac disease;
- abscess;
- endophthalmitis;
- contact dermatitis;
- hypothyroidism
Colds, sinusitis, and barley most often cause swelling and inflammation. For the latter, it is characterized by independent opening of the purulent head.
Chronic renal and heart failure lead to the development of non-inflammatory conditions.
Swelling of the lower eyelid in both eyes is a symptom that defines the condition.
ARVI is a group of viral diseases that affect various parts of the respiratory tract. There are viruses that affect the normal functioning of the eyes. Conjunctivitis is a manifestation of adenoviral infection. The disease is characterized by a sensation of a foreign body under the upper eyelid, profuse secretion of tears, and a burning sensation.
Inflammatory process on the eyelids and in the tear ducts
Inflammatory diseases very often develop around the lower and upper eyelids and tear ducts. They must be distinguished: inflammation of the eyelid and inflammation of the tear ducts. Because the treatment will take place differently.
Inflammation of the eyelid
The symptoms look like this:
- swelling appears around;
- redness of the eyelids.
Eyelid diseases, symptoms, treatment:
Barley. Inflammation of the eyes, most often developing against the background of blockage of the sebaceous gland or hair follicle. Causes: Staphylococcus aureus, duct blockage. Barley is a very common occurrence in children due to reduced immunity and as a consequence of respiratory viral pathologies.
Symptoms: itching, burning in the area of redness and swelling of the eyelid, enlarged lymph nodes. Over time, a visible purulent head. Barley almost always goes away on its own within a week. Many people begin to treat pathology with folk remedies, applying hot boiled eggs and other objects, which is absolutely forbidden to do!
Barley should be treated with Albucid, Tobrex, Hexa-Gentamicin drops, Levomycin, Tetracycline or Erythromycin ointment. As well as drugs to enhance immunity - Alviron, Immunoglobulin. You can relieve inflammation with a lotion of chamomile decoction.
Blepharitis. Characterizes multiple inflammatory diseases that occur with chronic inflammation of the eyelid margins. It is very difficult to treat such pathologies.
Causes of eye inflammation:
- damage to the eyelids by fungi, mites, bacterial infections;
- allergy;
- tuberculosis;
- diabetes;
- gastritis;
- farsightedness;
- astigmatism.
Since there are many causes of inflammation of the eyelid, treatment is prescribed in each individual case after identifying the cause. The basis of therapy is daily eyelid hygiene.
Herpes. Eye inflammation is often caused by the herpes virus. There are many types of herpetic lesions around the organ of vision. But almost all of them have the same symptoms: redness on the eyelids in the affected area, itching, burning, increased body temperature, swelling around the eye. Over time, bubbles filled with liquid appear.
Chalazion. Slowly developing inflammation of the eyes. Causes: blockage of the sebaceous gland or colds, blepharitis, chronic gastritis, colitis. The formation is very similar to stye in appearance. Since chalazion is very similar to stye, many people begin to warm the formation. You can't do this!
Treatment consists of hygienic treatment and massage of the eyelids. Physiotherapy is also prescribed. If therapy does not produce results, surgery is performed. In this case, the formation is removed.
Inflammation of the tear ducts
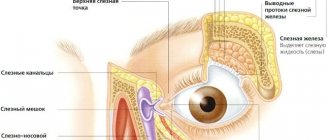
In medicine, such an inflammatory process is called dacryocystitis. The lacrimal canal is complex and tortuous in structure. Moreover, the duct in some places is narrow and closed. It is these areas that are the “best” for stagnation and blocking the outflow of tears. When tear fluid stagnates, an infection develops, resulting in an inflammatory process.
Causes of narrowing or infection of the tear duct:
- Anomaly in channel development.
- Consequence of injury.
- Infectious pathologies of the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, accompanied by inflammation.
- Foreign body – eyelashes, speck.
The following symptoms of pathology can be identified:
- lacrimation;
- redness in the corner of the eye;
- swelling;
- sharp pain in the corner;
- Pus may ooze from the corner of the eye when pressed.
Swelling sometimes develops to such an extent that the palpebral fissure narrows. Usually the pathology affects one eye.
For treatment, massages, hot compresses, a course of antibiotics, and rinsing are used. If these methods are not effective, you will have to resort to surgery to help restore the patency of the lacrimal canal.
Inflammatory eye diseases have different symptoms. But, nevertheless, many of them are similar. It is possible to determine which inflammatory diseases develop in a person only in a hospital setting. Therefore, doctors do not recommend self-medication. We should not forget that vision is a very fragile external sense that can be lost without timely treatment.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=vCEUo8mYxoI
Eyelid disease chalazion (with photo)
Chalazion eye disease is an inflammatory disease affecting the upper or lower eyelid. With this disease, a benign tumor-like neoplasm with clear boundaries is formed. Thanks to this manifestation, the disease got its name. Chalazion is a Greek word. And translated from this language it means “hailstone”.
The pathogenic process is based on the blockage of the meibomian gland and the accumulation of fluid in it. It must be said that there are up to 70 such glands in a century. They are located inside the eyelid immediately after the eyelashes. They work constantly, and their primary task is to prevent the eye from drying out due to the formation of a thin fatty film on the surface of the organ of vision. This is especially true in cases where there is little or no tear fluid in the eye. A chalazion on the eyelid is well illustrated by the photo that can be seen above.
It is worth noting that visually a “hailstone” is determined both from the outside and from the inside of the eyelid. This lump is usually painless
However, with a significant increase in size, such a formation can cause pain to its owner.
The described illness is very common. In particular, if we consider it in the structure of ophthalmological diseases, we can say that the share of this pathology is about 5%. And this despite the fact that not all sick people turn to doctors for help (but about half). The appearance of “hailstone” has nothing to do with age and gender: its appearance can be expected with equal probability in any segment of the population.
The eyelid disease chalazion, as mentioned above, can quite easily be confused with another ophthalmological disease called “stye”. The likelihood of such a diagnostic error is especially high in the initial stages of the development of the disease. Considering this circumstance, chalazion was given another name: “cold barley.” In addition, in relation to this disease, you can hear the term “nodule”, as well as “meibomian cyst”.
Signs and symptoms of inflammatory eye disease
Inflammation can affect any part of the eye or surrounding structures. Symptoms of inflammation in most cases depend on the surface at the site of inflammation. The most common signs and symptoms are:
- Pain;
- Redness;
- Decreased vision;
- Photosensitivity.
Eye pain, severe sensitivity to light, and any change in vision are considered signs of an emergency and require immediate attention from an ophthalmologist.
Back to contents
Accompanying illnesses
The most dangerous are inflammations that arise as a result of developing eye pathology. Most often, this symptom manifests itself in the following diseases:
- Barley. Inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelash or the duct of the meibomian gland exiting into it. The cause of inflammation is most often yellow staphylococcus. An abscess forms on the edge of the eyelid, upper or lower, which opens or resolves within 2-3 days. In rare cases, surgical intervention is resorted to;
- Meibomite. Inflammation of the meibomian gland, located in the thickness of the eyelid. The second name for the pathology is internal stye, since an abscess forms on the inside of the eyelid. The causes of the lesion are the same as with barley. The frequent occurrence of both external and internal barley indicates problems with immunity;
Read how to treat stye on the eye at home here.
- Impetigo. A superficial pustular skin disease that affects not only the eyelids, but also other areas. The cause of inflammation is Staphylococcus aureus, hemolytic streptococcus, or a combination thereof. Pathogens penetrate microcracks in the skin under favorable conditions: warm, humid climate, lack of hygiene, metabolic disorders, weak immunity;
- Erysipelas. The inflammation is infectious in nature, the causative agent is hemolytic staphylococcus. It penetrates the subcutaneous layer, affecting the blood and lymphatic vessels. The skin becomes red, shiny and glossy, and the affected area is sharply demarcated from healthy tissue;
- Abscess. Suppuration of the eyelid most often appears as a result of the development of other eye diseases (hordeolum, meibomitis). The main symptom is severe pain and limited eyelid mobility;
- Phlegmon. Generalized inflammation of the tissues of the eyelid can occur as a complication of inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract or otitis media (in children), as a consequence of barley or abscess, after eyelid injuries. Accompanied by high temperature, pain, tenderness of the lymph nodes;
- Furuncle. Acute purulent-necrotic inflammation can be localized in the upper eyelid or on the eyebrows, less often along the edge of the eyelid. The causative agent is staphylococcus, which penetrates microcracks in the skin or the outlets of the sebaceous glands. In addition to the eyelid, the process includes adjacent areas of the face;
- Blepharitis. Chronic processes accompanied by inflammation of the eyelids and difficult to treat can occur for a variety of reasons: damage by bacteria and mites, allergic factors, endocrine disorders, vitamin deficiency, bad habits, etc.;
- Molluscum contagiosum. A viral infection, most often caused by one of the smallpox viruses. In this case, the main symptom is the appearance of small papules, almost indistinguishable in color from the skin. Most often it appears in children under 10 years of age. It is not accompanied by any discomfort even after 6 months. disappears even without treatment.
Diseases of the eyelids: stye, blepharitis, meibomitis, trichiasis, edema, chalazion, abscess, volvulus, allergy
It develops most often after infected eyelid injuries or local purulent inflammations (stye, boil, ulcerative blepharitis). Inflammation can occur metastatically with septic foci in other organs. The abscess develops acutely with an increasing diffuse compaction of the subcutaneous tissue of the eyelid. The eyelid is swollen, the skin is tense, hyperemic, hot to the touch.
Emergency first aid.
- Prescribe 1 g of sulfadimethoxine, sulfapyridazine or another sulfonamide drug orally.
- An intramuscular injection of 500,000 units of benzylpenicillin or a single dose of another antibiotic is performed.
- The patient is immediately sent for inpatient treatment to the eye department of the hospital, where the abscess must be opened.
Treatment.
- At the beginning of the disease, in the infiltrate stage, dry heat and ultra-high-frequency therapy are prescribed.
- A 30% sodium sulfacyl solution is instilled into the conjunctival sac at least 5-6 times a day.
- It is necessary to prescribe sulfonamide drugs orally and intramuscular antibiotics.
- When fluctuations occur, the doctor or paramedic opens the abscess, drains the cavity, applies bandages with a hypertonic sodium chloride solution, and rinses the cavity with antibiotics.