What diseases can cause cervical discomfort?
Pain in the uterus is a fairly common phenomenon, so it is important to know what diseases and pathologies this symptom may indicate.
Most often, uterine pain occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle, which is absolutely normal in cases where such sensations pass quickly and do not cause severe discomfort. Around the end of the second week of the cycle, a healthy woman experiences ovulation, during which the follicle ruptures and an egg is released, ready for fertilization. This phenomenon is accompanied by minor nagging pain. In some cases, body temperature may rise (up to 37-37.2 degrees) and general well-being may deteriorate. Most women do not feel anything at all during this period.
Ovarian apoplexy
Apoplexy is the rupture of an ovary. The pathology occurs mainly in women of reproductive age (from 18 to 45 years). The cause of this phenomenon can be inflammatory processes of the uterus and appendages, hormonal disorders, and infectious inflammatory processes. Ovarian rupture is accompanied by internal bleeding, so it is important to know the signs of this pathology:
- acute, sudden onset;
- sharp pain in the uterine area on the side where the burst ovary is located;
- vomiting or nausea;
- signs of peritoneal irritation;
- enlargement and pain of the inflamed appendage (determined by palpation of the vagina).
If uterine pain occurs after sexual intercourse, it is worth visiting your local gynecologist, since this phenomenon also has its own causes, for example:
- abnormal structure of the genital organs (uterus, cervix, vagina, etc.);
- inflammatory processes of the mucous membranes of the cervical canal and cervix;
- cervical cyst;
- formation of adhesions in the pelvis;
- venereal diseases.
Sometimes the cause of painful intercourse is excessive vaginal dryness or narrowing of the genital opening, which often occurs in women after an episiotomy (incision during childbirth). The presence of bloody discharge in combination with pain in the uterus after sexual intercourse indicates inflammatory processes in the uterus or vagina.
Pain in the uterus during pregnancy is most often a physiological process that does not require medical correction. This is due to an increase in the size of the organ and stretching of the supporting ligaments. The painful sensations are pulling, and slight tingling may be felt on the sides (at the location of the ligaments).
Despite this, women carrying a child should closely monitor any changes and be sure to consult a doctor if:
- the pain intensifies and takes on a cramping character;
- bloody or pinkish discharge appears;
- You may notice watery spots on the underwear (may indicate damage to the amniotic membranes);
- the stomach becomes “stone”.
Other reasons
In some cases, uterine pain may indicate diseases of other organs, in which pain is simply radiated to the area of the uterus. This situation is typical for the following pathologies:
- inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system (cystitis, inflammation of the renal pelvis, etc.);
- cholecystitis;
- appendicitis (depending on the location of the appendix, the pain may seem to originate in the uterus);
- colitis;
- parasitic infections;
- spinal pathologies.
There are a large number of reasons why pain in the uterus may appear, so contacting a doctor if this symptom occurs is mandatory.
Cervical pain can be a symptom of inflammation and various precancerous diseases.
- Pseudo-erosion (ectopia) – this pathology is characterized by an abnormal position of the epithelium outside the canal cavity. The leading symptom is moderate pain in the cervical area. There is some slight bleeding.
- Erosion - the basis of this disease is the appearance of a defect in the multilayered epithelium (a scratch or a small wound). If the reparative processes proceed normally, and there are no foci of inflammation, then the wound heals. If pathogenic flora or disruption of the regeneration process is present, then healing does not occur.
- Leukoplakia - the formation is located on the cervix and consists of pale areas of keratinization. The process is a consequence of previous infections. The formation easily transforms into malignant.
- Ectropion is an eversion of the mucous membrane of the canal. The cause of formation is injury to the mucous membrane during abortion or curettage.
- Erythroplakia - the formation looks like a red spot located on the mucosa. The reasons for this process have not yet been established.
Pain in the cervix occurs not only when it is directly affected. They are present when the body of the uterus is damaged.
- endometrial cancer – with it, pain begins in the later stages;
- inflammatory diseases of the uterus;
- hypertension during pregnancy caused by progesterone deficiency;
- leiomyoma is a benign tumor originating from the endometrium;
- adenomatosis - considered a precancerous condition, uncontrolled growth of cells in the mucous layer occurs due to the high content of female sex hormones;
- stenosis - a sharp narrowing of the cervical canal, there is congenital and acquired (infections, tumors, consequences of operations and diagnostic procedures);
- endometriosis (adenomyosis) – pathology is characterized by uncontrolled growth of cells of the mucous layer beyond its boundaries;
- prolapse and prolapse - disruption of the position of the uterus due to weakening of its ligaments and muscles of the pelvic floor;
- lack of female sex hormones, which is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation;
- polyps are benign tumors localized in the cervix and its mucous layer;
- endometrial hyperplasia - proliferation of the glandular or basal layer.
All these diseases of the body and cervix cause pain. Differentiate using ultrasound, gynecological examination and laboratory tests.
Causes of pain in early and late pregnancy
During the period of gestation, the female uterus increases significantly in size. Such a change leads to an increase in the load on the ligaments that ensure its retention in the pelvis. Due to a violation of the anatomical position, a displacement occurs, tension in the abdominal muscles increases, and the expectant mother experiences pain in the lower abdomen of varying intensity and character.
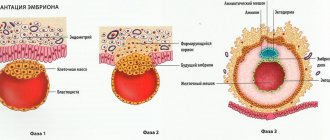
On days 6-8 after fertilization, the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus. Pain in the cervical area is normal at this time. Doctors reassure expectant mothers and assure that discomfort indicates the natural course of the process, so there is no need to worry again. A woman should lie down and rest, take a No-shpa tablet or another antispasmodic approved during pregnancy, the pain will go away.
Pain that occurs at short intervals in the early stages may indicate growing tone of the uterus. At this time, short-term pain in the lower abdomen may also be observed. The condition is considered dangerous, and in some cases critical, requiring immediate response.
During the second trimester of pregnancy, the fetus inside the woman's womb grows and develops rapidly. Pain that occurs periodically in the cervix is natural and does not require medical intervention, but this is not a reason to ignore the symptom. If the discomfort manifests itself abruptly and is paroxysmal in nature, it is worth visiting a doctor. Also dangerous is a condition when pain is accompanied by bleeding or spotting - placental abruption has probably occurred.
In the later stages of pregnancy, starting from 35-38 weeks, discomfort in the cervix appears with small frequency. This symptom indicates that the pregnancy will soon end, and at this moment the cervix is preparing for childbirth, softens and opens.
Pain in the cervix often worries pregnant women suffering from cervical insufficiency. This pathology is quite dangerous and can lead to irreversible consequences, including termination of pregnancy. In this condition, the muscles in the transition zone between the uterus and the cervix do not contract, and dilatation may occur ahead of schedule. Abortion for this pathology occurs at a later date, when the weight of the fetus becomes significant. The pathology is characterized by tingling. It can prick constantly or periodically, at characteristic intervals.
In addition, the cause of pain in the cervix may be various gynecological diseases that are infectious and inflammatory in nature. During pregnancy, these diseases require immediate intervention. The reasons that provoke the development of pathology are pathogenic microorganisms that exhibit their activity: staphylococcus, streptococcus, E. coli and other STD pathogens. Pathologies are not always accompanied by pain, but it is important to cure them before labor begins, otherwise there is a high risk of infection of the child as it passes through the birth canal.
Even more interesting:
The echo structure is not changed, what does this mean?
Tongue with pharyngitis photo
High tone
Uterine tone is the main cause of cervical pain in early pregnancy. The appearance of the symptom is due to contraction of muscle fibers; the reasons for tone during pregnancy are as follows:
Preface
Why does the uterus hurt so much? Are the causes of this symptom dangerous? Before you answer these questions, there is important information to know. The reproductive organ is a muscular sac. It is located in the very center of the small pelvis. In front is the bladder, and behind is the intestines. The uterus is an unpaired organ.
If a woman has pain in the uterus, there can be a variety of reasons. But in each case this is, as a rule, a pathological process. To reliably determine why this symptom appeared, you need to visit a doctor: a gynecologist or an obstetrician-gynecologist. Pain in the pelvic area can be different: cutting, stabbing, pressing, sharp, and so on. Let's look at why sometimes women have pain in the uterus. We will analyze the causes and consequences in detail.
Pain due to benign tumors of the cervix or uterine body
Pain in the cervix can be a manifestation of benign tumors - polyps and fibroids.
Polyps
The intensity of pain with polyps ranges from mild to intense. Women also note discomfort and feel that there is something in the cervix.
Unpleasant sensations in the cervix intensify with physical impact on it (gynecological examination, sexual intercourse). Polyps are usually combined with other pathologies of the female genital area. Upon examination, the expansion of the canal is visible and a formation is detected in it. Palpation creates discomfort. An additional examination method is ultrasound.
With fibroids, the pain is localized in the lower third of the abdomen and radiates to the cervical area. It enlarges and puts pressure on neighboring organs. Depending on the type of tumor, pain varies in intensity and location. Dull pain is typical and intensifies with changes in body position. Their intensity increases when urinating, and they haunt you at night.
It hurts for a woman to sit. She feels that the pain is radiating or as if it is hitting her neck. A woman notes that her cervix hurts when she sits. Reports heaviness in the lower abdomen. If the fibroid is localized along the posterior wall, the pain radiates to the back or anal area. Sometimes it goes to my feet. During menstruation, the pain intensifies and has a cramping character.
Inflammatory diseases of the neck and body are represented by cervicitis and endometritis.
Cervicitis
In pathology, the cervical canal and its vaginal part are affected. The woman notes that the cervix is enlarged and hurts.
- the cervical canal hurts;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- feeling of discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- stabbing in the cervix;
- discharge from the genital tract.
During a gynecological examination, you can notice redness and swelling of the cervix in the area of the cervical canal. Its mucosa is covered with areas of pinpoint hemorrhages. The neck is compacted, pseudo-erosions are formed. Touching the neck is painful. When touched with a finger, blood vessels are easily damaged and the mucous membrane bleeds.
Endometritis
This pathology most often takes on a secondary nature; it is a continuation of the ascending inflammatory process in cervicitis. It develops as a complication of adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages) and salpingitis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes).
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the groin area;
- mucopurulent discharge from the genital tract;
- signs of general intoxication.
If the cervix shoots with endometritis, this indicates generalization of inflammation. The process can spread to fatty tissue. Inflammation of the uterus can become chronic. It can only manifest itself as painful periods. The cervix is compacted, swelling and redness are noted. If you press on it, it is sharply painful. A slight touch causes injury to the vessels on its surface and bleeding.
Stitching pain in the vagina during pregnancy
It is unlikely that there will be at least one woman who has given birth who can say for sure that during the entire 9 months of pregnancy she never had any pain or at least no discomfort.
This is not surprising: with the appearance of a small belly, the body experiences significant changes (muscle fibers stretch, ligaments swell and stretch, and the pelvic organs “diverge”). But sometimes it happens that the expectant mother is truly frightened by the stabbing pains that appear here and there. But most of all they cause true panic if these pains are localized in the abdominal area.
However, a pregnant woman should know that during the period of bearing a baby, one should pay attention not so much to the nature of the pain, but to its intensity. However, if some sensations are truly alarming, it is better to consult a doctor. But we can describe some phenomena and their causes right now.
For example, stabbing (but more often pulling) pain can occur with so-called uterine hypertonicity. If the pain is minor, just lie down, rest and calm down. If it is intense, and even accompanied by discharge, seek medical help immediately!
Let us immediately note that there is unlikely to be at least one woman who has already given birth who can easily say for sure that literally during the entire 9 months of her pregnancy she simply never had anything hurt anywhere or at least simply did not cause discomfort. And this is not at all surprising: after all, with the appearance of a small, so-called belly, the female body experiences quite significant changes (muscle fibers stretch somewhat, as well as various ligaments swell and stretch, the pelvic organs “diverge” a little, etc.).
And this, in most cases, can explain the nagging or even tingling pain somewhere in the lower abdomen, often experienced by the woman herself in the first trimester of pregnancy. In addition, it was noticed that such minor pains often bother precisely those women who already had very painful menstruation before pregnancy.
But sometimes it happens that the expectant mother is truly frightened by sharp stabbing pains that literally appear here and there. However, this condition most of all causes simply violent panic if these sudden pains seem to be localized in the lower abdomen.
However, the pregnant woman herself should clearly know that it is during the period of bearing the baby that she should pay special attention not so much to the nature and course of such pain, but rather to its intensity. And, nevertheless, if some sensations really alarm you, it would be better to consult your doctor. But we can even describe some phenomena and their real causes right now.
So, for example, stabbing (but still more often - pulling) pain may well occur with the so-called, and well-known, hypertonicity of the uterus. If such pain is minor, then it will be enough to just lie down, rest and calm down a little. If they are intense, and possibly accompanied by some kind of discharge, urgently seek qualified medical help!
And, nevertheless, it is during pregnancy that acute “stabbing” pains may well arise somewhere in other organs. For example, the motility of the gastrointestinal tract itself decreases sharply during a certain period of pregnancy. This often leads to stagnation of certain fecal masses, and as a consequence to flatulence, and even constipation and further, as a consequence, to really stabbing pains already in the intestines.
Sometimes sharp stabbing pain may also indicate acute appendicitis. If stabbing and cramping pains are primarily felt in the right hypochondrium, then it is quite possible that this is cholecystitis (or inflammation of the gallbladder). And, of course, the pancreas itself may well “suffer” during pregnancy.
We invite you to read: What does it mean to dream about being pregnant?
So pancreatitis, or inflammation of this organ, often manifests itself in the upper abdomen with acute pain. Often during pregnancy, many women also complain of acute pains of a “pulling” nature, which, by the way, as the bladder gradually fills, become more intense and even acquire a stabbing character.
It has been noted that some women, while pregnant, complain of sharp stabbing pains in the tailbone. But in addition to stabbing pain, such pains can also be dull, they can also be localized, and may well radiate somewhere, say, to the perineum, or the lower abdomen, sometimes to the buttocks and even to the thigh.
A pathological condition such as isthmic-cervical insufficiency itself should also be highlighted separately. It is this that develops as a result of some injuries to the isthmus and even the cervix. The cause of trauma can often be previous abortions, childbirth (if the child was large), as well as the use of special obstetric forceps.
And as a result, the cervix opens and then cannot hold itself, but the fertilized egg then simply falls down and presses, creating pain. In this case, of course, the woman feels stabbing pain in the vagina. This is dangerous, first of all, because it can easily cause spontaneous and early termination of pregnancy. And most often this can happen precisely at the 16th week of pregnancy.
During pregnancy, many women experience various unpleasant sensations. But perhaps the most alarming of them is pain in the intestines or vagina. When such pain occurs, many expectant mothers immediately panic, because these pains are concentrated in the places closest to the baby. In this article we will try to figure out what can cause pain in the vagina during pregnancy and how dangerous they can be.
Why does the vagina hurt during pregnancy?
Pain in the vagina is a common occurrence in pregnant women. Such pain appears especially often in the third trimester of pregnancy. Let's look at the most common types of pain and the causes of their occurrence:
- Enlarged uterus. The growing uterus, which takes up more and more space in a woman's body, can put pressure on the vagina and surrounding muscles, thereby causing pain in this area.
- Sprain. As pregnancy progresses, the ligaments that support the pelvic area and vagina become stretched, and sometimes even overstretched. When this happens, a woman may experience an unpleasant, sharp or nagging pain in the lower abdomen. in the vagina or between the legs.
- Dilatation of the cervix. If sharp pain in the vagina is observed in the last stages of pregnancy, then it may be associated with the beginning of dilation of the cervix. This can happen several weeks before the expected due date. If such pain causes severe discomfort and does not go away, regardless of whether bleeding is present or not, you should consult a doctor immediately.
We suggest you read: Article. How do you know when labor has started?
Changes in hormonal levels. Hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy can cause vaginal dryness. In such cases, during sexual intercourse, a woman may feel stabbing pain in the vagina.
- Changes in the pelvic area. Of course, during pregnancy the pelvic area continuously undergoes changes: bones move apart, ligaments stretch, the uterus constantly enlarges, thereby putting pressure on many organs. It is for this reason that intimate intimacy for many women begins to be accompanied by unpleasant stabbing pain in the vagina. In such cases, doctors recommend trying other positions, for example, so that the woman is on top and can independently control the depth of penetration.
- Vaginal infection. Stitching pain in the vagina or external genitalia (vulva and peri-vaginal area) may be a sign of a vaginal infection. If you have these symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor to undergo diagnostic tests to find out the exact cause of your vaginal pain. During pregnancy, infections of any type must be treated without fail and immediately. The most common type of vaginal infection is thrush, or candidiasis. During pregnancy, a woman is most vulnerable to such infections as her immune system weakens. Treatment of infections with antibiotics and cortisone during pregnancy is rarely prescribed, so the process of getting rid of infections of the genitourinary system during pregnancy does not proceed very quickly.
- Ectopic pregnancy. If the stabbing pain in the vagina does not go away over time, but only intensifies, and even more so if accompanying symptoms appear in the form of bleeding, pain in the abdomen, shoulders and neck, this may indicate an ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancy is not always easy to diagnose, since its symptoms are very similar to typical signs of pregnancy - nausea, breast tenderness, absence of menstruation. However, if symptoms such as severe vaginal pain, vaginal bleeding, hypotension, back pain or dizziness are present, a pregnant woman should seek medical attention immediately.
Pain in the vagina during pregnancy: dangers
Uterine pain and menstruation
Mid cycle. Pain syndrome of moderate intensity appears at the moment of ovulation, when the egg is released into the cavity of the fallopian tube. If the pain is severe and lasts more than 1-3 days, this may indicate the presence of inflammatory or adhesive processes in the pelvic organs.
Beginning of menstruation. Pain that occurs at the beginning of menstruation is called dysmenorrhea. They may appear due to abnormal structure or location of the organ, as well as nervous excitement or physical fatigue. In most cases, such pain is physiological, as the process of rejection of the endometrium from the uterine walls occurs, which is accompanied by nagging painful sensations and a slight deterioration in general well-being.
After menstruation. Pain that does not subside after the end of menstruation is a rather dangerous symptom, indicating serious health problems, for example:
- inflammation of the appendages;
- endometriosis (overgrowth of the endometrium, in which it penetrates into other organs and surrounding tissues);
- adhesive process (fusion of adjacent organs or intestinal loops);
- cervical polyposis;
- myomatous nodes (uterine fibroids);
- cyst of the cervix or body of the uterus;
- cervical cancer;
- erosion.
Sometimes pain can be caused by the intrauterine device if it is worn for a long period of time. In such a situation, it may grow into the endometrial tissue, which will be accompanied by the appearance of spotting and painful sensations in the abdominal area.
Many women experience uterine pain during menstruation. The causes of this symptom are often physiological. Every second representative of the fairer sex complains of dysmenorrhea. However, on other days the woman’s health remains normal. Pain in the uterus appears 1-2 days before menstruation and ends on the 2-3rd day of bleeding.
Dysmenorrhea has no unpleasant consequences. It is important to contact a gynecologist in time and make sure that there are no other abnormalities. Many women report that monthly pain and discomfort go away after giving birth. Why is still a mystery.
Tingling in the uterus
Self-observation is the first and most important condition for maintaining health. Very often, when we feel pain or other unpleasant sensations, we ignore these signals from the body, put off visiting the doctor until “later,” take painkillers and conveniently forget about the signs that our body gives us. But such “bells” are very often symptoms of serious illnesses that can lead to complications of various kinds. This is why it is so important to independently monitor your own health, noting changes and trying to understand the signals sent to us by our own body.
In this article we will talk about a very common phenomenon among women - stabbing pain in the uterus, we will analyze what tingling in the uterus means (before, after and during menstruation, after ovulation), consider the reasons for this and what to do if you begin to notice regular tingling in the uterus. cervix.
One of the most common complaints in the gynecological office is tingling in the uterus before menstruation. Regular painful sensations in the lower abdomen, recurring a couple of days before the onset of menstruation, most often indicate the development of pathologies of both the uterus itself and its cervix or appendages. In addition, regular stabbing pain in the abdomen can be symptoms of other diseases of the pelvic organs (endometriosis, uterine cancer, cystitis, pyelonephritis, etc.). Self-diagnosis is impossible, since special medical studies are required to adequately determine it. To relieve pain, you can take a sedative (valerian infusion), antispasmodics (drotaverine, spasmalgon). But it is important to remember that taking these medications only relieves symptoms, but does not eliminate their cause. Only after a visit to the doctor and a medical examination will it be possible to determine the cause of the pain and prescribe the correct treatment. More neglected
Source
Pathologies of the uterus
Nagging pain in the projection of the ovaries, radiating to the cervix, is typical for inflammation of the appendages.
- adnexitis;
- salpingitis;
- salpingo-oophoritis.
The intensity of the pain syndrome can vary from mild pain in chronic processes to highly intense pain in acute conditions. A woman notes pain and discomfort during intercourse. Sitting down also hurts. There is a rise in body temperature to subfebrile levels. As the infection progresses, the pain has a jerking character.
There are various discharges from the genital tract and other signs of infection. With an exacerbation of the process, general infectious symptoms may occur (nausea, dizziness, loose stools, vomiting). On examination, the entrance to the cervix is painful. Palpation of the ovarian area is painful on the left and right. Touching the neck causes pain.
Endometritis
Why does the uterus hurt before menstruation? The reasons may lie in pathologies, both congenital and acquired. In women with similar complaints, partitions in the reproductive organ are diagnosed. Also, the uterus can be one-horned or two-horned, saddle-shaped. Sometimes hypoplasia or agenesis of the organ is determined. In the latter case, we are talking about the complete absence of the uterus. The pain is caused by displacement of neighboring organs.
Depending on the type of pathology, its consequences may differ. For example, agenesis does not respond to any treatment. With it, a woman cannot procreate, and the painful sensations persist for life. Modern medicine makes it possible to correct pathologies such as a bicornuate uterus, adhesions in the reproductive organ and septum.
Cervix and its changes during pregnancy
Under normal conditions, the outer surface of the cervix is pinkish in color. It is smooth and durable. The inner surface is bright pink and loose. During fertilization, the appearance of the cervix changes. For example, its color becomes bluish, which is due to increased blood supply. In the ninth month, the cervical tissue should soften. This is a signal that the woman’s body is ready for the birth of a child. Before childbirth, the cervix shortens.
When first examining a pregnant woman, the doctor must check the condition of the cervix: determine its shape, size, consistency and location. In the best case, the cervix should be tight and tilted back, and the cervical canal should be impassable for a finger. If, upon examination, the doctor determines that the canal is opening and the cervix is shortened or softened, this threatens miscarriage.
Pain associated with pathologies of the uterus and appendages
If the uterus hurts, the reasons may be hidden in a bacterial or viral disease. Most often, infections occur in women who are promiscuous and do not use barrier contraception. The consequences of such diseases are quite dire, and treatment is long. Remember that the sooner you contact a gynecologist and begin therapy, the less likely it is to develop complications.
Infections can be sexually transmitted or occur for other reasons. Women often suffer from E. coli. This microorganism normally resides in the digestive tract. But for various reasons (usually due to wearing tight underwear), it penetrates the vagina and settles in the uterus. Treatment of infectious pathologies is always complex.
Antibiotics for oral and topical use, antivirals and antiseptics, immunomodulators and probiotics are prescribed. It is not possible to choose the right therapy on your own. If the problem is not treated in time, the infection will spread to neighboring organs: fallopian tubes and ovaries. Pathology threatens the formation of adhesions, poor health and even infertility.
Endometritis
Pain in precancerous conditions and cervical cancer
These diseases pose an increased danger to the life and health of women and require special attention during diagnosis, treatment and observation.
Erosion
The cervix may hurt due to erosion, but most often there is no discomfort with this pathology. First, pain appears in the lower third of the abdomen during menstruation and radiates to the lower back. Outside of menstruation, the uterus occasionally ache or there is a slight tingling sensation. The woman feels that she is pulling her neck.
Discomfort often appears after sexual intercourse (the cervix hurts from sex). The cervix may hurt due to any mechanical impact, for example, after an examination by a gynecologist. The examination is accompanied by bloody discharge. The appearance of pain during erosion indicates the addition of a bacterial infection.
Dysplasia
Dysplasia is considered a precancerous disease. The disease has an asymptomatic onset and stings a little during sexual intercourse. Constant pain appears only in the later stages or after infection has occurred. It begins to ache in the vagina. It hurts a woman if you touch her neck.
Cervical cancer
IMPORTANT! Cervical cancer occupies one of the first places in the structure of mortality among young women among all oncological pathologies.
In the initial stages, this disease does not manifest itself in any way. Then bleeding appears after sexual intercourse or a gynecological examination. There is a cutting pain in the neck area, radiating to the sacrum area. In later stages, pain appears in the neck, which can shoot down the leg. General weakness, fatigue, and weight loss are added. The formation can compress internal organs. Touching the cervix is extremely painful.
Neoplasms in and around the reproductive organ
If the uterus and ovaries hurt, the reasons may be hidden in the growth of a tumor. Fibroids are often found in the reproductive organ. If the formation is small in size and does not bother the patient in any way, then it is usually not touched. With accelerated growth of mima, surgical and minimally invasive treatment methods are chosen.
Hormonal correction is often carried out. The uterus can also hurt due to the formation of cysts on the ovaries. Most often these are functional tumors that do not require medical intervention. But if we are talking about cysts such as dermoid, endometrioid, carcinoma, and so on, then they must be removed surgically.
Endometriosis is in second place in popularity among neoplasms. This is a benign growth of the endometrium on the outer layer of the uterus, intestines and inside the abdominal cavity. If the pathology is not treated, the woman will experience unbearable pain in the pelvis, adhesions will form, and ultimately infertility will occur.
The reproductive organ can hurt due to cancer, polyps and other neoplasms. The prognosis of treatment and consequences directly depend on the stage of the disease and its type.
Pain in the ovaries during pregnancy
Many pregnant women often complain of nagging pain in the ovarian area. To find out the reason, you should get acquainted with the work of the ovaries in the female body system.
The ovaries are paired female gonads. They are located in the pelvis, the main functions are endocrine and generative. Accordingly, they are responsible for the development, maturation of female germ cells and the production of female sex hormones. The inflammatory process in the ovaries is not a very rare phenomenon for young representatives of the fairer sex, which often leads to infertility. This process is accompanied by constant severe nagging pain. This occurs in women who are not pregnant. After fertilization, the ovaries temporarily lose their intended purpose and, accordingly, sensitivity.
Pain in the early stages
However, virtually every pregnant woman at one time or another may feel aching or nagging pain in the area of the ovaries. The pain is most noticeable in the early stages of pregnancy. Women should know that, losing their function for a while, the ovaries also change their location - they rise higher. Pain is felt exactly where it should be by nature. The conclusion suggests itself - the cause of pain is not in the ovaries, although the inflammatory process does occur.
Pain occurring in the second half of gestation
Pain in the cervix during short-term pregnancy indicates a possible pathology. In late pregnancy, if pain occurs for a short period, this is not a pathology. If this period is prolonged, you should contact an obstetrician-gynecologist. In any case, consulting a doctor will not do any harm and will help eliminate the possible latent course of severe pathologies.
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency - weakening of the muscle ring in the area of the internal os of the uterus;
- cervical hypertonicity - increased uterine tone due to insufficient progesterone production;
- congenital underdevelopment of the uterus - the cells of the muscle layer cannot increase normally during pregnancy and respond with an increase in tone.
All these diseases lead to the fact that a woman cannot bear pregnancy. Pain is one of the signs of an impending miscarriage. If urgent measures are not taken, this will end in spontaneous abortion.
Is it dangerous if the expectant mother has a sore uterus? The causes during pregnancy are often hidden in hormonal imbalance. In early gestation, the corpus luteum secretes progesterone. This hormone is necessary for relaxation of the uterus; sufficient levels prevent miscarriage. If there is little progesterone, then the reproductive organ becomes toned and begins to contract. The consequence of this process may be termination of pregnancy. But if you see a doctor in time, then everything can be fixed.
The uterus may hurt in the early stages due to accelerated growth. This happens especially often in women who have previously suffered from infectious diseases and have adhesions. As the uterus enlarges, these films stretch, causing discomfort and pain. This process does not pose any danger, but you must inform your gynecologist about any complaints you have.
In late pregnancy, the uterus may hurt for physiological reasons. The reproductive organ is preparing to expel the fetus. The uterus periodically contracts, causing discomfort. There is no danger in this if these are training contractions. Report them to your doctor.
The uterus can also hurt due to the threat of premature birth. If at the same time you experience unusual discharge, your water breaks, or other symptoms occur, you should immediately go to the hospital. The consequences of these processes can be very different.
If your due date has come and your uterus is very sick, then collect the necessary things and go to the maternity hospital.
Causes
If the expectant mother has a stabbing sensation in her stomach, this should not necessarily be a cause for alarm. Tingling in the uterus during pregnancy is familiar to almost all women who have carried a child to term and given birth to it safely. That is, despite the presence of this symptom, their pregnancy was not accompanied by any complications.
Tingling sensations can appear at any stage of gestation. Let's take a closer look at their causes in the early and late stages of pregnancy.
In the early stages
Minor tingling sensations that occur in the uterine area in early pregnancy usually indicate that the abdominal muscles are beginning to adapt to the growth of the reproductive organ. They lose their tone and adapt to changes in the shape of the uterus, trying not to interfere with its enlargement. A muscle strain may cause discomfort such as a stabbing sensation when laughing, coughing, or sneezing.
Some women perceive tingling in the uterus as a sign of pregnancy. Of course, such thoughts can only occur to experienced mothers who experienced exactly the same sensations during a previous pregnancy.
A tingling sensation can also occur with flatulence. Overstretching of the muscular walls of the large intestine against the background of increased gas formation can provoke discomfort, including pain. In the early stages, flatulence occurs in every second expectant mother. To eliminate this problem, it is necessary to follow a diet; carminative drugs, for example, Espumisan, are prescribed less frequently.
In the later stages
Tingling in the uterus during late pregnancy may be associated with training contractions. Typically, this condition is characterized by hardening of the uterus, but no pain is felt.
Additionally, the tingling sensation may be the result of excess pressure from the growing uterus on the bladder. To avoid this condition, it is necessary to follow a drinking regime - in the 3rd trimester, the amount of fluid consumed should not exceed 1.5 liters per day. It is recommended to empty your bladder on time.
If tingling sensations are accompanied by pulling sensations and rhythmic contractions of the uterus, this may be a sign of the onset of labor.
Periodic pain in the cervix during menstruation
Moderate pain in the cervix during menstruation is considered normal if it is not of high intensity and does not last long. They may appear if menstruation was preceded by heavy physical activity or sexual contact. This may be a pressing pain in the cervix. There may be pain in the cervix of a cramping nature, which intensifies with defecation.
- increased pain sensitivity;
- lack of production of natural anti-pain substances (endorphins, enkephalins);
- endometriosis;
- violation of the position of the uterus;
- increased production of prostaglandins;
- uterine fibroids;
- corpus luteum phase disorder.
If you have painful periods, it is better to consult a gynecologist.
The causes of pain in the uterus during menstruation are quite varied. The pain itself is called dysmenorrhea and can be primary or secondary. The primary form develops as a result of infantilism or abnormal position of the organ. The causes of secondary dysmenorrhea are infectious and inflammatory processes of the reproductive system, endometriosis, cystic and tumor formations.
Sometimes the uterus hurts due to increased excitability.
Pain that precedes the onset of menstruation and occurs in the first hours of bleeding is typical of primary dysmenorrhea. If the uterus hurts during all “menstruation”, then this is a symptom of secondary dysmenorrhea.
Uterine pain during menstruation can be a sign of inflammatory diseases. Depending on how the uterus hurts, the symptoms may indicate a specific pathology.
- If the cause is vaginitis, then the pain is accompanied by a feeling of a stone in the lower abdomen and pathological vaginal discharge.
- When endocervicitis becomes the cause, the disease is accompanied not only by pain, but also by purulent discharge.
- Sharp pain in the uterus may indicate endometritis. In this case, temperature (sometimes very significant) and symptoms of general intoxication are also added. Blood discharge during menstruation looks like meat slop, gray or brown in color.
- If the uterus hurts and hurts intensely, then the cause may be adnexitis - inflammation of the appendages. The disease is characterized by severe pain and a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen. The woman's body temperature rises, and she also develops nausea and vomiting.
The reason why the uterus hurts after menstruation may be the following pathologies:
- Benign tumors. These are considered large cystic and myomatous formations. Pain develops as a result of compression of neighboring organs, as well as dysfunction of defecation and urination. When a cervical cyst forms, pain in the lower abdomen may also develop.
- Endometriosis. The disease is the growth of endometrial tissue in places where it should not be. A typical symptom is pain before and after menstruation, as well as cyclical enlargement of the affected organs.
- Polypous formation of the cervix. Diagnosed only after hysteroscopy.
- Inflammation of the organs of the reproductive system. The cause of the pathology is STIs.
- Adhesive processes.
- Prolonged wearing of an intrauterine device. Sometimes it grows into the endometrial layer, which causes pain.
Causes of lumbago in the uterus during pregnancy
If there is a shooting in the uterus during pregnancy, then this can be a consequence of various processes in the body, both absolutely safe and harmful to a woman’s health. During this period, for the normal development of the fetus, physiological changes in the body begin, due to which the woman may experience various different sensations that were not there before. One of these phenomena may be tingling in the uterus during pregnancy. Almost all women experience it at this stage.
The main causes of tingling at different stages of pregnancy
Most often, tingling in the uterus is caused by normal changes in the body. But some tingling sensations along with other symptoms can become signs of a certain disease, so it is better not to skip all these details.
In the first trimester, tingling may occur due to the growth of the uterus. This process becomes more intense after the fifth week. The most common causes of tingling in the abdomen:
As the uterus grows, the ligaments that support it stretch. Pain occurs closer to the groin and occurs with sudden muscle movements. If you change your body position, the pain goes away;
In the second trimester, faster, more intense growth of the uterus begins. This results in less space available for other internal organs. This is why digestive problems may occur. To combat such pain, you need to change your diet.
In the final months of pregnancy, pain becomes more frequent. They are associated with the fact that the body is preparing for childbirth. After 35 weeks, the uterus can increase its tone and prepare to open. At this time, you need to be careful and strictly monitor the process.
It's time to see a doctor
pregnancy and menstruation in the first month of pregnancy the test is negative “I had my period through pregnancy” - this is the most common excuse for a woman who comes to register at a period of more than 12 - 15 weeks, when she already begins to feel fetal movements. Really
In some common cases, lumbago is not an event that accompanies the usual course
Source
What to do if pain occurs
- Ultrasound of the uterus;
- histological examination;
- taking smears for examination;
- tank sowing the contents of the cervical canal;
- colposcopy.
After carrying out diagnostic procedures, the doctor will make a diagnosis. Treatment is carried out according to the detected pathology.
IMPORTANT! Among the diseases that cause discomfort and pain in the cervix are many precancerous diseases.
After treatment, a woman should be regularly monitored by a doctor and follow all his recommendations. These measures will allow you to notice oncological degeneration in time and begin appropriate treatment. Thereby avoiding serious operations, maintaining a high quality of life and reproductive function.