Atheroma (lat. Atheroma) is a benign tumor (wen). Doctors characterize it as an epidermal cyst of the subcutaneous sebaceous gland, formed as a result of blockage of the fat duct. It can appear in a person on any part of the epidermis, but most often affects the scalp of the skin. Cysts appear on the scalp, lower part of the face, on the genitals, on the back - in the interscapular area or on the lower back. Adult men and women aged 30 to 40 years are most susceptible to this disease. It occurs much less frequently in children and adolescents.
What is atheroma?
Atheroma is a pathological cystic formation. It appears due to the fact that the ducts of the sebaceous glands are clogged and the outflow of constantly produced secretion does not occur. As a result, it accumulates in the resulting cavity (capsule).
It is filled with secretions of the sebaceous gland - a thick (cheesy) mass of grayish color with an unpleasant odor.
Atheroma on the back develops without causing discomfort, so it can be difficult to detect it in a timely manner. The formation can grow to the size of a chicken egg.
This benign sebaceous cyst is a fairly common skin problem.
In its most common location, on the back, there are many ducts that secrete sebum. Penetration of infection into atheroma is dangerous because pus mixed with blood appears in its contents.
In the future, an abscess may develop. Men are more susceptible to the disease, since testosterone affects the functioning of their glands.
More often, atheroma is diagnosed in patients aged 20–30 years, as well as during puberty. In childhood, wen formation is rare; this may be a consequence of congenital pathologies.
How to treat
Conservative treatment of atheroma without surgery is mostly a myth. Traditional medicine cannot make a tumor disappear without a trace. So even an atheroma that has gone inside under the influence of Vishnevsky ointment will still appear again. In order to avoid a relapse of the unpleasant disease, the atheroma must be removed completely - along with the capsule around it. And only a surgeon can do this.
Therefore, at the first signs of the disease, you need to contact a plastic surgeon. Only this specialist will be able to not only remove atheroma on the head, but also make sure that the consequences in the form of scars and cicatrices do not overshadow your life in the future.
Reasons for appearance
There are many reasons for the development of atheroma, but in general they are divided into two groups: internal factors and factors acting from the outside, that is, external causes.
External factors include:
- damage to the sebaceous gland canal and blockage of its ducts;
- skin injuries;
- weather influence - high air temperature, high humidity;
- unfavorable working conditions – frequent stay in a hot and stuffy room;
- the use of cosmetics that contribute to the narrowing and blockage of the sebaceous gland ducts;
- insufficient body hygiene.
Internal factors include:
- increased sweating (hyperhidrosis);
- dermatological problems - acne, acne, seborrhea;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body;
- hereditary predisposition;
- changes in hormonal levels, especially during certain periods - puberty, menopause.
Post-operative care
After the operation has been performed, do not forget about postoperative rehabilitation.
If the removal was performed traditionally or using a laser, antibacterial therapy is usually prescribed to avoid suppuration and inflammation of the scar.
The scar needs to be regularly disinfected and bandages changed (if any). You can wash your hair 1-2 days after removing the atheroma. After complete healing, regular hygiene of the scalp with gentle cleansers is important. For a while, you should refrain from dyeing and curling your hair, and you should also think about regulating the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
Symptoms
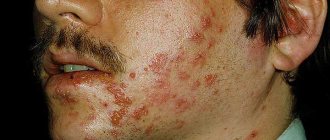
It is worth noting that atheroma does not have characteristic, pronounced clinical symptoms. These cysts do not cause any discomfort, and when they are located on the back, they are usually noticed late, when the formations have already reached a large size.
Inflamed atheroma does not cause pain, but is a purely visual, cosmetic inconvenience.
External signs of a cyst are:
- the wen looks like a bulge protruding above the surface of the skin;
- the lump has a clearly defined contour;
- the shape of the cyst is round, and to the touch it is dense and elastic;
- atheroma is mobile, it can be slightly moved from its location;
- the size of the formation is different - from a pea to a chicken egg;
- on the surface of the atheroma you can see a clogged duct of the sebaceous gland - a black dot.
An inflamed wen has its own symptoms:
- swelling and redness are observed;
- atheroma becomes painful;
- sometimes it can open and then the purulent contents, which have an unpleasant odor, come out;
- the process is accompanied by a general deterioration in health and an increase in temperature.
Differential diagnosis
It is necessary to differentiate atheroma from lipoma, fibroma, hemangioma, dermoid. In appearance, the neoplasms are very similar. If an external examination does not allow the doctor to make an accurate diagnosis, he punctures the contents of the lump and sends the extracted biological material for microscopic examination. This procedure helps to differentiate atheroma from a malignant tumor.
If a lump on the head is just beginning to grow and its appearance does not allow the disease to be identified, the patient is referred for an X-ray of the skull and Doppler sonography. If necessary, ultrasound and CT are used.
When there are signs of atheroma suppuration, the cyst is removed surgically. After surgery, the cyst is sent for histology. Examination of tumor particles makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis.
Under no circumstances should you diagnose yourself. Atheroma of the scalp is quite similar to a lipoma. Therefore, only a qualified specialist can make a diagnosis. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe additional examination methods:
- Ultrasound;
- CT scan;
- histology (allows us to exclude malignancy of the formation).
Photo
You can find out what atheroma looks like on the back in the photo below:
Surgical methods
There are effective ways to remove atheroma on the head. The doctor decides which one to use.
Criteria:
- stage of cyst development;
- size of education;
- the presence or absence of an inflammatory process.
Proven methods:
- Laser cyst removal. Used in the early stages. The essence: the lump is opened, the laser processes the cavity, removing all particles and cauterizing the surface. The wound heals quickly, and relapses occur infrequently.
- Traditional method. Suitable for getting rid of bumps of any size. The cyst along with the membrane is removed through a puncture. Advantages: absence of postoperative scars. The procedure takes 10–15 minutes.
- Radio wave method. Many doctors choose this method. Using waves of a certain frequency, a radio knife removes formations of various sizes. Advantages: relapses are excluded, there are no stitches or scars, a short postoperative period.
Note! The radio wave method does not require getting rid of hair in the surgical area. With the classical method, it is necessary to remove hair around the tumor.
Treatment
Do those who have encountered atheroma have any hope that it can be cured with folk remedies? Or maybe there is a possibility that it will resolve on its own?
Unfortunately this is not possible. Even if you manage to open this cyst, after some time it will appear again. The fact is that the subcutaneous capsule will remain and will produce secretion that fills it. The process of formation of atheroma on the back will begin again.
Today, the following treatment methods for sebaceous cysts are possible:
- Removal using laser.
- Radio wave therapy.
- Surgical excision.
increasingly popular - it is safe and does not entail any complications. The recovery period does not exceed 5 days; no traces of the removed atheroma remain, since the procedure does not require incisions or punctures of the skin.
Laser treatment is recommended for mild forms of atheroma , when the size of the formation is small. The method is bloodless, there are no scar formations after its use. After laser therapy, relapses are extremely rare.
Laser and radio wave treatment are conservative treatment methods. When they don't help, the only option is surgery.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. It does not last long and includes the following stages:
- a small incision above the surface of the cyst;
- opening the capsule;
- removal of the capsule with its contents.
After surgery, the doctor applies stitches and bandages until the skin heals. All procedures are carried out only under sterile conditions.
After surgical excision, antibiotic therapy is often prescribed. Local drugs that have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and healing effects are also used - for example, Levomekol or Vishnevsky ointment.
If the atheroma is inflamed, it cannot be removed immediately. First, suppuration therapy is carried out - the cyst is opened and the purulent masses are removed. The drainage is left for some time (up to several days). The patient usually requires a course of antibiotic therapy.
A few months after treatment of the inflammatory process, the atheroma can be removed.
ICD10 code
ICD10 is an international classification of diseases that collects coded information about diseases. The list is updated at regular intervals; today’s version of classified diseases is already the 10th.
The ICD was created to facilitate the work of medical specialists; it includes all diseases, including skin diseases, which include atheroma.
This disease is included in the section on neoplasms of the skin and appendages (benign). In the ICD-10 encoding it is included in the interval from L72 to L72.9.
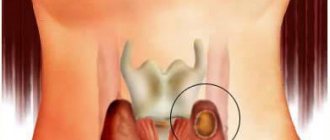
Diagnostic procedures
Atheroma puncture for laboratory research
Diagnosis of back atheroma begins with an external examination and questioning of the patient and does not pose any problem for a qualified doctor. During palpation, a formation of dense consistency is felt under the skin, which moves when you press on it. Since the skin above the surface of the epidermal cyst becomes thinner, the fibrous capsule is visually visible through it. It has a white or yellowish color, characteristic of the fatty and epithelial tissue filling it.
The initial examination is usually carried out by a general practitioner, who then refers the patient to a dermatologist, surgeon or oncologist. Atheroma must be differentiated from pathologies that have similar symptoms:
- fibroids;
- hygromas;
- lipomas.
For this purpose, a biopsy is performed - a laboratory test of tissue samples taken with a syringe from the fibrous capsule of the formation. The patient is also given blood tests - general and biochemical, which help determine the degree of development of the inflammatory process. After establishing an accurate diagnosis, a decision is made on how to correct this pathological situation.