Melanocytic nevus is a skin neoplasm accompanied by a benign course. It is localized on the skin and can occur against the background of dysfunction of melanin formation. Growth is a type of age spots. It can be primary or secondary, based on the reasons for its development. The main factor that provokes the appearance of a growth is a failure in the hormonal system.
The characteristics of the lesion are variable, depending on the age category to which the patient belongs. The diagnostic procedure is traditionally based on instrumental research aimed at certain types of education. The selection of treatment tactics is carried out individually for each patient, but minimally invasive intervention is most often used. The international classification contains several parameters characteristic of each individual form of pathology.
What is a pigmented nevus?
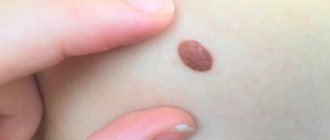
Accumulations of melanin on the skin, most often brown, but sometimes black, purple or another shade, are known to dermatologists as pigment nevus. Formations can be present in the form of inclusions in the skin or protrude on top of the integument. They are benign in nature and consist of melanocytes (cells responsible for the production of melanin). Pigment synthesis can be caused by ultraviolet radiation and melanotropic hormone produced by the pituitary gland.
According to the reference book of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), nevi belong to the section of neoplasms (C 00-D 48), the subsection of benign neoplasms (D 10-D 36) and have the final code D 22 (melanoform nevus). This code denotes the following species recorded in the classification:
- NOS (giant pigmented, borderline form);
- cyan (blue);
- hair;
- pigmentary.
What kind of pathology is this?
Pigmented, or melanocytic formation - limited, modified areas of the skin that were formed as a result of a failure in the production of melanin pigment. Despite the fact that nevi initially have a benign etiology, with a confluence of unfavorable factors there is a risk of the neoplasm transforming into a malignant tumor. Nevus appears equally in males and females. The formations can be congenital or acquired, but if the behavior of nevi changes, both require careful study, diagnosis and removal.
Symptoms and signs
Pigment formations are easy to detect by their characteristic appearance. Difficulties may arise if the formations are poorly saturated with melanin or are located in places that are difficult for the eyes to see (folds of skin, back). Under the influence of hormones, barely visible formations can begin to gradually grow in the distribution area and change color. If such a spot undergoes similar changes, then it is most likely a pigment spot.
Sometimes the area of education begins to feel itchy. This indicates that there are processes going on inside that are associated with cell division. Itching may occur due to contact of the stain with clothing. The cause of the irritation should be determined to prevent complications. For a complete understanding of the characteristics of formation, you need to refer to the classification of species. Each of them has a number of features (pictured).
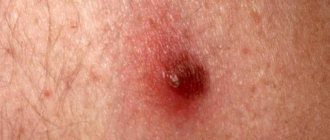
Signs of malignancy
A nevus is a benign formation, but it carries the risk of transformation into malignant melanoma. Careful observation of education should become a habit. You should be alarmed if you notice the following atypical signs:
- Increased education. Pigment spots with a diameter of more than one centimeter have a tendency to degenerate into cancer.
- The edges of the mole began to sharpen, changing the shape of its location.
- The occurrence of itching, pain.
- Clusters of dangerous small black nodules form on the surface of a pigmented mole.
- The consistency has changed (thickened or softened) or color.
- Blood began to ooze from the surface, and the skin began to dry out or peel.
- Hair fell out from the surface of the formation.
- Irritation or pinpoint growths have appeared around the mole.
Risk factor
There are factors that contribute to the development of melanoma. These include:
- Large melanoma neoplasms.
- The appearance of nevi in old age.
- A giant nevus that occupies a significant area on the body. It has been proven that the larger the tumor, the higher the risk of transformation into melanoma. Medicine has established that increased formation of moles occurs during periods of immune weakening. Therefore, melanoform neoplasms may indicate weak immunity. Subsequently, such non-dangerous cells can be activated into aggressive ones.
- High quantitative indicator of melanoform moles (from 50 pieces). If you regularly expose them to ultraviolet rays, the risk of developing malignant pathology increases.
- If a melanoform nevus is subjected to constant friction in contact with clothing, then there is a risk of malignant formation.
Types of moles
These factors are the most common, so in order to protect yourself from serious consequences, you should treat melanoform nevi with caution.
Causes
The mechanism of formation of melanocytic nevi is excessive cell division. Compared to cancer, division has a limit and occurs slowly. Moles are a congenital phenomenon that manifests itself as the body grows and stops upon completion of the main stage of body formation (22-25 years). Factors determining their formation:
- Heredity.
- Ultraviolet radiation: stimulates the functioning of melanocytes.
- Hormonal changes: Pregnancy or changes in adolescence involve the pituitary gland, which is responsible for melanotropic hormone.
- Injuries: inflammatory processes can provoke local growth of pigment cells.
Pigmented nevus in a child
In newborn children, the skin often does not have formations visible to the eye, but as the body grows, the area of the skin increases, and the nevi acquire a formed appearance. At the age of 5-10 years, moles manifest themselves in the form of seals of various shapes and sizes, having a brown tint. Some doctors call this formation juvenile melanoma.
A child's mole is a plaque-like, spherical formation, delimited from adjacent tissues, diameter: 0.5-0.7 cm. A characteristic sign is angiomatosis (pronounced capillaries). The skin on the surface of the formation is thinned. It requires extremely careful handling, because trauma can activate the mechanisms of malignant degeneration.
Types of nevi
The variety of nevi has given rise to the need to classify them by type. The key point is the division into melanoma-free and melanoma-hazardous formations. The first include:
- Intradermal nevus. Appears during adolescence and changes throughout life. Located in the dermis layer.
- Papillomatous nevus. It has a pronounced shape and color, rises above the surface of the skin, soft and painless to the touch.
- Pigmented halonevus. The mole is round or oval in shape and has a pale border at the base. It manifests itself in individuals with hormonal system disorders and weak immunity.
- Mongolian spot. A genetically determined birthmark, found predominantly in people of Mongolian nationality. It disappears with age.
- Fibroepithelial. Round in shape, up to half a centimeter in diameter, reddish or pinkish in color.
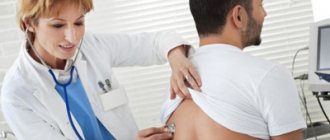
Patient examination
The examination of a patient with a birthmark begins with a conversation and examination. During the interview, the doctor establishes such important details as the period of appearance of the mole (from birth or with age), its recent behavior (for example, has it changed color, increased in size, etc.), previous diagnosis and treatment .
After interviewing the patient, he is examined. The doctor evaluates the size, shape and location of the spot, the presence of hair on it and other features. Next, he makes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes treatment measures.
If necessary, the doctor conducts additional diagnostics. To do this, swabs are taken from the mole. Indications for this research method are: bleeding, cracks on the surface of the birthmark.
Taking a smear from a nevus has a significant drawback. During this process, microtrauma may occur, which can subsequently provoke malignant growth. In this regard, such research is carried out only in specialized oncology clinics.
Group of melanoma-dangerous nevi
Melanoma-hazardous formations require timely diagnosis and qualified treatment. They have the following classification:
- Blue nevus. The mole is raised above the skin and often has a dark blue tint. The risk of degeneration increases due to injury.
- Borderline nevus. This is a congenital type of mole, 0.7-1.2 cm in size. It is saturated with melanin and can be degenerated due to injury or ultraviolet radiation.
- Giant pigment. Congenital formation of large sizes, sometimes up to 40 cm in diameter. It protrudes strongly above the skin of the limbs, is pigmented dark brown and covered with hair.
- Dysplastic nevus. Half a centimeter in diameter, brown or black, flat spot. Without removal, the precursor of melanoma undergoes malignant transformation in 9 out of 10 cases.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the formation and distinguish it from skin diseases, a differential approach is used. To do this, examine the mole according to the ABCDE system - asymmetry, uneven bumpy borders, different color areas, diameter (critical is considered to be over 6 mm). To check the malignancy of the formation, a smear is taken for microscopy, and sometimes a luminescent study is performed. Histological biopsy is prohibited as a diagnosis, since it provokes the degeneration of a benign mole into a malignant formation.
Treatment
Noncellular nevus is treated depending on its size and characteristics. If the mole is small, does not change in size and color, do not touch it. Previously, treatment with hormonal ointments was used in relation to nevi, but this practice did not justify itself. Today, surgery is popular. Sometimes symptomatic treatment with the prescription of analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and hypercoagulants is indicated instead. To alleviate the condition, physiotherapy is used, sedatives and mild cytostatics are taken.
Classification
Melanocytic nevi are classified depending on their size and color, which can vary from light brown to black, as well as localization in the thickness of the skin. There are these types of formations:
- A borderline nevus is a brown spot located on any part of the skin. In this case, melanocytes accumulate between the inner layers of the skin.
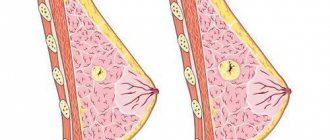
- Intradermal nevus - this type of melanocytic nevus is more often observed than others. Melanocytic intradermal nevi are localized in the middle layer of the skin - the dermis.
- Complex-pigmented - a complex nevus is a formation of a convex shape, while its color may vary, and hair may grow on the surface of the formation.
- Intradermal - usually the formation of melanocytic intradermal nevi occurs on the face, neck and trunk. The formation has an uneven surface and rises somewhat above the skin.
- Papillomatous - melanocytic papillomatous nevi that appear on the body look like bumpy moles. In most cases, they are localized in the scalp, but such a mole can also be found in other places above the surface of the skin. Removal of papillomas is indicated if they are frequently injured or have inflammation.
- Basal - also called a birthmark, which does not contain melanin.
- Mixed nevus - the formation may have characteristics of several different types of melanocytic nevi.
To determine the exact type of melanocytic formation, it is necessary to use special equipment in a medical facility. What kind of diagnostic tests are needed is determined by a dermatologist. Melanocytic congenital nevi can be detected in only 5% of newborns. If they cover a significant area of the body, this can pose a serious threat and cause the development of melanoma.
Traditional methods
Doctors do not advise using traditional medicine methods in the treatment of nevi, because exposure to herbs and acids can lead to malignancy of moles. If the patient is confident that the formation is benign, then a small non-pigmented spot can be treated with the following recipes:
- apply pure celandine juice or mixed with petroleum jelly to the affected area several times a day;
- lubricate the affected areas with hemp oil 3-4 times a day for a month;
- Apply lemon juice to moles five times a day.
Prevention of malignancy
Currently, there are no effective measures to prevent the formation of age spots. Popular methods of protecting moles from transforming into malignant vascular tumors include:
- protection from solar radiation - tanning in the shade, during safe hours (before 11 a.m. and after 4 p.m.), using sunscreen;
- regular examination of moles on your own or with a dermatologist;
- prohibition on scratching to avoid injury to the spots.
Moles present on human skin can be dangerous (they can become malignant over time) and harmless. Intradermal nevus is a benign formation that does not threaten human health. But in some cases, it can degenerate into a dangerous neoplasm, so you need to monitor external changes in birthmarks.
This type is distinguished by a dark shade (brown or dark brown), defined boundaries and softness. At the same time, there are no inflammatory processes in it, and in appearance it is similar to a wart and has a bumpy surface. Intradermal nevi can be single or multiple, the size of small neoplasms is about 3-5 millimeters, large ones reach 5 cm. Moles of a non-pigmented form are rare.
Types of neoplasms
Intradermal melanocytic nevus is the most common. This type is acquired over time and is found in the entire population, with up to 15 moles on the human body. The outside has a round shape with clearly defined edges, from red to dark brown. In medicine, there are various forms of melanocytic formation:
Noncellular. They form on the face and neck and do not cause discomfort, so therapy is carried out at the patient’s personal request. Rarely occur in adolescence and transform into dangerous neoplasms. Removal is indicated only in case of a serious defect. With age, the shade of the neoplasm loses its original color saturation.- Intradermal pigmented nevus. They differ in that moles have an intradermal location, that is, in the dermis itself. These formations are safe, but if they change (size, structure), you need to undergo an examination.
- Papillomatous intradermal nevus. The appearance is similar to a pedunculated papilloma. Often forms on the scalp and scalp. Its distinctive feature is that it has a heterogeneous structure and large dimensions. It happens that papillomatous nevus has a hairy surface. If the tumor interferes with hygienic procedures, is often damaged, it must be urgently removed.
Intradermal pigmented nevus (borderline). It is black in color due to its high melanin content. At the initial stage of development, a mole looks like a nodule without a leg; over time, the surface becomes lumpy and uneven. The color of the formations does not change and always remains black. Pigmented formations appear on the neck, armpits, and genital area. There are both single and multiple moles.
For many years, scientists have tried to unravel the meaning of the appearance of moles, congenital birthmarks. Namely, they studied the areas of the skin on which they are located.
Why are doctors alarmed? Because an ordinary atypical mole can develop into melanoma. Intradermal nevus is safe, but according to histology, it is a background for the development of melanoma, observed in 16 out of 100 cases.
Etiology
Thanks to scientific research in the field of dermatology, clinicians became aware that almost all types of pigment spots related to melanocytic nevus, including those acquired during life, are caused by congenital disorders associated with the development of the skin. It is such deviations that cause the occurrence of benign neoplasms.
Congenital melanocytic nevus has the following sources as the main predisposing factors:
- excessive changes in the content of hormones, namely progesterone and estrogen, during the period of bearing a child;
- ailments of the genitourinary system suffered by the expectant mother during pregnancy;
- prolonged influence of unfavorable factors on the pregnant woman’s body, including toxic substances, all kinds of radiation and addiction to bad habits;
- genetic disorders.
Due to the influence of the above reasons, the incorrect formation of melanoblasts occurs, which are special cells that are the source of the development of melanocytes. Against this background, melanoblasts stagnate in some areas of the skin, causing them to transform into age spots.
Secondary skin nevus is caused by the following etiological factors:
- hormonal imbalance - most often such formations develop in adolescence during puberty, with a large number of nevi appearing in various parts of the body;
- long-term exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the skin;
- abuse of solarium or prolonged exposure to direct sunlight;
- the period of bearing a child and the onset of menopause;
- uncontrolled use of contraceptives;
- the occurrence of inflammatory processes on the skin, in particular dermatitis, acne and acne;
- allergic skin lesions;
- diagnosing close relatives of a disease such as melanoma.
Diagnosis and treatment
What are the challenges in diagnosing? Initially, the type of formation is determined, then treatment tactics are prescribed. During the examination, they find out when the tumor appeared, its location, type of shape, size and possible changes that occurred until recently, whether there was treatment before and what results it led to.
If it is not possible to recognize the type of formation, then resort to additional diagnostics. They can take a smear directly from the lesion, or rather from the bleeding cracks that are often found on the surface of the mole.
Smear analysis helps determine the risks of intradermal papillomatous (safe) nevus degenerating into a malignant form. The process of taking a smear itself has an unpleasant side; the neoplasm is damaged, which contributes to the development of melanoma.
There is also a method of fluorescent microscopy, when the study is carried out using a microscope. The most expensive method is diagnostics using a computer.
Basically, the formations do not need treatment if it is a safe type of mole, but their growth cannot be prevented in any way, so they resort to surgical intervention, and in the presence of a small scattering of formations, a laser is used.
Indications for surgical removal
A frequent indication is disfigurement of a person’s appearance or location in a hard-to-reach area of the body (head, back, perineum), which makes it difficult to control its injury, the presence of a large number of neoplasms throughout the body, the location of a nevus under the nail plate, limbs or mucous membrane, which constantly rubs and causes discomfort. when touching them with clothing.
Besides this, there are more significant reasons:
- sudden growth of intradermal formation;
- inflammation around the birthmark;
- itching, cracking and bleeding;
- unevenly pigmented areas of the mole;
- the appearance of pigmented nevus, small neoplasms.
When does a melanoform nevus degenerate into a malignant tumor?
If you look at the tumor under a microscope, you will notice special cells - melanocytes. Therefore, a nevus can easily transform into a life-threatening form - melanoma. There is no need to hide that a melanoform nevus is a pathology because it consists of altered cells. Therefore, it is extremely important to monitor all kinds of changes in such neoplasms.
Signs of healthy moles
Early symptoms indicating the development of malignant pathology:
- The size of the nevus increases significantly.
- On palpation, discomfort and pain are felt.
- Sometimes there is a feeling of tingling or itching in the area of the tumor.
- The color of a melanoform mole changes.
- The nevus becomes black or deep blue.
- Lumps or roughness appear on the surface.
- There are no clear contours of the nevus.
- Bleeding.
- Sputum manifestations on the surface of the nevus.
- The appearance of peeling.
Is it dangerous! If you notice several of the above symptoms, you should immediately contact a specialist and undergo a detailed diagnosis.
Video - Mole (nevus): causes of appearance, growth and changes
Melanin and melanocytes
Melanin is a natural pigment dye that is found in human skin, retina, iris, hair and even in the brain. Weak or intense skin color depends precisely on the number of melanocytes. The same applies to eye color. An effect such as tanning is also due to the presence of melanin.
There are three types of melanin:
- neuromelanin is a special type of melanin that is found in the brain;
- eumelanin - black or brown color - melanocytic nevus;
- pheomelanin is yellow.
In the body, melanin appears in melanocytes. These are special cells that have many processes. They take the hormone thyroxine from the blood, which is secreted by the thyroid gland. After undergoing an oxidation procedure, thyroxine is converted into melanin. Then, along the processes of melanocytes, the newly formed melanin passes to the skin cells. This is where it is deposited.
In addition to pigmentation, melanin has many other functions in the body :
- increases the body's resistance to stress;
- it is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from the negative effects of radioactive radiation and toxins;
- actively participates in the normalization of sleep and wakefulness;
- prevents excessive emotionality and stabilizes the emotional background.
Albino people have colorless eyes, white or light red hair, and completely white skin. Their body is completely devoid of melanin. These people are weakly resistant to various types of diseases and often die young.
Reasons for the formation of nevi
Melanocytic nevus
Usually these are hormonal changes in the body. Often this manifests itself in adolescence , but there are others:
- During pregnancy, a change in sex hormones occurs in the female body.
- Inflammatory and allergic skin diseases.
- Exposure of skin to ultraviolet radiation. Frequent solariums and sunbathing provoke activation of age spots.
- Menopause.
- Use of contraceptives.
Dysplastic nevus
Today, most dermatologists are inclined to think that many pigmented nevi, even those that appear in adulthood, are congenital malformations of the body. These disorders, after which the nevus appears, are already present in the embryonic state.
The factors responsible for the appearance of dysplastic nevi have not yet been fully elucidated. But there are main reasons for the development of the process:
- infection of the genitourinary system of a pregnant woman;
- changes in sex hormones (estrogens, progesterones);
- genetic disorders;
- the effect of negative factors on the body of the expectant mother (toxic substances, radiation).
Under the influence of all or certain factors, the development of melanoblasts—tissues that form melanocytes—is disrupted. As a result, melanoblasts accumulate in certain areas of the skin and transform into nevocytes.
There are two features that distinguish melanocytes from neocytes:
- Dysplastic nevi on the skin weakly obey regulatory processes in the body, but have not completely lost this ability, which cannot be said about cancer cells.
- Neocytes do not have processes along which the pigment could move to other skin tissues.
It is believed that new nevi do not appear with age. It’s just that they were completely invisible before and showed themselves only after a while.
Symptoms and classification of nevi
Hemangiomas are characteristic vascular tumors . The most common is “strawberry nevus”, which has a red tint. These neoplasms appear in many newborns and disappear within a month of the baby’s life.
Melanocytic nevi vary greatly in shape, color and size. Today, there is no consensus among dermatologists as to what formations are classified as nevi. Therefore, nevi are often called benign tumors that do not contain melanin.
Preventive measures
In practice, there are no special measures that could help avoid the development of education.
In order to reduce the likelihood of a pathological process occurring, it is necessary to follow a number of recommendations:
- avoid prolonged exposure to the sun and solarium;
- treat the skin with special tanning protection compounds;
- do not visit the solarium;
- undergo an annual examination by a doctor in the field of dermatology and oncology.
In the lion's share of medical situations, the prognosis for the patient is favorable, even if surgery is performed to remove the malignant growth.
After surgery, it is forbidden to expose yourself to the sun, wet your skin or use cosmetics for several days. In order to prevent relapse, after a couple of months it is recommended to contact an oncologist and show him the location of the removed mole.
Types of nevi
Intradermal nevus is considered the most common type of melanoform nevus. It is so called because the accumulation of melanocytes occurs in the dermis - the middle layer of the skin.
A noncellular border nevus is a simple, non-raising spot above an area of skin. In some cases, the border nevus stands out slightly above the surface. This species has strictly defined contours and a brown color. The size and location of the nevus on the body can vary greatly. This type of melanoform nevus is characterized by an accumulation of melanocytes between the dermis and epidermis.
An intradermal nevus is slightly convex, but differs in that it has an uneven and bumpy surface. It is almost always found on the head or neck, but sometimes it can be seen on the torso. The critical age for the manifestation of such a skin infection is 15-35 years. Over time, the intradermal nevus seems to move away from the body and is supported only by a thin stalk.
As a rule, it turns into a papillomatous or otherwise warty nevus, however, warts are growths that are slightly different in appearance. A large number of irregularities and cracks form in them, where dead epithelial cells accumulate. This is an excellent environment for the emergence of pathogens, which later lead to dangerous infections.
A complex pigmented nevus has the shape of a mole, and it is this that defines the concept of a “mole.” As a rule, it rises above the skin and has a variety of complex colors: from black to light brown. Often there are coarse hairs on the mole. The surface of the mole is smooth, and it can be located anywhere on the body.
A basal nevus is also similar to a regular mole, but there is usually no pigmentation. The standard color is flesh.
Blue nevus has a characteristic color because it is associated directly with melanin deposits under the skin. Residents of Asian countries usually have these moles. Moles rise slightly above the body, have a smooth surface, are hard to the touch, and in rare cases, hair grows on them. The diameter of the neoplasm is usually no more than 6 mm.
Halo nevus or Seton nevus is an unusual type of dermal nevus; in this case, on the contour of the pigment spot there is a light rim of skin, completely devoid of pigmentation. This type of neoplasm has not yet been fully studied. These spots are often adjacent to melanomas and vitiligo. Often there is slight skin inflammation in the area of the halo nevus.
Nevus Ota. Localized on the face in the form of “dirty” spots.
Nevus Ita is localized under the collarbone in the area of the shoulder blade, neck and chest.
Becker's nevus or epidermal pilar nevus, usually formed in young men and adolescents, is completely different from the nevus of Ota. Initially, several small spots appear on the body, which are light brown or brown in color. They are crowded together, but after a certain time they unite, creating large spots (up to 25 cm) with uneven contours. In this case, the spots get a warty surface, with a hair growth.
Papilomatous or warty nevus is characterized by its large diameter. As a rule, it is localized on the neck or surface of the head, but in some cases it can be seen in other places. In appearance it looks like a wart, hence the name. The surface of the tumor is usually covered with hair.
A nevus of the eye is located on the iris. This is a clearly visible spot that comes in a variety of shapes and sizes. The tumor can also be located in the retina, and it can only be determined through a thorough examination by an ophthalmologist.
Linear nevus - this growth forms on the human body from birth. It can consist of a whole group of small nodes of various shades: from black to light flesh. They are located on the body in the form of a chain. This growth can cover several centimeters of skin, or can completely occupy the surface of the arms or legs. Hairs often form on it.
Separation of nevi by size:
- small ones have a diameter of 0.6-1.6 cm;
- average neurodermal their size is 1.6-11 cm;
- large pigment ones, their diameter is more than 11 cm;
- gigantic, found over most of the body.
As the body grows, the appearance of the growths also changes. Their number can also change, and not only in the direction of increase.
Giant nevi of infants have a high risk of transformation into melanoma .
- Dermal nevi can be found in 85% of adolescents aged 10-16 years.
- In people 20-25 years old, up to 40 birthmarks can be observed on the body.
- After 35 years, a person has only 20-25 moles on his body.
- In people over 85 years of age, nevi are almost impossible to detect.
This dynamics is explained by changes in hormonal levels that occur throughout a person’s life.
So, we have examined a large number of nevi, and only one thing becomes completely clear - to determine the growth, its classification and name, naturally, perhaps, paying attention to the size, color, appearance and other characteristics, but how correct is this definition, if today the number of varieties Are there already hundreds of nevi? Is it really possible that any of us, without special education, can establish an accurate diagnosis and determine the danger in advance?
Therefore, we recommend that you consult a doctor if you have any concerns about tumors. Moreover, an experienced doctor can not only define a growth, but will also tell you why it formed on the head or arm, what are the reasons why an ordinary pigmented nevus, which is called a mole, manifests itself incomprehensibly, will tell you what a congenital neoplasm is and what – acquired. This information received from the doctor will make it possible to assess the situation and determine whether it is necessary to remove an ordinary mole, how to do it, and how to care for the place on the body after removing the growth.
Population Prevalence
The prevalence of pathology is influenced by a certain set of circumstances:
- race;
- genetics;
- floor;
- age threshold;
- environment.
Some nevi occur predominantly in infants, but maximum manifestation occurs between the ages of 20 and 30. Subsequently, there is a gradual reduction in their number and consistent disappearance without a trace. New growths tend to appear rapidly during puberty. The statistical picture shows that girls are more susceptible to the disease. Localization does not depend on gender.
Studies have shown that representatives of the Caucasian race have to deal with such growths more often than Asians and indigenous inhabitants of Africa. The following trend is also observed: the lighter the skin, the more susceptible it is to the formation of pathological growths. Genetics is generally accepted as the determining factor. If melanoma has occurred among relatives, it will be inherited with a 70% probability. The type of inheritance is autosomal dominant.