Gout is a rheumatic disease caused by the accumulation of crystallized uric acid salts in the joints and kidney structures. Its leading clinical manifestations are recurrent, progressive attacks of arthritis, accompanied by intense pain and the formation of specific nodules - tophi, provoking deformation of the joints. After some time, the kidneys become involved in the pathology process, which causes the development of urolithiasis and renal failure.
To diagnose gout, a number of instrumental studies are performed: radiography, MRI, CT, and, if necessary, arthroscopy. The most informative is a biochemical analysis of synovial fluid for the presence of urates. The main goals of therapy are to relieve inflammatory processes in the joints and prevent the progression of pathology by reducing the level of uric acid in the body. For this purpose, pharmacological drugs are used and the patient’s diet is adjusted.
Gout: what kind of disease?
Gout is a pathology (failure, disorder) of metabolic processes associated with excessive formation or insufficient removal of uric acid from the body. There are 4 stages of gout formation:
- The accumulation of uric acid in the body, which is recorded by an increased level of its content in the blood.
- Formation of salt crystals in joints.
- Aggression of immune cells against urate formations and inflammation of the damaged joint.
- Long-term manifestations of gout, kidney damage, joint deformities.
Gout is a purely age-related disease. Almost all older people over 65 years old show signs of this disease. And in children and young people, gouty changes are recorded in exceptional cases.
Men suffer from gout more often; the disease usually takes them by surprise after the age of 40. This fact is due to the physiologically high content of uric acid in male blood. The risk of developing pathology in women increases significantly with the onset of menopause (over 50 years). The causes of this “royal” disease will help you better understand what gout is.
The presence of gout in a person is an indicator of an irrational life (low physical activity, poor diet). That is why gout has been called “the disease of kings” since ancient times because of their idle lifestyle.
The concentration of uric acid in the blood increases for the following reasons:
- Gastronomic addictions - overeating, fatty foods (fish/meat, smoked foods, pickles), alcohol abuse (including beer) and, as a result, obesity;
- Physical inactivity is a lack of physical activity on the body;
- Sudden weight loss due to illness or improper diet;
- Smoking (nicotine is actively integrated into metabolic processes);
- Long-term microtrauma of joints (tight shoes, excessive loads on the foot);
- Hormonal disorders (in women, primarily menopause);
- Long-term use of Aspirin and diuretics.
However, not only external factors can provoke the formation of urate deposits. Gout often develops against the background of:
- chronic kidney failure;
- kidney stones, gall bladder;
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypothyroidism;
- serious allergic pathology (eczema, psoriasis, bronchial asthma);
- hypertension and high blood cholesterol;
- hereditary predisposition (gout in blood relatives in previous generations).
Gout in adults
The disease gout is mostly diagnosed in the adult population. The average age for men to experience an acute attack of gout is 35 to 45 years. But in recent years, the disease has become noticeably “younger”, and the age of patients may be younger and younger.
“Foot in a trap” is the name for gout translated from ancient Greek. And this literally indicates the most common damage to the joints of the lower extremities in gout. However, this disease can manifest itself as pathological processes in the tissues of various organs, causing significant harm to health.
Gout disease in men
Men are approximately 20 times more likely to develop gout than women. One of the main causes of the disease is unhealthy diet and alcohol consumption, which disrupts purine metabolism in the body. Since men are much more likely to subject their bodies to such stress, an increase in uric acid levels in the blood and the formation of salt crystals in the stronger sex is more likely.
With a disease such as gout, symptoms of metabolic disorders in the body in men usually appear after the age of 30. However, in the presence of provoking factors, gout can develop much earlier. In men, the disease is usually diagnosed in the later stages, since they consult a doctor only when acute attacks become frequent or external manifestations of gout in the form of tophi are already observed.
Gout in women
In women, an increase in the level of uric acid in the blood and the formation of salt crystals (urates) in soft tissues occurs mainly during menopause. Women are less susceptible to gout, which develops due to a hereditary predisposition. This is explained by the fact that the gene responsible for the production of most of the enzymes that take part in the metabolism of purine compounds is located on the X chromosome. Women have two X chromosomes, and men have one. Therefore, if the gene is damaged, men are 100% likely to develop gout at some point in their lives. In the female genome, the dysfunction of a damaged gene on one X chromosome will be “overlaid” by the intensive work of a normal gene on the other.
Signs and treatment of gout, photo
photo of an exacerbation of gout, the process of manifestation of the first symptoms
The signs of gout cannot be confused with another disease, its manifestations are so specific. The first symptoms appear in the area of the joint of the big toes (one or both). It is this joint of the thumb that gout chooses as its first target.
Gouty arthritis does not produce symptoms until a provocative moment: tight shoes, a feast with overeating and drinking alcohol.
A typical pattern of symptoms for a gout attack:
Pain
Suddenly at night there is pain in the joint. This is one of the most severe pain sensations a person will ever experience. Even strong and resilient people note its unbearable intensity, which practically immobilizes the entire foot. The situation is aggravated by the absolute ineffectiveness of painkillers.
Inflammation
Signs of gout, photo of inflammation
The affected joint swells, diffuse hyperemia appears. Body temperature often rises to high numbers (39-40ºС).
An attack of gout lasts up to 4 days, and then disappears on its own even without taking medications. Self-removal of painful symptoms is based on the inclusion of phagocytes in the fight against inflammation. Temporary relief, sometimes lasting several years, does not mean recovery.
Pathological changes affect the phalangeal joints of the fingers, larger ankles and wrist joints, and often the knee. The increase in size of the joint and limited mobility do not disappear with the disappearance of the gout attack.
progression of the disease - joint deformation
Progressive gouty pathology is characterized by the following symptoms:
Tophi
Painless bumps under the skin are a collection of urates. Typical localization: behind the ears, elbows, skin over the affected joint. Tophi are prone to spontaneous opening, and a white curdled mass is released from the wound. A similar picture is observed 5-6 years after the first attack of gout.
Joint deformity
The accumulation of urate deposits in the joint leads to its permanent deformation (subluxation) and significant limitation of mobility in it. With a prolonged course of the disease, the patient cannot move without a cane.
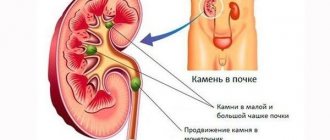
Kidney damage
The kidneys, as a “cleaning station” of the blood, accumulate urates without ensuring their full removal from the body in the urine. This process gradually forms sand/kidney stones.
Diagnosis of gout
If you suspect gout, you should contact a rheumatologist. The diagnosis is made taking into account:
- specific symptoms of the disease;
- visual examination (inflammation of the joint, detection of subcutaneous tophi);
- biochemical blood test (high urate level);
- X-ray (damage to the articular surfaces and tophi inside the joint capsule, leading to a narrowing of the intra-articular space; in case of severe damage - a symptom of a “punch” - germination of tophi into the bone tissue);
- puncture of a diseased joint (needle-shaped urate inclusions, no detection of an infectious agent of inflammation, leukocytes up to 20x109/l with exacerbation of gout);
- puncture of tophi (composition - urates).
Gout: symptoms, stages and forms of the disease
The disease gout is characterized mainly by a clear clinical picture and the sequence of changes in the stages of its development. But in some cases, the symptoms of the disease may be blurred or hidden behind the “masks” of other pathologies. Only a doctor can help determine gout, and you should contact him when the first signs of the disease appear. In the absence of timely diagnosis, treatment and special nutrition, signs of gout, manifested by acute attacks with severe pain, can become more frequent and cause significant discomfort to the patient.
Stages of gout
Based on symptomatic manifestations, uric acid content and the presence of formed urates (solid salt crystals), three stages of gout development are distinguished:
- The premorbid stage is the beginning of the disease, when the patient has only hyperuricemia, and the formation of urates with signs of damage to the urinary system or joints is absent.
The premorbid stage of gout can only be determined by taking a blood test for biochemistry. Nonspecific signs of the disease may include a feeling of general weakness, increased sweating, a predisposition to obesity and disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract, itchy skin and constipation.
- The intermittent, otherwise called interval, stage of gout development is characterized by the beginning of the formation of salt crystals in the periarticular soft tissues and, occasionally, in the kidneys.
At this stage, the patient begins to experience acute attacks of gout, lasting from 3 to 7 days and ending in remission. The duration of the latter depends on many factors. Mainly from the patient's compliance with the diet and taking the treatment prescribed by the doctor. Thus, an exacerbation of gout can be triggered by surgery, alcohol abuse, damage to the body by an acute infectious process, hypothermia and other negative factors.
- The chronic stage is accompanied by regular exacerbations of gout and subsequent remissions.
At this stage in patients, small salt crystals join together and form tophi. Formed tophi can have different sizes and be quite hard, causing pronounced pain to the patient. With chronic gout, patients may develop urolithiasis. At this stage, the clinical picture of the disease is clear and, in addition to the formation of tophi, is manifested by severe redness of the affected joints, inflammation of nearby tissues, limited mobility and increased temperature in the affected area.
Each stage of gout development has its own characteristics of the manifestation of the clinical picture and certain diagnostic measures are relevant.
Pain due to gout: features of localization and manifestations
An acute attack of gout at the intermittent and chronic stages of the disease is accompanied by severe pain that occurs mainly at night. Painful sensations are not only localized in the area of the affected joint, but also spread throughout the entire limb. The cause of acute pain is the presence of hard urates in the soft tissues, which injure both them and the cartilaginous parts of the joints. Also, the pain of gout is to some extent caused by the inflammatory process.
The pain of gout is quite acute, and it is usually impossible to relieve it with painkillers. Even minimal external pressure on a joint whose nearby tissues are affected by gout greatly increases the pain. In more than half of the patients, the first acute attack with severe pain affects the first metatarsophalangeal joint, located at the base of the big toe of the lower limb. In addition, urates can form in nearby tissues of the phalanges of the fingers, wrist, elbow, ankle, hip, knee joints, etc.
Forms of gout
Approximately 60-80% of patients suffering from this disease are diagnosed with a typical acute attack of gout. In the chronic stage, the attack occurs suddenly, ending the state of remission and subsequently being replaced by it again. The duration of an acute attack depends on the stage of development of the disease and the type of treatment received. Exacerbation of gout is determined primarily by acute pain in the affected joint and around it. Patients also experience general weakness, headaches, redness of the skin in the affected area and sometimes a bluish color, and an increase in temperature to a subfebrile level or higher. In addition to an acute attack of gout, the following main forms of development of the disease are also distinguished:
- The subacute form is characterized by a more weakened expression of the clinical picture. With this form of the disease, patients usually affect the area of one joint. But there is no severe swelling or acute pain.
- The pseudophlegmonous form is not accompanied by symptoms characteristic of the classical clinical picture of gout. With this form, the patient develops an acute inflammatory process in the periarticular tissues, in which the patient’s body temperature rises above 39°C and chills are observed.
- The rheumatoid-like form has a course that is as similar as possible to the clinical picture of various rheumatological diseases. With gout of this form, as a rule, the joints of the fingers and wrist joint are affected. The duration of exacerbations of gout in the rheumatoid-like form can last from several weeks to several months.
- Gout, the course of which is similar to the signs of infectious-allergic polyarthritis, is diagnosed in 5% of patients. In this case, the onset of the disease may be characterized by symptoms similar to the clinical picture of migratory polyarthritis.
- The low-symptomatic form, the name of which speaks for itself, is distinguished by a mild clinical picture. Patients suffering from this form of gout usually complain of moderate pain localized in the area of one joint. External signs may also include the development of slight swelling and redness of the tissue.
Each of the above forms of the disease is characteristic of the onset of gout, but as it progresses, patients in all cases may experience typical acute attacks, alternating with periods of remission.
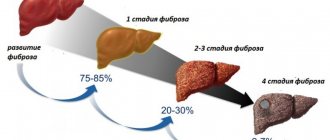
Also, 30-50% of patients suffering from gouty arthritis, or so-called gout of the joints, may develop gouty nephropathy in the later stages of the disease. This complication consists of damage to the urinary system, in which hard salt crystals form in the soft tissues of the organs.
Articular manifestations of the disease
Gouty arthritis, better known as joint gout, has various external manifestations. During an acute attack, as pain intensifies and blood rushes to the affected area, its skin turns red. Among other joint manifestations of gout it is worth noting:
- an inflammatory process in the soft tissues surrounding the joint, leading to the development of bursitis, tendinitis or tenosynovitis;
- limitation of joint mobility, characteristic mainly of an acute attack of gout with a clear manifestation of pain in the joints, but which can partially persist during remission;
- an increase in temperature, manifested locally by an increase of 1-2 degrees.
One of the specific signs of gout in the later stages of its development is the formation of tophi. Tophi are subcutaneous and intradermal formations formed from hard salt crystals that arise due to the accumulation of uric acid in the soft periarticular tissues. As a rule, the formation of tophi occurs in the 3-5th year of gout development. However, in some cases, the appearance of such a symptom may occur earlier.
Tophi gradually increase in size as the disease progresses, reaching several centimeters in diameter. Impaired blood circulation in the affected area can subsequently lead to the formation of fistula openings, from which a thick white mass or powder, which is salt crystals formed from uric acid, is periodically released.
Tophi, as a rule, form in the area of the ankle, elbow, knee, metatarsophalangeal and phalangeal joints, on the ears and brow ridges. Gout of the fingers and joints of other localizations may be accompanied by the appearance of tophi in earlier periods of the development of the disease.
Treatment of gout
The first step in treating gout is pain relief. Patients suffering from gout should know a list of measures that can reduce pain during an exacerbation:
- Rest the injured limb.
- Cold on the painful area: wet towel, ice pack, cold water bottle.
- NSAID drugs (Ortofen, Voltaren, Naproxen, Diclofenac) in tablets or injections (injections slightly increase a/d, it is recommended to do it in the first half of the day).
When seeking medical help and persistent pain, intra-articular administration of steroid drugs and intravenous injection of Colchicine are possible.
Only a qualified doctor can tell you how to treat gout and achieve stable remission, based on the diagnostic results of a particular case. We consider general measures of therapy.
To prevent relapses and development of the disease, the following drugs are prescribed (treatment courses):
- NSAIDs - take with caution, they irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa;
- Corticosteroids - prescribed taking into account immunosuppressive properties and leaching of calcium from bones;
- Colchicine - normalizes uric acid metabolism, negatively affects the composition of the blood and gastrointestinal tract;
- Vitamins P and C - promote the dissolution and removal of urates;
- Uricodepressants (Allopurinol, Orotic acid) - reducing the production of uric acid;
- Uricouretics (Benzbromanol, Ketazone, Probenecid) - remove uric acid from the body, are contraindicated in chronic renal failure, gastrointestinal diseases (especially liver).
Read also: How to relieve pain from gout
If there are high blood levels of uric acid and low excretory capacity of the kidneys (urine excretion less than 3.56 mmol/day), the combined use of uricosuretics and uricodepressants is advisable. Doses and duration of taking drugs for the treatment of gout are determined individually. Treatment courses are long (up to 1 year) with a break of 2 months.
Physiotherapy procedures have a beneficial effect on the affected joint: ultraviolet irradiation (during exacerbation), medicinal phonophoresis, paraffin treatment and ultrasound exposure (during remission).
Surgical treatment (arthroplasty, prosthetics) is indicated for significant joint deformation and a significant degree of immobility. Often surgical procedures are performed under local anesthesia using arthroscopy (endoscopic treatment method).
Treating gout at home
When treating gout at home, it is possible to use the following, the most effective recipes for gout: tincture of lilac or spruce cones, bay leaf decoction.
- The use of medicinal raw materials is approved by the attending physician.
- Such recipes have their contraindications. For example, bay leaf is strictly prohibited for use by pregnant women (it provokes premature birth and bleeding), patients with gastrointestinal ulcers, diabetes mellitus, and constipation.
- Treatment with home remedies does not replace drug therapy prescribed by a doctor.
Diagnosis of gout
The main complaint of patients suffering from gout is pain in the joints of the fingers, feet, elbows, knees, etc. This fact significantly complicates the diagnosis of the disease, since such a symptom can indicate a huge variety of rheumatological pathologies. An experienced specialist will be able to determine gout based on the external features of the clinical picture, as well as the results of paraclinical studies prescribed for the patient. The speed and complexity of diagnosis depends on the severity of symptoms and the factors that provoked the development of the disease.
An integrated approach to diagnosis will allow you to accurately determine the disease and the stage of its development. In addition, a general examination, medical history, and paraclinical diagnostic techniques will reveal:
- hyperuricemia, in which the level of uric acid, determined in the serum of venous blood, is stably elevated;
- accumulation of salt crystals;
- deposition of urates (salt crystals) in the periarticular tissues;
- acute inflammation, causing severe pain with gout, decreased joint mobility.
With a long course of the disease, the kidneys are often involved in the pathological process, the examination of which should be regular.
Patient Interview
If you experience pain in the joints, you should consult a rheumatologist. Having extensive experience in diagnosing rheumatological diseases, a specialist of this profile will be able to quickly confirm or refute the diagnosis of gout, the symptoms of which are mostly non-specific. Taking an anamnesis plays a significant role in making a diagnosis. At the first appointment, the doctor will definitely ask the patient:
- what symptoms are bothering him, when they appeared and with what intensity they developed;
- whether joint pain was observed before and where exactly it was localized;
- whether there were cases of gout in close relatives in the family;
- what foods predominate in the diet and whether there are any bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol, etc.);
- how much fluid a person consumes per day;
- whether the patient has had any surgical interventions in the past, long-term use of certain medications, or kidney diseases that negatively affected their filtering ability.
Also, when collecting anamnesis, it is important for the doctor to know whether the patient often exposes his body to physical activity.
Gout: signs of the clinical picture of the disease
After collecting anamnesis, the doctor will perform a detailed examination of the area affected by the disease at the first appointment. If you have the appropriate qualifications, a specialist will be able to make a preliminary diagnosis even before conducting certain laboratory and instrumental studies. It is worth noting that regular examination is necessary not only for making a diagnosis of gout, which should be treated as early as possible.
During an external examination, the doctor will be able to assess the presence of an inflammatory process in the periarticular tissues, the mobility of the joint itself and other features of the course of the disease. It is worth noting that regular examinations by a doctor to assess the clinical picture and condition of the patient are important not only for determining the diagnosis, but also in the treatment of gout.
Instrumental studies
Certain types of hardware examinations help determine the etiology of joint pain. Thus, pain due to gout is a reason for ultrasound diagnostics, scintigraphy using technetium pyrophosphate, computed tomography and radiography. The object of examination for any instrumental diagnostic method is the affected joints. But it is worth noting that with gout in the initial stages, such studies are not very informative, since destructive processes in such cases have not yet occurred. However, instrumental studies make it possible to exclude the presence of many rheumatological diseases, the symptoms of which are quite similar to the signs of such a disease as gout of the joints. The purpose of instrumental diagnostics is relevant in the following cases:
- An ultrasound examination, carried out 3-4 days after the onset of an acute attack, allows one to determine the expansion of the joint space, the presence of edema and thickening of the periarticular soft tissues. There is no point in conducting such research later, since it will turn out to be uninformative.
- A CT scan is intended to determine the location of tophi. Such a study is relevant in the later stages, when solid salt crystals in the periarticular tissues combine into tophi. But it is worth noting that even in the early stages of gout development, using computed tomography, it is possible to determine the compaction of periarticular tissues.
- X-rays performed in the early stages of the disease are designed to exclude signs of other rheumatological diseases. With a confirmed diagnosis of gout, X-ray examination is relevant only in the chronic form of the disease.
Scintigraphy using technetium pyrophosphate is prescribed to patients in cases where the clinical picture of the disease is blurred. During the procedure, technetium pyrophosphate is injected into the patient's blood, which makes it possible to accurately determine where salt crystals are deposited. Thus, such a study makes it possible to determine gout even in the early stages of its development, when urate deposition is just beginning.
Tests for gout
With the help of laboratory tests, it is possible to determine not only gout in the early stages, but also the presence of conditions conducive to its development, namely an increase in the level of uric acid in the blood serum. In addition, the results of appropriate tests help differentiate this disease from various rheumatological pathologies. As a rule, patients are prescribed:
- General blood analysis.
The study is informative for acute attacks of gout. Based on its results, leukocytosis is determined with a shift of the leukogram to the left and an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
- Biochemical analysis of venous blood.
The main purpose of such a study is to determine elevated levels of uric acid. Based on the results of biochemical analysis, an increase in C-reactive protein and calcium, an increase in the level of lipoproteins and lipids, and hyperglycemia can be determined.
- General urine analysis.
A study of this type is informative only if the patient has signs of damage to the urinary system, in particular the kidneys. Then specialists determine the presence of urates in the material being examined.
- Urine analysis for biochemistry.
Thanks to this test, the doctor can estimate the amount of uric acid excreted in the urine. But it is worth noting that its volume may vary depending on the causes of gout. Thus, during normal kidney function, uric acid levels may increase as the volume of toxins in the blood increases. And in the presence of pathological processes in the kidneys, the volume of excreted uric acid is usually minimal.
In gout, the amount of uric acid in urine and blood serum is one of the main indicators. Normally, the volume of this substance in urine should be in the range of 250-750 mg. Normal uric acid levels in male patients range from 0.27-0.48 mmol/l, and in female patients they range from 0.18-0.38 mmol/l. In addition to the above studies for gout, to assess the condition, specialists can take synovial fluid from the joint cavity and the contents of the formed tophi for analysis.
Features of differential diagnosis
At different stages of development of a disease such as gout, its symptoms may be similar to various rheumatological pathologies. For example:
- at the initial stages of the development of the disease, which occurs with damage to one joint, its symptoms are similar to those of acute infectious arthritis;
- an acute attack of gout in the fingers and other joints, occurring as polyarthritis, without appropriate examination can be confused with the onset of the development of rheumatic allergic polyarthritis;
- Chronic gout is characterized by symptoms similar to the clinical picture of rheumatic allergic polyarthritis, which also occurs in a chronic form.
In addition, with a disease such as gout, treatment, its features and effectiveness depend on the correct determination of the primary or secondary nature of the disease.
Nutrition: menu for gout
Without nutritional correction, the effectiveness of drug therapy is significantly reduced. To normalize metabolic processes and prevent the development of exacerbations, be sure to adhere to the following diet:
- with reduced fat intake,
- limiting sodium intake,
- with an emphasis on plant proteins and vitamins;
- excluding preservatives.
The diet for gout prohibits the consumption of foods:
- Salt (complete exclusion or daily consumption of no more than 1/2 teaspoon).
- Cream cakes.
- Herbs and spices (you can use vinegar, bay leaf).
- Fatty meat/fish, smoked meats, offal dishes (especially jellied meat).
- Mushrooms.
- Figs, raspberries, raisins and fresh grapes.
- Legumes.
- Chocolate, cocoa, strong brewed tea, coffee.
- Alcohol.
- Greens - spinach, cauliflower, sorrel, lettuce.
- Bread (white, rye), pasta.
- Vegetables (preferably fresh), fruits (citrus fruits and cherries are especially useful).
- Milk, cottage cheese, kefir, butter.
- Poultry, lean fish (boiled 2-3 times in the weekly menu are recommended).
- Sugar without restrictions and honey (with normal blood glucose levels).
- Juice, mineral water.
Drinking warm mineral water or a glass of water with lemon juice will speed up your metabolism. Also, metabolic processes are normalized with a weekly fasting day.
Complications of gout
- Severe joint deformation, disability.
- Gouty kidney, acute/chronic failure, stones.
- Hypertension, cardiac ischemia.
- Osteoporosis.
Prevention
Only a healthy lifestyle (physical activity, giving up bad habits, proper nutrition) will help you avoid the appearance of gout. This “hackneyed” and often not taken seriously phrase protects the body from many diseases, including gout.
To stabilize the condition and avoid complications, you should strictly follow medical recommendations and strictly adhere to the diet prescribed for gout. Only then will a long fight against the disease bring results.
Gout - symptoms and treatment at home
Gout is a rheumatic pathology caused by the formation of uric acid salts in the joints. The signs and treatment of this disease are described in great detail in our material. The disease is one of the common types of arthritis and occurs more often in middle-aged men.
What kind of disease is this? Gout is a chronic disease associated with a disorder of uric acid metabolism, in which uric acid salts, also known as urates, are deposited in the joints.
The pathology is otherwise called “the disease of kings”; it is an ancient disease that was already known in the time of Hippocrates. In the past, gout was considered a sign of genius. Such famous people as Leonardo da Vinci, Alexander the Great, many members of the Medici family from Florence, Isaac Newton, Charles Darwin suffered from it.
Nowadays, according to epidemiological studies conducted in European countries and the USA, in recent years, up to 2% of the adult population has developed gout, and among men aged 55-64 years, the incidence of the disease is 4.3-6.1%.
The first signs of gout are characterized by an acute onset with the appearance of severe pain, redness and stiffness in the joints. Gout most often occurs on the big toe, which should be treated immediately. The main recommendations for reducing the symptoms of chronic gout are adherence to treatment regimen and lifestyle. We will try to consider this article about gout, the symptoms and treatment of this disease in detail today.
What it is? Gout is caused by the deposition of uric acid crystals (urates) in the cartilage tissue of the joint. Their accumulation leads to inflammation, accompanied by severe pain. Sodium urate crystallizes and is deposited in the joints in small particles, which ultimately leads to complete or partial destruction of the joints.
- Abuse of certain pharmaceutical drugs: aspirin, diuretics, cyclosporines.
- The presence of conditions and diseases such as diabetes, coronary heart disease, obesity.
- Consumption of fatty meats, seafood, carbonated and alcoholic drinks greatly contribute to the accumulation of purines in the body.
- Men aged 30-50 years are more susceptible to the disease.
Attacks of gout can be triggered by stress reactions to alcohol, citrus fruits, viral infections, physical or mental stress, injuries and hypothermia, bruises, pressure fluctuations, and medications. At the first attack of gout, the signs are very clear, and treatment should be started as soon as possible to relieve pain.
There are three types of disease: metabolic, renal and mixed.
- Metabolic form with the highest amount of uric acid.
- Renal form, moderate amount of uric acid with increased salts,
- With the mixed type, reduced or normal uraturia and normal clearance are possible.
The diagnosis is made by a rheumatologist during examination and interview of the patient. Laboratory diagnostics are also used: a high level of uric acid is detected in a biochemical blood test.
Gout in children
An increase in uric acid (hyperuricemia) in childhood is usually secondary and occurs against the background of other diseases. For example, active cell death, in which there is an increased production of purines, can be caused by dehydration, malignant neoplasms, fasting, renal failure, etc. Also, the development of gout in children can be triggered by the complete or partial absence of hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyltransferase, or increased activity of phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase.
Gout symptoms
Arthritis of the joints of the lower extremities is usually observed. The inflammatory process often affects the big toe, followed by the ankle and knee joints. Less common is arthritis of the small joints of the hands and elbows.
With gout, symptoms develop during an attack - this is pain that develops quite quickly, and reaches its highest sensation in just a couple of hours. Attacks occur more often at night or in the early morning.
A person is not only unable to move his leg, but even a light touch of a sheet to the affected joint causes unbearable pain. The joint rapidly swells, the skin becomes hot to the touch, and redness of the skin at the joint site is noted. An increase in body temperature is likely.
After 3-10 days, the attack of gout subsides with the disappearance of all signs and normalization of functions. A second attack usually occurs three months after the first, or the disease does not manifest itself in any way for two decades.
Read also: Salt deposition in the joints of the fingers, treatment
Chronic gout is characterized by attacks becoming more frequent and symptom-free intervals becoming shorter.
Clinical picture
Attacks of gouty arthritis are characterized by sharp, piercing, “gnawing” pain, the intensity of which may not decrease for several days. The pain syndrome occurs suddenly, accompanied by stiffness of movement and swelling of the joints. The inflammatory process involves nearby soft tissues, resulting in redness of the skin. It smooths out and becomes hot to the touch. On palpation, the intensity of the pain increases, and it radiates to healthy areas of the body. The soft tissues around the source of inflammation become denser and swell. Most often, the small joints of the big toes are the first to be affected by gout. Then inflammatory foci form in large joints:
- ankle;
- knee;
- elbows;
- hip
In the absence of medical intervention, uric acid crystals are deposited in the Achilles tendon and phalanges of the fingers. An increase in arthritis attacks leads to the formation of specific gouty nodules in the form of bumps on the joints, irreversible changes in the joints, expressed in their visible deformation. The range of movements is significantly reduced, the patient gradually loses professional skills and the ability to care for himself at home.
Problems arise in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. During the day, blood pressure may increase several times, vascular spasms and heart failure may occur. Although some cases of hyperuricemia are asymptomatic, the risk of heart or blood vessel problems is not reduced. The most dangerous consequences of lack of treatment are cardiac arrest or stroke. 20% of patients with gout develop kidney stones, and almost all of them develop chronic renal failure. Stones formed from uric acid crystals provoke severe pain in the joints and often clog the ureters.
| Forms of gout | Clinical manifestations |
| Attack of acute arthritis | The first pain occurs suddenly, usually at night. Arthritic gout is provoked by drinking alcohol or fatty, fried foods, trauma, and hypothermia. The pain syndrome is severe and localized in the metatarsophalangeal joint of the first toe |
| Polyarthritis of infectious-allergic type | There are wandering pains in many joints. The joint swells, turns red, and becomes hot to the touch. Signs of damage to the first metatarsophalangeal joint are moderate. Young patients have a high probability of developing oligo- or monoarthritis of the knee, ankle, and hip joints |
| Rheumatoid-like form | Primary involvement of the joints of the hands is noted, manifesting itself in the form of oligo- or monoarthritis |
| Periarthritic form | Inflammation affects the tendons and bursae, usually the ankles. Articular tissues are deformed, the edges of bone plates grow, incomplete dislocations become more frequent, and a crunching sound occurs when moving. |
| Pseudophlegmonous form | It manifests itself as monoarthritis with localization of the inflammatory process in the joints and paraarticular tissues. Often this form of gout is accompanied by a fever. |
Complications
Hyperuricemia and accumulation of urate salts in gout leads to their deposition in the kidneys with the development of:
- nephropathy;
- gouty nephritis;
- arterial hypertension with subsequent transition to chronic renal failure.
40% of adults develop urolithiasis with renal colic at the height of an attack of gout, complications in the form of pyelonephritis. To avoid the consequences of gout on the legs, you need to be puzzled right away about how to treat the disease.
Symptoms and signs in men and women
Below is a table with symptoms and signs of gout in men and women:
| Signs and symptoms in men | Signs and symptoms in women |
| Acute, burning, severe pain in the joints (big toe, arch joints). Most often occur early in the morning or at night | Acute joint pain (usually the toes and hands are affected first) |
| Sharp enlargement of the joint, redness and swelling, inability to move the joint | Redness, swelling, joint enlargement, swelling |
| When drinking alcohol and fatty junk foods, the pain worsens | When touched, the pain intensifies |
| Alternation of acute periods and temporary attenuation of symptoms | General malaise |
| Against the background of gout, urolithiasis and pyelonephritis can develop | Possible increase in body temperature |
| Possible increase in body temperature | If symptoms disappear, they may reappear with alcohol intake, dietary changes, or excessive physical and emotional activity. |
| General weakness and malaise | Possible cracking of joints |
Treatment of an acute attack
Treatment of gout involves the gradual implementation of several stages of therapy. First of all, it is very important to relieve the acute symptoms of the disease. Further treatment is aimed at preventing future worsening of gout symptoms.
During an attack of gout, it is necessary to ensure sufficient rest for the affected joints and try to injure the joint as little as possible with clothing or shoes. In case of unbearable pain, you can apply ice. After which it is advisable to apply a compress to the sore spot with Vishnevsky ointment or dimexide.
To relieve acute signs of gout, doctors recommend taking colchicine or nimesil, as well as NSAIDs - diclofenac, butadione, indomethacin, naproxen. A specialist should decide how to treat gout on the legs; he will prescribe the necessary medications, suggest a dosage regimen and warn about side effects.
It is better to limit your food consumption greatly; you can consume liquid porridges and vegetable broths. It is recommended to drink enough water, green tea, jelly, milk, mineral or plain water, but with the addition of lemon juice.
Treatment of gout
For gout, treatment is prescribed individually and includes medications, physiotherapeutic methods and diet. It is necessary to take into account all the side effects of drugs in the presence of other diseases, therefore constant medical supervision is necessary.
The basis of therapy is a special diet aimed at reducing purine-rich foods in the patient’s diet. If the patient can adhere to the prescribed diet therapy, then the resulting lumps on the joints will begin to disappear and the body will recover.
The diet should include dishes boiled in water or steamed. Salt should be almost eliminated. Fish and meat broths and jellied meat are also contraindicated. It is recommended to eat plenty of vegetables. They should be taken raw; to add variety to the menu, you can sometimes bake or boil them.
To reduce the level of uric acid, anti-gout drugs (sulfinperazone, alopurinol, uralit and others) are used. Herbal medicine is also used in combination with physiotherapy and medications. A doctor should treat gout; he will tell you exactly what can be used at home to get rid of the disease.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics consists of several stages: questioning, examination, instrumental and laboratory tests.
Correct diagnosis is very important because... Other diseases are often mistaken for gout. During the examination, the doctor pays attention to the problem joint and tries to feel it if possible.
Then the patient is sent for a blood test - general and biochemical to determine the concentration of leukocytes, uric acid and the presence of concomitant diseases.
It is necessary to examine the joint fluid. The operation itself is quite unpleasant, but it helps to alleviate the patient’s condition. Often this test will remove excess fluid and administer medication. The seized fluid is sent to the laboratory, and after examining it, a diagnosis can be made with almost complete certainty.
If the disease has reached the stage of formation of bubbles and blisters, their contents and nature are analyzed.
To diagnose the condition of the joints, x-rays and ultrasound are prescribed.
Diet for gout
Patients with this diagnosis should be more careful about their diet, in particular, exclude purine-rich foods from the diet. It is important to note here that it is necessary to exclude both overeating and starvation; in addition, sudden weight loss should not be allowed, as this can lead to an exacerbation of the disease.
How to treat gout at home? The most correct diet for gout involves switching to a vegetarian diet or diet No. 6.
- Vegetables, preferably boiled, steamed, baked in the oven with a little salt;
- dairy products;
- berries, mainly currants of various varieties, watermelons;
- bran, bread made from bran;
- nuts, fruits and dried fruits;
- mineral water.
- fat meat;
- offal (kidneys, liver, tongue of farm animals);
- red fish;
- it is important to minimize salt intake;
- alcohol, coffee;
- sweet carbonated drinks.
It has been proven that strawberries, cherries, currants and other berries of dark red and blue colors cause a decrease in the concentration of uric acid in the blood, so patients with gout can eat them in any form and quantity.
Treatment of gouty arthritis
The disease in question can only be treated with complex therapy - it is impossible to take medications and refuse nutritional correction; traditional medicine also has a good effect. There is only one thing that is certain – visiting a doctor at the first symptoms of gouty arthritis increases the chances of complete relief from the pathology significantly.
Drug treatment
At times of exacerbation of chronic gouty arthritis, it is advisable to undergo drug therapy. And doctors make the following prescriptions :
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - ibuprofen (as substitutes can be imet or nurofen), indomethacin, rheumoxicam, movalis. The listed medications are considered the most effective during acute attacks of gouty arthritis. Moreover, doctors first prescribe them in the form of injections (this way the effect is faster and more complete), and then gradually transfer the patient to using the same drugs, but in tablet form.
- A specific anti-inflammatory drug used specifically for gout is colchicine.
- Ointments based on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - remisid, deep relief, indomethacin. These ointments are intended for application to the skin over the joint affected by the inflammatory process.
- Compresses/lotions made on the basis of dimexide (25% solution) or a regular semi-alcohol solution (alcohol is diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio).
- Physiotherapeutic procedures. They are prescribed against the background of the subsidence of an acute attack of gouty arthritis - magnetic therapy, laser therapy, paraffin baths and more.
But even if the disease in question occurs in a latent form, or the chronic process is in remission, then taking medications should under no circumstances be stopped! Doctors simply make other prescriptions, adjust the treatment regimen - for example, prescribe medications that reduce the synthesis of urates. To get rid of any pathological process, it is necessary to eliminate the cause - the same applies to gouty arthritis. This means that it is necessary to get rid of excess uric acid in the body. To do this, make the following appointments :
- uricozyme - it acts directly on already formed urate crystals, destroying their structure;
- allopurinol - actively reduces the amount of uric acid secreted by the body. Doctors can also prescribe an analogue of this drug – Zylorik;
- probenecid – removes excess uric acid crystals.
Allopurinol is of greatest importance in the treatment of gouty arthritis - it is prescribed in the case of high levels of uric acid in the blood, with developing renal failure, in the case of already formed tophi. You need to know that after taking this drug in the first 5-7 days, all the characteristic symptoms of gouty arthritis can become greatly aggravated, and that is why it is advisable to take allopurinol simultaneously with anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs. Please note: allopurinol is never used as a pain reliever if it is the first time an attack of gouty arthritis has occurred. During treatment with this drug, an allergic reaction such as a skin rash may occur. Probenecid and uricozyme are never prescribed for progressive renal failure, too high levels of uric acid in the blood. A contraindication to the use of these groups of drugs is previously diagnosed peptic ulcer of the stomach and/or duodenum.
Please note: during treatment with all of the above medications, you must drink a large amount of water - at least 2.5 liters per day. Patients should understand that treatment for gouty arthritis will be long-term; they will definitely need to follow a diet and undergo monthly tests to monitor the level of uric acid in the body. If the dynamics of the disease in question are positive, then patients can supplement the main therapy with physical therapy, massages and physiotherapy.
Diet for gouty arthritis
If the patient ignores the nutritionist’s prescriptions, violates the diet and continues to consume large quantities of meat products, coffee, chocolate and other harmful products, then even with specialized treatment there will be no results. There are clear restrictions and permissions regarding the products :
- The following are completely excluded from the diet for at least 12 months:
- lamb and veal meat;
- offal - liver, lungs, heart and others;
- aspic;
- herring, mackerel and sardines in any form - smoked, pickled, salted, fried;
- soups and broths with meat.
- It is necessary to limit the use of:
- poultry meat, ham, liver sausage;
- cod, sprat, pike perch, sprat;
- peas, beans, lentils, beans;
- cauliflower, radish, spinach, sorrel;
- coffee, beer and cocoa.
- You can safely enter into your daily menu:
- any dairy products, including hard/soft cheese;
- chicken and quail, goose and duck eggs;
- nuts of absolutely all types;
- jelly and gelatin;
- vegetable soups (except those prohibited for consumption);
- porridge of all varieties/types, except oatmeal;
- vegetable and butter.
Fish and meat with diagnosed gouty arthritis should be eaten only boiled and no more than 3 times a week. It is necessary to limit the consumption of salt, including in the form of marinades and brines for preserving vegetables. During the treatment of the inflammatory joint disease in question, it is very useful to use rosehip decoction, cranberry juice, linden tea, berry compotes - just do not forget to make sure that there are no diseases of the cardiovascular system. In general, for gouty arthritis you need to eat according to diet No. 6, but only with some clarifications. Below is a sample patient menu :
Monday
- Breakfast - cottage cheese with fresh or canned fruit jelly, coffee with plenty of milk.
- Second breakfast – a glass of apple juice.
- Lunch – rice soup with vegetable broth, rye bread, a glass of dried fruit compote.
- Afternoon snack – black tea (slightly brewed), marmalade, apple.
- Dinner – a glass of green tea, potato pancakes.
Tuesday
- Breakfast - any porridge with milk (except oatmeal!), rye bread, a glass of pineapple juice.
- Second breakfast – walnuts, pear of any kind.
- Lunch – vegetable stew, stewed rabbit meat, a glass of compote.
- Afternoon snack – a glass of orange juice.
- Dinner – a glass of black tea with milk, a sandwich with hard cheese.
Wednesday
- Breakfast - fresh carrot cutlets, sour cream, a glass of black tea.
- Second breakfast – one or two bananas.
- Lunch – borscht in vegetable broth with sour cream, a glass of rosehip broth.
- Dinner – pumpkin casserole, herbal tea.
Thursday
- Breakfast - sandwiches made from wheat bread with any type of cheese, black tea.
- Second breakfast – a glass of cherry juice.
- Lunch – potatoes baked in the oven with trout, vegetable salad with vegetable oil, a glass of cranberry juice.
- Dinner – muesli with any kind of nuts, a glass of green tea.
Only an approximate menu is given - from it it is clear that the nutrition of a patient diagnosed with gouty arthritis, despite the restrictions and exceptions, is quite varied and cannot be called inferior. Although for many patients even such a menu is very meager, you cannot break the diet - this will lead to an exacerbation of the disease in question. Please note: the specified diet must be strictly followed by patients for 12 months. This is followed by a thorough examination of the patient’s body, and if the dynamics of gouty arthritis are positive, some dietary allowances may be allowed.
Treatment of gouty arthritis with folk remedies
Important: in no case should remedies from the category of traditional medicine be considered a panacea - the inflammatory joint disease in question should be treated by medical professionals. But even official medicine recognizes and “gives the go-ahead” for the use of folk remedies during therapy. Naturally, patients must obtain permission for such treatment from their doctor, and exclude possible hypersensitivity and/or individual intolerance to any medicinal plants or products.
Black radish
The juice of this vegetable is considered the most effective for removing salts from joints, but only if you use only freshly prepared product. Preparing black radish juice is quite easy - the vegetable is peeled, grated and squeezed through cheesecloth, but you can use a blender for chopping and a juicer. Scheme for taking black radish juice for gouty arthritis: on the first day, take 1 teaspoon of juice 60 minutes after a meal, once a day. Then we increase the dosage daily and bring it first to a tablespoon, and then to ½ glass at a time. This regimen of taking black radish juice allows you to determine the absence/presence of side effects and not harm your own body. Please note: if, while drinking black radish juice, pain is noted in the epigastric region, liver (on the right), then taking the drug should either be stopped altogether or the daily dose should be significantly reduced. For the entire period of treatment with the folk remedy in question, sour and spicy foods are completely excluded from the diet. The duration of the course is individual, but it is necessary to consume at least 3 liters of black radish juice in total.
pharmaceutical camomile
A decoction of the flowers of this healing decoction will help with an acute attack of pain in a joint affected by gouty arthritis, but it must be prepared in an unusual way. Moreover, adherence to technology is a must :
- First, a saline solution is prepared - 20 g of ordinary table salt per 10 liters of hot water;
- then dip 100 g of chamomile flowers into it and simmer over low heat for 10 minutes.
After the finished broth is cooled to a temperature that the skin can withstand, a bath is applied to the sore joint.
Fir cones
A decoction is prepared from unopened fir cones with seeds - one cone is poured with 500 ml of boiling water and infused for 6-8 hours. Take the decoction 3 times a day, half an hour before meals. This decoction effectively cleanses the joints and the body in general of excess uric acid. The duration of taking this decoction is determined individually - traditional healers recommend not interrupting treatment until complete recovery.
Bay leaf
Such a common product in cooking turns out to be an excellent way to cleanse joints of monosodium urate crystals. The medicine is prepared as follows :
- take no more than 5 grams of bay leaf and fill them with 1.5 glasses of water;
- cook the product over low heat, at a low simmer for 10 minutes;
- remove the broth from the stove, wrap the dishes in a towel or scarf and leave for 3 hours.
The resulting decoction should be drunk in small portions throughout the day.
Unusual means
Some people are surprised by unusual folk remedies, others actively use them – this is a purely individual matter. According to official medicine, there is nothing harmful in the following remedies, but it is still necessary to consult with your doctor. Fresh lard Many people use lard to treat gouty arthritis - cut a small piece from it and rub it into the area of the affected joint until the piece is reduced by 2-3 times.
If attacks of pain in a joint are too frequent, then you should simply tie a piece of lard to the sore joint and leave it there overnight. As a rule, after such a procedure in the morning there is significant relief - the pain almost disappears. Traditional healers recommend eating millet porridge cooked in water when treating the disease in question with lard - it helps remove salts from the joints. Butter
Take butter (unsalted and it is advisable to find a homemade product) and alcohol in equal proportions. The oil is heated in a water bath or low heat until foam begins to appear on its surface. At this moment, remove the oil from the heat, pour the prepared alcohol on top and set it on fire. Only after the fire in the bowl with oil burns out will the ointment be considered ready. It should be used in moments of acute pain in the affected joint - it is simply rubbed into the skin until the pain subsides. The butter-based ointment is stored in a warm place for no more than 5 days. Mustard Mix 1 teaspoon of honey, mustard (ready-made, not powder) and baking soda in a bowl. Next, we steam the limb on which the diseased joint is located and apply the resulting product to the steamed skin. We put plastic wrap on top, then wrap the area with something warm (scarf, handkerchief) - such a compress should remain on the affected joint all night. The course of treatment with such compresses is 10-15 days. Fish
You will need 2 kilograms of fish trimmings - this amount must be divided equally into 10 bags and put everything in the freezer, having first cleared the backbone and all the bones from the product. Then every evening take out one bag, defrost it and put it on the sore leg directly with the fish, and on top - a warm sock. Such a strange compress should be done for 6-8 hours, and in the morning everything is removed and thrown away, the leg is washed thoroughly. It is believed that after 10 days of such daily fish compresses, the pain in the joint affected by gouty arthritis disappears for a long time. Gouty arthritis is a rather complex disease that is difficult to treat. But with all this, doctors assure that if you carefully follow all the recommendations and prescriptions of specialists, the disease in question is either completely cured or goes into long-term remission. Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical observer, therapist of the highest qualification category.
21, total, today
( 188 votes, average: 4.59 out of 5)
Clubfoot in children: symptoms and treatment
Carpal tunnel syndrome (tunnel syndrome): symptoms and treatment
Related Posts
How to treat gout with folk remedies
Since many are interested in the question of how to treat gout using folk remedies, let us dwell on this point in more detail.
- Fish compresses. Divide the fillet of any fish into 10 parts, put them in small bags, and put them in the refrigerator. Before going to bed, pull out one bag, defrost it, place the resulting piece of fish on the affected joint and wrap it with plastic, then pull on thick socks. Lie like this until the morning.
- Activated carbon . A handful of tablets must be ground in a coffee maker, bringing the amount of the mixture to less than half a glass. A small amount of water and one tablespoon of flax seeds are added to the powder. Everything is stirred to a paste-like state. Apply this mixture to the affected skin areas overnight.
- Buy regular lard and cut it so that you can put small pieces of lard on each finger. And now rub each piece into the skin until the pieces become very small.
- Prepare the mixture: melt 250 g of unsalted butter, after it boils, remove all the foam and add 250 g of wine alcohol to the butter. Light the resulting mixture immediately until the alcohol burns out. Apply warm ointment to sore areas.
This home treatment will not get rid of gout, but it will relieve its painful manifestation for some time.
Is it possible to cure joint disease with folk remedies?
Some Internet users share their little secrets of fighting gout on forums. People write about medications and ointments that help or don’t help. As well as treatment with folk remedies.
First of all, these are compresses that reduce inflammation of the affected areas. You can use gout ointment. They contain activated carbon and iodine. Some people prepare compresses from them using chamomile flowers.
They prepare decoctions and tinctures, make baths for sore joints based on iodine, chamomile and other medicinal plants. An infusion of red madder roots and an extract from fir cones are useful. You can use iodized salt compresses.
Thus, gout can and is worth fighting. In tandem with proper nutrition, uric acid salts will be gradually eliminated from the body. As a result, the patient will get rid of attacks of gouty pain. So don't neglect healthy eating. Lead a healthy lifestyle and don’t let anything bother you!
The occurrence of gout: causes
This is what a diseased joint looks like, in which uric acid crystals have accumulated
Gout is a disease associated with metabolic disorders. During this disease, urate (uric acid salts) is deposited in the joints. In most cases, gout develops in men after 40 years of age. Women are exposed to this disease mainly after menopause.
Gout often affects the joints of the fingers, both on the hands and feet. The disease can easily become chronic, so it is important to start treatment on time.
Causes of gouty arthritis
Most often, the disease in question is diagnosed in males aged 40-50 years, but in women, gouty arthritis is rare and only after 60 years. The pathology often occurs in men 25-50 years old - this age “dispersion” is associated with a direct connection between gouty arthritis and male hormones, which can either be actively produced or be in normal quantities. That is why doctors include women during menopause at risk for gouty arthritis. Please note: it is extremely rare that gouty arthritis is diagnosed in childhood - in this case, we will be talking about a genetic predisposition. Modern medicine cannot name specific reasons for the development of the disease in question - the etiology of gouty arthritis is not fully understood. But the factors that can provoke gouty arthritis are known for certain. These include :
- genetic predisposition;
- violation of the diet - we are talking about excessive consumption of meat, sausages, coffee, chocolate. Previously, gouty arthritis was generally called a disease of aristocrats based on the list of foods that should be consumed in limited quantities;
- a long period of taking certain medications for medical reasons or on their own - for example, diuretics, drugs against high blood pressure, cytostatics and others can provoke the development of the disease in question.
Gouty arthritis can also occur as a secondary disease - it is often diagnosed against the background of kidney disease, heart failure, and hormonal imbalances. Please note: the deposition of uric acid crystals can be completely asymptomatic for a long time, but even with a small “push”, gouty arthritis will manifest itself very intensely. Such a “push” can be an infectious disease, stress, severe physical fatigue, forced starvation, and more.
Why does gout occur and how does it manifest?
The causes of gout lie in a stable and elevated level of uric acid in the human blood. As the disease develops, urate crystals are gradually deposited throughout the body, including in the joints. As a result, a process of joint destruction begins, which is called microcrystalline.
The causes of elevated uric acid levels are the inability of the kidneys to cope with the removal of this substance from the body. Gout can be caused by frequent consumption of foods high in purines: fatty fish, meat, alcohol, etc.
Read also: Gout symptoms in women
You now know what causes gout (causes), but what are the first signs of this disease? First of all, an inflammatory process occurs in one of the joints. As a result, the person is subject to an attack of gouty arthritis. In most cases, the disease affects the joints of the big toes, slightly less often - the ankle and knee joints.
Most often, gout makes itself felt early in the morning. The pain is characterized as sudden, pressing and very strong. In some cases, redness and swelling of the affected joint may occur. Such an exacerbation can last up to several days; the patient requires urgent treatment. A repeated attack is dangerous because there is a risk of the disease spreading to nearby joints. This usually ends with partial destruction of the joint.
Gout is characterized by growths (tophi) in the area of the affected joint. The amount of uric acid in the patient’s blood during this period is very high.
One of the most serious complications of the disease is considered to be gouty arthritis with the formation of nodes on the joints susceptible to the disease. In addition, gout can cause urolithiasis. Patients complain of renal colic.
Tophi or gouty nodules (a conglomerate of sodium urate crystals) can form in any part of the human body. When deposits are retained in a joint or periarticular tissue, the body perceives them as a foreign body. As a result, white blood cells accumulate, leading to a serious inflammatory process known as gouty arthritis.
What causes lead to gout?
The only reason for the development of this type of disease, such as gout, is a consistently increased level of uric acid, leading to the formation of salt crystals and their deposition in tissues. The accumulation of uric acid in the blood in the initial stages does not lead to the formation of urates (salt crystals). This condition is called hyperuricemia. Various factors contribute to increased uric acid levels. This is mainly a genetic predisposition, excessive intake of purine compounds or an increase in their catabolism, as well as a slowdown in the process of natural excretion of uric acid through urine.
Gout and uric acid
Uric acid is released against the background of the processing of purine bases that enter the body with food or as a result of the breakdown of cells in its own tissues. Once in the blood, uric acid undergoes a filtration process by the kidneys and is excreted from the body along with urine. If any disturbances occur at any stage of this process, optimal conditions are created for the accumulation of uric acid and the development of hyperuricemia in the patient. The latter is not a 100% symptom of gout, as it may indicate other diseases.
In a disease such as gout, uric acid reacts with sodium, calcium and other chemical elements, forming specific crystalline compounds - urates. Urate deposition can occur both in the soft tissues of the joints and in the organs of the urinary system. The reason that urate is predominantly deposited in the periarticular tissues is the peculiarities of their blood supply. Salt crystals in the tissues near the joints cause the development of gout.
Urate can also be deposited in the kidneys as stones, formed from smaller crystals that accumulate in the renal pelvis and, in some cases, end up in the bladder. This happens when the disease is neglected, there is no treatment and there is no diet.
Enhanced synthesis of purine nucleotides
Since uric acid is a breakdown product of purine bases, the rate of synthesis plays an important role in determining the volume of its production. Purine bases enter the body not only with food during gout, but also enter the blood after the death of cells of its own tissues. If, against the background of any pathological processes in the body, a large number of cells die, an excess of purine nucleotides occurs, an increase in the level of uric acid and, accordingly, all the conditions are created for the development of gout. This phenomenon can be temporary or quite long-lasting due to severe chronic diseases.
Increased synthesis of nucleic acid bases can be caused by long-term use of cytostatics, treatment with radiotherapy and chemotherapy, hemolysis and various types of surgical interventions.
Delayed excretion of uric acid
Uric acid is excreted from the body along with urine, first undergoing processing in the kidneys. If a person suffers from chronic kidney disease, the removal of the main breakdown product of purine bases is impaired, and the level of uric acid in the blood increases. This occurs against the background of partial closure of the lumen of the tubules in the filtering organ, which occurs due to inflammatory edema or proliferation of connective tissue. If gout develops, the disease is considered secondary.
Excess of purine nucleotides entering the body
Since purines are the so-called “raw materials” for the production of uric acid, the more there are, the more toxins are contained in the blood plasma. That is why the main measure for the prevention and treatment of the disease is to reduce the amount of foods high in purine nucleotides in the diet. Although it is worth noting that eating them does not cause the development of the disease. This is just a factor that creates an ideal aid for increasing the level of uric acid in the blood, its penetration into the soft tissues and the formation of hard salt crystals called urates.
Hereditary predisposition
A group of certain enzymes is responsible for processing purines. Enzymes are proteins whose structure is determined by the human genome. If a person is diagnosed with a genetic disease such as fermentopathy, then certain types of enzymes are produced in insufficient quantities. Thus, with a lack of protein substances responsible for processing purine bases and excreting uric acid, the latter accumulates in the blood plasma and subsequently leads to the development of gout.
Often, a deficiency of enzymes involved in the processing of purine nucleotides is part of the disorders caused by genetic metabolic syndrome. In addition to creating ideal conditions for the development of gout, this syndrome causes a tendency to gain excess weight, develop diabetes, hypertension or hyperlipidemia.
Uric acid as a main factor in the development of the disease
The most vulnerable are the joints of the big toes. The onset of gout most often manifests itself within a year. Treatment can relieve the exacerbation, the disease is stopped, but it will not be possible to forget about it forever. As a rule, the interval between attacks gradually decreases.
Gout contributes to serious metabolic disorders. Purines enter the body with food, and the body is also able to produce them independently. When purines are broken down, uric acid is formed. As you know, it is excreted by the kidneys. When the acid level increases, salt deposits occur in tissues with poor blood supply, since the crystals are better anchored in these places. This primarily concerns cartilage, tendons and joints.
People who are susceptible to developing gout are:
- overweight;
- with a hereditary predisposition to this disease;
- leading a sedentary lifestyle;
- those who prefer to wear tight or uncomfortable shoes;
- eating unhealthy, fatty foods.
Prevention and treatment of gout
As practice shows, in most cases treatment does not give immediate results; an attack of gout goes away after some time. Before this happens, the patient is tormented by severe pressing pain. First of all, treatment requires strict adherence to bed rest. It is recommended to place a hard pillow under your feet with affected joints.
To dull unbearable pain, apply ice over the affected joints. After the pain has subsided, you can rub dimexide or Vishnevsky ointment into the sore spot. In addition, treatment and prevention of gout require careful nutritional monitoring. Include vegetable broths and not too thick porridges in your diet. It is recommended to consume about 3 liters of fluid per day. Alkaline-containing products are good for this:
- jelly;
- oat broth;
- milk;
- lemon juice added to plain water;
- mineral water.
Taking painkillers has virtually no effect. A certain effect in the treatment of gout can be achieved with the help of anti-inflammatory drugs that do not contain steroids. Prevention of the disease is carried out with the help of drugs prescribed by the patient’s attending physician.
Prevention of gout is necessary in order to prevent exacerbation and prevent recurrence of the disease. Very often the disease affects previously injured joints. This suggests that any injury received requires some kind of treatment. Make it a rule to wear only comfortable shoes. Tight shoes can seriously damage the big toe joint. To prevent gout from causing complications and exacerbations, do not forget to carefully follow your diet.
Prohibited foods for the patient
Try to minimize your consumption of foods containing proteins, including:
With the help of this diet, the patient’s body weight is normalized, which will reduce the load on the affected joints. Try to consume as little coffee, cocoa and tea as possible.
Special gymnastics will help to avoid exacerbation of the disease. In this case, special attention should be paid to the affected joints. Take walks more often.
Prevention of gout
Prevention of gout is especially important for people predisposed to developing this disease. The main preventive measure is to follow a certain menu for hyperuricemia and gout. In addition, it is necessary to carefully monitor your health and prevent the emergence of risk factors for the development of the disease. Thus, the likelihood of a violation of purine metabolism increases significantly with rapid loss of body weight, taking cytostatics and diuretics, drinking alcohol, dehydration, excessive physical exertion, various types of injuries, stress, acute infections, etc. If the diagnosis has already been made, adherence to a certain diet and careful attitude towards your health will help to significantly prolong the period of remission and avoid the development of complications.