Modern diets have long ceased to pursue rapid weight loss. Now the diet helps us fight poor health and bad mood. Including the one that, according to the laws of nature, appears in girls once a month - yes, yes, we are talking about PMS. The founders of the Woman Code brand of nutritional bars spoke about the magical processes of the female body in an accessible language and explained that it is better to eat at different phases of the cycle in order to remain energetic and positive.
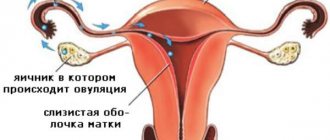
Menstrual cycle in women
The phases of the female cycle are a complex process that is sometimes disrupted. Very often the reason for this is hormones. They are the ones who ensure conception and further birth of the baby. Violation of the amount of hormones leads to disruption of the menstrual cycle. Doctors identify several main reasons:
- Long-term depression or stress;
- Taking strong medications or COCs - oral contraceptives with hormones;
- Bad ecology;
- Excessive physical activity;
- Puberty of girls or menopause;
- Bad habits;
- Gynecological diseases;
- Injury or surgery on the reproductive organs.
All women are individual, so any provoking factors can affect the cycle. Some women have periods that are too long, while other women suffer from PMS. In order for all phases to proceed harmoniously, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle and monitor your intimate health.
The phases of the cycle in women are a regular and unchanging phenomenon. They successively replace each other, but the duration is always individual. Knowing all the nuances of your body, you can accurately calculate favorable days for conception and predict the onset of PMS. For convenience, a special diary is kept, then any violations will be noticeable immediately.
Low progesterone in the luteal phase may be due to the following reasons:
- malfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary system due to psycho-emotional shock, traumatic brain injury or infectious diseases with brain damage;
- adrenal gland diseases;
- diseases of the ovaries and fallopian tubes;
- hyperprolactinemia;
- diseases of the thyroid gland, which are accompanied by hyper- or hypofunction of the organ.
Progesterone deficiency in the luteal phase can only manifest itself as a failure of the monthly cycle, that is, the woman will not have any external signs of hormonal failure.
Before you begin treatment for progesterone deficiency, you need to determine the causes of its occurrence.
Treatment of progesterone deficiency in a woman’s body is carried out using hormone replacement therapy (luteal phase support), which stimulates the onset of ovulation. The drugs of choice in this case may be Utrozhestan, Ingesta, Endometrin, Luteina and others.
Treatment will be more effective if it is combined with physiotherapeutic methods (intravaginal phonophoresis), acupuncture and spa treatment.
A timely visit to a specialist and strict adherence to his treatment recommendations will help a woman successfully become pregnant and find the happiness of motherhood.
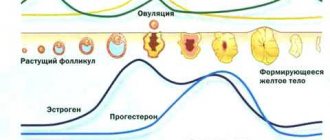
The female body is adapted for conception, gestation and birth of offspring. In this it is helped by certain hormones responsible for regulating reproductive function. The menstrual cycle consists of three phases:
- follicular;
- ovulatory;
- luteal
Menstruation itself (bloody discharge) indicates that conception has not occurred (the egg has not been fertilized). The luteal phase in the cycle falls exactly in the middle, which is why it is called the equator.
After the bleeding is completed, a new cycle begins - the formation and growth of follicles. The hormone estrogen is responsible for this process. The inner layer of the uterus (endometrium) gradually thickens. This phase lasts until the egg ruptures, which then travels into the fallopian tubes and uterine cavity.
The luteal phase begins immediately after ovulation. At this stage, the corpus luteum matures. The yellow color is characteristic of lutein, which contains the walls of the follicles.
These hormones control muscle contractions of the uterus, which can cause miscarriage or premature birth. In addition to control, hormones promote the production of milk in the mammary glands to feed the baby.
The corpus luteum regulates the production of hormones. If the egg is not fertilized, much less hormones are produced. The body receives a signal to complete the phase and transition to menstruation itself - the rejection of the endometrium and mucus from the inner walls of the uterus. An unfertilized fertilized egg is released along with mucus and blood.
Since the luteal phase always replaces ovulation, it is not difficult to find out about its beginning. If a woman keeps a diary of her menstruation and knows exactly the duration of her cycle, then the luteal phase falls in the second third. You need to divide the number of days in your cycle by 3 to get the date the corpus luteum begins to form.
How long does the luteal phase last? With a correct menstrual cycle without deviations, this phase lasts 2 weeks, that is, 14 days before bleeding begins. The days of formation of the corpus luteum with stable menstruation fall on the 14th, 15th and 16th of the individual cycle. However, the duration of the phase may increase if:
- fertilization of the egg;
- malfunction of the reproductive system.
Are there physiological signs of the beginning of the formation of the corpus luteum? The luteal phase can be calculated by the increase in progesterone production, which is detected in blood tests. During the formation of the corpus luteum, the rectal temperature increases by 4-5 degrees, that is, it becomes slightly elevated - up to 37C.
Also, the formation of the corpus luteum can be determined by vaginal discharge: it becomes somewhat more abundant than usual. This occurs due to the activity of the body's secretory function. In some women, the beginning of the formation of the corpus luteum is accompanied by swelling and enlargement of the breasts. Sometimes swelling of the glands is accompanied by mild pain when touched. In the case of pathological abnormalities in the reproductive system, pain in the mammary glands can be severe.
The female cycle is divided into two main parts: the follicular phase and the luteal period. Some doctors may divide the cycle into four parts: menstruation, time before ovulation, the ovulatory period, and the luteal phase.
The female cycle lasts on average 28 days, but a slight shift in one direction or another is not a deviation and does not require medical correction. In the first half of this period, the follicular phase of the cycle lasts. After this, the time comes for the egg to leave the ovary, and the second part of the cycle begins.
It is worth noting that the follicular phase can last from one week to 20 days. This is an individual feature of the female body.
Medicine knows that transformation in the follicles and their preparation for new growth begins two days before the onset of the next period. Despite this, this time cannot be included in the follicular phase. This period is still the luteal period.
The follicular phase of the cycle begins with the arrival of the next menstruation. Many doctors distinguish this time separately, calling it the menstrual period. However, this does not contradict the fact that the days when menstruation occurs are included in the phase under consideration.
On what day of the cycle does the luteal phase begin?
The entire period after the end of menstrual bleeding is divided into 3 periods. The first is the follicular phase, during which the formation and maturation of the follicle with the egg occurs under the influence of the hormone estrogen.
Then ovulation occurs - this is the next period, which lasts no more than 2 days. Characterized by favorable conditions for conception.
The last period of the menstrual cycle is the luteal phase. It occurs after ovulation and provides the necessary conditions for the development of the embryo in the event of conception, as it promotes the accumulation of nutrients in the muscles.
The luteal phase always begins in the middle of the cycle. If the cycle lasts 28 days, then this phase occurs on the 15-16th day, if 30 days - on the 16-17th day. Sometimes it is difficult to calculate the first day of the luteal phase, since its onset also depends on the duration of menstruation.
Pathologies
Due to insufficiency of the luteal phase, the chance of successful conception is reduced, even to the point of infertility. Lack of complete ovulation is a widespread pathology among women. This is facilitated by:
- chronic stress;
- physical damage to the pituitary gland due to TBI;
- hyperandrogenism of the adrenal glands and ovaries;
- excess prolactin in the blood;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- inflammatory processes in the internal genital organs.
Phase failure is caused by external factors, which can be avoided if desired. This is not a congenital, but an acquired pathology. Women often underestimate the impact of stressful circumstances on reproductive function, succumbing to the temptation to prove that they are right or defend their own point of view at any cost. The nervous system directly influences hormonal function. Therefore, with chronic stress, hormones stop being produced.
Hormonal therapy can restore a disrupted monthly cycle, but not without side effects. A regimen for taking hormonal medications is drawn up by a gynecologist after a comprehensive examination of the patient. It is strictly prohibited to arbitrarily stop or otherwise change the medication regimen. A side effect may be hormone dependence or uncontrolled weight gain. Also, hormonal therapy is sometimes accompanied by pathology of the nervous system - breakdowns, depression, neurosis.
Luteal phase deficiency is often caused by abortion. Forced termination of pregnancy disrupts the harmony in the functioning of the reproductive system, namely the production of the hormone progesterone by the corpus luteum.
This pathology occurs due to insufficient amounts of the hormone progesterone in the blood. The corpus luteum produces the hormone, but its concentration is not enough for the successful development of the egg. Fertilization has taken place, but the woman cannot carry the fetus to term: a miscarriage occurs in the early stages of pregnancy.
For early miscarriages, a comprehensive diagnosis is necessary to identify the cause of fetal rejection. In most cases, this occurs precisely because of insufficient production of the hormone progesterone.
Diagnostics is carried out using the following methods:
- blood test for progesterone;
- biopsy to diagnose the endometrium;
- rectal measurement of body temperature immediately after waking up;
- clarification of the onset of ovulation (according to the menstrual calendar);
- Ultrasound of the uterus during the release of the egg into the cavity;
- diagnosis of discharge during the ovulation period;
- examination of the cervix in a gynecological chair.
A blood test will help to accurately determine the amount of hormones produced: enough or not enough. Sometimes it is necessary to conduct an examination of endometrial tissue (do a biopsy) to clarify the health of the reproductive system. Temperature measurement is required only to clarify the diagnosis. The basal temperature during ovulation slightly exceeds 37C.
A period diary is a valuable assistant in determining the exact timing of ovulation; it is advisable to keep it constantly. If it is possible to determine the exact date of ovulation, the woman undergoes an ultrasound at this time. The nature of vaginal discharge, the production of which becomes more intense these days, will also help clarify the diagnostic picture. The discharge of a healthy woman resembles transparent egg white and should be elastic.
The condition of the cervix is determined by examination in a gynecological chair. If the tissues are characterized by looseness and softness, we are talking about a pathological condition of the reproductive system.
Before making a diagnosis, you should prepare your body well:
- stop taking antibiotics several days before blood sampling;
- exclude alcohol and tobacco;
- give up spicy, salty, smoked and pickled foods a couple of weeks before the examination;
- exclude fried and overly peppered foods from the diet;
- In a couple of days, you should exclude intimate contacts with your partner.
Like all tests, blood sampling for hormones is carried out on an empty stomach and without drinking liquid.
When testing for hormones, it is important to exclude stressful circumstances a few days before taking blood. You need to completely calm your psyche in any way possible. This could be a walk in the forest or in the park, a fishing trip or a mushroom picking trip. Meditation and listening to audio recordings of the sounds of nature help to calm down.
This condition is also considered pathological, along with the short phase, if it is not a consequence of successful conception. An increased time of this phase may also indicate the formation of a corpus luteum cyst. In adulthood, a long luteal phase indicates the onset of menopause. Which shows the direct dependence of luteinizing hormone on the woman’s age and the general health of the body.
With age, the concentration of luteinizing hormone increases, thereby reducing the production of estradiol. When the level of luteinizing hormones becomes absolute, menopause occurs. An excess of the hormone is explained by the body’s lack of request for its use.
Norm of progesterone in the luteal phase
Progesterone levels change throughout the menstrual cycle. During the luteal phase, it ranges from 7 to 56 pmol/l. After ovulation, the level of progesterone is minimal, then its concentration constantly increases, but by the beginning of menstruation it decreases if conception has not occurred.
A decrease or increase in the concentration of progesterone in the luteal phase may indicate disturbances in the woman’s hormonal system. The level of the hormone can be determined exclusively in the laboratory - by performing a blood test. It is important to properly prepare for donating blood in order to get the most accurate values.
Before analysis, it is necessary to exclude fatty and fried foods from the diet. Alcohol and coffee are not recommended. Nervous shock or physical stress can also affect test results.
In addition, it is important to correctly calculate the phase period. To do this, it is advisable to mark the menstrual cycle on a calendar for several months.
Follicle stimulating hormone
Phase 1 lasts on average two weeks. The first 3-7 days of the follicular phase are accompanied by the release of bloody secretion. On the seventh day of the cycle, menstruation stops, after which the endometrium is actively renewed. Simultaneously with the proliferation stage, the follicle and egg cell mature. During this period, estrogens and follicle-stimulating hormones are actively produced.
After a week, one follicle overtakes the others, which is why they stop growing and developing. The leader vesicle grows the egg cell until it reaches 20-25 millimeters. After the end of the follicular phase of the cycle, the entire reproductive system prepares for possible fertilization. At the end of the proliferative phase, ovulation occurs.
At the same time, the level of estrogen increases significantly, which serves as a signal for the production of another hormone - luteinizing hormone. It is what prepares the body for ovulation. A high concentration of estrogen helps the endometrium to be saturated with useful substances and blood, so that during pregnancy the uterus can normally contain the egg, promoting its growth and development. At this point, the first phase of the cycle ends and the second menstrual phase begins. It is the shortest, as it lasts only 24-35 hours.
Having understood what the follicular phase is and which days of the cycle it affects, we can begin to consider the ovulatory phase.
The level of progesterone in the blood of women varies not only throughout life, but also throughout the month, depending on the phase of the cycle. The normal level of this hormone ranges from 6 to 56 pmol/l. During the corpus luteum phase, progesterone levels peak.
If the level of progesterone is low during the luteal phase, then most likely this means that some kind of malfunction has occurred in the body.
The level of progesterone in the blood is determined using a blood test, and the blood must be taken during the expected luteal phase, that is, in the second half of the cycle.
To exclude an erroneous result of a blood test for sex hormones, it is necessary to properly prepare for the test, namely:
- several months before the test, you need to count the duration of the menstrual cycle in order to find out the date of ovulation and choose the optimal day for blood sampling;
- 24 hours before blood sampling, you need to remove foods that contain a lot of fat, fried and spicy foods, coffee and alcoholic drinks from your diet.
- the day before the analysis, you should limit physical activity and protect yourself from nervous shock;
- the analysis is carried out strictly on an empty stomach, so the last meal should be no later than eight hours before blood sampling;
- If you are taking any medications, you should inform the doctor who referred you for this study, since oral contraceptives and other medications can affect progesterone levels.
The consequences of low progesterone in the luteal phase can be infertility, spontaneous miscarriages, premature birth and other pathological conditions.
Based on the results of a blood test, a gynecologist may consider carrying out hormone replacement therapy.
When progesterone is elevated in the luteal phase, drugs are used that restore the balance of sex hormones in a woman’s body.
If a pregnant woman has a low level of progesterone in the blood, then progestins are also prescribed, since a deficiency of this hormone can lead to miscarriage or premature birth.
Also, when testing blood for hormonal sex panel, the level of estradiol in the blood is necessarily determined. The norm for this indicator in the corpus luteum phase is considered to be 91-861 pmol/l.
Elevated estradiol in the luteal phase is also a sign of hormonal imbalance in the body or some disease.
Quite often, representatives of the fair sex have to donate blood to study hormonal levels. The amount of the substance obtained depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle.
The follicular phase is usually selected for the delivery of the following hormones:
- follicle-stimulating;
- anti-Mullerian hormone;
- luteinizing;
- prolactin;
- estradiol;
- progesterone;
- androgens;
- thyroid hormones.
What values of these test substances are normal?
One of the most frequently prescribed tests is the study of this substance. Follicle stimulating hormone is responsible for the growth and development of follicles before ovulation. It is from them that the egg will subsequently be released, ready for fertilization by a male sperm.
If the follicular phase is selected, FSH should have the following values: from 3 to 11 mU/ml. The analysis is carried out mainly on the 5th day of the cycle. It is worth noting that in order to obtain a reliable result, you should not consume food or drinks containing caffeine before taking the material. Otherwise, you may get an overestimated or, conversely, low result.
A deviation from normal values in one direction or another can be due to the following reasons: the presence of tumors on the gonads, improper functioning of the pituitary gland. Also, the amount of the substance has different values during pregnancy.
In most cases, together with follicle-stimulating hormone, a luteinization test is prescribed. It reaches its peak several hours before the release of the egg from the ovary. It is under the influence of this substance that the follicle ruptures and, as a result, a mature female cell emerges from it.
The follicular phase must be selected for the study. Your doctor will tell you which day of the cycle is preferable to choose. Quite often, FSH and LH are tested at the same time.
Normal values of this substance in a woman’s blood range from 2 to 14 mU/ml. The material should be taken strictly on an empty stomach. Before donating blood, you should not be nervous and expose your body to stress. Try to get a good night's sleep, rest and be in a positive mood.
A decrease or increase in the hormone can occur with various neoplasms on the ovaries. Also, when the functions of the pituitary gland are impaired, deviations from normal values are observed. When the level of eggs in the ovaries decreases, the level of the hormone can greatly increase. This occurs in combination with a decrease in follicle-stimulating hormone.
To analyze for these substances, both the follicular phase and the period after ovulation can be selected. What are the normal values of these hormones for a woman?
Thyroxine should be in the range from 64 to 150 nmol/l.
Triiodothyronine has normal values in the range from 1.2 to 2.8 nmol/l.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone has values from 1 to 4 mU/ml.
With various deviations in the amount of these substances, we can talk about improper functioning of the thyroid gland. This may also be due to improper functioning of the pituitary gland.
The amount of LH in a woman’s blood fluctuates over time depending on the phase of the cycle and time of day - at night its concentration is slightly higher. The release of LH occurs unevenly, as does FSH.
Table 1. LH in the blood of women is normal
| Cycle phase | Period | Contents of FSH |
| Follicular | from the 1st day of menstruation until the end of bleeding | 4 – 12.5 mIU/ml |
| from 5 – 6 days before ovulation | 2.4 – 12.5 mIU/ml | |
| Ovulatory | from 13 to 16 days (ovulation) | 14 – 96 mIU/ml |
| Luteal | from 16 to 28 days | 1 – 11 mIU/ml |
The amount of LH production and the follicular phase of the cycle are directly related. From the moment the cycle begins, FSH promotes the growth of the follicle, the division of its membrane cells and their proliferation. The membrane begins to produce large quantities of estrogens, which accumulate throughout the first phase.
When the amount of estrogen reaches its maximum, they are released into the blood and reach the pituitary gland receptors. At this moment, a large amount of luteinizing hormone is released into the blood. The concentration of LH at the end of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle reaches its highest level, 10 times higher than normal.
After reaching the LH peak within 10–20 hours, ovulation occurs. The hormone stimulates the work of the ovaries, together with follicle-stimulating hormone it promotes the beginning of follicle growth.
The amount of LH in the blood can fluctuate over a significant range, and for a better diagnosis, an analysis of the FSH content should be performed. These hormones are closely interrelated, and their ratio indicates the state of the reproductive and endocrine system as a whole.
Normally, the ratio of LH and FSH in any phase should be 1.5 - 2 to 1, respectively. If, despite fluctuations in absolute values in any direction, this ratio is generally maintained, then serious problems, as a rule, are not identified. An alarming signal is its shift by more than 2.5 - 3 times, that is, when the amount of one of the hormones significantly exceeds the amount of the other.
The reason for the increased levels of LH and FSH are usually external unfavorable factors:
- Stress, nervous tension, obsessive states, in which the production of adrenaline and cortisol increases;
- Taking incorrectly selected contraceptives;
- Use of steroid drugs or passion for sports nutrition;
- Harmful effects of R-radiation: radiography, MRI;
- Smoking and alcohol abuse.
Elevated LH levels with normal FSH levels indicate that serious systemic endocrine changes are occurring in the body. Since pregnancy is impossible in principle without a normal amount of LH, it is the excess of this hormone that is a common cause of hormonal infertility.
When this hormone is produced, ovarian receptors sense signals that it is time to start producing estrogens. There is a direct relationship between them and LH: in the follicular phase, the higher the LH, the higher the estrogen, and, conversely, with an increase in estrogen levels, LH also increases. As a result, it is this relationship that leads to the peak of luteinizing hormone and the onset of ovulation.
If the functions of the ovaries are impaired and there is no increase in the amount of estrogen in response to the production of LH, then ovulation and pregnancy are impossible, the egg does not mature to the end, and the corpus luteum is not formed. As a result, the normal course of the cycle is disrupted, and the remaining egg inside the ovary turns into a cyst. With systemic endocrine diseases such as polycystic disease, the functions of the ovaries are impaired and the follicles simply do not mature, remaining inside.
What happens during the luteal phase?
When the egg matures, the follicle bursts. Ovulation begins. It lasts 1-2 days. Then comes the luteal phase. At this time, the synthesis of the corpus luteum hormone, progesterone, begins. The hormone creates favorable conditions for the development of pregnancy.
If conception has occurred, the corpus luteum hormone will provide support for pregnancy until the placenta is formed. From this moment on, the placenta itself will begin to produce progesterone. If conception does not occur, menstruation begins at the end of the luteal phase.
Progesterone and estradiol
This hormone controls the development of the follicle and the growth of the endometrium, which is needed to secure the fertilized egg in the event of pregnancy. Estradiol is produced by women's ovaries. It can also be produced by the adrenal glands.
The follicular phase is also selected for its study. What day of the cycle should be chosen for donating the hormone?
Estradiol can be tested both at the very beginning of the female cycle and in the middle of the follicular phase. It is worth noting that, if necessary, the doctor can prescribe a test for this hormone after ovulation, but in this case the amount of the substance will be significantly reduced. What is the norm of estradiol? Standard values can range from 110 to 330 pmol/L.
If there is a significant deviation from them, we are talking about disruption of the functioning of some female organs. For example, with polycystic ovary syndrome, during diseases of the thyroid gland or liver. During pregnancy or when taking hormonal medications, estradiol levels may differ significantly from normal.
Typically, the study of this substance in a woman’s body is carried out in the second half of the cycle, a few days after ovulation. However, in some cases, the follicular phase may be selected for analysis. What are the normal values?
The amount of progesterone in a woman’s blood during this period should be in the range from 0.32 to 2.23 nmol/l.
If progesterone is increased in the follicular phase, this may indicate the presence of cysts or various tumors on the ovary. It is also possible for the adrenal glands to malfunction. An irregular menstrual cycle may be a consequence of high levels of this substance in the first phase.
A decrease in progesterone levels can only mean something if the material was collected after ovulation.
Progesterone in women can increase for several reasons, including:
- pregnancy;
- failure of the monthly cycle;
- corpus luteum cystosis;
- adrenal gland diseases;
- kidney dysfunction;
- stimulation of ovulation by progestins.
Women who have elevated progesterone may experience the following symptoms:
- hypersensitivity of the mammary glands;
- lability of the nervous system, which is manifested by tearfulness, nervousness and sudden changes in mood;
- bleeding from the vagina;
- headache;
- complete absence or decrease in sexual desire;
- flatulence.
17-OH progesterone is an adrenal hormone that controls sexual and reproductive functions. In the female body, the amount of this hormone is much lower than in the male body. Therefore, any changes in its level should not be ignored and require consultation with specialists - an endocrinologist and a gynecologist.
In the follicular phase of the cycle, the synthesis of 17-OH progesterone is at a minimum level, but increases towards the onset of ovulation and remains at this level until the arrival of menstruation.
If 17 OH progesterone is elevated in a woman, this means that pathological changes are occurring in the adrenal glands or ovaries, for example, a benign or malignant tumor has formed.
As a result, we can conclude that the corpus luteum phase is one of the most important periods of the monthly cycle, and changes in progesterone levels in this phase may indicate female infertility.
The hormone progesterone regulates reproductive processes in a woman’s body. In tandem with estradiol, it controls the production of insulin, the disruption of which is provoked by excess glucose. Insulin is produced by the body after eating; the pancreas takes part in this process. If the pancreas produces excess progesterone, the patient's body cannot control blood glucose levels. Since the body's perception of glucose levels is impaired, progesterone encourages a woman to consume sweets.
Excessive consumption of sweets inevitably affects weight gain, which is often observed in diabetes mellitus. Along with excess weight, other pathologies appear:
- high blood pressure;
- increase in cholesterol concentration.
The listed pathologies can lead to cardiovascular diseases or the formation of blood clots. Excess weight is often an indirect sign of increased progesterone concentrations.
Impaired production of estradiol provokes the pathology of insufficiency of the luteal phase of the monthly cycle. Estradiol helps the body react sensitively to blood glucose levels and correct them in a timely manner. It is estradiol that reduces the need for sweets when glucose levels are high, stabilizing body weight.
Lf deficiency is often observed in premenopause. The number of ovulations gradually decreases. Hormone replacement therapy will help improve the functionality of the reproductive system and resume ovulation.
Increased progesterone in the luteal phase
The following signs may indicate increased levels of progesterone in the luteal phase:
- acne;
- memory problems;
- swelling of tissues;
- increased anxiety;
- difficulty concentrating;
- bloody spotting;
- frequent headaches;
- anxiety, depression.
Important! Hormone levels may increase during pregnancy. In other cases, exceeding the norm indicates the development of pathology of the urinary or reproductive system (renal failure and other kidney diseases, neoplasms, etc.), so patients are prescribed additional studies to determine the cause.
Insufficiency of the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle: causes, symptoms and treatment
There are no clearly defined symptoms of pathology. You should contact a gynecologist for diagnosis in the following conditions:
- irregularity of the monthly cycle;
- ovulation or vaginal discharge is accompanied by pain;
- spotting and spotting appears before menstruation;
- habitual miscarriage in the early stages;
- inability to get pregnant if you have regular sex life.
Hardware diagnostics (ultrasound) will help to identify the dynamics of follicle development and blood flow in the ovaries, determine the thickness of the endometrium, and see defects in the structure of the corpus luteum or the pathology of its blood supply.
An indirect symptom of problems can be a decrease in desire for a partner, premature (delayed) sexual development, unscheduled uterine bleeding, and the appearance of body hair. Sometimes an excess of luteinizing hormone can appear with unexpected hair growth concentrated in the facial area.
Treatment and prevention
It is not possible to independently identify violations. Visually, you can only notice a violation of the cycle, but it is possible to determine the real picture of what is happening using a complex of laboratory and instrumental examination methods.
The main emphasis is on eliminating the root cause of pathological disorders and the use of hormonal therapy to stimulate ovulatory function. For additional therapy, physiotherapeutic treatment (using intravaginal phonophoresis), acupuncture and sanatorium treatment (hydrogen sulfide baths, mud of the Black and Mediterranean Seas) are used.
Only careful attitude towards your health, adherence to hygiene rules and daily routine, timely treatment of systemic diseases, absence of stress in combination with modern infertility treatment techniques will help prevent dysfunction of the reproductive system.
Read
Also:
- Calculate body mass index for women
- Everything about the menstrual cycle: normal duration and phases
- Normal endometrial thickness by cycle day
- Follicles in the ovaries: normal and abnormalities
Therapy
What drugs, other than hormonal ones, can cure the pathology? If the cause of the deviations is immune deficiency or genetic prerequisites, non-hormonal drugs duphaston and others are used. If there is an excess of progesterone, only hormonal therapy is indicated. Hormones are also used in the case of hyperandrogenism and hyperprolactinemia.
You can get rid of hormonal deficiency by using contraceptives in tablet form. Oral contraceptives help regulate the production of hormones and establish their balance in the body.
In the absence of ovulation, medications are prescribed to stimulate the ovaries. For endometrial pathology, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and immunomodulators are prescribed. To improve the immune status, the gynecologist prescribes vitamin complexes, acupuncture and physiotherapy.
If the pathology was caused by a nervous breakdown or an acute mental reaction to stress, patients are prescribed sedatives. If the medications do not work enough, a consultation with a psychologist or psychotherapist is necessary.
Menstrual period
The process of preparing the body for the beginning of fertilization of an egg in girls begins at different ages. The menstrual cycle phase consists of several parts:
- Directly menstruation.
- Follicular cycle.
- Ovulation.
- Luteal phase (LP).
For all women, the length of the cycle consists of a different number of days. But on average this happens in 21-23 days. First of all, it depends on hormonal levels, strength loads, and the general condition of the body.
The most painful phase 1 is associated with bleeding , which may or may not be heavy. After bleeding stops, the follicular cycle begins, during which hormone synthesis occurs. During this period, the ovaries produce estrogen, which leads to renewal of the upper layer of the uterus.
After about two weeks, a round or pear-shaped body is formed - a follicle, in which the egg is formed. During ovulation, the follicle breaks down and releases the egg, which begins to move towards the uterus. The egg lives only two days, all this time it waits for fertilization.
The period between ovulation and menstrual bleeding is called the luteal phase. What it is, what its function and task are, married couples planning the birth of a child should know this.
Prevention
Any irregularities in the menstrual cycle should raise reproductive health concerns. One of the common disorders is irregular menstruation. To detect it, you should keep a diary in which the dates of the beginning and end of menstruation are noted. Only a diary with regular entries will help identify deviations in the cyclicity of menstruation.
Even in the absence of visible problems and the regularity of the cycle, it is necessary to visit the gynecologist twice a year for a preventive examination. Any inflammatory processes or asymptomatic diseases of the internal female organs can become an impetus for the development of luteal phase pathology and cause infertility.
For your reproductive system to function well, you need to exercise and eat right.
In addition to moderate physical activity and good nutrition, it is necessary to monitor your mental balance. It is necessary to completely eliminate stressful events or limit them as much as possible. Reconsider the circle of your acquaintances, with whom you communicate, stop overreacting to the criticism of others. Meditation and listening to audio recordings of the sounds of nature will help balance the psyche and relieve nervous and physical tension. It relaxes the muscles of the body, clears thoughts of negative memories and calms the soul.
You can control the production of hormones by drinking freshly squeezed juices from pomegranates, citrus fruits, and apples. Flaxseed, berry tinctures and teas, and herbal preparations are useful for a woman’s hormonal background. Among the herbs are red brush and hogweed, as well as a collection of hop cones, linden blossom and mint leaves.
What does the duration depend on?
In medical practice, there are two pathologies regarding the duration of the luteal phase. In the first case, its duration is too short. This may be due to insufficiency of the corpus luteum or hormonal abnormalities. Conception in this case is impossible. Menstruation occurs earlier, before the embryo has time to attach to the uterine cavity.
An increase in the length of the luteal phase of the cycle can be caused by two reasons. These include pregnancy and the appearance of cystic formations .
There are different types of cysts: some resolve as menstruation approaches, while others can increase in size. If the cystic formation affects reproductive function, a decision is made about surgical intervention . Signs of a cyst include the following:
- Delay of menstruation.
- Painful sensations in the lower abdomen.
- Presence of spotting.
- Increased body temperature.
- Pain during intercourse.
IMPORTANT! Treatment of a cyst requires the help of a competent specialist. Most often, women are prescribed hormonal medications.
Prolactin
This hormone is responsible for normal milk production during breastfeeding. At this time, its level is quite high and this is normal. If a woman is not breastfeeding, then prolactin levels should be in the range from 130 to 540 mU/ml.
Deviations from the norm may indicate that the pituitary gland is not working properly. The functioning of the adrenal glands may also be impaired. Before taking the test, you should not engage in physical activity or eat food. It is advisable to have a good rest and be in a pleasant mood. Only in this case you will get the most reliable result.
The main task of the luteal phase and corpus luteum
The luteal phase is also called the corpus luteum phase . This name comes from the fact that the follicle emerging from the egg acquires a yellow tint and the so-called “corpus luteum” begins to form.
The corpus luteum is a gland that produces progesterone and estrogen.
If pregnancy does not occur , the level of hormones decreases, the corpus luteum is destroyed and the uterine epithelium is rejected. After this, women begin their next menstruation.
If pregnancy occurs , the fertilized egg turns into a blastocyst and an embryo begins to develop from it. It is enveloped by the placenta, which is formed from the uterine epithelium and serves as a source of nutrition for the developing fetus.
Identifying the luteal phase is very important for every woman who wants to get pregnant and give birth to healthy offspring.
Duration of the luteal period
Many women and girls are interested in the question of how to determine the luteal phase. Its duration is individual for each woman. On average it ranges from 12 to 14 days. When it starts depends on the length of the menstrual cycle. With a short cycle of 28 days, the period begins on average from the thirteenth day, and with a longer cycle of 31 days it is expected from the 18th day.
The length of the luteal phase is closely related to ovulation. At this time, until the next menstrual cycle, body temperature increases. Women who control their period using the temperature method notice an increase in temperature by 0.3-0.5 degrees. Ovulation tests will also help determine the onset of the phase.
Temperature method
With this method, the base (or basal) body temperature is determined. Measure your temperature at the same time in the morning, at least after six hours of sleep. It usually rises before ovulation. There are basic WHO standards for this method:
- if ovulation occurs, the temperature will increase within 48 hours;
- within three consecutive days there should be an increase of 0.2 degrees from the previous 6 days;
- If the temperature level remains the same throughout the cycle, it is unlikely that ovulation has occurred.
In a healthy body in the luteinizing phase, elevated temperature takes 13-14 days of the cycle. Before the start of menstruation it falls again.
The length of the LF contains information about the level of progesterone. If its duration is less than 10 days, then the body cannot produce enough of the hormone.
Progesterone deficiency has several causes:
- hormonal disorders;
- thyroid diseases;
- overweight;
- anorexia;
- increased physical activity;
- age;
- stress.
You can test progesterone levels in the middle of LF, when its concentration in the blood is highest. This happens during the phase of creation of the corpus luteum.
Short secretory cycle
The importance of the luteal period in the menstrual cycle is very large. It is important that all processes take place in a strictly defined sequence. A reduction or increase in the time interval of one of the phases indicates problems with childbirth.
Disturbances in the corpus luteum mean low production of progesterone, and therefore determine a short period of LF. Completion of the luteal phase ahead of time affects the process of epithelium formation. In this case, the placenta will not be able to mature, even if the fertilized egg has been attached to the uterus. This leads to miscarriage or infertility.
Main signs of a problem situation:
- prolonged bleeding during menstruation and cycle disruption;
- miscarriage;
- inability to become pregnant;
- lingering spotting.
Infertility and shortness of the luteal period are the most common causes of female infertility.
Features and duration of the follicular phase
This stage of the cycle, starting on the first day of menstruation, when the corpus luteum dies due to the cessation of progesterone production. The follicular phase got its name by analogy with the follicles, which are located deep in the cortical layer of the ovary. Due to the action of hormones after menstruation, the size of the structural components of the ovary increases. Over time, a dominant unit emerges from them, in which the strongest egg matures, preparing for fertilization. As a result of the influence of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), the dominant begins to grow:
- during the first 5 days all follicles grow;
- by days 5-7, one of the components of the ovary becomes the main one;
- on the 10th day the dominant grows to 1 centimeter in diameter.
After the tenth day of the menstrual period, the dominant unit, in which estradiol is actively produced, can be visualized on ultrasound examination in the form of an echogenic formation of a round shape. At the next stage of the functioning of the reproductive mechanism, a daily increase in the size of the follicle begins. At the time of ovulation, the diameter of the dominant increases to 1.9-2.5 cm. For the remaining follicles, the reverse process occurs due to a decrease in the level of FSH against the background of an increase in the volume of follicular fluid.
We recommend reading: 7 benefits of Clearblue pregnancy tests.
Together with the follicles, the thickness of the endometrium, the uterine layer, increases, ensuring the reliability of the embryo in the uterine cavity. During the first half of the cycle, the uterine layer grows to the thickness necessary to accept the fertilized egg. In the absence of conception, the function of the endometrium fades, and its tissues are rejected and come out with bloody discharge.