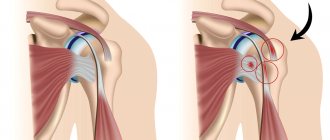
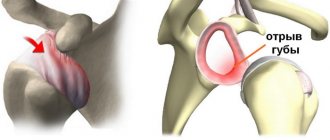
Periarthritis of the shoulder is a degenerative-inflammatory pathology that affects the soft tissues located near the joint - muscles and ligaments, but not the joint itself. As a result, there is a decrease in his functional activity, and difficulties arise with raising his arm or placing it behind his back. Clinically, periarthritis is manifested by pain, the intensity of which increases with physical activity, limited range of motion, and swelling. The causes of the pathology are varied - previous injuries, inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
To diagnose periarthritis, instrumental and biochemical studies, including differential ones, are carried out. Treatment is often conservative, consisting of taking medications, using orthopedic devices, following a gentle regimen, and performing special exercises.
Classification system
In accordance with the generally accepted ICD-10 system, pathology is not identified as a separate disease. Humeral periarthritis is a generalized name for functional disorders in the shoulder joint.
According to the code, several forms of lesions are distinguished:
- M75.0 Adhesive capsulitis – “frozen shoulder” syndrome: damage to the synovial bursa of the shoulder joint.
- M75.1 Rotator compression syndrome – tendon entrapment due to a collision between the humerus and scapula.
- M75.2 Biceps tendinitis - reactive inflammation of the biceps tendons.
- M75.3 Calcific tendinitis - deposition of calcium salts in the rotator cuff.
- M75.4 Impact syndrome - mechanical injury to periarticular tissues.
- M75.5 Shoulder bursitis - expansion of the joint capsule due to the production of synovial fluid in increased quantities.
The pathological process can develop on one side of the body or on both sides at once.
Periarthritis of the humerus: treatment and symptoms
Periarthritis is a disease characterized by inflammation of the periarticular tissues of large joints (capsule, joint ligaments, surrounding muscles and tendons).
The disease occurs most often in middle-aged and elderly people. Humeral periarthritis is called inflammation of the shoulder tendons and capsule of the shoulder joint, and it occurs very often. Both men and women are equally susceptible to this disease. The disease most often begins after a blow to the shoulder, injury, falling on the shoulder or on an outstretched arm. The development of the disease can be facilitated by surgery to remove the mammary gland in women, and certain diseases of the internal organs.
Pathogenesis
Depending on the type of periarthrial lesions, the factors determining their development are determined.
Degenerative changes (osteochondrosis) or displacement of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs in the cervical spine. Pathological deviations lead to dystrophy of the shoulder tendons due to pinching of nerve fibers associated with the brachial plexus, impaired blood flow, and lack of nutrients to the tissue.
Injuries to the shoulder joint resulting from a fall, impact, dislocation, accompanied by subcutaneous hemorrhages, tears of tendon and muscle fibers.
A relationship between the development of shoulder periarthritis and the following diseases has been identified:
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- spondylosis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- hormonal imbalance;
- myocardial infarction;
- violations of the functional abilities of the liver;
- connective tissue dysplasia;
- calcification;
- oncological neoplasms;
- lesions of the peripheral nervous system;
- radical mastectomy.
The formation of pathology is facilitated by the same type of movements performed monotonously over a long period of time, hypothermia, and excessive physical exertion.
What is glenohumeral periarthritis?
The pathology occurs in 25% of the population, more often in middle and old age. Mostly localization is one-sided.
- Periarthritis consists of two words - “peri” (around, around) and arthritis. The disease is characterized by inflammation in the tissues around the shoulder joint. These can be ligaments, muscles, tendons, joint capsules. Arthrosis differs from periarthritis in the degree of damage to the cartilage and internal structures of the shoulder.
- The glenohumeral region is the area surrounding the shoulder joint where pathology develops.
Causes of periarthritis
The most common reasons are:
- Injuries. Occupy a large percentage of cases in the appearance of glenohumeral periarthritis. Moreover, the injury can be mild in the form of a bruise, or, on the contrary, severe, with cracks and fractures. The bone loses its integrity and the load is distributed unevenly. This causes the disease to appear.
- Infectious diseases. They provoke periarthritis of infectious origin not only in the shoulder area, but also in more distant locations.
- Poor blood supply is the second most common cause of periarthritis due to lack of nutrients and oxygen.
- Immunity. The so-called autoimmune factor may consider the joint structures dangerous to the body and attack them. The consequence is a disease similar to rheumatoid arthritis.
- Problems with the spine - changes in the cervical spine, disc displacement, hernias, protrusions. All this leads to pinching of blood vessels, nerve endings and disruption of blood supply.
- Hypothermia.
- Endocrine disorders in the body - diabetes, menopause.
- Oncology.
At-risk groups
Why are some people susceptible to this disease, while others know nothing about periarthritis?
There is a group of people who should beware of this pathology:
- People engaged in heavy physical labor - athletes, loaders, etc. Their risk of shoulder injury is quite high. In addition, joints by their nature are not designed for regular heavy load. And as soon as the body gets tired, problems with the musculoskeletal system begin.
- Persons who have had myocardial infarction . There is no exact explanation why periarthritis develops against this background, but apparently it is due to poor circulation.
- Those who have a history of chronic diseases , even caries and sore throat.
- Patients with arthritis . These are pathologies that accompany each other.
Forms of periarthritis
Simple tendinitis
Inflammation of the tendon. The lesion may affect the tendon sheath, the bursa, or both areas at once.
Typically, glenohumeral periarthritis affects not only the tendon, but also nearby muscles. Tendonitis can be treated well at any stage of the disease.
Acute calcific tendobursitis
It also affects the tendons. But it is manifested by inflammation of the tendon bursa. Unlike tendonitis, it shows itself more aggressively. During the development of pathology, calcium salts are formed in the synovial cavity, which leads to difficulty in moving the arm in the shoulder.
Pain can occur not only from touch in the shoulder area, but also at rest. The body temperature rises to 37.5 degrees, changes in the blood test are noticeable - an increase in ESR. The disease can make a person disabled.
Chronic periarthritis
It includes several pathologies at once - tendonitis, tendobursitis, myotendinitis, etc. All forms can manifest themselves differently - either acutely or sluggishly. The pain is usually tolerable; often, with a sudden movement of the hand, “lumbago” appears.
At rest, pain appears in the morning and at night, disturbing the patient’s sleep. In this case, the acute stage does not necessarily turn into chronic. Symptoms may not be expressed or even hidden for many years.
Sclerosing capsulitis
Inflammatory process in the capsule and synovial cavity of the shoulder joint. A very serious disease with degenerative changes in the joint and the formation of ankylosis. The shoulder stops moving. This pathology requires immediate surgical attention.
These forms of periarthritis are its stages. That is, tendinitis initially appears, then the lesion spreads further, and its nature becomes more and more serious.
Symptoms of the disease
Humeral periarthritis cannot boast of any pronounced symptoms. And it can often be confused with arthritis.
But still, let’s look at the main and characteristic features:
- Painful sensations . During the development of the disease, the patient does not suffer from pain. It is minimal and most often occurs at night and in the morning. But after sleep, relief comes again. This period can last from 2 to 9 months. As periarthritis progresses, the pain increases and lasts for a long time, manifesting itself during waking hours. At the last stage, pain always accompanies a person.
- Impaired joint mobility . A symptom characteristic of the third and subsequent stages. There is a noticeable restriction of movement. The patient cannot raise his arm up or move it back. Relief comes when the hand is pressed tightly to the body. If the joint is not developed at this stage, muscle atrophy will begin.
- Complete loss of mobility of the shoulder joint . A serious pathology that appears in the last stage of the disease.
Read also: Arthrosis and arthritis, what is the difference?
Typically, symptoms do not appear suddenly, but gradually, in an increasing stage.
Diagnostics
To make a correct and accurate diagnosis, one cannot do without diagnostics. There are several methods. But first you need to visit an orthopedic doctor for a consultation. He will take an anamnesis, listen to complaints and the nature of pain, duration, intensity. He will compare the symmetry of both parts of the body, protrusions, conduct a palpation examination and make a decision on further diagnosis.
- X-ray . As a rule, this method is not very informative for diagnosing periarthritis, because the bones do not undergo deformation during the disease.
- MRI or CT . This method allows you to examine soft tissues and bones. Recognized as the most preferable, but inaccessible.
- Ultrasound . The shoulder joint is clearly visible. The most informative method for identifying periarthritis.
- Laboratory research . They will not accurately indicate exactly the problems with the shoulder, but they can show the general picture of the inflammatory process. Sometimes it becomes necessary to use tests to determine the presence of rheumatoid factor, then a general urine test and blood biochemistry will help.
The treatment plan is drawn up by the doctor, based on the condition of the shoulder joint and the stage of the disease. We can immediately make a reservation that if the periarthritis is complex, then surgical intervention will be necessary.
Treatment of uncomplicated periarthritis
Simple periarthritis at the initial stage can be treated at home with the help of homeopathy, physical education, and manual therapy. Conservative treatment consists of a number of measures.
Drug therapy
This includes the appointment and reception of:
- anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs - ointment, gel, tablets. Often prescribed are Nise, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Ketorolac, Nimesulide, etc. These medications can only be taken for a short time, due to their negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract and a large list of side effects;
- hormonal drugs , which are based on corticosteroids, for example, Prednisolone, Diprospan, Flosterone. However, they are used in extreme cases and in the form of injections. Very strong drugs;
- painkillers to relieve pain (Analgin, Tempalgin, etc.), as well as the use of novocaine blockades;
- Chondroprotectors are often prescribed if the disease is accompanied by arthritis. Drugs in this group will help protect cartilage tissue.
Immobilization of the shoulder, that is, fixing this part of the arm in a motionless state to relieve tension.
The doctor will recommend this method only after completing drug treatment, so as not to put stress on an already suffering shoulder.
The exercises are performed at the same time every day with a gradual load.
Here are 7 basic ones to do at home:
- Performed in a standing or sitting position with straight arms. On the count of one, the hands should be squeezed very tightly, fixed for a few seconds, and for two, the hands should be unclenched and relaxed.
- In a standing position with your arms straightened, bend them at the elbows once, and return them to the opposite position twice. Repeat up to 10 times.
- Standing, feet shoulder-width apart. Once - the shoulders rise as close to the ears as possible, fixate for 4 seconds. On two - they return to the starting position.
- The arms are extended along the body. One – the hands touch the shoulders, two – the arms fall back.
- A familiar exercise to everyone is scissors.
- Hands in front of you, elbows bent. First, the shoulder blades move apart, then the arms straighten and then return to their original position.
- Inhale - the arms rise and the body stretches upward. Exhale - return to the starting position.
Physiotherapy
- electrophoresis with medicine;
- magnetic therapy, which restores damaged tissue and increases the motor function of the joint;
- laser therapy, which is the best treatment for pathology;
- currents;
- ultrasound, which warms up the site of inflammation, restoring blood flow and reducing pain;
- mud therapy – it warms up the muscles and improves metabolism;
- manual therapy;
- swimming, which has a beneficial effect on the joint, without loading it, but at the same time developing it well.
Massage . It is forbidden to use this method in the treatment of arthritis, so making an independent decision about the possibility of massage can become disastrous. Massage for periarthritis is carried out to relieve tension, improve blood circulation, and prevent muscle atrophy.
Eastern medicine , which has long proven itself on the positive side, is effective. But not every patient can use it as a complex therapy due to the presence of contraindications. Vacuum therapy, manual and acupuncture techniques are popular. It is possible to use several simultaneously.
Treatment of complicated glenohumeral periarthritis
If periarthritis manifests itself as complications in the form of immobile areas, then there is only one solution - surgical intervention.
The so-called ankyloses (places of immobility) appear in the last stages. This complication often occurs with arthritis. The operation is called subacromial decompression. Its purpose is to excise the tissue that prevents the joint from moving. Often this is some kind of process on the shoulder blade and a ligament from this area.
Traditional treatment
There are many traditional medicines in the treatment of periarthritis, but we recommend that you consult with your doctor before using the chosen method.
- Chamomile decoction . You need 1 tbsp. chamomile and 250 ml of water. The decoction is rubbed onto the damaged area.
- Burdock leaf compress . The entire sheet is heated and applied to the shoulder for 10 minutes.
- Honey compress - apply a thin layer to the skin of the sore spot, wrap it in polyethylene and cover it with a warm thing overnight.
- Calendula infusion . Apply by rubbing into the sore shoulder. Purchased at a pharmacy.
- Tincture of mint , dandelion root, plantain, birch leaves.
- Horseradish . Grate to a paste, wrap in gauze and apply to the shoulder. Do it 2 times a day for 15 minutes.
- Saline dressings are done at night. Stir 100 grams of salt per 1 liter of water until dissolved. Take gauze, fold it into 8 layers and place it in the solution for 3 hours. After this time, the solution warms up along with the gauze. Then, after a short squeeze, the gauze is applied to the shoulder and secured with a rag.
Manifestation of pathology
Shoulder periarthritis in its classic form is not burdened with severe manifestations. Pain develops along the outer surface of the shoulder, aggravated by rotational movements, an attempt to raise the arm, or put it behind the back. The pain syndrome limits movement, but in this phase the disease can be successfully treated. There are known cases of spontaneous disappearance of pathological abnormalities.
As the disease progresses to the acute stage, the intensity of the pain increases. The pain spreads through nerve receptors to the arm and neck. The peak activation of the inflammatory process occurs at night. Swelling appears in the area of the shoulder joint. The limitation of movements is clearly expressed; moving the arm away from the body becomes almost impossible.
The patient experiences slight relief by bending his arm at the elbow joint and pressing it to his chest in this position. General well-being worsens: temperature increases, insomnia begins, and the potential for opportunities decreases. If the damage to the shoulder is a consequence of osteochondrosis, headache, dizziness, pain under the shoulder blade, and numbness of the fingers are added. The pathological process in an acute state lasts for several weeks, after which there is a high probability of transition to the chronic stage.
Characteristic symptoms for chronic shoulder periarthritis: dull pain in the shoulder joint, discomfort when moving the arm. Deviations worsen in the second half of the night. When you rotate your hand, a sharp pain syndrome occurs, causing unbearable suffering to the person. The duration of the chronic form of periarthritis is calculated in years. This condition increases the risk of developing adhesive capsulitis.
If polyarthritis is not treated in a timely manner, it leads to chronicity of the process, loss of motor functions - “blocking” of the shoulder joint.
Gymnastic exercises
No matter how minor the symptoms may be, and no matter how effective the treatment may be, at the discretion of the attending physician, the patient may be prescribed a set of gymnastic exercises to perform at home. Thanks to them, the healing process will go faster. The disease can be treated in this way only for those patients who have passed the acute stage of the disease. As soon as the pronounced symptoms pass, the doctor will help you choose the optimal exercise therapy complex.
Diagnosis
To confirm the diagnosis and receive medical care, the patient should contact a rheumatologist, neurologist, traumatologist, or orthopedist. A visit to a doctor begins with a basic examination of the patient. Using special tests, a specialist assesses the degree of limitation of mobility of the shoulder joint and decrease in muscle tone. To identify the causes that provoked the pathology and to study the clinical picture in detail, additional instrumental and laboratory tests are prescribed.
Blood sampling analysis - in the acute stage, the study reveals an increased rate of erythrocyte aggregation - ESR, the presence of C-reactive protein.
X-ray of the shoulder joint indicates the accumulation of calcium microcrystals in the affected areas, degenerative changes in the periarticular tissues.
X-ray of the cervical spine is prescribed if the development of periarthritis due to osteochondrosis is suspected.
Ultrasound – detects ruptures of tendons and muscles, degenerative changes in muscle tissue and bone structures, defects of the articular labrum, and calcification deposits.
MRI – performed in severe cases to determine joint contractures.
Annual voluntary medical examination is an important process that makes it easier to diagnose the disease.
Diagnostics
Scapulohumeral periarthritis of any side indicates inflammation of the ligament. The goal of differential diagnosis is to understand the reasons that led to this condition.
Diagnosis of glenohumeral periarthritis includes:
- X-ray examination - for a general assessment of the shoulder joint, identifying bone-traumatic changes and developmental anomalies. Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging are considered the most informative;
- CT scan – allows you to evaluate the joint in detail, build a three-dimensional model, and exclude traumatic and tumor processes that led to the development of pain;
- MRI is the method of choice for studying the rotator cuff (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis and teres minor muscles), glenohumeral, acromioclavicular joints, and adjacent soft tissues.
If a possible cause is diseases of the spine, the doctor will prescribe an additional examination of the cervical spine using one of the available radiological diagnostic methods. For example, the provoking factor for glenohumeral periarthritis on the right is a right-sided hernia or protrusion in the neck.
Therapeutic measures
Of fundamental importance in the treatment of glenohumeral periarthritis is the elimination of pain and the return of lost motor abilities.
Drugs that have non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesic potential help stop the inflammatory process in the periarticular tissues:
- Celebrex;
- diclofenac;
- artrosilene;
- ketoprofen;
- meloxicam;
- indomethacin
The use of these products in the form of tablets, ointments, and gels is effective for simple forms of pathology.
In case of exacerbation, a support bandage or plaster splint is used to reduce the load on the diseased joint. To relieve acute pain, intramuscular injection of glucocorticosteroids into the area of localization of painful changes is practiced. Novocaine blockades are used - injection of an anesthetic into the periarticular capsule, surrounding vessels, and muscle tissue.
Additionally assigned:
- applications with dimexide - the high bioavailability of the drug allows it to penetrate through the skin directly into the pathogenic cell;
- muscle relaxants – relieve muscle tension;
- angioprotectors – have a positive effect on the condition of vascular walls, normalize blood flow;
- chondroprotectors – nourish cartilage tissue and promote its restoration.
In case of impingement syndrome - compression of the rotator cuff, arthroscopic subacromial decompression of the shoulder joint is indicated. With the help of minimally invasive surgery, the surgeon is able to clear the affected area of scar tissue and eliminate sclerotic areas. The method allows you to create sufficient anatomical space for pinched rotator cuff tendons. The patient's motor functions are restored, and it becomes possible to return to the usual rhythm of life and stress.
Causes of glenohumeral periarthritis, symptoms and treatment
Despite the apparent strength of the human musculoskeletal system, it is no less vulnerable than other human organs.
There are many diseases, and there are cases where only cartilage is affected, without affecting or deforming the joints even in the later stages of the disease.
The disease is called glenohumeral periarthritis. This is an inflammatory disease of the periarticular musculoskeletal structures.
That is, periarthritis affects soft tissues - ligaments, muscles, joint capsules. But despite this, the pathology is serious and can deprive the shoulder of motor function.
Physiotherapy
After relieving the inflammatory reaction, physiotherapeutic procedures occupy an important position in the treatment of glenohumeral periarthritis:
- shock wave therapy – activates the regeneration of tissue structures at the cellular level;
- electrical stimulation – restores the functions of affected tissues, nerve and muscle fibers, enhances metabolic processes;
- medicinal electrophoresis – delivers the largest amount of necessary pharmacological substances directly to the lesion using electric current;
- pharmacopuncture – injection of a small amount of medicine into biologically active points of a person;
- hirudotherapy - the use of specially grown medicinal leeches; penetration of their secretions into the patient’s bloodstream has an anti-edematous effect and improves tissue trophism;
- Magnetic therapy – activates blood circulation in pathological areas, eliminates swelling, helps eliminate pain impulses.
To eliminate motor restrictions, manual impact on the damaged structures of the shoulder joint is recommended. Postisometric relaxation is a special exercise in which the patient tenses a certain group of muscles, and the physiotherapist resists their contraction. The complex eliminates stiffness and restores range of motion.
Massage – prevents the formation of scar tissue and the occurrence of muscle atrophy. Restores the functional abilities of the shoulder joint. The collar area, deltoid and pectoral muscles, shoulder and the entire surface of the arm are manipulated.
For glenohumeral periarthritis, sanatorium-resort treatment using natural factors is encouraged.
Danger of disease
Periarthritis of the shoulder joint without proper treatment poses a serious danger to humans. After all, the disease can progress to the “frozen shoulder” stage (ankylosing or chronic stage). This situation develops in 30% of cases. This pathology is characterized by compaction of the shoulder and its stiffness. At the same time, the sensation of pain increases many times over, which can cause shock. Over time, there is a blockade of the scapulothoracic joint, leading to the fact that the shoulder joint stops moving. To avoid such developments, you need high-quality and timely treatment.
Nutrition rules
Products that make up a larger volume of the diet:
- omega-3 fatty acids, which reduce inflammation and enhance regenerative functions;
- stewed vegetables, fresh fruits;
- protein can be obtained from nuts;
- adding gelatin to the diet improves the condition of joint cartilage.
It is necessary to exclude spicy, fatty and fried foods, canned food, and alcohol from the diet. It is important to minimize salt intake because it interferes with fluid loss.
It is advisable to divide meals into 5 or 6 meals.
Expert opinion
Traumatologists, therapists and neurologists agree that a favorable treatment prognosis is determined by an integrated approach to this issue - medications, massage, physical therapy (PT), physiotherapy.
To maintain a positive effect, doctors recommend adhering to a dietary style not only at the time of treatment, but also after the pain has reduced. Regular physical exercise will allow you to maintain mobility in the joint for a long time.