- "Calcium gluconate";
- "Calcium D3 Nycomed";
- "Calcimin";
- "Aquadetrim";
- "Vitacalcin";
- "Vitrum Calcium".
The product will relieve pain and inflammation.
If your hand hurts badly, it is recommended to use analgesics - Analgin, Nurofen, Ibuprofen. During the recovery period of the right or left limb, you can use the following anti-inflammatory liniments:
The drugs can only be applied if there are no wounds on the skin.
Surgical intervention
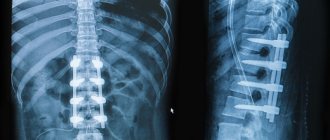
Surgical treatment is more often required if a closed, comminuted, displaced fracture of the arm is diagnosed. An operation is performed with a plate—a metal synthesis instrument that is used to fasten bone fragments. During surgery, the doctor also cleans and drains the wound, and sutures torn nerves and blood vessels. Since the heads of the humerus are often broken during injury, the injury takes a long time to heal.
Rehabilitation of a humerus fracture
Physiotherapeutic methods
For the treatment of humeral epiphysis fractures, the following physiotherapy procedures are recommended:
- infrared and ultraviolet irradiation;
- inductothermy;
- electrophoresis;
- phonophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser treatment;
- thermal applications with ozokerite and paraffin;
- radon and hydrogen sulfide baths;
- massage.
Physiotherapy has the following therapeutic effects on shoulder injuries with fragments:
- restores motor functions;
- improves lymph flow and relieves swelling;
- normalizes blood circulation;
- accelerates tissue regeneration;
- regulates metabolic processes in the bone structure;
- eliminates inflammation.
Return to contents
Physiotherapy
Fractures of the shoulder bone require prolonged immobilization, during which the muscles atrophy and the functioning of the limb deteriorates. Therefore, exercise therapy is aimed at developing the entire arm and includes the following exercises:
- clenching and unclenching fingers;
- rotational movements of the hand, elbow and shoulder joint;
- swing your hand back and forth, left and right;
- flexion-extension of the elbow joint;
- raising your arm up and down;
- interlocking fingers at the back of the head;
- exercises with dumbbells weighing no more than 2 kg.
You should start the exercises with a massage. This helps improve blood flow and warm up the muscles. It is recommended to palpate the fracture site with light pressing movements, as well as stroking and pinching. If there are postoperative wounds, massage should be done by a specialist. During the rehabilitation period, swimming is recommended, since staying in water has a beneficial effect on the soft tissues of a broken arm. During healing, you should not sleep on the side of the affected arm so as not to impair blood circulation.
Complications
If the humerus is broken, but medical care was provided in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. In advanced cases, injury is dangerous due to dysfunction of the radial nerve. The main consequences of an untreated fracture are as follows:
- improper bone fusion;
- limb deformity;
- reduction or loss of the function of grasping and holding an object;
- unnatural hand position;
- formation of calluses and false joint;
- arthrosis;
- arthritis.
The condition is accompanied by chronic pain and discomfort in the arm. An equally dangerous complication is infection with pathogenic microorganisms: Pseudomonas aeruginosa and tetanus, streptococcus, staphylococcus. The bacteria cause sepsis, which can be fatal.
Why does injury occur?
Fractures of the humerus with displacement and without displacement of bone fragments occur due to the following unfavorable factors:
- falling on an elbow or outstretched arm;
- direct blow to the shoulder with a heavy object;
- dislocation, in which the greater tubercle is torn off;
- extreme sports or oriental contact martial arts;
- industrial and vehicle accidents;
- diseases that cause bone fragility;
- poor nutrition and calcium deficiency.
Main manifestations
The clinical picture differs for different types of fractures. If the upper forearm is injured, there is limited function in the elbow joint. If the lower part is damaged, hand movements are difficult. But at the same time, there are general symptoms that are characteristic of all types of fractures. The main ones are presented below:
- pain at the fracture site reaches its maximum at the time of injury, and subsequently has a dull, aching character;
- any movement of the injured limb is accompanied by increased pain;
- deformation of the forearm is visually noticeable. If the fragments have shifted along the length, shortening of the limb is observed. In some cases, bone fragments protrude outward, forming a protrusion at the fracture site;
- swelling may spread to the entire forearm;
- with closed injuries due to rupture of blood vessels, subcutaneous hemorrhages and bruises occur, but if the fracture is open, bleeding is observed;
- movements in the hand are sharply limited, the patient holds the limb by the elbow or wrist;
- axial load (effleurage) on the base of the palm or olecranon brings sharp pain at the fracture site.
Fracture of the proximal forearm
Injury to the ulna and coronoid process of the ulna, as well as the head of the radius, has a similar clinical picture. It is difficult to determine which structure is damaged without x-ray examination. Fractures of all of the above structures are characterized by pain in the elbow joint. It is enlarged, swollen, and hemorrhages occur under the skin. It is possible for blood to accumulate in the joint capsule; in medicine this phenomenon is called hemarthrosis.
There is practically no movement in the elbow joint; attempts to bend or straighten the limb are accompanied by increased pain. Upon palpation, fragments and violations of the bone structure can be determined, since the skin in this place is thin and the processes are easy to palpate. A characteristic symptom of damage to the olecranon process is a violation of Huther's triangle. Normally, it is isosceles and the angles are formed by both condyles of the humerus and the olecranon.
Fracture of the diaphysis of the radius and ulna
Damage to the middle part of the forearm occurs due to a violation of the integrity of the body of the ulna, radius, or both. Pain, swelling, and hemorrhages at the site of injury come to the fore. Pronation and supination of the hand (rotational movements of the forearm in and out) are sharply limited. It is not always possible to determine the presence of damage, since the bones in the middle part are located under a layer of muscles. With a displaced fracture, shortening of the limb may occur.
Fracture of the distal forearm
In the lower part, the head and styloid processes of the ulna and radius form a joint with the wrist. Therefore, if these structures are damaged, movements in the wrist joint are limited.
Among the injuries to the lower part of the forearm, the most common is a fracture of the radius in a typical location. The line of damage is located several centimeters above the joint - in the thinnest place of the radius. This is where damage is most common, hence the name. There are two main types of injuries:
- A Smith fracture occurs as a result of a fall on a limb bent at the wrist joint. As a result, two fragments are formed: the lower (distal) one moves back and to the side, the upper one moves forward. In some cases, damage to the styloid process of the ulna occurs in parallel;
- with a Colles fracture, a person falls on his arm, which is extended at the wrist joint. The lower fragment moves anteriorly and slightly laterally (to the side). Movement in the joint is limited, swelling and redness occur at the site of injury, and bone fragments can be felt.
What types of damage are there?
A fracture occurs as a result of a strong blow.
The classification of fractures is determined by the location of the injury as follows:
- Trauma to the proximal upper third, in which the surgical neck and head of the humerus are broken.
- Diaphyseal, when the integrity of the bone body in the middle is disrupted. A comminuted fracture may be accompanied by a violation of the integrity of blood vessels and the radial nerve.
- A fracture of the lower end is characterized by damage to the capitate eminence, internal epicondyle, and medial condyle. Transcondylar fracture of the shoulder joint is more often observed in children.
Diagnostics
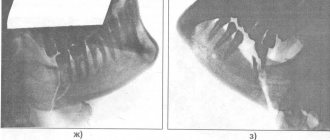
Upon arrival at the hospital, the doctor examines the patient to accurately determine the type and type of fracture, and radiography is performed. Pictures are taken in two projections for a more accurate medical picture of the damage. If necessary, an ultrasound of the damaged area or MRI is also performed. Thus, damage to muscles, blood vessels or nerves is detected in time, and an appropriate course of treatment is prescribed. An examination by a doctor includes the following steps:
- Light pressure or tapping on the elbow. At this point, the pain should increase significantly.
- Feeling the damaged area. In this case, you can hear the characteristic sounds of fragments rubbing against each other.
- The doctor makes movements with the shoulder, and at this moment he feels which areas of the bone are subject to displacement.
- When a shoulder fracture is accompanied by a dislocation, the doctor cannot feel the head of the shoulder joint in the place where it should be.
Symptoms: how to recognize an injury?
An impression fracture of the shoulder has the following symptomatic features:
- Injury in the upper part is accompanied by mild swelling and limited mobility.
- A fracture of the humeral body is characterized by unnatural mobility, as well as the inability to bend the fingers.
- Intercondylar and supracondylar fractures are combined with dislocation, limb deformation, and subcutaneous hemorrhage.
Injury to the humerus can be open or closed. The nature of the fracture can be helical or lateral, as well as transverse. How the injury manifests itself depending on the type is shown in the table:
| Nature of the fracture | Signs |
| Closed without displacement (crack) | Soreness |
| Swelling | |
| Limited mobility | |
| Muscle weakness that makes it almost impossible to lift your arm | |
| Closed with offset | Strong pain |
| Edema and hematoma | |
| Severe arm deformity or shortening | |
| Crunching and creaking in bones | |
| Unnatural bone mobility where it shouldn't be | |
| Open with displacement of fragments | Intense pain |
| Wound formation due to bone fragmentation | |
| Heavy bleeding | |
| Feeling of numbness that extends to the hand | |
| Extensive swelling and hematoma | |
| General deterioration in health, fainting |
Structure
The humerus is located at the top of the arm. Above it borders with the shoulder girdle, below with the elbow.
It is important! Many people mistakenly refer to the shoulder as the area between the shoulder joint and the edge of the neck. However, this name is given to the part of the upper limb that is located between the elbow and shoulder joints.
The humerus is tubular in structure. It has three parts, located from top to bottom: proximal , middle and distal .
The most complex structure is the upper one, which is involved in the formation of the shoulder joint. Movements in it are possible due to the presence of a spherical head covered with cartilage.
a neck on the top of the bone . In this area, the thickness of the bone is reduced, as a result of which fractures often form in it. Below the anatomical neck there are two tubercles on which muscles are attached. Even more distal is a second narrowing called the surgical neck . Fractures often occur here as well.
The distal part connects to the ulna through the elbow joint. Condyles are located on it - bony protrusions, due to which the surface of contact of the articular surfaces increases.
How to provide first aid?
An open fracture with displacement is dangerous due to large blood loss, since an artery is located nearby. Therefore, you should immediately apply a tourniquet above the wound, making sure to include a note indicating the time and date.
Before the doctor arrives, you must apply a cold compress to the injury site.
Immobilization for a humerus fracture is carried out only after bleeding has stopped. The algorithm for providing first aid is as follows:
- Provide complete rest to the limbs.
- Wrap the injury site with a cold compress, wrapping the ice in a cloth, avoiding direct contact with the skin.
- Disinfect the wound with an open fracture without touching bone fragments.
- Secure your hand with planks so that the edges of the clamps protrude above the injury site. Fixation of the hand with the wound surface is carried out with sterile materials.
- Wrap it with a bandage, making sure that the bandage is not tightened too tightly.
- Place a cotton-gauze roll between your hand and armpit.
- Place the limb on the wide edge of the scarf, tying the ends around the neck.
- Give painkillers.
- Take the victim to the first aid station. Transport immobilization for a shoulder fracture in winter is carried out after warming the limb to avoid frostbite.
Shoulder fracture - first aid
Immediately after receiving an injury, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Before doctors arrive, you must do the following:
- Give the victim a pain reliever. If possible, it is advisable to administer it by injection. This way the active substance will quickly enter the bloodstream and begin to act.
- If the victim is very nervous or feels afraid, it is advisable to give him a sedative. For example, you can give her a tincture of motherwort or valerian.
- If there is a suspicion of a shoulder fracture, the victim should be seated and the injured arm should be firmly secured. Boards, metal plates or thick plywood will do for this. One base should be bandaged to the forearm, and the second to the shoulder. Then you need to tightly tape your hand to your body.
When your shoulder is broken, you cannot probe the injured limb yourself, as this will cause unbearable pain to the victim. In addition, you should not adjust the shoulder before the doctors arrive. Any sudden movements will only aggravate the situation! For example, an artery or nerve bundle will rupture. In addition, inept actions increase the risk of injury to muscle fibers.
Closed shoulder fracture - first aid
With this type of injury, you need to act very carefully and quickly. If there is a suspicion of a closed fracture of the shoulder, first aid is performed as described above. The only thing that needs to be changed is that before bandaging the metal or wooden base, you need to cover the shoulder and elbow joints of the injured arm with cotton wool. After fixing the limb to the body, it is recommended to apply a cold dry compress: it will prevent the accumulation of intra-articular fluid and reduce pain.
Open shoulder fracture - first aid
This type of damage is characterized by a violation of the skin: the damaged bone can be seen through the wound.
When an open fracture of the shoulder is present, first aid should be provided as follows:
- Free the injured hand from clothing (the fabric will have to be torn or cut).
- Give the victim a painkiller or inject it.
- If there is bleeding, apply a tourniquet above the fracture. Be sure to insert a note under it with the exact time when it was applied. You can hold the tourniquet for a maximum of one and a half hours! If such a medical fixator is not at hand, it can be replaced with a belt, rope or thick fabric.
- Remove dirt from the wound and treat it with an antiseptic. In this case, it is forbidden to touch the protruding bone fragment or try to set it back!
- A sterile bandage is applied to the wound, and a cold, dry compress is applied on top.
Diagnostic methods
The study will determine the extent of bone tissue damage.
A closed shoulder fracture is diagnosed by a traumatologist or orthopedic surgeon. The doctor determines the circumstances of the injury, conducts a visual examination, determining the degree of motor impairment and the characteristics of symptoms characteristic of certain types of fractures, and sends for x-rays. The procedure shows the presence or absence of displacement, whether the small external condyle or epicondyle of the humerus is broken, the metaepiphysis of the radius, the condition of the nerves, blood vessels, ligaments and muscles. To obtain a detailed clinical picture, it is recommended to undergo:
- MRI;
- arthroscopy;
- Ultrasound;
- scintigraphy;
- CT.
Causes of fractures and factors predisposing to injury
A fracture is a relative or absolute disruption of the bone structure. All fractures based on their causes can be divided into two large groups: pathological and traumatic. Risk factors also play a special role, which are determined individually for each person, taking into account gender, age and occupational hazards.
Factors that provoke the development of fractures include:
- passion for dangerous sports;
- work associated with prolonged lifting and carrying heavy weights;
- overweight or underweight;
- menopause;
- presence of chronic diseases.
Table: causes of fractures
| Pathological causes of fractures | Mechanical causes of fractures |
| Tuberculous bone disease | Beats |
| Syphilitic bone lesion | Falls from height |
| Leaching of calcium from bone matter | Lifting weights |
| Congenital enzyme and mineral deficiency | Sports injuries |
| Disturbances in the absorption of calcium from food | Occupational injuries |
| Hormonal deficiency | Sharp jerks and dislocations |
| Ovarian diseases associated with decreased synthesis of female sex hormones | Industrial disaster |
| Eating disorders (anorexia, bulimia) | Accident |
| Gastrointestinal diseases associated with poor absorption of nutrients | Natural disaster |
Treatment: the most effective methods
Traditional methods
The drug accelerates the process of bone tissue formation.
A closed fracture of the humeral shaft requires the application of a fixator. Under favorable conditions, the shoulder heals in 1-1.5 months. In older people, the healing time may increase due to thinning of the bone structure. During the period of walking in a cast, it is recommended to take control radiographs. You should also stick to a diet, focusing on foods rich in calcium and vitamin D. Taking the following dietary supplements is effective:
- "Calcium gluconate";
- "Calcium D3 Nycomed";
- "Calcimin";
- "Aquadetrim";
- "Vitacalcin";
- "Vitrum Calcium".
The product will relieve pain and inflammation.
If your hand hurts badly, it is recommended to use analgesics - Analgin, Nurofen, Ibuprofen. During the recovery period of the right or left limb, you can use the following anti-inflammatory liniments:
- "Dolobene";
- "Diclofenac";
- "Apizartron";
- "Fastum gel";
- "Deep Relief";
- "Voltaren."
The drugs can only be applied if there are no wounds on the skin.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment is more often required if a closed, comminuted, displaced fracture of the arm is diagnosed. An operation is performed with a plate—a metal synthesis instrument that is used to fasten bone fragments. During surgery, the doctor also cleans and drains the wound, and sutures torn nerves and blood vessels. Since the heads of the humerus are often broken during injury, the injury takes a long time to heal.
Additional points
The broken limb is cast. The victim wears a cast for a long time - 13-14 weeks, in more complex cases up to 18 weeks. The muscles of the hand, being without movement for a long period, atrophy, the same picture occurs with the tendons and the joint itself. In order for the arm to function normally after a fracture, doctors prescribe a rehabilitation course for the patient, which depends on the severity of the injury. The most effective rehabilitation measures:
- therapeutic and health-improving physical education,
- physiotherapeutic procedures – ultrasound, magnetic resonance therapy, electrophoresis,
- massotherapy,
- Diets that strengthen bone tissue
- at home, the patient is prepared with warm salt baths for greater effectiveness in developing the arm - 3 times a day for 15 minutes.
If first aid was provided correctly and on time, the prognosis is favorable and full recovery occurs within 3 months. Severe cases - for example, open fractures - take a longer period to recover - up to 5 months.
Rehabilitation of a humerus fracture
Physiotherapeutic methods
Under the influence of current, the medicine acts at the cellular level.
For the treatment of humeral epiphysis fractures, the following physiotherapy procedures are recommended:
- infrared and ultraviolet irradiation;
- inductothermy;
- electrophoresis;
- phonophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser treatment;
- thermal applications with ozokerite and paraffin;
- radon and hydrogen sulfide baths;
- massage.
Physiotherapy has the following therapeutic effects on shoulder injuries with fragments:
- restores motor functions;
- improves lymph flow and relieves swelling;
- normalizes blood circulation;
- accelerates tissue regeneration;
- regulates metabolic processes in the bone structure;
- eliminates inflammation.
Physiotherapy
Exercises must be performed slowly, without sudden movements.
Fractures of the shoulder bone require prolonged immobilization, during which the muscles atrophy and the functioning of the limb deteriorates. Therefore, exercise therapy is aimed at developing the entire arm and includes the following exercises:
- clenching and unclenching fingers;
- rotational movements of the hand, elbow and shoulder joint;
- swing your hand back and forth, left and right;
- flexion-extension of the elbow joint;
- raising your arm up and down;
- interlocking fingers at the back of the head;
- exercises with dumbbells weighing no more than 2 kg.
You should start the exercises with a massage. This helps improve blood flow and warm up the muscles. It is recommended to palpate the fracture site with light pressing movements, as well as stroking and pinching. If there are postoperative wounds, massage should be done by a specialist. During the rehabilitation period, swimming is recommended, since staying in water has a beneficial effect on the soft tissues of a broken arm. During healing, you should not sleep on the side of the affected arm so as not to impair blood circulation.
How does recovery occur after a fracture?
The most difficult stage after healing of a fracture is the person’s return to the normal process of normal work activity. Being in a cast has a bad effect on the function of not only the forearm, but the entire hand as a whole. Medical rehabilitation specialists are involved in the processes of restoration and normalization of blood circulation and innervation of the damaged limb.
Exercises to restore hand motor skills
The muscles of the forearm, which have been completely immobile for a long time, lose their tone. The primary goal of the exercises is to restore fine motor skills, strengthen the grasping function of the hand and build muscle mass in the forearm so that the difference between the hands is not noticeable. The second stage involves restoring the sensitivity of the skin.
Exercises prevent the occurrence of contractures and false joints, making them an important part of rehabilitation
- Take small dumbbells weighing up to five hundred grams in both hands. Gradually slowly bend your arms at the elbow joints, trying to touch the shoulder. Repeat the exercise at least fifteen times.
- Stretch your arms with dumbbells in front of you, then alternately move them to the side and return them back. Try to make all movements a little slower with your injured hand. The number of repetitions is at least ten.
- Take an expander or a small elastic ball with the injured hand. Squeeze it as hard as you can at least twenty times. If your arm gets tired, start with fewer repetitions and gradually increase their number.
Video: therapeutic exercises after forearm fractures
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/t9_BPPPfGoA
Massage to speed up rehabilitation processes
Massage is a universal remedy for restoring blood circulation and sensitivity in an injured hand. After being in a cast for a long time, the fingers lose their former ability to move quickly, and the patient also feels tingling and numbness in the area of the fracture for a long time. Massage helps combat such unpleasant sensations. You can carry it out either at home or make an appointment with a competent specialist in the field of medical rehabilitation.
The massage roller has a targeted effect on the affected area
How to properly massage at home:
- Warm the skin of the affected hand with light stroking movements.
- With your healthy hand, begin to slowly squeeze the patient in the direction from the hand to the shoulder. It is required to repeat this movement at least seven times.
- Using gentle pinch movements, pull back the skin on the surface of the forearm. Its redness indicates the restoration of microcirculatory processes.
- Using a foam roller, slowly roll over your forearm twice in one direction and twice in the other. This will help stretch your muscles and improve their nutrition.
Using folk remedies to recover from injury
Unfortunately, the fracture itself cannot be cured using traditional medicine, since such means are not able to provide the necessary fixation. Traditional medicine recipes can be used during the recovery stage after injury: they cope well with pain and relieve swelling. Also, such medications are easy to prepare at home, they are practically harmless and are tolerated without visible side effects.
- Chop two large onions into pieces and fry in vegetable oil. Pour the resulting solution into a saucepan with a liter of boiling water, cook for half an hour, stirring constantly. Drink one glass three times a day before meals: this will have a beneficial effect on the general condition of the body and allow you to restore strength. The course of treatment is at least two weeks.
- Brew twenty grams of chamomile in a glass of boiling water. After cooling, soak a gauze bandage in the resulting mixture and place it on the fracture area. Hold this compress for fifteen to twenty minutes: this will help relieve pain and irritation, and also reduce inflammation. Treatment should be carried out four times a week.
- Boil three large eggs and peel them. Using a blender, grind it to a powder. Add half a teaspoon to your food throughout the day. Eggshells contain a large amount of calcium, which is absorbed by the body and helps strengthen bone tissue.
Complications
Arthrosis may develop against the background of a fracture.
If the humerus is broken, but medical care was provided in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. In advanced cases, injury is dangerous due to dysfunction of the radial nerve. The main consequences of an untreated fracture are as follows:
- improper bone fusion;
- limb deformity;
- reduction or loss of the function of grasping and holding an object;
- unnatural hand position;
- formation of calluses and false joint;
- arthrosis;
- arthritis.
The condition is accompanied by chronic pain and discomfort in the arm. An equally dangerous complication is infection with pathogenic microorganisms: Pseudomonas aeruginosa and tetanus, streptococcus, staphylococcus. The bacteria cause sepsis, which can be fatal.
How to properly prevent the disease
In the modern world, it is not possible to completely eliminate the possibility of a forearm fracture: a hundred dangers await us every day. But you can try to minimize the risks by following a few simple rules and slightly adjusting your usual lifestyle
Doctors strongly recommend paying attention to certain aspects of everyday life and being more attentive to your health.
- Compliance with safety regulations at work. Any work associated with lifting and carrying heavy objects should be limited strictly according to standards. If possible, such work should be mechanized or at least two or three people should participate in its completion, which will ensure an even distribution of weight.
- Performing vigorous physical exercise and warming up before exercise. Keep in mind that before starting sports, the muscle frame is in a tense and spasmodic state: this increases the risk of developing traumatic fractures. Ten to fifteen minutes before the main workout, warm up your muscles with exercises or a light massage. Also, you should not use heavy weights for exercise, which are difficult to keep in a static state for a long time.
- Treatment of chronic diseases. Many pathological processes occurring in the human body negatively affect the condition of the skeletal system. Infectious diseases such as tuberculosis or syphilis contribute to the formation of pathological fractures, and if timely treatment is not carried out, the patient may develop serious complications, including death.
- Proper nutrition and strengthening the overall immune status of the body. Remember that the strength of our bones directly depends on the diet and proper nutrition. Food should be easily digestible and contain large amounts of protein and calcium. Doctors recommend eating medium-fat cottage cheese: this will improve calcium absorption. Be sure to take vitamins and mineral complexes that will make the bone skeleton less fragile.
- Wearing shoe protectors in the winter and spring seasons. Protecting your shoes from slipping is a fairly effective and efficient method to avoid unfortunate falls. Such rubber pads with spikes can be purchased at any sports store or ordered online.
Unfortunately, not every person is able to avoid injury during the spring-winter period. Injuries to the bones of the forearm heal quite quickly and painlessly if the fracture is not complicated. In severe cases, it is necessary to resort to a second fracture in order to connect the fragments as accurately as possible. The recovery period after a fracture lasts at least three months. If you follow all the doctor’s instructions, do exercises and eat healthy foods at least three times a day, healing will take place without negative consequences for the body.
Duration of treatment
In case of a closed fracture without displacement, the plaster cast is removed after 30 days and active exercises are started - exercise therapy and, at the same time, physiotherapy. If no complications arise, after two to three months of rehabilitation the arm will fully restore its functionality, but this does not mean that you can immediately put a full load on it. At first, it is advisable to wear a special support bandage.
If displacement occurs during a fracture, before repositioning it is attempted to be combined in a conservative – closed way and, if this is successful, the rehabilitation period does not differ from non-displaced injuries. If the pearl is complicated, the rehabilitation period increases. For a period of at least one and a half months, an abduction splint based on the Kramer splint is applied, after which a plaster cast is made, which is removed after a month and only after that physiotherapy and therapeutic and preventive exercises - exercise therapy - begin.
In the most severe cases, surgical intervention is performed - combining the fragments and fixing them with the help of auxiliary devices. To secure fragments, plates, screws, knitting needles or systemic skeletons, like the Ilizarov apparatus, are used.
If for some reason surgery is contraindicated, there is only one treatment option left - skeletal traction. In this case, the treatment algorithm is as follows: traction of the bone in the elbow area for a period of 25–30 days, two-month plaster immobilization, after which the plaster is removed and a set of standard rehabilitation measures is carried out. The duration of rehabilitation directly depends on the patient’s age and his body’s ability to regenerate injured tissue. Regular and complete implementation of a complex of physical therapy exercises is also important.