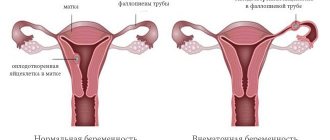
The most significant transformations of the fetus occur in the early stages of pregnancy. Within a few days from the moment of conception, it turns from one cell - a zygote - into a millimeter-sized embryo. The formation of the fertilized egg begins immediately after the fusion of the sperm and egg in the fallopian tube. After this, the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus. Is it possible to feel the moment of implantation of an embryo into a woman’s body?
How does conception occur?
In order for conception to occur, the participation of two gametes is necessary - a sperm and an egg. In the first half of the menstrual cycle, the oocyte matures - under the influence of the gonadotropin FSH, it is formed in the ovarian follicle. Around the middle of the cycle, usually on the 14th day, the dominant follicle ruptures and a mature egg is released. This phenomenon is called ovulation.
After leaving the ovarian follicle, the egg travels into the fallopian tube. If sexual intercourse occurred on this day or 2-3 days before, then some of the sperm could reach the fallopian tube. It is there that the male gametes wait for the female gamete to fuse with her and fertilize her.
If there are no sperm in the oviduct, the egg continues its movement, descends into the uterus, dies and comes out along with menstrual blood. If male gametes are present, then they all together begin to attack the surface shell of the egg - the corona radiata. One sperm cannot destroy it; the effort of several is required. However, only the one who first manages to reach the inner layer - the zona pellucida - fertilizes the oocyte.
What conditions are necessary for successful embryo implantation?
For the successful attachment of a fertilized egg in the uterine cavity and the beginning of pregnancy, certain conditions must be met. Here is the list:
- The thickness of the uterine mucosa should be no more than 1.3 cm.
- In order for the embryo to develop further and continue its vital functions, the walls of the uterus must contain a sufficient amount of nutrients.
- Sufficient production of progesterone by the female body. This hormone delays menstruation and promotes further development of the fetus.
Zygote implantation during natural conception and IVF
As a result of the fusion of a sperm and an egg, a zygote is formed. This is the one-cell stage of the embryo's existence, which lasts 26–30 hours. Then, as a result of mitotic division, the zygote begins to fragment. By the 4th day of pregnancy, the embryo consists of 12–16 cells, and by the 5th day it already consists of 30. At this stage of development, it is called a blastocyst.
At what time does the blastocyst attach to the uterine wall? During the first 5–6 days, the embryo moves along the fallopian tube and descends into the uterine cavity. During this time, progesterone, which is secreted by the corpus luteum, manages to prepare the endometrium of the uterus for implantation of the fertilized egg - it becomes more loose. The cells of the surface layer of the blastocyst - the trophoblast - throw out finger-like processes and cling to the endometrium. This is how the embryo is implanted.
Implantation during in vitro fertilization is carried out differently and is most often late. The transfer of a fertilized egg is done 3 or 5 days after the fusion of gametes. Due to this late transfer, the process of implantation of the blastocyst into the uterine wall is delayed. That is why, after the transfer of IVF embryos, late implantation of the embryo occurs. In this case, there are usually no symptoms such as spotting or implantation bleeding.
Symptoms
One of the most significant stages of pregnancy is embryo implantation. This is explained by the fact that a fertilized egg is perceived by the female body as a foreign object, because half of its genes are from the father and in some cases the uterus tends to reject the embryo. After the sperm penetrates the egg, it is covered with a special protective film, which it preserves until it enters the uterus. Having reached its destination, the fertilized egg separates from the protective membrane and attaches to the uterine wall.
During this period, signs are observed that indicate success. Doctors divide them into objective and subjective.
How to understand that the embryo has attached to the wall of the uterus?
Are there certain signs of implantation of the fertilized egg into the endometrium? Despite the fact that this stage of gestation may be asymptomatic, some women, based on certain signs, can determine that they are pregnant even before their period is missed. The process of embryo implantation is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- bloody issues;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- change in basal temperature.
Bloody discharge not of a menstrual nature
Approximately 7 days after unprotected intimate contact, a woman notices spotting red-brown discharge on her underwear. Even before the delay of menstruation, this symptom indicates that fertilization has occurred and the implantation of the blastocyst has been successful.
The nature of the discharge during embryo implantation:
- scanty, spotting bleeding;
- last no more than 48 hours;
- color of varying intensity - from pink to brown;
- There is no unpleasant odor.
Why is the attachment of the embryo to the uterus accompanied by bloody smears? This is due to the fact that during the implantation of the blastocyst into the surface layer of the uterus, the smallest capillaries of the endometrium are injured. There is no need to worry, microtraumas heal very quickly.
Not all women experience implantation bleeding, but this does not mean that implantation of the fertilized egg did not take place. Women who have gone through the IVF procedure eagerly await these signs, but ultrasound diagnostics can more accurately determine whether the embryo has taken root.
Basal temperature
Another symptom of implantation of the fertilized egg is changes in basal temperature. Basal is the temperature of the body in a state of complete calm. It can be used to track ovulation. Basal temperature is measured immediately after waking up; women are advised to keep the thermometer by the bed so as not to get out of bed to get it. When the value increases by 0.2–0.4 degrees, the woman ovulates; this is the most favorable period for sexual intercourse if the couple wants to conceive a child.
The same changes occur at the time of implantation of a fertilized egg into the endometrium. The thermometer readings are 37.0–37.3°C. Typically, a woman does not feel unwell, as with a fever during a cold, because the body temperature quickly returns to normal.
Nausea, weakness, nagging pain in the lower abdomen
Some women are very sensitive. They feel the moment the follicle ruptures, when the egg comes out of it, and they feel the separation of the endometrial elements. It’s the same with the attachment of the blastocyst - the expectant mother physically feels how this happens.
Similar sensations during embryo implantation can manifest themselves in the form of aching, pulling pain in the lower abdomen, closer to the pubis. Some people note that they begin to pull in the lower back on the sides.
Typically, toxicosis appears later, but despite the fact that there are general norms for the course of gestation, each woman experiences pregnancy with its own individual characteristics. That is why, immediately after fertilization, a pregnant woman will feel weak, drowsy, and lethargic. Some people begin to feel sick in the morning, and their taste preferences change.
Mood swings
With the onset of pregnancy, the hormonal levels in a woman's body change. After ovulation, progesterone begins to enter the blood, the concentration of which does not decrease after 2 weeks, as during the normal menstrual cycle, but continues to increase. After implantation of the embryo, the chorion begins to produce human chorionic gonadotropin. Hormones affect all systems of the body, including the central nervous system, which affects the emotional state of a woman.
In the morning, a pregnant woman is in a joyful and elevated mood, which for no apparent reason gives way to anger and irritability, and in the evening she becomes whiny and sad. Such sudden mood changes can accompany a woman throughout her entire gestation, but may also go away after she adapts to her new state.
Implantation process
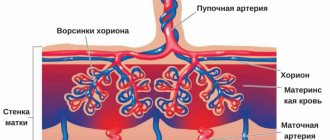
Even before fertilization occurs, literally from the first day of the cycle, the processes of preparation for the development of a possible pregnancy began in the uterus. The endometrium, which lines the inside of the uterus, begins to grow. If conception does not occur, the endometrial cells will leave her with menstrual flow. But if pregnancy occurs, the endometrium will play an important role in attaching the embryo to the uterus: implantation is both physical and chemical contact between the endometrium and the blastocyst. Implantation is the process of attachment of an embryo to the inner wall of the uterus.
Twelve-day human blastocyst
The outside of the blastocyst consists of special cells - trophoblast, and the internal cells are called embryoblast. The top of the blastocyst is covered by a membrane called hatching. By the time of implantation, the blastocyst resets hatching, and the trophoblast throws out processes, with the help of which it will be more convenient and reliable to plunge into the endometrial layer.
This is how the egg attaches to the uterus, and the endometrium, which nourishes it, continues to grow, surrounding the egg on all sides at the same time. The trophoblast begins to perform a new function - to produce a special pregnancy hormone, hCG, and from now on, pregnancy can be confirmed by a blood test, and a little later hCG will appear in the urine, then pregnancy will be confirmed using a pharmacy test strip.
When will the pregnancy test show?
All existing pregnancy tests react to the content of hCG in the urine, which begins to be secreted only after the implantation of the fertilized egg. Previously, it is pointless to conduct home tests; they will give false results.
How long is it better to wait before the test and on what day can it be done? A week after unprotected coitus, it is too early to do the test, because the concentration of hCG will not be sufficient to be detected by reagents. Depending on the type of test, it should be done 2-3 days before the expected delay or immediately after it.
There are several types of pregnancy tests:
- Stripes. The cheapest and most accessible test, at the same time it is one of the most unreliable. However, this does not mean that the strip gives false results; the probability of error is only 4–5%. It has low sensitivity; in order for the strip to detect hCG in the urine, the hormone concentration must be at least 20 mIU/ml, which is achieved 2–3 weeks after sexual intercourse.
- Tablets. This test consists of a cassette with a urinal hole and a window on which the results are displayed, and a pipette for collecting urine. This analysis is close to laboratory ones and detects the hormone at a concentration of 15 mIU/ml.
- Electronic device. It is considered the most accurate method of testing pregnancy at home. Susceptibility – 10–15 mIU/ml. It is allowed to carry out the analysis 10 days after intimate contact, but the more time passes between coitus and the test, the higher its accuracy.
Increase in hCG level after egg implantation by day (table)
| Term | HCG level, mIU/l |
| 1-2 weeks | |
| 2-3 weeks | |
| 3-4 weeks | |
| 4-5 weeks | |
| 5-6 weeks | |
| 6-7 weeks | |
| 7-11 weeks | |
| 11-16 weeks | |
| 16-21 weeks | |
| 21-39 weeks |
What can prevent egg implantation?
There are times when fertilization has occurred, but pregnancy has not occurred. There are reasons for this.
The most common cause is the presence of chromosomal abnormalities in the embryo. The inferiority of the fertilized egg is identified by the woman’s body and then simply rejects it.
Other reasons for this condition are the poor condition of the endometrium - its insufficient thickness and the absence of secretory transformations that are necessary for normal implantation and nutrition of the embryo. This can happen if there is insufficiency of the progesterone component and a decrease in the level of progesterone in a woman’s body due to:
- endometrial polyps;
- hyperplasia;
- tumors that deform the uterine cavity (submucous myomatous formations).
Sex and egg implantation
Regular sexual activity, if it is not accompanied by any intricate positions and excessive physical activity, cannot harm the physiological implantation of the embryo, therefore sexual intercourse after ovulation is not prohibited.
If the course of pregnancy is compromised by any factors, for example, insufficiency of progesterone in the body, then sex, causing the release of oxytocin and uterine tone, can cause the threat of miscarriage. To be fair, it should be noted that the same condition can be caused by a regular trip to the store or a trip on public transport.
Signs of failed egg implantation
The consequence of unsuccessful embryo attachment may be:
- appearance during menstruation;
- a negative pregnancy test, confirmed by a biochemical determination of the level of hCG in the woman’s blood, the levels of which will be lower than necessary for pregnancy;
- lack of visualization of the fertilized egg in the uterus during ultrasound examination.
What are the consequences of unsuccessful implantation?
The result of unsuccessful implantation is the absence of pregnancy. This can cause severe psychological stress for a woman, which affects the regulation of the ovarian-menstrual cycle, which subsequently interferes with the onset of future pregnancies. If the implantation process is unsuccessful, it is necessary to contact qualified specialists to identify the cause and subsequently correct it.
How to increase the chances of successful egg implantation?
- Reducing physical activity, leveling out excessive physical activity.
- Refusal of procedures that have hyperthermic effects (visiting saunas, baths).
- Maintaining psychological peace.
- Long walks, accompanied by positive emotions and increased oxygen supply.
- Maintaining a balanced diet.
- Refusal to drink alcohol and smoke.
- Compliance with the work and rest regime.
Why might an embryo fail to implant in the uterus?
Some women encounter a problem when fertilization itself occurs successfully, but the embryo cannot consolidate in the uterus and is brought out. Reasons why the embryo does not attach:
- Hormonal imbalance. For attachment to be successful, a sufficient amount of progesterone must be produced. It prepares the uterus to receive the baby and reduces the immune response to a foreign organism so that the mother’s body does not reject the embryo. When there is not enough progesterone, conditions for attachment are not created, and the embryo comes out. The cause may be insufficiency of the corpus luteum or its absence. This condition is treated with hormonal therapy, such as Utrozhestan or Duphaston.
- Endometrial changes. It happens that the embryo simply does not find a suitable place to implant in the uterus, because the surface of the endometrium is scarred. This condition of the endometrium can be a consequence of abortion with curettage, surgery on the uterus, inflammatory or infectious diseases. Late implantation at the os of the uterus can be a consequence of such pathologies.
- Tumor processes. New growths in the uterus - polyps, fibroids, fibroids - prevent the blastocyst from gaining a foothold in the cavity.
- Genetic abnormalities. Due to mutations in germ cells during fertilization, a non-viable zygote is formed. For example, two sperm get inside at the same time, or one of the gametes does not carry genetic information. Such an embryo does not develop, cannot attach, and miscarriage occurs before its implantation.
After the IVF procedure, doctors carefully monitor whether the embryos have taken root. At this stage of medical development, not all embryos take root, so patients undergo artificial insemination again.
Often, pre-implantation miscarriages are asymptomatic and the woman may not realize she was pregnant. Typically, such patients turn to gynecologists with the problem of infertility, not knowing that the problem is not conception, but the ability to implant. The doctor can help solve the problem by choosing the appropriate treatment method.
Loading…
Share with friends!
Other symptoms
It should be noted that body temperature does not always increase when the embryo implants into the uterus. Sometimes it may remain normal or even be slightly reduced. Also, not all women experience spotting. As for unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen, almost every representative of the fair sex notes this symptom during embryo implantation. Moreover, these feelings can vary significantly in nature and intensity.
As a rule, during such a moment, women can observe spotting, which is much lighter in comparison with menstruation, and is also quite scanty. If you experience heavy bleeding accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, you should immediately consult a doctor. After all, this condition may indicate termination of pregnancy.
It should be noted that during implantation, so-called “natural selection” occurs. In other words, incapable of development and defective fertilized eggs are rejected by the mother's body, preventing the life of embryos with any disorders or pathologies.
How do pinopodia affect implantation?
Pinopodia are formations on the endometrium that facilitate the attachment of the embryo. They are absent throughout almost the entire monthly cycle. They appear in the implantation window: the mucosa is then most prepared for the implantation of a fertilized embryo.
The appearance of pinopodia depends on the presence of estrogens in the blood. They contribute to the fact that the mucous membrane begins to thicken, and a significant number of glandular formations develop in it. After ovulation, increased production of progesterone occurs. It is under the influence of this important hormone that the process of formation of pinopodia occurs.
Medical studies have shown that pinopodia take approximately 20 to 23 days to form. At the same time, attachment of the oocyte into the cavity occurs.