- 1. Removal methods
- 2. How to remove a uterine cyst: general conditions
The uterus consists of the fundus, body and cervix. Cysts are most often formed on the outer and inner surface of the cervix as a result of blockage of the gland ducts, injuries, and hormonal imbalances. On the body and bottom, neoplasms form less frequently. A cervical cyst is removed if it:
- causes discomfort and pain;
- grows quickly, new bubbles appear;
- puts pressure on the bladder or intestines;
- blocks the cervical canal (cervical) and causes infertility, and the woman wants to get pregnant;
- filled with purulent contents or surrounded by inflamed tissue;
- A biopsy showed the presence of cells prone to degeneration and oncology.
The cyst on the cervix itself is considered a relatively harmless formation. It is removed only when there are aggravating circumstances.
Endometrioid cyst of the cervix
Endometrial cysts are quite common in women, so it is necessary to explain in detail what they are.
A benign neoplasm is formed from the epithelium of the mucous membrane of the internal cavity of the uterus. Most often it develops as a result of changes in the formation of the endometrium or disruption of the outflow of secretory fluid from the glandular layer of the organ.
Typically, the cyst is hormone dependent and affects a number of anatomical structures at once. During its formation, their own mucous membrane begins to react to the functioning of the menstrual cycle. When menstruation arrives, they begin to bleed. Inflammation occurs and infection may occur. Such processes sometimes lead to the occurrence of adhesions and scar changes.
The greatest danger of the disease is the onset of infertility. In general, endometrial hyperplasia is a rather complex pathology, accompanied by a wide variety of signs and symptoms.
The essence of the disease, its causes and prevalence
The disease, as a rule, is characterized by a very specific clinical picture.
Most often it includes:
- severe pain symptom;
- constant cycle disorders;
- bloody marks during the intermenstrual period;
- discomfort during intimate relationships;
- uncharacteristic discharge;
- slight hyperthermia;
- discomfort in the anus;
- an increase in the volume of discharge during critical days, etc.
The main factors that most often lead to the development of cysts are multiple pregnancies, difficult childbirth, and chronic inflammatory processes. Its occurrence is often also promoted by endometriosis, pathologies of the pelvic organs, and benign neoplasms.
Various uterine injuries, artificial termination of pregnancy or invasive procedures have a provoking effect.
The cause of the development of the disease is sometimes hormonal imbalance, lack of progesterone, or a change in the amount of cervical mucus.
Promiscuous sex life, STIs, and chromosomal heredity often lead to the appearance of cysts.
The risk group also includes people suffering from frequent hormonal disorders, chronic endocrine disorders, and those who have approached the period preceding menopause.
Endometrioid cysts are found in patients who have used IUDs for a long time, have repeatedly undergone artificial termination of pregnancy, have had polyps removed, have undergone surgery on the gynecological organs, and have also become victims of sexually transmitted infections.
What diagnostic methods are used
It must be said that these neoplasms in the cervical area are less common than in other parts of the uterus. This feature is explained by the greater homogeneity of the endometrium of the corresponding part of the organ than the ovaries.
Most often the disease is diagnosed when passing:
- Hysteroscopy.
- Colposcopy.
- Ultrasound scanning.
- Preventive examinations.
- X-rays.
- Cytological or histological analysis.
- Palpation of the uterus.
- Regular gynecological examinations.
A combination of different procedures can effectively identify single or multiple fluid-filled lesions. Usually several cysts occur, since the secretory activity of a number of glandular structures is disrupted. They are localized in one zone or scattered over the entire surface.
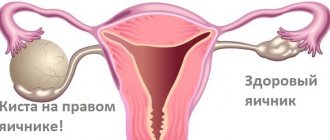
Ultrasound diagnosis of endometrioid cyst of the cervix
In a photo taken using ultrasound equipment, signs of endometriosis can be distinguished.
The uterus looks enlarged, spherical in shape. Its echogenicity is enhanced. The inner surface is thickened and looks heterogeneous due to the large number of pathological foci. The vascular pattern is significantly enhanced.
A cervical cyst on ultrasound is visible as a black spot of varying localization. Most often, the cyst is found in the area of the cervical canal, but sometimes it is also located in the organ itself. It resembles a sphere and is filled with liquid of various structures.
The procedure allows you to confidently diagnose single or multiple anechoic inclusions in organ tissue. However, hyperechoic foci of heterogeneous structure are sometimes encountered. They look uniform inside. There is no vascular pattern.
If there are various fluid inclusions in the cervix, then additional differential diagnosis is always required. Typically, such situations require constant ultrasound monitoring in order to have an idea of the progression of the disease.
Sometimes the neoplasms merge together to form quite large cavities. The vascular pattern is usually not visible.
Sonography of an ovarian cyst most often reveals a unilateral location of the cavity with heterogeneous fluid inside. It is usually localized behind the uterus. In the picture we can distinguish the organ itself, the outlines of the bladder and the pathological focus.
The inclusion looks like an echo-positive spherical or ellipsoidal formation ranging in size from four to ten centimeters in volume, with an uneven, smooth capsule. The presence of an adhesive process is often encountered.
Then ultrasound examination becomes one of the main and most informative methods of its diagnosis.
Cervical cyst is a disease that occurs for many reasons. Two types of cysts can form in the cervical area: retention cysts (Nabothian cysts) and endometriotic cysts. Embryonic cyst of the cervix in ICD-10 has the code Q51.6, retention cyst - 88.8 (other specified non-inflammatory diseases of the cervix). For the treatment of cervical cysts, the Yusupov Hospital has created the necessary conditions:
- Chambers with a European level of comfort;
- Qualified personnel;
- The latest diagnostic methods to determine the cause of the disease;
- Individual approach to the treatment of each patient.
Cervical cyst - what is it? Photos can be seen on the Internet. A Nabothian cyst is an enlarged cervical gland with a blocked excretory duct, inside which mucous contents accumulate. Retention formations of the cervix occur in 10-15% of women of reproductive age, who often have a history of childbirth. An endometrioid cyst is a consequence of endometriosis, which affects the vaginal part of the cervix. They are often combined with endometrioid heterotopias of other localizations.
In the presence of a nabothian cyst, cavitary formations form on the cervix (vesicles on the surface usually from 2 to 15 mm in diameter, filled with mucus or inflammatory contents), which are clearly visible during a gynecological examination. They do not transform into a malignant tumor and do not affect hormonal balance, pregnancy or fetal development. A cervical cyst does not provoke the appearance of similar formations in other organs and does not affect menstruation.
The danger comes from bacteria that accumulate in it. They cause repeated inflammatory processes:
- Cervix (endocervicitis, cervicitis);
- Vagina (colpitis);
- Uterine mucosa (endometritis);
- Ovaries and tubes (oophoritis, salpingitis, salpingoophoritis).
Chronic inflammatory process leads to ectopic pregnancy and infertility. Large retention cysts of the cervical stroma (more than 1 cm in diameter) can block the cervical canal, which is a mechanical cause of infertility. Gynecologists at the Yusupov Hospital use innovative methods for treating cervical cysts and take an individual approach to the choice of surgical intervention for each patient.
Diagnostics
The following methods are used to diagnose a cyst:
- Ultrasound is always prescribed, although it is really informative only for formations of a significant size, while small ones are not visible;
Cyst on ultrasound - Hysteroscopy is informative for a certain location of the cysts, that is, not always, since some parts of the uterus may not be visible during it;
- Laparoscopy has the same degree of information content as laparoscopy and the same features;
- Examination with mirrors is sometimes quite informative; with the help of it alone, cysts on the vaginal part of the cervix can be diagnosed;
- Cytology and tissue biopsy are necessary in order to exclude the possibility of developing an oncological process, because, despite the fact that cases of oncological degeneration of a cyst are very rare, all neoplasms are subject to such testing;
- A smear from the uterus to determine the causative agent of endometritis in order to prescribe the most effective treatment;
- Vaginal smear for the same purposes;
- Bacteriological culture, etc. to determine concomitant infections, viruses and fungi.
This helps not only to document the fact of a cyst, but also to identify the causative agent of endometritis and eliminate the possibility of an oncological process.
Types and symptoms of cervical cysts
There are single and multiple cervical cysts. Single cysts are formed when there is a small defect and disruption of the outflow of secretions from one gland. Multiple retention cysts of the cervix are more common, since in most cases the outflow of secretions from several glands is blocked at once. Such cysts can be located throughout the cervix or be concentrated in one place.
Cysts on the cervix - is it dangerous? The danger of cervical cysts is that they are often asymptomatic and are diagnosed only when complications occur. Small cysts of the endocervix of the cervix are detected during a preventive gynecological examination or during an ultrasound examination, which is performed for another pathology. Since nabothian cysts of the cervix are not proliferative, they do not disrupt the normal ovario-menstrual cycle and do not affect the general condition of the woman.
Symptoms of the disease appear in the presence of multiple or large cysts. The first signs of a cervical cyst may be discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse, as well as the discharge of bloody or purulent contents from the vagina when the cysts become infected. These signs are not always expressed. They depend on the size and number of tumors. When a cyst ruptures, light-colored discharge may appear, which women usually do not pay attention to.
If the integrity of the epithelium is violated and an infectious process is added, the following symptoms are added to the clinical picture of the disease:
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- Purulent vaginal discharge;
- Systemic reactions in the form of a rise in temperature and severe intoxication syndrome.
If a cyst is detected on the cervix, why is it dangerous? Sometimes cervical cysts are diagnosed during pregnancy. Then postpartum septic complications may occur due to infection of the cyst. Therefore, when a nabothian cyst is diagnosed in a pregnant woman, it is removed using minimally invasive methods. Gynecologists at the Yusupov Hospital individually select a treatment method that has minimal impact on the condition of the fetus and the birth canal. When a cervical cyst develops in older women, further metaplasia of the cervical epithelium may develop as functional changes in the columnar epithelium occur. For this reason, when a cervical cyst is detected, gynecologists recommend removing it without waiting for complications.
What kind of cyst is this?
Such cysts are formed from endometrial cells, the tissue lining the inside of the uterus. Each menstrual cycle, this layer gradually grows, preparing to receive a fertilized egg. Without waiting, at the end of the cycle it is rejected and removed from the uterus. Menstruation begins.
But these cells are insidious. They are extremely hardy and can accidentally take root on another organ, for example, the cervix. In this case, these same endometrioid formations appear on it. This is only a special case of endometriosis and not the most common, but more than real, especially in the presence of predisposing factors.
What factors can trigger the appearance of a cyst?
Until now, doctors cannot answer this question with confidence. But a number of factors that increase the likelihood of its occurrence have been known for a long time. First of all, these include everything that can disrupt the integrity of the mucous membrane of the cervix. Endometrial cells can invade this weak spot. Therefore, it is often fixed after surgery or manipulation affecting this organ. These include:
- Natural childbirth
- Abortion
- Diagnostic curettage
- Installation or removal of a fallopian device
- Erosion, true and false (ectopia)
- Removal of any cysts and polyps from the cervix
- Taking a biopsy.
But these are not all the causes of endometriosis; there are others that increase the activity of endometrial cells:
- Endocrine disorders
- Obesity
- Age 30-40 years
- Excessive consumption of alcohol and caffeine
- Genetic predisposition
- Personal history of endometriosis.
And the more factors coincide, the higher the likelihood of this disease occurring. Fortunately, it is almost always diagnosed on time.
How do such cysts manifest themselves?
Endometriosis itself is an extremely diverse disease. Endometrial cells can take root in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervical canal, abdominal cavity, rectum and many other organs. And in each case there will be its own specific signs that tell the doctor where to look for the cyst. And in the case of a location on the cervix, you can expect the following:
- Pain or simply discomfort during sexual intercourse
- Light extramenstrual bleeding
- Longer menstruation.
The listed signs are already enough to visit a doctor, because they indicate the presence of gynecological diseases. But such cysts rarely appear only in one place. Therefore, along with the above, many other symptoms can be expected.
Examination of patients with cervical cysts
Nabothian cysts of the cervix are most often discovered accidentally or when complications occur. A simple consultation with a gynecologist with a speculum examination of the cervix does not always make it possible to establish a diagnosis, but changes in the cervix often suggest the development of cystic formations. Then, to confirm the diagnosis, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital conduct additional research methods.
Ultrasound examination using cavity sensors - cervical cysts are defined as anechoic inclusions of a round or ovoid shape. They can be either single or multiple. Most often, cystic formations are located in the endocervix, but cervical stromal cysts are also found. The internal structure of cysts is often homogeneous and anechoic, but sometimes heterogeneous finely dispersed or hyperechoic contents with uneven contours are found. This is due to the fact that cysts occur when the outflow of secretions from glands located not only in the mucous membrane of the cervical canal, but also in the muscle layer is disrupted. When the cyst is located cervically, the internal contents of the cysts do not contain vessels. There is no enhancement of the vascular pattern in the adjacent stroma.
Colposcopy is an examination of the cervix with a special device that has a magnifying power of several tens of times. This examination allows you to examine the cervix and see any changes in the epithelium. The columnar epithelium looks like a network of cells with pronounced glands, having the appearance of a papillary structure. If the outflow of gland secretions is disrupted, blockage of these glands and areas of their expansion can be seen. If there is concomitant erosion or other damage, they are also detected during colposcopy.
A smear of the cervical canal can exclude inflammatory diseases and metaplasia of the cervical epithelium. Histological examination of the smear shows the expansion of the gland and its deformation with the accumulation of secretions. In general clinical analysis of blood, urine and bacterial culture from the vagina, there are no characteristic changes.
Gynecologists at the Yusupov Hospital carry out a differential diagnosis of Nabotian cyst with diseases that are accompanied by damage to the epithelium of the cervix. Externally, cysts may resemble polyps, but upon ultrasound examination, the polyp has a dense structure, in contrast to the cavity of the cyst. Differential diagnosis of nabothian cyst with endometrioid heteropias is carried out on the basis of visual differences and histological examination of the material.
What is pathology
Nabothian, or retention, cyst of the cervix is formed due to blockage of the excretory ducts of the glands. As the secretion continues to be produced, the gradual filling of the blocked canal leads to its stretching. As a result, the iron begins to protrude onto the surface of the mucous membrane.
A nabothian cyst looks like a follicle (therefore sometimes called follicular) or a vesicle filled with transparent contents, several millimeters in diameter. In rare cases, the formation reaches a size of two centimeters. There are single and multiple cysts; the tactics of observation and treatment depend on their number.
Nabothian cysts look like blisters filled with fluid.
Nabothian cysts never become malignant (they do not turn into a cancerous tumor). But their long-term existence helps maintain the inflammatory process in the epithelium of the cervix.
Such formations differ from true cysts:
- lack of a capsule. In a true formation, the capsule is thick, consisting of several layers capable of cell division. A retention cyst has only a thin shell;
- growth characteristics. A true cyst enlarges due to the growth of the capsule, while a nabothian cyst enlarges due to the accumulation of fluid that stretches the membrane;
- asymptomatic;
- plurality. A single nabothian cyst is a very rare occurrence.
Treatment of cervical cysts
Gynecologists at the Yusupov Hospital take an individual approach to the choice of management tactics for patients with nabothian cysts. If a cyst is found in a woman under 45 years of age, surgical intervention is required. If there is an asymptomatic cervical cyst measuring less than one centimeter in diameter, a wait-and-see approach is followed. Such cysts do not transform into a malignant tumor, do not grow and do not cause discomfort.
To relieve swelling, pain and other signs of inflammation, patients are prescribed Dicloberl vaginal suppositories. Sometimes treatment is carried out with ichthyol ointment. This method has been used for a long time, but it is not always effective. Tampons are moistened in ichthyol ointment and placed in the vagina for 10-20 minutes. They have anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effects. In the presence of accompanying microflora, ichthyol destroys microorganisms and prevents septic complications. Conservative treatment methods are used as symptomatic therapy, which affects the development of the cyst. If a cervical cyst is accompanied by severe symptoms, gynecologists at the Yusupov Hospital perform surgery with removal of the lesion and further symptomatic therapy.
Consequences of wait-and-see tactics in the presence of a cyst
Uterine cysts of endometrioid origin almost never degenerate into malignant formations and do not pose a danger to the partner. A small cyst does not interfere with sexual activity and is practically painless. But you should know that cysts do not resolve on their own. As they continue to grow, they can partially deform organs and also create conditions for favorable growth of bacteria. It should be noted that in women of childbearing age, the chances of becoming pregnant decrease in proportion to the duration of the disease.
Is it possible to get pregnant and carry a child to term with such a cyst?
Genital endometriosis in combination with pregnancy is not a rare phenomenon. If it occurs in the presence of a small cyst, then you should not worry. Pregnancy creates a hormonal background in which endometriosis does not progress. But for conception itself, endometriosis can present a certain obstacle. Factors preventing conception:
- An existing hormonal imbalance that contributed to the appearance of the cyst.
- Tubal adhesions, which are common in this disease, prevent the capture and advancement of the egg. They require surgical treatment (excision).
- Obstacles to implantation due to pronounced changes in the uterine mucosa, as well as disturbances in the trophism of an already attached fertilized egg.
- Inflammatory diseases caused by the cyclic transformation of endometriosis foci.
- Reduction of ovarian reserve (loss of a certain number of follicles due to a constant inflammatory process).
- Impaired maturation and release of the egg from the follicle.
Endometrioid cyst of the cervix
Endometriosis is a tumor pathological process in which benign growth of tissue occurs outside the uterine cavity, which is similar in morphological and functional properties to the endometrium. Clinical manifestations of endometriosis depend on the localization of the process, the degree of damage to the genital and adjacent organs, and the individual pain threshold. The following main symptoms of genital endometriosis are distinguished:
- Dysmenorrhea (menstrual irregularities), mainly algomenorrhea - painful menstruation;
- Pain syndrome of varying severity;
- Dyspareunia (pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse).
When an endometrioid cyst is located on the cervix, infertility develops.
At the Yusupov Hospital, examination of patients with endometriosis is carried out in the following scope and sequence:
- Standard clinical and gynecological examination, including rectovaginal examination;
- Extended colposcopy;
- Oncocytological examination;
- Ultrasound of the pelvis and kidneys;
- Study of tumor markers (CA-125, CEA, MCA).
The Yusupov Hospital uses a “pragmatic”, that is, an individual approach to the treatment of each patient suffering from endometriosis. Doctors develop optimal diagnostic and treatment programs. The goal of treatment is determined by the patient’s main problems (elimination of pain or bleeding, restoration of fertility or improvement of quality of life).
According to the recommendations of the American Association for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), endometriosis is considered a chronic disease that requires the development of a long-term management plan for the patient with the maximum use of drug therapy to avoid repeated surgical interventions. To destroy the endometrioid cyst of the cervix, various types of energy are used during operations - electric, cold, laser, argon beam. Drug therapy is used as independent treatment and to prevent relapses after surgery. At the Yusupov Hospital, patients with endometrioid cysts of the cervix are prescribed modern medications registered in the Russian Federation. They are highly effective and have a minimal range of side effects. To get advice about cervical cysts, call the hospital contact center.
Cysts in the female reproductive system form quite often, which is associated with the functioning and structure of the glands and endometrium, and the characteristics of hormonal regulation in the female body. Most often, such neoplasms pose a significant health hazard and can affect reproductive function, which is why they require timely and immediate treatment. This article will talk about such a variety as endometrioid cyst of the cervix. What is it, how to recognize such a formation and get rid of it in a timely manner before unpleasant consequences occur?
Types of therapy
The method of treating a cyst is determined by many combined factors, starting with the patient’s age, location of the formation, stage of the disease, and others. Basic methods: In the initial stage of the disease in young patients, it makes sense to use drug treatment using hormones and anti-inflammatory drugs.
The following are used as hormonal medications:
- COCs (combined estrogen-gestagen-containing drugs) are effective only in the initial stages of the disease with local foci;
- Synthetic progestins that effectively reduce the level of estrogen, which contributes to the progression of the disease.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists are the most powerful drugs that can inhibit the development of endometriosis, but due to the mass of side effects they are used as an emergency measure. If hormone therapy has no effect, surgical treatment is performed.
Surgical removal:
- Minimally invasive (if the cyst is located on the cervix). Produced by electrocoagulation. It is a safe and effective treatment method. After surgery, additional hormone therapy is indicated to prevent recurrence of the cyst.
- Laparoscopic removal (up to stage 2-3 of the disease).
- Embolization of vessels by introducing special particles, which, by blocking the lumen of the vessel feeding the pathological formation, help to reduce it.
- Removal of the inner lining of the uterus using ablation. In this case, the deep layers of the endometrium are destroyed. This type of treatment is effective when the formation does not penetrate too deeply into the wall of the uterus.
- Extirpation or complete removal of the uterus along with the ovaries (in the most advanced cases).
Methods for treating endometrioid cysts with folk remedies
The main methods of alternative medicine are herbal medicine and treatment with leeches. Hirudotherapy is effective for all female diseases accompanied by hormonal imbalance. The saliva of this animal contains more than 150 biologically active substances that have a complex healing effect on the body. Recipes for treating cysts with herbs have been tested by more than one generation of women .
There are several most effective recipes:
- Tincture of acacia flowers. 250 grams of fresh medicinal raw materials are infused in half a liter of vodka. Take two tablespoons three times a day.
- Fresh burdock juice. The leaves should be selected small and juicy. The squeezed juice is stored in a glass container in the refrigerator. Take the same as in the previous recipe.
- Infusion of walnut partitions. Two-thirds of a glass of leaves are boiled in a liter of water and left for about a week. Take small sips throughout the day. This infusion should be enough for the entire 10-day course (approximately 100 grams per day).
- Raisin tincture. Take seedless raisins (about 300 grams) for half a liter of vodka. Infuse and take 30 grams for at least 14 days continuously.
- Healing candles with honey. Onions are infused with honey for half a day. Insert into the vagina at night. Duration of treatment is 10 days.
- Clover decoction. Take 3 dry plants per liter jar of boiling water. Drink during the day. Duration of treatment is 60 days.
- Aloe juice tampons. Cotton balls, moistened with juice and wrapped in gauze, are inserted deep inside the vagina. Course 2 weeks.
- Baths with a decoction of celandine. A glass of dry herbs to 4 liters of boiling water. The broth is poured into a warm bath. Treatments last 20 minutes per cycle.
Important! Traditional methods of treatment are carried out after consultation with a gynecologist. There are a lot of concomitant diseases of the genital organs, for which the use of certain herbal components is excluded.
Definition
An endometrioid cyst of the uterus is a benign neoplasm, which is a kind of capsule with dense walls that has a cavity inside. This cavity is filled with one or another liquid separable. This can be pus, serous fluid, hemorrhagic discharge, any type of gland secretions, etc. The cyst is located in the thickness of the tissue and can grow both towards the surface (into the lumen of the organ) and inward (into the thickness of the organ tissue). It is for cysts of the reproductive system in general, and endometrioid cysts in particular, that they grow into the lumen of the organ.
What features does the endometrioid cyst of the uterus have? Its peculiarity is that it occurs exclusively against the background of an inflammatory process in the uterus - endometritis. Endometritis is a process of inflammation of the endometrium of the uterus under the influence of infectious agents, as a result of the activity of bacteria. Such a cyst occurs strictly in the place where the activity of these bacteria actively occurs.
That is, if a neoplasm appears with endometritis, but in an area of the uterine wall that is not affected by it, then, most likely, such a cyst is not endometrioid and has other causes of origin.
How do Nabothian cysts form?
The content of the article
The cause of these cysts is a blockage of the glands of the cervix (endocervix), which interferes with the outflow of fluid. As a result, mucus accumulates, forming bubbles filled with liquid contents. When several glandular ducts are blocked, multiple cystic lesions occur, making the cervix lumpy.
Violation of the outflow from the glands is provoked by:
- Inflammatory processes in the uterus and vagina, leading to the destruction of the squamous epithelium of the cervix and its replacement with cylindrical epithelium, which normally should not be there. Tissue cells that are not intended to come into contact with the moist, acidic environment of the vagina become irritated and inflamed. In them, the outflow of secretions is disrupted, leading to the appearance of cysts.
- Childbirth and surgical interventions accompanied by cervical trauma. The epithelium grows together incorrectly, and tissue that should remain inside ends up outside.
- Cervical erosion, which has almost the same mechanism of occurrence. Often these two diseases are combined. Sometimes cysts form after treating erosion with outdated methods, for example, electrocoagulation or surgery. After radio wave treatment of erosion, such complications do not occur.
Causes
What are the reasons for this phenomenon, and what is the mechanism of development of this neoplasm in the reproductive system? During the activity of the pathological organism and the development of inflammation, blockage of the ducts of some glands in the endometrioid layer may occur. In this state, the secretion of the glands has nowhere to flow, and it accumulates near the duct. As a result, a cavity is formed filled with it, which, as the process develops, acquires fairly dense internal walls. At this stage, it is already a formed cyst, which grows more actively, the more actively the gland works, and the more secretions it produces.
What factors are predisposing, and in what cases does an endometrioid cyst of the uterus form especially often? A number of prerequisites have been identified:
- Hereditary predisposition associated with structural features of the ducts, for example, narrowed duct, fusion, etc.;
- Low tissue immunity due to inflammatory and/or infectious processes, trauma and surgical interventions, which increases the likelihood of developing endometritis;
- Hormonal imbalance of one type or another, which increases the amount of secretion, etc.;
- Frequent pregnancies, abortions, childbirth, miscarriages, as all this leads to a decrease in tissue immunity;
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules, neglect of barrier contraception when changing partners frequently - all this also increases the likelihood of developing an infectious-inflammatory process.
The disease develops with endometritis, regardless of how the patient acts and behaves. Sustainable and effective measures to prevent this phenomenon have not been developed. Although it is clear that the earlier treatment for endometritis is started, the lower the likelihood of developing a formation on the endometrium.
Symptoms
Endometrioid cysts of the cervix can manifest themselves in different ways. It forms a clinical picture, which can often be indistinguishable against the background of endometritis symptoms, therefore such a neoplasm is often diagnosed by chance. The following symptoms occur:
- Pain in the lower abdomen, periodic or constant;
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- Minor bleeding or blood in vaginal discharge;
- Increase in the number of discharges;
- Menstrual dysfunction.
Since the symptoms are quite obvious, patients consult a doctor in a timely manner and, often, significant growth and development of the cyst can be avoided. However, this is not true in the chronic course of the disease, when the symptoms are not so pronounced.
Treatment
Therapy for this type of cyst takes place in two stages. Both combined and surgical treatment are used. After completing a course of taking medications, the doctor selects the most optimal way to remove the tumor itself.
Conservative
Endometrioid cyst of the uterus cannot be treated directly with conservative methods. It will not go away with medication. But conservative treatment is prescribed in order to suppress the infectious process that caused endometritis. This is due to the fact that intervention to remove the tumor is impossible in the presence of a background inflammatory process, since there is a high risk of infection, as well as the reappearance of the cyst for the same reasons (relapse).
Conservative treatment of endometritis is carried out with broad-spectrum antibiotics, such as Metrogyl, Ceftriaxone. They are prescribed in a course of 5 to 10 days, depending on the degree of development of the process, in dosages calculated based on the patient’s weight (usually 250-1000 mg). At the same time, throughout the course of treatment, it is advisable to take non-steroidal drugs such as Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Diclofenac. They relieve not only inflammation, but also pain.
Also during this period, vitamin therapy and immunostimulating therapy can be carried out. Only after complete recovery from endometritis is treatment of the cyst possible.
Minimally invasive
Minimally invasive methods include, for example, cauterization (electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, chemical cauterization with drugs). They help when there is more or less easy access to the tumor. For example, this is how endometrioid cysts of the cervix are often treated. Also, this is feasible and effective only for small and single cysts.
In addition, radio wave, ultrasound and laser treatments are also considered minimally invasive methods. These methods are quite expensive and not widely used. Treatment with their help takes a long time, so it is used quite rarely.
Operational
Surgical treatment is carried out when the minimally invasive method is not effective enough or is not feasible. An invasive surgical intervention means any operation in which access to the uterus is carried out through a cavity incision. During such an intervention, the cyst itself or the uterus is completely removed (in women of the post-reproductive period, those who do not want to have children in the future) with a very large number of cysts.
Sometimes access can also be obtained laparoscopically or hysteroscopically. But these methods are also effective only for small diameters of the cyst and its location, when it is possible to gain access using this method.
Treatment and removal methods
Nabothian cysts rarely resolve on their own, so this pathology requires treatment. But it should be noted that for small tumors that do not show symptoms, experts recommend dynamic monitoring.
Drug treatment of nabothian cysts of the uterus is used only to relieve infectious inflammation and primary symptoms that bother the patient. After such exposure, large nodes are removed through surgery.
Surgery to remove nabothian cysts is performed using the following techniques:
- Diathermocoagulation, which involves cauterizing the affected area with an electric current. Various chemicals are also used for these purposes. The disadvantage of this procedure is the high probability of relapse of the disease.
- Cryodestruction (or removal using liquid nitrogen).
- Removal of a nabothian cyst using laser or radio wave technology.
Traditional methods and means of treatment for this disease are not effective. It is also necessary to take into account that some herbs contain substances that can accelerate the growth of nodes. That is why independent treatment of nabothian cysts of the cervix must be agreed with the attending physician.
Complications
What consequences and complications can the presence of such a cyst lead to?
- Its significant growth, which causes constant unpleasant symptoms, abdominal pain, bleeding, as a result of which anemia develops;
- An inflammatory process that can lead to peritonitis, sepsis, abscess and sometimes requires urgent surgical intervention to save the patient’s life;
- Deformation of the organ with a large size of the cyst or a significant number of them in the uterus;
- Infertility.
All these consequences can be quite severe. For this reason, when diagnosing such a tumor, doctors always recommend its removal as planned. Especially in cases where education is actively growing.
Abdominal intervention is prescribed quite rarely, as it is traumatic and has a long recovery period.
Pregnancy
If there is an endometrioid cyst of the uterus, then it is possible to become pregnant. But the likelihood of conception is significantly reduced, since in the presence of inflammation, the likelihood of the embryo attaching to the wall of the organ is quite low. Even if endometritis is completely cured, but the cyst remains, the likelihood of attachment to the wall of the fertilized egg is still reduced. In addition, when formations are localized in the cervical canal, a situation is possible when the formation blocks the lumen of the canal and sperm cannot penetrate the uterine cavity for fertilization.
But if pregnancy does occur, is it possible to carry it to term? In general, such cases are known, but this can be associated with a number of difficulties. For example, there is always the possibility of developing uterine hypertonicity, which can lead to miscarriage. In addition, there is a possibility that at some point the fetus will no longer receive enough nutrients, which is very dangerous at an early stage of its development and can lead to a frozen pregnancy. If endometritis has not been treated, there is a possibility that the inflammatory process will spread to the fetus, which will cause its death. The same danger is present if inflammation of the formation begins during pregnancy, which sometimes happens.
Symptoms
Most case reports confirm that while Nabothian cysts are small and not complicated by infection, they do not cause unpleasant symptoms. If their size increases, then the following are possible:
- weak nagging pain over the pubic area;
- discomfort during intimacy, sensation of a foreign object;
- heaviness, pressing pain during menstruation, prolonged periods.
This occurs in rare cases when the tubercles of the ovule grow over large areas of the mucous surface of the cervical canal, closing its lumen and preventing the natural easy outflow of menstrual blood from the uterus.
Do you use folk remedies?
Not really