Nowadays, it is common to encounter women, especially young ones, who suffer from infertility. None of them had early abortions, did not undergo any operations, where did infertility come from? The reason for the inability to get pregnant is often the problem of obstruction of the fallopian tubes. This pathology does not harm a woman’s health.
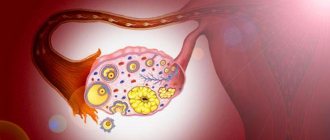
The fallopian tubes play a very important role in the process of fertilization. They help the fertilized egg reach the uterus, where further development of the embryo occurs.
Physiotherapeutic methods
Physiotherapy is part of a comprehensive treatment. Thanks to it, the effectiveness of drug treatment can be increased.
For this purpose, the following physiotherapeutic procedures can be used:
| Balneotherapy | Its purpose is to stimulate the immune system and combat functional disorders. It is recommended to visit sanatorium-resort areas with nitrogen-siliceous and hydrogen sulfide waters. |
| Electrophoresis | The procedure is carried out using electromagnetic fields with the introduction of Mg and Ca salts and enzyme preparations into the pelvic cavity. The procedure helps to enhance the effect of drug therapy. |
| Ultrasound massage | Ultrasonic waves are used for tissue micromassage. Thanks to the procedure, it is possible to stimulate blood circulation, soften adhesions, and reduce pain. |
| Electrical stimulation | It can be used from the 6th day of menstruation, its use is intended to improve the general condition of the patient. |
| Gynecological massage | It is carried out simultaneously with a course of drug treatment. This type of massage cannot be used in the acute phase of inflammation. The purpose of use is to normalize blood circulation and eliminate adhesions. |
Types of pathology
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes, or salpingitis, is classified into several types depending on the location of the formation of the pathology, its nature and the process of progression. Salpingitis can be:
- chronic;
- sharp;
- right - or left-handed;
- purulent in nature;
- occurring along with the development of oophoritis.
Development of acute salpingitis
This form of pathology begins with the penetration of infectious microflora into the cavity of the fallopian tubes against the background of a sharp drop in the level of the immune defense system. Most often, the formation of such a process occurs against the background of oophoritis, characterized as inflammation of the ovaries, or during an ectopic pregnancy.
The development of acute inflammatory reactions in the area of the fallopian tubes is characterized by the formation of pronounced symptoms, in the form of:
- a sharp increase in temperature indicators;
- weakness and malaise throughout the body;
- increased heart rate;
- the appearance of acute pain in the groin area;
- discharge of pathological vaginal secretions, which may be purulent, foamy or bloody, depending on the type of pathogen;
- violation of the functional ability of the urinary system of organs.
There may also be a decrease in the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract, manifested by stool disturbances and signs of diarrhea.
Development of chronic pathology
Salpingitis, which has a chronic nature of manifestation, is characterized by the formation of mild symptomatic signs and the preservation of satisfactory health. There is the appearance of scanty vaginal discharge and constant aching pain in the lower abdomen. Temperatures rarely exceed normal limits, but if this happens, they do not exceed 37.2 degrees.
This type of pathology is characterized by a wave-like course with alternating periods of relapse and exacerbation. Chronic salpingitis often provokes disturbances in the cyclicity and abundance of menstrual flow and has the highest likelihood of developing infertility.
Course of purulent salpingitis
The formation of a purulent form of salping pathology is preceded by the penetration of gonorrheal infectious microorganisms into the cavity of the uterine organ and tubes, which can occur against the background of:
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- premature surgical termination of pregnancy;
- using an expired intrauterine device.
The main signs of purulent inflammation of the fallopian tubes are the appearance of the following symptoms: chills, fever, severe pain in the lower abdomen.
Salpingo-oophoritis
The most common form of development of salpingitis is considered to be its formation in combination with oophoritis, that is, inflammation of the ovaries, which in medicine is referred to as salpingoophoritis.
Causes:
- decreased immunity;
- hypothermia;
- negative impact of frequent stressful situations.
Timely treatment of this form of pathology will have a favorable prognosis, otherwise complications may arise that can lead to infertility and the development of ovarian hypofunction.
Treatment of fallopian tube obstruction without surgery with drugs
Treatment of fallopian tube obstruction without surgery can only be recommended by a doctor. With multiple adhesions, such treatment may be ineffective. It is necessary to adequately assess the possibilities of medicine - and, if necessary, to perform an operation, agree to it.
Drug treatment involves the use of three categories of drugs:
| Anti-inflammatory | To eliminate the inflammatory process, tablets or suppositories can be used. The most common drugs are Diclofenac, Indomethacin. In addition to the anti-inflammatory effect, these drugs are also characterized by analgesic and antipyretic effects. |
| Antibacterial drugs | Necessary for eliminating pathogens of bacterial nature. As a rule, broad-spectrum drugs are used: tetracyelin, metronidazole. |
| Hormonal treatment | Hormones are used when the inflammatory process is caused by hormonal imbalance. |
Some folk remedies
| Hog queen | One of the popular folk remedies used in the treatment of gynecological diseases is boron uterus. This herb has helped many women recover from infertility. In addition to the treatment of gynecological diseases, the medicinal effect of boron uterus helps strengthen the immune system and normalize the hormonal balance in the body. To treat obstruction of the fallopian tubes, an infusion with boron uterus is prepared. To do this, 5 tablespoons of the dried plant are poured onto the floor with liters of vodka. The medicine should be infused for 15 days in a dark place. During this period of time it must be shaken periodically. The medicine should be taken three times a day - 40 drops an hour before meals. |
| Milk thistle + cinquefoil | Cinquefoil and milk thistle can also be used for treatment. 1 tsp pour milk thistle seeds with a glass of boiling water and keep covered for 15 minutes. Take hot three times a day half an hour before meals, take another serving before bed. A tablespoon of cinquefoil is poured with 300 ml of vodka and left for 21 days. Take by diluting a tablespoon of tincture in 50 grams of water. A day – 3 doses. |
| Aloe + honey + plantain | To treat tubal obstruction, a recipe based on aloe, plantain and honey can be used. Aloe should not be watered for a week. Then its leaves are cut off and placed in the refrigerator for 3 days. After this time, the leaves are taken out, crushed and poured with honey and melted butter in a ratio of 1:6:6. The finished medicine is stored in the refrigerator. Drink it a tablespoon twice a day, mixing it with a glass of hot milk. The duration of treatment is 2 months. At the same time as this remedy, take a decoction of plantain. To prepare it, pour a tablespoon of grass seeds into 0.5 liters of water and boil for 10 minutes. The dosage is kept the same. |
| Bergenia root | There is another recipe that is suitable for treating fallopian tube obstruction without surgery. Bergenia root is crushed (50 g), poured with 1.5 cups of boiling water and left for 8 hours. After straining, the infusion is placed in the refrigerator. This product is intended for douching. Carry out the procedure 2 times a day - morning and evening, taking 150 ml of infusion. Tampons are placed from the roots overnight. To make them, a teaspoon of the roots from which the solution was made is wrapped in cotton wool, gauze and tied with thread. The tampon is first soaked in the solution and then inserted into the vagina. It is recommended to place a pillow under the buttocks at night. An infusion with bergenia root can also be taken orally. The course of treatment involves taking the drug 3 times a day an hour before meals. The drug is taken for 3 days in a row, followed by a 3-day break. So the intake is alternated with breaks for 4 weeks. At the same time, take a tincture of marina root. 50 grams of crushed root are poured into a dark glass bottle and poured with half a liter of vodka and infused for 10 days. Take several times a day, diluting 1:3 with water. |
| Flax seeds | To get rid of adhesions, you can prepare a compress from flax seeds. Several flax seeds are wrapped in a bandage or gauze and placed in boiling water - boil for about 3 minutes. Immediately after boiling, do not remove the gauze - leave it to cool in the water. When the temperature drops and the water is well warm, the gauze is wrung out and placed on the lower abdomen. Next, this area is wrapped in cellophane film and wrapped in a towel. The compress is left until the morning. The course of treatment involves 8 procedures. |
| Propolis + honey | It is also recommended to place tampons with honey and propolis in the vagina. The components are combined in equal proportions; if necessary, the honey must be heated (if it is too thick). The ingredients must be mixed so that they form a homogeneous mass. The tampon is inserted before bed and left overnight. The procedure is repeated every other day for a week. This recipe should be used with caution by those who are allergic to bee products. |
Clinical picture
As practice shows, signs of inflammation of the fallopian tubes may vary depending on the specific type of pathology.
The acute form of salpingoophoritis is characterized by the appearance of painful discomfort in the lower abdomen and lower back. In addition, many women note an increase in temperature, a general deterioration in their condition, chills, and excessive sweating. In rare cases, purulent vaginal discharge is possible.
The chronic form of salpingoophoritis is characterized by the occurrence of dull aching pain in the lower abdomen and vagina. Women complain of problems with the menstrual cycle, decreased libido and discomfort during sexual intercourse. Tests show a decrease in the level of female hormones and the formation of ovarian hypofunction.
At the initial stage of development, salpingitis is characterized by painful discomfort in the lower abdomen and problems with urination. As the disease progresses, these symptoms are accompanied by purulent vaginal discharge, and sexual intercourse is accompanied by severe pain. In some cases, there may be a slight increase in temperature, general malaise and periodic attacks of weakness.
Symptoms of inflammation of the fallopian tubes are varied. The clinical picture of the disease is influenced by the location of the pathological focus, its type, as well as concomitant diseases.
- Pain is one of the main signs of the disease. Painful sensations are localized mainly in the lower abdomen, although they can radiate to the groin and lumbar region and even to the lower extremities. In addition, pain often intensifies during urination, defecation, during sexual intercourse, and also during menstruation. As a rule, intense pain, aggravated by physical activity, is characteristic of an acute process. Dull pain indicates a chronic form.
- Irregular menstruation
- Mucopurulent discharge with an unpleasant odor appears, as a rule, in an acute form. In a chronic process, there may be no discharge.
- In acute illness, body temperature often rises to 38.5°C, accompanied by chills and intense sweating. With a chronic disease, low-grade fever is noted, but in some cases there is no increase in temperature.
- Weakness, muscle pain, nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite, etc. are also possible - these signs are caused by the effect of toxins on the body.
Hirudotherapy
Leeches can also be used to eliminate obstruction of the fallopian tubes. This procedure is quite common and is used in many clinics. The duration of the procedure is about an hour. The qualifications of a specialist are important for efficiency. The course of treatment includes 10-15 sessions.
Leeches are applied to the skin in the uterine area. The procedure requires 3-4 leeches. They can also be placed in the vaginal area. Leeches are not removed - they fall off on their own. How does this method work? During contact with the skin, the leech produces special enzymes, under the influence of which scars and adhesions are resolved, the inflammatory process is reduced, and hormonal levels are restored.
Causes of pathology
Often, infection occurs from the bottom up, that is, through the vaginal cavity. From there, infectious microorganisms move along the cervical canal into the cavity of the uterine organ, and finally, the final point of their movement is the uterine tubes, where the process of inflammation begins to progress.
It is also worth noting that inflammation of the fallopian tubes can begin through descending routes of infection, that is, through the sigmoid colon or the appendix. Much less often, the formation of pathology occurs through the bloodstream from any progressive focus of an infectious disease developing in the female body.
There are a huge number of provoking factors contributing to the development of this pathology; the most common are infectious diseases transmitted through sexual intercourse of partners, in the form of:
- chlamydia;
- gonorrhea;
- papillomavirus infection;
- genital herpes;
- trichomoniasis;
- cytomegalovirus infection.
The progression of these diseases in a woman contributes to the development of inflammation of the urinary system and fallopian tubes. The insidious development of most of these diseases lies in the fact that they occur without the manifestation of any symptomatic signs, as a result of which women do not visit the gynecological office for a long period, and the pathology becomes chronic. The presence of bacterial microflora over a long period on the mucous surfaces of the genital organs helps to reduce the immune defense system and reduce the intensity of blood circulation in these organs. Against this background, at the slightest exposure to an additional provoking factor in the form of a cold, depression or stress, the inflammatory infection begins to move upward to damage the fallopian tubes.
Salpingitis due to venereal disease
After the penetration of infectious microorganisms into the mucous structure of the fallopian tubes, their intensive reproduction begins. As a result, the inner walls of the fallopian tubes become inflamed, which leads to impaired blood circulation. Then, inflammatory processes penetrate all layers of the fallopian tubes, which increases their thickness and activates adhesive reactions, which leads to blockage of the passage in the tubes and the development of infertility. As a bacterial infection progresses, purulent accumulations may appear in the pipes. Often, inflammation of the fallopian tubes, which develops due to the negative impact of sexually transmitted diseases, has a bilateral course.
It is worth noting that when leading a promiscuous sex life and entering into intimacy with various sexual partners, the likelihood of the formation of an inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes increases several times. This is due to the fact that such a way of intimate life increases the risk of contracting a sexually transmitted disease, and possibly several of their varieties at once, which is referred to as a microbial association. All this leads to a decrease in immunity and destruction of the barrier that protects the mucous surfaces of the genital organs from the penetration of bacterial microorganisms.
Mechanical causes of salpingitis
The development of inflammation of the tubes can be facilitated by various mechanical damage to the mucous surfaces, which include:
- injuries received during childbirth;
- premature termination of pregnancy;
- placement of an IUD, which can be perceived by the body as the penetration of a foreign body, against the background of which allergic reactions of an inflammatory nature can occur, which also leads to a decrease in the local immune defense system;
- carrying out intrauterine diagnostics: salpingoscopy or metrosalpingography.
Prevention
Preventative measures involve taking care of your health. It is recommended to maintain sexual relations with one partner, as well as to use contraceptive methods. This will protect against unwanted pregnancy and, therefore, will not lead to abortion. In addition, it will warn against contracting sexually transmitted infections.
You need to regularly visit a gynecologist - timely detection of inflammatory processes and diseases, as well as treatment started on time, reduces the risk of complications.
Inflammatory processes should not be started - having become chronic, they often cause the formation of adhesions, and therefore obstruction of the fallopian tubes.
Treatment
The tactics for treating inflammation of the fallopian tubes depends on the cause and form of the disease, as well as on the complications and concomitant diseases that have arisen.
- Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating infection and inflammation, as well as strengthening the immune system. For conservative treatment, antibiotics are used, but before prescribing them, it is recommended to conduct a sensitivity test of the body. Also, for a more effective effect on the pathological focus, suppositories can be prescribed - local preparations that have an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. To stimulate the body's defense reaction, autohemotherapy is indicated. To reduce pain and to resolve adhesions, physiotherapy is often used: low frequency currents, balneotherapy, reflexology, etc.
- The operation is performed when conservative treatment methods are ineffective and consists of removing part of the pipe. The most optimal method is laparoscopy - surgical intervention using a laparoscope through holes in the anterior wall of the peritoneum. In some cases, a laparotomy may be necessary - in this case, an incision is made in the abdominal wall for full access. Indications for surgery are: purulent formations and tumors in the area of the appendages, tubal obstruction as a result of adhesions, etc.
How to treat inflammation of the fallopian tubes can only be decided after a thorough examination of the woman.