Most of the world's population is familiar with herpetic rashes on the lips and nose. However, these are not all the places where a characteristic rash may appear. The manifestation of herpes in the intimate area is a rather delicate problem, with which one is not in a hurry to consult a doctor. The virus itself does not pose a mortal threat to health and does not negatively affect the functioning of vital organs, but only if it is deactivated in time. The disease brings a lot of discomfort, reduces the level of quality of life, and in its neglected form it can spread throughout the body, which is already fraught with disastrous consequences.
How to treat herpes in the intimate area?
You need to be prepared for the fact that it is impossible to completely cure genital herpes using home methods, as well as medications. The main goal of therapy is to kill foci of the disease, increase the level of the body’s immune defense, prevent the development of relapses, and deactivate the virus.
You need to be prepared for the fact that it is impossible to completely cure genital herpes using home methods, as well as medications. The main goal of therapy is to kill foci of the disease, increase the level of the body’s immune defense, prevent the development of relapses, and deactivate the virus.
The presence of herpes on the genitals constantly causes itching, pain, and the desire to scratch in an intimate place. As a result of infection by the virus, an increase in temperature and enlargement of lymph nodes may occur. It is necessary to use complex therapy methods to get rid of herpes in intimate places. Treatment involves the use of the following methods:
- Taking medications.
- The use of traditional medicine.
- Boosting immunity.
- Maintaining a protected sex life.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules.
Stages of infection
There are primary and recurrent cases of herpes. The primary stage of infection is usually acute, manifested by a bright outbreak of rashes and an increase in body temperature.
Symptoms of a recurrent case of herpes in an intimate area are usually more blurred, unless we are talking about moments of a sharp drop in immunity, for example, during pregnancy or against the background of a long illness (ARVI, influenza, treatment of cancer, AIDS).
Recurrent cases are divided into:
- Typical with standard manifestations in the form of bubble formations on the mucous membranes;
- Atypical , which are manifested by various inflammations of the genitourinary system, rectal ampulla, urethra. This course of the disease is difficult to diagnose; only a virological examination will help accurately determine the cause of the disease.
Treatment of genital herpes at home with folk remedies
How to treat herpes in the intimate area? Sexual transmission of herpes is very common among people of all ages. The first manifestation of the disease is a rash in an intimate place. You can treat genital herpes at home at this stage with the following folk remedies:
- Calendula tincture.
- Propolis.
- Aloe or Kalanchoe juice.
- Decoctions of walnuts, sage, oak bark, lemon balm.
The method of using these medicinal drugs is very simple. You need to soak a cotton swab in the tincture or decoction and wipe the affected areas 1-2 times a day. After a few days, the number of bubbles should decrease. If this does not happen, then genital herpes must be treated with other drugs, since the disease has penetrated deeper.
How to treat herpes in an intimate place? Treatment with decoctions and tinctures can be supplemented with auxiliary folk remedies, which include viburnum tincture. For preparation you will need 20 g of dried berries. They are ground and poured with 1 glass of boiling water. The decoction must be infused for 4-5 hours, and then taken 3-4 times a day, 0.5 cups. The duration of therapy ranges from 7 to 20 days.
An infusion prepared with birch buds helps in treating herpes at home. This medicine is an excellent anti-inflammatory agent. You need to take 10-15 g of kidneys and 1 glass of milk. The mixture must be brought to a boil, boiled, and allowed to cool. Then the kidneys are taken out, wrapped in gauze and applied to the affected area.
You can also use celandine mixed with honey. It is necessary to take only fresh celandine, which is crushed and mixed with honey in equal proportions. The prepared ointment should be applied to the affected intimate areas several times a day.
Aloe juice is a good anti-inflammatory agent for genital herpes.
A mixture prepared from onion juice helps in therapy. You need to squeeze the juice out of 1-2 onions, add applesauce to it, 10 tbsp. l. pumpkin juice, 2 tsp. honey The resulting product should be eaten 4 times a day, 2 tbsp. l.
In the treatment of genital herpes, an infusion made from arnica flowers is used. Healers and doctors who are supporters of traditional medicine also recommend using decoctions made from thyme, chamomile, lemon balm, motherwort, raspberry leaves, and juniper.
Diagnostics
The clinical picture of the genital form of herpetic infection is quite specific and difficult to confuse with any other genital tract infections. However, to make a diagnosis, a woman needs to see a gynecologist and dermatovenerologist. To confirm herpes on the genitals of women, laboratory tests are performed.
- Examination of vaginal scrapings. The presence of HSV is determined by culturing the virus.
- Blood test to detect antibodies to HSV in serum. Allows you to make a diagnosis even in asymptomatic cases, with atypical forms.
To increase the accuracy of diagnosis, it is recommended to do the analysis repeatedly - 2-4 times with an interval of several days. In this case, material for research is taken from different areas. Diagnosis is carried out on days 18-20 of the menstrual cycle.
How to treat genital herpes with essential oils and baths?
These are natural medicines that are used to treat many diseases, including herpes. Esters are also used for the prevention of genital herpes in affected intimate areas. To get rid of skin rashes caused by herpes, relieve inflammation and itching, you need to use cedar, lavender, eucalyptus, geranium, and tea tree oils. To strengthen the immune system, eucalyptus, verbena, rosemary and orange oils are best suited.
Essential oils should be applied in small quantities so as not to cause burns to the mucous membranes in intimate areas.
Herpes in the intimate area can also be treated at home with baths prepared using medicinal herbs. Melissa, sage, lungwort, and oak bark work well against the herpes virus. All of the above herbs should be taken 2 tbsp. l., pour into the bathroom and pour boiling water, leave for an hour. The tincture should be added to the bath every time before taking water procedures. Itching and inflammation are perfectly relieved by salt baths. To enhance the effect, add salt and a few drops of iodine to the water.
Features of treatment for pregnant women
The herpes virus poses the greatest danger to pregnant women; it can cause serious disruptions during pregnancy and provoke the appearance of abnormalities and deformities in the unborn child. Therefore, in the acute form, especially if it is a primary infection, you need to start treatment as quickly as possible. During pregnancy there are some nuances during therapy.
Acyclovir and its analogues are used only in exceptional cases due to possible harm to the pregnant woman and the fetus. The following drugs are used with caution:
- Panavir;
- Zovirax;
- Vivorax and others.
The acute phase immediately before childbirth is dangerous, including. As long as the fetus is inside the womb, infection is unlikely. Most newborns become infected during childbirth, passing through the birth canal or touching the mother's genitals. Therefore, if an exacerbation or relapse occurs at the expected time of delivery, a cesarean section is offered.
Treatment of herpes at home with medications
How to cure genital herpes? Home treatment methods must be supplemented by taking pills and other medications. A doctor should prescribe medications after undergoing tests. Treatment must be carried out at home. The list of essential medications prescribed by the attending physician includes:
- Acyclovir (tablets).
- Lavomax (tablets).
- Isoprinosine (tablets).
- Allokin-alpha (injections).
- Panavir (injections).
- Medicines containing interferon. This could be the same Panavir, Gerpovax or Cycloferon.
The treatment regimen is prescribed by the doctor, who decides how many tablets a patient with a genital virus should take during the day. Usually the treatment period lasts from 1 month to six months.
It is recommended to take the tablets together with suppositories, which are excellent for treating genital herpes. These drugs have a number of advantages:
- Can be used by pregnant women and nursing mothers.
- Dissolves in genital tissue.
- Helps improve the immune system.
The composition of the candles is similar to each other. Often doctors, to cure herpes, prescribe suppositories such as:
- Panavir;
- Viferon;
- Galavit;
- Genferon.
Their action is complemented by special ointments that can be used for genital herpes. They need to be applied to the intimate area to relieve itching and eliminate blisters. Ointments such as:
- Acyclovir;
- Zovirax;
- Levomekol;
- Zinc ointment;
- Panavir;
- Helepin;
- Foscarnet;
- Oksolin;
- Alpizarin;
- Tromantadine.
What is "herpes"?
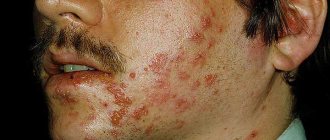
Herpes is a viral disease that manifests itself as characteristic rashes. They are small bubbles filled with liquid. Bubbles can appear both on the skin and on mucous membranes. Genital herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus type 2. After a person is infected, this microbe penetrates the nervous system, and therefore provokes extremely unpleasant sensations when activated.
The virus lives in the human body constantly, and causes severe clinical symptoms only at the acute stage. It is especially dangerous for people with weakened immune systems.
Herpes type 2 is transmitted exclusively through sexual contact, affecting the genital and anal areas, as well as the perineum. The infection itself is asymptomatic, but when immunity decreases or provoking factors act, painful blisters or ulcers suddenly appear. In a healthy body with a strong immune system, the virus can live throughout life and not manifest itself in any way.
One of the characteristic symptoms of the disease is very severe itching, which is quite difficult for a woman to control. In many cases, this leads to scratching of the affected area, the appearance of wounds and worsening of the disease.
You can become infected with herpes through mucous membranes, which is why not only vaginal sex with a carrier, but also oral sex is dangerous. The main category of patients is women from 18 to 35 years old. Promiscuous sexual intercourse, a large number of partners, and unprotected sex greatly increase the likelihood of infection. Clinical manifestations for each woman may vary from slight redness and discomfort to severely itchy large blisters. The acute period of the disease does not last long, but during this time you need to have time to recover so that the process does not become chronic.
Outside the human body, the virus loses its activity, so sexual transmission can be considered practically the only possible one. A very small percentage of infections occur from using the personal belongings of another person infected with herpes.
Use of immunomodulators and lifestyle changes
The complex of therapeutic measures should also include immunosuppressants that help cope with herpes in the intimate area. When we treat with immunomodulators, it is necessary to apply the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor. This will help cope with the consequences of the disease and prevent relapses. Increasing immunity is one of the important conditions for a home therapeutic course. The most common immunomodulators include:
- Vitamins that are found in tomatoes, celery root, apples, parsley.
- Carrot juice, which contains a lot of carotene.
- Ascorbic acid.
You can also boost your immunity with herbal teas. During the treatment period, you should give up black and green tea. It is recommended to take teas brewed with rose hips and St. John's wort.
It is necessary to treat genital herpes in other ways. For example, take care of personal hygiene: you need to wear underwear only made from natural fabrics, and do not visit public bathing places (swimming pools, beaches, saunas). You should not be in the sun for a long time so that the sun's rays do not interfere with the healing of ulcers. After visiting the toilet and returning from the street, you need to wash your hands with soap so that herpes does not get on your eyes, lips, or mouth.
You should not touch genitals that are susceptible to herpes, and you should avoid scratching. This will help prevent infection from entering and spreading. During the period of relieving exacerbation and inflammation, you need to abstain from sexual intercourse. Then you need to use condoms so that the remission is long-lasting. A prerequisite for a speedy recovery is compliance with the following rules:
- Stop smoking forever so that the virus is completely blocked and deactivated.
- Play active sports.
- Douse yourself with cold water.
- Eat only healthy food.
- The diet should contain fruits, vegetables, herbs, and vitamins. It is not recommended to eat fatty and spicy foods.
- You should give up coffee and strong tea for a while.
Mandatory conditions for the treatment and prevention of genital herpes are personal hygiene and hardening of the body.
As a preventive measure, you need to make it a rule: once every six months, drink tinctures of echinacea, chamomile, calendula, tea with ginger and honey, and light candles that will help improve the health of the microflora. You can eat a little honey every day before your main meal, which will significantly strengthen your immune system. Cloves help fight infections such as herpes. It is enough to add it to drinks and food as a seasoning. Prevention should be carried out regularly, once every 3-6 months, depending on the severity of the disease. Any tinctures should be taken only orally with water. It is prohibited to make lotions, compresses or applications from them, since they can cause burns to the mucous membrane, the development of hypersensitivity and an allergic reaction.
Thus, treating genital herpes at home is possible, but before doing so, you should consult a doctor. Only a therapist can correctly determine which medications in the home medicine cabinet - medicinal and traditional - should be chosen, how to take them correctly, etc.
Tweet
Pin It
Tags:Intimate herpes
- What herbs are used for herpes?
- Conspiracy: how to get rid of herpes forever
- Herpes virus and hydrogen peroxide
- The use of homeopathy in the treatment of herpes
Prevention
To prevent the disease from occurring after therapeutic treatment, it is necessary to adhere to preventive standards:
- use contraceptives;
- monitor the hygiene of the intimate area;
- undergo preventive examinations from a specialist;
- exclude the possibility of sexual intercourse if there are rashes on the genitals;
- maintain a healthy lifestyle, eat well;
- strengthen the immune system;
- during the season of exacerbation, you can use immunomodulatory suppositories.
Not a single type of treatment, even the most effective, can completely eliminate the virus from the body, and therefore it is important to carefully follow preventive measures, not to have sexual relations before the age of 18 and to avoid unprotected acts.
Increased immunity during treatment
An integral part of the treatment of genital herpes is considered to be increasing the body's immunity. Before starting therapy, the patient's immune status is determined. Depending on this, the doctor selects special drugs - immunomodulators, to form an immune response and suppress the activity of the virus.
Genital herpes is treated by using the following immunomodulators as part of complex therapy:
- Cycloferon;
- Genferon;
- Viferon;
- Lavomax;
- Immunofana;
- Panavira et al.
Each of these drugs has its own contraindications, which must be taken into account during treatment. For relapses of the disease, effective immunomodulators Panavir and Lavomax are prescribed in tablet form. Panavir is used with extreme caution by people with diseases of the spleen and kidneys. Taking Lavomax is prohibited for pregnant and lactating women, children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
The effect of treatment with antiviral drugs is greatly enhanced by the simultaneous administration of immunoglobulins. To increase the overall resistance of the patient's body, injections of vitamins B1 and B6 are often prescribed.
For frequently recurrent herpes, the antiviral vaccine Herpovax or Vitagerpavac is administered once every six months, and suppressive therapy is prescribed.
It is important to treat both sexual partners at the same time for genital herpes. Sex is prohibited throughout the entire period of therapy.
Manifestation in women
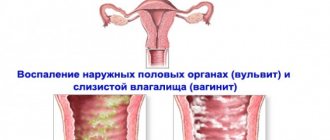
Genital herpes is more severe in women than in men. The female body reacts more actively to infection, therefore, she experiences pronounced symptoms. At the same time, women almost immediately experience redness of the intimate area, itching and swelling.
Sexual intercourse in women infected with genital herpes is very difficult and painful, and in some cases bleeding occurs. There is also an increased rash not only on the vagina, but also on the urethra, cervix and vulva. In addition, in women, the rash almost always appears on the buttocks and thighs.
Causes
Genital or genital herpes is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the herpes simplex virus. There are two main types of the virus known. Type 2 herpes most often causes damage to the reproductive system. Moreover, this pathogen can manifest its activity in other parts of the body. According to statistics, 80–90% of the adult population of the planet is infected with the herpes simplex virus. The pathogen is present in the body for a long time without manifesting itself.
With a decrease in the body's defenses, an exacerbation of the pathological process occurs, which causes the appearance of a corresponding clinical picture. Relapses are also common for this disease, when after the symptoms disappear, the pathology makes itself felt again. Among the main reasons for the recurrence of the disease:
- stress;
- poor nutrition;
- frequent overwork;
- diabetes.
Knowing about the classic form of the disease, which mainly affects the mucous membranes, face and lips, patients ask the question of whether herpes is sexually transmitted. Studies have shown that transmission of the pathogen occurs through skin-to-skin contact. The penetration of the virus is facilitated by the presence of microcracks and scratches on the surface of the skin. Taking this into account, transmission of the virus is also possible through sexual contact with an infected partner.
The possibility of infection cannot be ruled out during oral sex, when the pathogen enters the mucous membranes of the mouth and face, causing skin rashes. Household transmission is unlikely, as the virus quickly dies in the environment. Newborn babies often become infected when they pass through the birth canal of an infected woman.
Damage to the body by the herpes virus is the root cause of the disease, without which the disease naturally cannot begin. Several factors increase the likelihood of contracting herpes - unprotected sex, poor personal hygiene, damage to the mucous membranes or skin of the genital organs.
However, the causes of the disease are not limited to the presence of the virus in the body, since many carriers of the virus do not show external signs of pathology. Moreover, the overwhelming majority of such people are 85-90%.
The main factor resulting in an exacerbation of viral herpes infection is weakened immunity. In turn, a decrease in the body’s protective functions can occur due to stress, taking certain medications (for example, glucocorticosteroid drugs), other infectious diseases, diabetes, and hypothermia.
Symptoms and manifestations
After infection has occurred, the pathogenic agent enters the blood and travels through the blood vessels. After entering the nodes of the nervous system, it is located there and lives in them permanently.
The onset of symptom development occurs when initiated by the following factors:
- chronic or acute diseases;
- periods of increased stress;
- long-term sleep disturbances;
- surgical interventions;
- hypothermia or overheating.
A factor that can provoke the onset of the disease is often monthly fluctuations in the hormonal cycle before the onset of menstrual periods, which reduce the body’s protective potential.
Primary flow
Manifestations of the typical nature of the disease begin with an increase in temperature to subfebrile levels (37.5-38 ° C), dizziness, increased fatigue and headaches. Sometimes a woman associates such symptoms with colds or premenstrual syndrome.
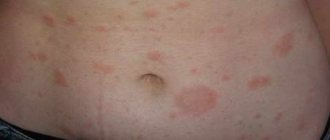
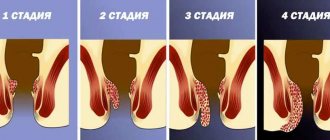
The second stage is the development of a rash. This happens according to the following algorithm:
- in the area of the intimate organs, itching, local increase in temperature, and redness begin;
- the skin or mucous membrane swells and becomes hyperemic;
- on the same day or every other day, small vesicles appear containing liquid in the bubbles;
- after 2-4 days, the vesicles open, and ulcers with pus at the bottom and a keratinized surface remain in place of their previous location;
- Over the course of a week, the sores dry out. This process is accompanied by a gradual subsidence of itching and swelling;
- after complete healing of the wounds, there are no scars or other marks left.
The rashes can be single or group. Groups are able to grow and turn into one large focus.
Locations of herpetic rash in the female body:
- folds of the labia majora and minora;
- vagina;
- cervical canal;
- entrance to the urethra;
- crotch;
- perianal region;
- pubis;
- buttocks;
- hips.
In addition to the rash, standard signs of the disease are enlarged lymph nodes located near the affected areas, pain in the lower pelvis, mucopurulent vaginal discharge, muscle aches, nausea and sleep disturbances.
If the disease spreads to the urethra, then urination occurs with intense pain, burning and stinging, especially at the beginning of the process. In cases where the rash has occupied the rectum or areas adjacent to the anus, the act of defecation becomes problematic, it is painful for the woman to push, and after this bleeding may occur.
Sometimes the rash affects several places at the same time, which signals the body’s inability to stop the process.
Once the initial episode is over, the disease subsides for a short or long period.
Secondary flow
After the body is affected by factors that cause a relapse, another exacerbation is observed. Often this factor is the hormonal surge that precedes the onset of menstrual periods. Such a significant change in hormonal balance is an immunosuppressive circumstance that can cause a relapse of genital herpes.
In addition, the frequency of repeated exacerbations depends on the type of virus that caused the pathology. The most common relapses are caused by the HSV-2 type.
Depending on the nature of its course, recurrent herpes comes in the following forms:
- arrhythmic course - the time of remissions varies greatly from one person to another (from several weeks to several years);
- monotonous course - with systematic short remissions and frequent relapses;
- subsiding course - with a mild clinical picture for a short time followed by long intervals.
In the secondary course, all symptoms are expressed less sharply; such an acute onset as during the first appearance is not observed. The time of relapse is shortened, but the localization of the rash remains the same, and it appears again.
Atypical course
Symptoms in this form are subclinical (mild) in nature. Atypical herpes can develop without pain, but have the following symptoms:
- erythematous - characterized by severe swelling and inflammation in the groin area, redness of the skin occurs;
- bullous - characterized by long-healing ulcers with extensive suppuration due to secondary bacterial infection attached to the wounds;
- hemorrhagic - appears when the rash is localized near the anus and in the rectum, complicated by hemorrhoidal flows;
- itchy - can occur without the formation of a vesicular rash, but is accompanied by itching, which sometimes leads to scratching and the formation of sores in the groin area.
This form occurs without the appearance of any symptoms. Carriers are predominantly women, while asymptomatic disease is much less common in men.
This form can be detected only on the basis of specific tests that detect the pathogen in the blood.
A characteristic sign of the disease is rashes in the groin area and external genitalia. Herpes on the labia appears in the form of small blisters that are filled with fluid. They contain a pathogen inside, so after opening, the pathogen spreads to new areas.
Initially, patients notice the appearance of redness, swelling, itching and burning in the groin area. In some cases, pain and cramping when urinating are possible. After the virus begins to release toxins into the blood (approximately on the 7th day), signs of an acute form of the disease appear:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- increased body temperature;
- weakness;
- fast fatiguability.
With such a form of the disease as herpes in the intimate area, the symptoms in women are more pronounced than in men. The first signs of the disease appear a week after infection. Patients complain about:
- temperature increase;
- sudden weakness;
- joint pain;
- enlarged inguinal lymph nodes.
After a while, blistering rashes appear in the genital area. In women, they are localized mainly on the vulva, vagina, buttocks, thighs, and perineum. The skin becomes red and swollen. After opening the blisters, ulcers remain in their place. They may take up to 3 weeks to heal.
As the pathology progresses, swelling of the inguinal lymph nodes is noted. Urination becomes painful, general health worsens, and body temperature rises. Patients observe an increase in the number of elements of the rash, which in some cases spreads to the anus. After oral sex, rashes appear on the tongue, lips, and inner surface of the cheeks.