In the second trimester of pregnancy, expectant mothers may be offered to undergo another screening, which in terms of the set of procedures is even simpler than the previous one - in the first trimester.
The second prenatal screening is a less popular procedure and is carried out only if indicated or at the request of the woman in labor.
Since 2012, the Order of the Ministry of Health has slightly changed the regime for screening pregnant women in the second trimester. If the results of an early examination carried out during the period from the 11th to the 14th week of pregnancy are favorable, then the expectant mother will only receive a referral for an expert ultrasound at 22–24 weeks of pregnancy.
However, if desired, mommy can also undergo a paid biochemical examination.
At what weeks are 2 screenings performed during pregnancy?
Screening, as a method of identifying possible abnormalities in the fetus, began to be done for expectant mothers only in 2000. The first diagnosis is aimed at determining the risks of developing intrauterine chromosomal problems; it is carried out at 10-13 weeks.
The timing of the second perinatal examination is 16-20 weeks, while the most reliable test results can be obtained if the diagnosis is carried out before the end of the 18th week. If during the first screening there were no obvious abnormalities in the blood test, then in the second trimester you can only do an ultrasound at 19-22 weeks.
Deviation from norms
After performing an ultrasound and receiving the results of a blood test, the doctor not only compares the results with standard values, but also calculates the degree of risk based on the likelihood of a particular pathology occurring.
Actual screening rates are divided by the average obtained by processing data from previous studies that included women of approximately the same age living in the area.
The result obtained is denoted by the abbreviation “MoM”.
If the MoM value is between 0.5 and 2.5, this is considered normal. The closer the obtained result approaches one, the better the screening result.
The total result of the second screening is recorded as a fraction, for example, 1:500.
- If the denominator in this expression is greater than 380 , this is a normal result (for example, 1:400 or 1:1000).
- If the number in the denominator is less than 380 (for example, the result is 1:290), then the likelihood of certain abnormalities in the fetus is quite high.
- If the obtained indicator is in the range from 1:250 to 1:360 , it is advisable for the expectant mother to consult a geneticist.
- At a risk level of 1:100, invasive diagnostics are recommended to determine the chromosome composition of the fetus.
The expectant mother should remember that the probability of receiving a false positive screening result is about 10%, and a false negative one – up to 30%.
additionally You should not panic if the doctor reports the presence of some possible abnormalities in the fetus. In this case, it is necessary to undergo additional types of examinations in order to clarify the data obtained.
It is very important to remain calm and confident when undergoing screening, because the level of hormones in the blood largely depends on a woman’s psychological mood.
After passing the second screening, you should also follow the doctor’s recommendations regarding nutrition, lifestyle, and physical activity to increase the likelihood of having a healthy child.
Why is screening done in the second trimester?
The main objective of second trimester screening is to confirm or refute the results of the first prenatal diagnosis. All indicators are carefully analyzed, the specialist compares them with standard values, which allows you to understand how correctly the baby is growing.
When is screening prescribed in the second trimester:
- the age of one or both parents is more than 35 years;
- the presence of hereditary diseases of a genetic nature;
- the expectant mother suffered a viral infection in the early stages of pregnancy - many harmless diseases have a negative impact on the development of the fetus;
- if a woman has previously had cases of fetal death, miscarriages, or stillbirth;
- use of drugs with teratogenic effects;
- dependence on alcohol or drugs in one of the parents;
- chromosomal abnormalities in already born children;
- the presence of autoimmune pathologies and chronic diseases in the mother, which can negatively affect the growth and development of the child;
- detection of malignant neoplasms after 3 months of pregnancy;
- work in hazardous industries, radiation exposure shortly before the conception of one of the parents.
Screening in the second trimester allows you to detect problems that cannot be detected at earlier stages, establish the risks of developing pathological conditions, and identify deviations in the structure of the main systems in a growing body. But examination in the first trimester is still considered more informative.
What is included in the 2nd screening during pregnancy?
Diagnostics consists of two components - ultrasound and biochemical examination of blood components.
What diseases can be diagnosed in the fetus?
Conducting a second trimester screening allows doctors to diagnose the likelihood of several diseases in the fetus:
- Down's disease
- Edwards syndrome
- Neural tube disorders
Indications for conducting a second trimester screening study are:
- When a woman is over 35 years old.
- There is a threat of miscarriage.
- There is already a child with congenital abnormalities.
- A woman needs to take medication that is contraindicated during pregnancy.
- When the first screening revealed a risk of pathological changes in the fetus.
To conduct the second screening, special preparation for the ultrasound is required, for example, you will have to drink a glass of water.
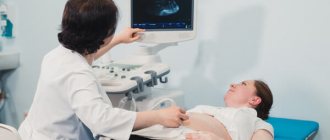
Ultrasound during pregnancy - what to look for in the second trimester
The baby in the womb develops rapidly; by the beginning of the second trimester, the physical and appearance of the baby has already noticeably changed. An ultrasound examination allows you to see how well the fetal parameters correspond to the norms, whether there are signs of pathologies; during the procedure, the condition of the uterus and placenta is studied; for a more accurate assessment of blood flow, an ultrasound with Doppler is prescribed.
What is looked at at the second screening during an ultrasound:
- facial structure - the size and condition of the nasal bones, whether there is a cleft in the oral and nasal cavities, how the eyeballs form and develop;
- carry out a full measurement of the size of the fetus, determine the number of fingers and toes;
- determine the correspondence of the degree of lung maturity to the obstetric stage of pregnancy;
- identify pathologies of the spinal cord, brain, and heart;
- in the second trimester, most of the internal organs are already partially formed, ultrasound allows you to see their structure and location;
- Be sure to record the amount of water, the tone of the uterus and the condition of the appendages, determine the degree of maturity of the placenta and the thickness of its walls;
- study the blood flow in the uterine vessels, assess the condition of the umbilical cord arteries and the middle vessel of the child’s brain.
The performance of the uterine vessels is assessed alternately in the right and left arteries; a one-sided study almost always turns out to be false. This is explained by the fact that with the development of gestosis, the movement of blood in only one uterine artery is disrupted. Preeclampsia or late toxicosis is a dangerous pathology that can result in fetal death and premature birth.
If the situation is successful, at the second ultrasound you will be able to find out the gender of your unborn child - primary sexual characteristics have already been formed.
There is no need to specially prepare for the second ultrasound; the examination is carried out even with an empty bladder - there is already a sufficient amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus to conduct a quality examination.
The Its Kids team advises that the day before the procedure it is better to refrain from consuming strong allergens - citrus fruits, cocoa products, seafood, fatty and fried foods.
Ultrasonography
A planned second ultrasound can coincide with the screening and be carried out at 17-20 weeks. The obtained research will allow us to develop a further plan for managing pregnancy, if deviations are identified and its possible termination.
Functions of ultrasound II screening:
- analysis of anatomical features of fetal development and compliance with standards;
- measurement of indicators that make it possible to accurately determine the relationship between the actual age of the child and obstetric timing, ascertaining delayed development;
- the presentation of the fetus is only of an evaluative nature, its position is noted nothing more, during this period, the baby changes its position, the final result can only be discussed in the third trimester;
- examination of the cervix, identifying dangerous symptoms that threaten spontaneous miscarriage;
- determining the condition of the placenta and umbilical cord to detect pathologies of the circulatory system.
Carrying out mandatory tests allows you to monitor the formation and development of the fetus, as well as prevent possible pathologies. Comprehensive studies help the doctor monitor health indicators, developing a pregnancy management plan according to the results obtained.
Second screening during pregnancy - ultrasound norms
Ultrasound in the second trimester is performed using the transabdominal method; to improve the passage of waves, a special gel is used, which is absolutely safe for mother and baby. Based on the picture on the monitor, all the necessary measurements are taken, and the doctor makes a general visual assessment of the baby.
Norms of ultrasound indicators
| Index | Week 16 | Week 17 | Week 18 | Week 19 | Week 20 |
| Weight (g) | 100 | 140 | 190 | 240 | 300 |
| Length(cm) | 11,5-11,7 | 12,9-13,1 | 14,1-14,3 | 15,2-15,4 | 16,2-16,5 |
| Abdominal circumference (mm) | 88-116 | 93-131 | 104-144 | 114-154 | 124-164 |
| Head circumference (mm) | 112-136 | 131-149 | 144-161 | 134-174 | 144-186 |
| Distance between the frontal and occipital bones – LZR (mm) | 41-49 | 46-54 | 49-59 | 53-53 | 56-68 |
| BPR (mm) | 31-37 | 34-42 | 37-47 | 41-49 | 43-53 |
| Leg bone length (mm) | 15-21 | 17-25 | 20-28 | 23-31 | 26-34 |
| Femur Length(mm) | 17-23 | 20-28 | 23-31 | 26-34 | 29-37 |
| Humerus Length(mm) | 15-21 | 17-25 | 20-28 | 23-31 | 26-34 |
| Forearm length | 12-18 | 15-21 | 17-23 | 20-26 | 22-29 |
| Amniotic fluid index | 73-201 | 77-211 | 80-220 | 83-225 | 86-230 |
To assess the condition of the uterine vessels, the resistance index is used; at 20 weeks, indicators of 0.38-0.7 units are considered optimal. To properly conduct this study, the fetus must be in a calm state, the baby’s pulse should be 119-161 beats/min.
With pathological processes in the middle artery of the brain, the child develops hypoxia, the pulsatility index (PI) decreases, and with cerebral hemorrhage, the PI increases. At week 20, the pulsation index is normally 1.35-2.32 units.
What is examined at the second ultrasound: results and interpretation of indicators
The timing of the second ultrasound during pregnancy is not regulated by chance. After twenty weeks, favorable conditions are created for identifying dangerous nonconformities. The examination protocol is composed of several parts:
- regulatory parameters;
- fetometric indicators;
- anatomical characteristics;
- provisional authorities;
- analytics of the female reproductive system.
Each of the subparagraphs describes a number of important parameters and criteria. The protocol ends with summary information for all sections. The result is obtained in the form of a picture where the expectant mother sees her child, and the doctor analyzes the indicators and tracks the pathologies of the embryo.
Standard indicators for the second trimester
The obtained embryo examination data is analyzed and checked for compliance with established standards. To evaluate the material in relation to the standards, the doctor performs the following steps.
- Conducts calculations. The first calculation concerns the size of the body, the length of the arms and legs, and the weight of the baby. To determine his genetic abnormalities, the face in general and the mouth in particular are examined. Everything is measured and verified against standards. Based on the results of all measurements and calculations, the gynecologist can indicate a fairly accurate date of birth.
- Examines the condition of the placenta. Its thickness is determined. The placenta is protection for the baby. The optimal standard is 20 mm for 20 weeks of pregnancy. The study shows whether placenta previa is present or not.
- Estimates the amount of amniotic fluid. There can be three options: oligohydramnios, normal, polyhydramnios. The state of the water is determined.
- Counting the baby's pulse and comparing it with standards. The correct rate for this stage of pregnancy is 110-180 beats per minute.
- Umbilical cord examination. Standard: three vessels - two arteries and one vein. It is determined whether the umbilical cord is entangled around the neck or other organs.
- The size of the uterus and its condition are examined. The standard is at least 30 cm, the throat is tightly closed.
Fetometric parameters
The development of a child is determined by special fetometric characteristics. Fetometry is the examination of embryo parameters on ultrasound. The data has been analyzed many times, and now the following are considered standard standards (for periods of 19/20/21/22/23 weeks):
- biparietal size. The distance between the bones of the crown is 36-52/39-56/42-59/45-63/48-66 mm;
- fronto-occipital size – 48-70/53-64/56-79/61-83/65-87 mm;
- average chest diameter – 31-49/36-53/38-56/40-61/43-64 mm;
- average abdominal diameter – 35-54/39-56/41-60/43-64/47-67 mm;
- head circumference – 144-182/156-194/168-206/180-218/191-229 mm and abdominal circumference – 116-166/127-176/139-189/150-201/161-212 mm;
- ratio of head circumference to abdominal circumference – 1.04-1.25;
- distance between the eye sockets (along the outer edge) – 24-35/26-38/28-39/30-42/31-42 mm;
- eye diameter – 7-11/8-12/8-13/9-14/9-14 mm;
- length of bones of the lower extremities: tibia (19-31/21-34/24-38/26-39/28-41 mm) and fibula (18-29/20-32/22-35/25-38/27 -41 mm), femur (21-35/23-38/38-42/39-44/41-47 mm);
- length of bones of the upper limbs: humerus (21-34/24-36/26-39/28-41/31-43 mm), radius (17-31/19-32/21-34/23-36/25-38 mm), ulnar (18-31/20-33/22-36/24-38/26-39 mm);
- Additionally, the interhemispheric size of the cerebellum (16-20/18-22/19-23/20-26/21-27 mm) and heart is determined.
The first four indicators are for reference purposes. With their help, the gestational age is clarified, the weight of the child is calculated, the symmetry of development and the correspondence of its dynamics to the expected gestation date are assessed.
Everything is summarized in a table, where there are sizes of other bones (even the foot). These indicators are secondary for identifying pathology of fetal development and are considered additional. They allow us to judge the age of the embryo. Any embryo grows in its own way, so it is a matter of the doctor’s experience to judge the presence of a disorder or developmental feature.
Fetal anatomy
Using ultrasound, doctors determine the anatomy of the fetus, the presence of all organs, the appearance of the skeleton and face. By this point, the baby is already moving freely, grimacing and even smiling. Its task is to accumulate fat, and the mother must eat properly and well. The beating of his heart, biparietal size, length of tubular bones, chest size, and brain structure can already be determined. Assessing the presence of organs and their structure, finding deviations is included in the determination of the anatomy of the embryo.
Brain and spine
At the 22nd...24th weeks of pregnancy, an examination of the brain structures is done. The inspection is carried out in the axial plane, making several sections. The review makes it possible to study the structure of the ventricles of the brain, the cerebellum, the fissure between the hemispheres and the visual thalamus. If the study shows deviations, then scanning is carried out in other planes. The doctor can see pathologies:
- hydrocephalus;
- abnormalities of the corpus callosum;
- cerebellar pathologies;
- ventriculomegaly.
Color Doppler testing is used so as not to miss possible pathology of the vascular bed.
The spine is examined along its entire length in two planes perpendicular to each other. Its bends, structure, vertebral arches and their integrity, and surrounding muscle tissues are examined. Upon examination, hernial protrusions may be detected.
Respiratory system
During the examination, much attention is paid to the division of the bronchi and the homogeneity of the lung tissue. The compliance of their sizes with the norms at this stage of pregnancy is established. When calculating the size of the lungs, use the ratio of the size of the chest and abdomen. The formula is rarely used due to the large calculation error. The lungs are fully formed in the third trimester, so at the stage of the second ultrasound only large deviations can be seen without details.
Heart
Diagnosis of heart defects during the second ultrasound is especially difficult. The examination protocol includes an assessment of a four-chamber section of the baby’s heart. If during an examination with ultrasound equipment deviations in this position are detected, then doctors recommend using detailed echocardiography of the embryo. This procedure is a separate study. Carrying out a second ultrasound provides the heart rate as productive information (the norm is 110-180 beats). In the case of a slow or rapid beating, we can already preliminarily talk about deviations in the development of the embryo.
Digestive system
The stomach, liver and intestines are indicated in the protocol as separate points. Diagnosis of these organs is facilitated by the fact that they contain echogenic content. This makes it possible to examine the structure of organs and their shape. A detailed analysis of the digestive organs makes it possible to timely exclude the overgrowth of natural openings. When examining the liver, specialists pay great attention to the condition of its vessels and bile ducts. Determining the size of the formed elements of the hepatobiliary system is carried out if the child has an enlarged liver, visible visually (hepatomegaly).
urinary system
Ultrasound of the second trimester diagnoses the urinary system in full. The kidneys look like paired bean-shaped formations in the lumbar region. The diameter of the renal pelvis in the second trimester should not be more than 4-5 mm. At the 20th...24th weeks it is possible to examine their internal structure. Violations may be established:
- absence of one kidney or both organs (agenesis);
- location of the organ in the wrong place (dystopia);
- cysts;
- non-standard sizes.
The bladder is clearly visible at this stage due to the urine it contains.
Determining the sex of the child
It is impossible to determine the sex of the unborn baby in the early stages, since the genitals have not yet formed. Determination based on ultrasound data is possible only from the 15th week. A boy is identified by the presence of a scrotum and penis, a girl by the presence of the labia. An inexperienced specialist may well mistake a child’s fingers or umbilical cord loops for a genital organ. Girls sometimes have swelling of the labia, which can also be mistaken for the scrotum. There are cases of sex determination at 12-13 weeks, but parents should not wait for results from the first ultrasound at this time.
Blood test in the second screening
A biochemical test of blood serum is prescribed only if ultrasound indicators are unsatisfactory, but each woman can conduct a full screening at her own discretion.
What indicators are taken into account in a blood test?
| Index | Week 16 | Week 17 | Week 18 | Week 19 | Week 20 |
| hCG (mg/ml) | 10-58 thousand | 8-57 thousand | 8-57 thousand | 7-49 thousand | 7-30 thousand |
| Estriol (E3)(mmol/l) | 4,9-22,75 | 5,25-23,1 | 5,6-29,75 | 6,65-38,5 | 7,35-49,5 |
| ACE (IU/ml) | 34,4 | 39 | 44,2 | 50,2 | 57 |
In addition to the main indicators, sometimes the amount of inhibin A is additionally determined.
What abnormalities can a blood test show? With Down syndrome, the level of hCG increases, the amount of other essential hormones decreases. With Edward's syndrome, all the main indicators are below acceptable standards, and with defects in the formation of the neural tube, Meckel's syndrome, liver necrosis, the concentration of AFP and E3 increases, while hCG is within normal limits.
A decrease in the level of free estriol is observed after taking antibiotics, with infection of the fetus, and with placental insufficiency.
If a blood test shows significant deviations of the main indicators from the norm, amniocentesis is prescribed - a sample of amniotic fluid is taken through a puncture in the abdominal wall for laboratory testing; the reliability of this type of diagnosis is 99%.
When the second screening is done, blood should be donated on an empty stomach, try not to be nervous before the test, avoid intense physical activity, and abstain from sexual intercourse.
Diagnostic technique
Such a study after 20 weeks can also occur in the presence of the husband of the expectant mother. To perform an ultrasound, the abdominal method is used. The patient should lie on her back; you can use a couch, placing a cushion under her right side.
The stomach should be open to the pubis. The sensor is installed on its front part, pre-lubricated with gel.
When conducting a study, after week 20, the sonologist changes the location of the ultrasound transducer. The woman does not feel any discomfort. The child moves much more actively at this time.
How is risk calculated?
Interpretation of the results of ultrasound and blood tests, the woman’s age, the presence of bad habits and chronic pathologies - all this data is analyzed by a special program that calculates the MoM coefficient. The optimal indicator is 1 unit, permissible deviations are 0.5–2.5 units.
Based on the MoM coefficient, the risk of having a baby with chromosomal abnormalities is calculated; values of 1:380 are considered normal. With a decrease in indicators, the chances of giving birth to a full-fledged child decrease proportionally.
Poor performance
All deviations from the norm of the above hormones may indicate the possible development of fetal pathologies:
- Elevated levels of the AFP hormone may indicate the presence of defects in the neural tube of the fetus, the occurrence of an umbilical hernia, improper formation of the digestive system, and other pathologies.
- A low level of ACE in the blood indicates the development of Down or Edwards syndrome in the fetus, an undeveloped pregnancy, or an incorrectly determined gestational age.
- An elevated SE level may indicate multiple pregnancies, a large fetus, or liver disease.
- A reduced level of estriol is most often a consequence of placental insufficiency and may indicate a threat of miscarriage or premature birth, the development of Down syndrome in the fetus, disorders in brain development, and diseases of the fetal adrenal glands.
- Elevated human chorionic gonadotropin may indicate a multiple pregnancy, an incorrectly determined gestational age, the presence of diabetes mellitus in the mother, or the development of Down syndrome in the baby.
- A reduced hCG level mainly indicates a threat of spontaneous abortion, undeveloped pregnancy, or placental insufficiency.
All pregnant women need to undergo such important examinations as first and second screening. This will help to timely determine the risk of developing pathologies in the fetus and determine further actions.
Share with friends:
Poor results of the second screening
Screening in the second trimester does not provide a 100% guarantee of the birth of a child with chromosomal abnormalities; often, with poor indicators, completely healthy babies are born. But you still shouldn’t count on luck; listen to the opinion of a gynecologist or geneticist, weigh the pros and cons.
Why the results are false:
- carrying twins, triplets, large fetus size;
- incorrectly established time of conception;
- conception occurred through IVF;
- obesity or underweight in a pregnant woman;
- presence of diabetes.
What to do if the results are still bad? Since the second screening is carried out already in the middle of pregnancy, there can be no talk of abortion for medical reasons.
If the results of the second screening are unsatisfactory, if the risk of developing anomalies is 1:360 or higher, the woman is recommended to have an artificial birth, provided that the pathology is irreversible and cannot be corrected medically.
But since today screening is not a sufficiently informative method, the decision to keep the child or terminate the pregnancy always remains with the parents.
If there is a chance to eliminate or correct the disorders, the expectant mother is told in detail about treatment methods, possible risks, complications, and the chances of carrying and giving birth to a strong child.
When do they do it: timing
It is important not to be late in carrying out all diagnostic procedures before the period when termination of pregnancy is allowed for medical reasons - up to the 22nd week.
Expert ultrasound, which allows you to assess the condition of the internal organs of the grown baby, and, possibly, identify signs of chromosomal developmental abnormalities, if any, as well as the state of the fetoplacental complex is considered informative no earlier than the 22nd – 24th week.
Therefore, during the second screening of the gestation period, data from the ultrasound protocol carried out as part of the first screening are used.
If for some reason the results of a screening ultrasound for the 11th – 14th week of pregnancy are not available, then you should undergo it at least to clarify information about the duration of pregnancy and whether the size of the fetus corresponds to its age.
The timing of the second screening (triple test) is very limited. The biochemical test should be taken strictly from the 16th week to the 6th day of the 18th week of pregnancy. ]