Leukocytes (Le) are the formed elements of blood. Under a microscope, they appear as white cells with a clearly defined nucleus. Their amount in urine can be counted by a laboratory assistant or a specialized automatic counter.
Normally, a child’s urine contains a small amount of leukocytes. Their number does not depend at all on age, but varies depending on gender.
The number of leukocytes in a boy’s urine should not exceed 5 units in the field of view; in a girl’s urine, a level of up to 10 units in the field of view is acceptable.
- Collection of urine for research according to Nechiporenko
What are leukocytes in a blood test?
Leukocytes are a group of blood cells of different morphology and functions, united by the lack of natural coloring. Therefore, they are often also called white blood cells. There are 5 subpopulations of leukocytes:
- neutrophils - destroy small foreign particles and cells by phagocytosis;
- lymphocytes - provide a humoral (B-lymphocytes synthesize antibodies) and cellular (natural killer cells and cytotoxic T-lymphocytes kill infectious agents through direct contact with it) immune response;
- monocytes are the largest type of leukocytes, capable of active phagocytosis. A distinctive feature is that they do not die after the process of phagocytosis, if the cells they destroyed did not contain toxic substances;
- eosinophils – provide antiparasitic immunity and allergic reaction by activating class E immunoglobulins;
- basophils - upon contact with foreign antigens, they are instantly destroyed. In this case, histamines and leukotrienes are released, which contribute to the accumulation of all other subpopulations of immune cells.
White blood cells are determined in a blood test for the purpose of early diagnosis of infectious infection, allergic reaction and oncological process.
Read further: What are tumor markers, how much can you trust them, how to get tested correctly
How do white blood cells get into the urine?
Leukocytes in the urine of infants and older children in single quantities are considered a variant of the physiological norm. However, as soon as the cascade of protective immune reactions is launched, their magnitude increases sharply. With the blood flow, leukocytes rush to the location of the source of infection. Immune cells are able to penetrate all human organs and tissues, and in the genitourinary tract they are identified at all levels - from the pelvis to the urethra.
After realizing their function in the genitourinary system, subpopulations of leukocytes are excreted from the human body along with urine.
Elevated white blood cells due to allergies
One of the reasons for elevated white blood cells may be the body’s reaction to an allergen. But the number of units of white cells should not exceed 20. To exclude kidney pathology, be sure to tell the doctor that the child was tested during an exacerbation of allergies or after a recent attack of the disease. As a rule, if the cause was an allergen, a repeat analysis will show only a slight excess of the norm or will be completely fine.
Symptoms
Parents are concerned about the question - what are the symptoms of increased leukocytes in the urine of an infant? As a rule, this is a change in the color and smell of urine, its turbidity, the appearance of sediment, as well as a sharp decrease/increase in daily diuresis (the amount of urine excreted). The child may suffer from abdominal pain, and sometimes the body temperature rises.
Adults experience similar symptoms, as well as itching and pain when urinating. In addition, blood may be found in the urine excreted.
Table of norms of leukocytes in the urine of a child
Once you receive the test results, you should not try to determine the disease on your own.
Important: the norm of leukocytes in the urine of children is selected for each age and gender separately.
Making a diagnosis is the job of a doctor, this is especially important when diagnosing children. The information in this section is presented for informational purposes only, but not for self-diagnosis.
| Age | Floor | Number of leukocytes in the field of view of the microscope |
| Up to 1 year | Male | 3-7 |
| Female | 4-9 | |
| From 1 year and older | Male | 4-7 |
| Female | 5-10 |
It should be noted that the norm of leukocytes in the urine of a child under one year of age is slightly higher than the standard indicators of older patients. This situation is associated with the need to ensure maximum protection for the child while he does not have acquired immunity, and his natural immunity is not fully formed.
At this age, the concentration of lymphocytes in the blood can reach 70-75%. The lifespan of natural killer cells (NK-) does not exceed 1 week, B cells - 2 weeks, while T lymphocytes can remain in the blood for up to 5-6 years. After natural death, NK and B lymphocytes are excreted in the urine.
Read further: Leukocytes in the stool of a child, infant - the norm and reasons for the increase
Analysis methods
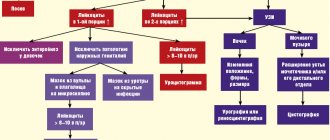
Leukocyturia in children is detected after a general urine test, which is performed routinely according to the child’s age or prescribed when signs of the disease appear. If the analysis data is unsatisfactory, you should consult a doctor.
For the first time, the doctor will prescribe a repeat control study and additional diagnostic methods. To confirm true leukocyturia, it is necessary
- repeat general urine test;
- urine collection according to Nechiporenko;
- Amburger's test;
- analysis for “live” leukocytes;
- Addis-Kakovsky sample.
Before repeating the general analysis, it is necessary to take into account all the rules for collecting urine.
- Prepare a sterile container (pharmacy container) in advance.
- In the morning, before the first urination, the child is washed (for a girl, movements should be directed from front to back, for a boy - in any direction).
- Collect “medium” urine in a container and screw the lid on tightly.
- You can store the collected material in the refrigerator, but no more than 2 hours.
Sterile urine bags are used for the baby. They are glued to clean and dry skin of the perineum, around the urethra.
As part of additional diagnostics, the number of leukocytes, erythrocytes - red blood cells and cylinders - “casts” of connections located in the kidneys is examined. These methods are accurate and specific for inflammatory diseases of the urinary system.
Test according to Nechiporenko
The collection of material according to Nechiporenko differs in that only the middle portion of urine is taken into the container. For analysis, at least 10 ml is required. In the laboratory, the number of formed elements in 1 ml of urine is calculated.
Analysis according to Amburge
The Amburge analysis determines the formed elements excreted in the urine in 1 minute. For this method, the first urination (the time of which is recorded) is performed in a potty, diaper or toilet. After 3 hours, the child urinates again, but in a prepared container. The entire volume of urine excreted is delivered to the laboratory.
Addis-Kakovsky Study
In a study using the Addis-Kakovsky method, the number of leukocytes is determined in urine collected per day. On the eve of the test, the child is fed protein foods and is not allowed to drink much liquid. The material is collected within 12 hours, and laboratory assistants do a 24-hour count.
In pyelonephritis, active or “live” white blood cells are continuously released from the inflamed kidney. But when the density of urine decreases, they turn into specific cells that are invisible to standard methods for diagnosing leukocyturia.
To identify such leukocytes, distilled water and a special dye are added to the urinary sediment. The cells absorb fluid, swell and become visible. With inflammation in the pyelocaliceal system, the number of such cells increases significantly relative to the total number of leukocytes.
Leukocyturia and its types
Elevated leukocytes in the urine of a child or adult in medical practice are referred to as leukocyturia. The first classification is based on the clinical significance of leukocyturia, distinguished:
- true, when the cause of an increase in leukocytes in my child or adult is a pathology of the genitourinary system;
- false, when lymphocytes found in the urine are the result of improper preparation of the patient for the collection of biomaterial. For example, insufficient hygiene of the external genitalia in the presence of inflammation, minor injuries or bruises.
The dogma that human urine is sterile has not retained its relevance in the 21st century. Many studies have shown that moderate amounts of representatives of the normal microflora of the human body can be found in urine. However, leukocytes in the urine of infants and older children do not increase.
In this regard, leukocyturia of infectious and aseptic nature is distinguished. The first type is characteristic of infectious lesions of the urinary system, the second is the result of an allergic reaction, exposure to certain medications or glomerular nephritis (damage to the kidney glomeruli, as a result of which leukocytes diffuse freely into the urine in unlimited quantities).
Depending on the degree of deviation from the norm, leukocyturia is distinguished:
- insignificant - no more than 30 cells in the field of view of the microscope. It has no diagnostic value in the absence of concomitant symptoms of the disease. It can be triggered by improper preparation of the patient for the collection of biomaterial or daily fluctuations in all physiological parameters;
- moderate – up to 100 cells, typical for infectious infection of mild to moderate severity;
- severe - more than 100 leukocytes. The condition accompanies severe infectious and oncological diseases.
Prevention
There are some preventive measures you can take to reduce your chance of developing a urinary tract infection. It is extremely important for girls to learn to wipe their perineum from front to back to avoid introducing fecal bacteria into the urinary tract.
The doctor should examine your child if you think there may be white blood cells in his urine. If your child took extra vitamin C or ate a lot of protein, you should tell your pediatrician. According to research, excess protein or vitamin C can lead to a negative result, even in the presence of white blood cells.
Alena Paretskaya, pediatrician, medical columnist
just today
( 37 votes, average: 4.62 out of 5)
Ultrasound of the vessels of the brain and neck: indications and diagnostic value
Allergy tests: how they are performed, examination methods
Related Posts
Reasons why leukocytes in a child’s urine are elevated
During the general analysis, the general norm of leukocytes in the urine in children and adults is determined, without specifying a specific subpopulation. However, moderate and significant leukocyturia is a sufficient reason to prescribe additional diagnostics.
A more detailed result can be obtained by cytological examination of urine sediment. As a result, the quantitative content of each type of leukocyte is described. Such a detailed analysis is necessary to make a correct diagnosis.
It is known that neutrophils increase in tuberculosis and pyelonephritis. Both diseases are bacterial in nature, and the immune system begins to actively protect a person from foreign biomaterial. The processes of synthesis of immune cells are launched, which, after fulfilling their functions, die and are excreted in the urine.
Mononuclear leukocyturia (increased monocytes) indicates the non-infectious nature of the pathology. For example, glomerular nephritis is an autoimmune disease in which the defense mechanisms are directed against healthy cells in the body. In children, this condition is often accompanied by a sharp increase in blood pressure, nosebleeds and back pain.
Consistently high levels of lymphocytes in the urine indicate systemic diseases, such as lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis. Lupus is characterized by excessive unnatural deposition of immune system cells of unknown etiology. The nature of arthritis also remains a matter of debate. Most scientists are inclined towards infectious, since the pathology is accompanied by an increase in leukocytes and erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
The number of eosinophils increases sharply when a person comes into contact with allergens.
Read further: What does leukocyte esterase in urine mean; norms for children
Leukocytes in urine – treatment with medications and folk remedies
What to do if leukocytes in a child’s urine are elevated? Initially, you need to establish the severity and cause of this condition. Thus, slight leukocyturia in children can be observed against the background of teething. In this case, symptomatic treatment is appropriate, for example, the use of antipyretic drugs.
If the increase in leukocytes is provoked by an infectious process, then the pathogen must be identified. It is strictly forbidden to select antibiotics for children on their own. For many antibacterial drugs there is an age limit, and only the attending physician can calculate the required dose and course duration.
For young children, the preferred form of antibacterial therapy is bacteriophages, which are viruses that destroy pathogenic bacteria. The drugs have less pronounced side effects and do not cause the death of the child’s normal microflora.
A viral infection requires the administration of antiviral drugs in combination with immunomodulators. Allergy therapy consists of antihistamines and avoiding contact with the allergen.
Folk remedies are not an alternative to official methods of medicine. They can act exclusively as auxiliary treatment methods and only in agreement with the attending physician.
It is known that honey and bee products (propolis), which exhibit an antibacterial effect, help against infection. They are taken both in pure form and as part of tinctures and decoctions with herbs. It has been proven that garlic contains antibiotics that are active against E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus and microscopic Candida fungi.
In the treatment of allergies, infusions of string, dead nettle or fragrant celery help.
Useful tips for parents
Parents should know what to do before collecting urine for testing in children. Violation of requirements also provokes incorrect indicators.
What to do:
- consult a doctor, find out the rules for collecting urine, the timing of delivery of the material to the laboratory;
- if the baby is taking medications, be sure to notify the attending physician and laboratory assistant;
- Antibacterial therapy should be completed 2 weeks before the control study;
- shortly before collecting the material, you cannot perform physical procedures, ultrasound, or x-rays of various parts of the body;
- If there are dietary restrictions, adhere to them, otherwise the results will be incorrect or incomplete.
How to properly prepare a child for urine testing?
The correct preparation for collecting biomaterial determines the accuracy of the analysis results obtained. It is important to collect the first portion of morning urine. For children, no special preparation is required. However, if the baby is prescribed antibacterial drugs, then a laboratory employee should be notified about their use.
Urine is collected naturally. It is allowed to pour from a previously washed and wiped dry pot. For infants, special urinals have been developed that are glued to the child’s genitals. It is recommended to keep the baby in an upright position. You can stimulate the process of urination by turning on tap water near your child.
The biomaterial should be delivered to the laboratory department as soon as possible.