Atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis is considered one of the types of coronary heart disease. It is not a separate diagnosis, but only indicates one of the manifestations of IHD.
The mechanism of development of pathology can be described in several stages:
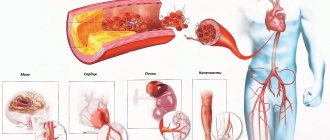
- Violations of cholesterol and protein metabolism provoke the deposition of cholesterol on the inner wall of the arteries in the form of plaques. This is how atherosclerosis of blood vessels appears, including coronary ones.
- Sclerotic damage to the arteries supplying the heart leads to insufficiently effective blood supply to the myocardium.
- As a result, this becomes the cause of local atrophy and partial necrosis with subsequent replacement of its normal connective tissue.
- Scar tissue does not perform the necessary functions, which leads to heart failure.
There are several types of cardiosclerosis
Classification
In medical practice, it is customary to divide these types of cardiosclerosis, depending on the prevalence:
- Focal cardiosclerosis. This pathological condition is accompanied by the formation of individual scars in the heart muscle. It can be small-focal - when insufficient oxygen is supplied, or large-focal - formed as a result of a heart attack or myocarditis.
- Diffuse. Characterized by the replacement of muscle tissue over the entire area of the myocardium. The formation of this pathological condition occurs as a result of the presence of coronary heart disease.
The pathological condition is also classified depending on the factors that caused its formation. Highlight:
- Primary cardiosclerosis (congenital). It is formed as a result of the presence of connective tissue diseases that are systemic in nature. They can be hereditary or acquired during fetal development.
- Post-infarction cardiosclerosis is formed due to a history of a pathological condition such as myocardial infarction. In places where muscle fibers die, connective tissue appears that looks like scars; myocardial hypertrophy is observed on their peripheral parts. This is necessary to restore the normal ability of the heart to contract. Over time, the cavities of the heart muscle expand, because its functionality is exhausted.
- Atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis of the heart. The formation of this pathological condition requires a considerable amount of time, because the cells of the heart muscle must suffer from prolonged hypoxia. This type of cardiosclerosis and ischemic heart disease are closely related, and this is the main factor in the development of heart attack. With this pathology, special attention should be paid to prevent complications.
- Postmyocardial cardiosclerosis. This pathological condition appears as a result of the formation of an inflammatory process in the myocardium. It is necessary to emphasize that this type of disease differs from all others in that it manifests itself in young people if they have a history of infectious diseases, allergies, infectious and inflammatory processes in the body cavity. It can affect various parts of the heart muscle.
Prevention of diffuse cardiosclerosis
The main goals of preventive measures to prevent the development of diffuse cardiosclerosis are aimed at eliminating the causes of myocardial ischemia and timely treatment of cardiac pathologies. Those people who are predisposed to developing coronary heart disease should be especially careful about their health.
The main measures to prevent diffuse cardiosclerosis are:
- maintaining an active lifestyle;
- compliance with the principles of rational nutrition;
- eliminating bad habits;
- combating stress;
- promptly consult a doctor if symptoms of cardiovascular diseases are detected.
The development of diffuse atherosclerosis is preceded by many factors. Timely visits to a doctor for preventive examinations, compliance with all his recommendations after identifying other diseases and maintaining a healthy lifestyle will allow many people to avoid such a serious heart pathology as diffuse scarring of myocardial fibers.
Possible factors
Like any disease that is acquired, cardiosclerosis acquired over time is formed as a result of exposure to contributing factors.
It could be:
- Hypertonic disease. This pathological condition is accompanied by an increase in blood pressure to high levels and an acceleration of blood flow, which in turn complicates the functioning of the heart and causes the appearance of cholesterol plaques and blockage of blood vessels. The heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen, and hypoxia forms.
- Metabolic disorder (especially fat). This pathological condition, like the previous one, is accompanied by the appearance of cholesterol deposits and hypoxia of the heart muscle.
- Bad habits (especially smoking) lead to a narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels and a decrease in the amount of oxygen that flows to the heart.
- Overweight. This pathological condition leads to a double load on the heart, because it must move a larger volume of blood. As a result, the heart muscle, so to speak, wears out and ages.
- Long-term exposure to stressful situations. Overstrain of the nervous system is accompanied by the production of excessive amounts of hormones by the adrenal glands, the action of which is aimed at suppressing this condition. They are the cause of loss of elasticity of blood vessels and disruption of metabolic processes. All this causes cardiac hypoxia and the formation of cardiosclerosis.
- Radiation exposure leads to deformation or death of myocardial cells and their replacement with connective tissue.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Eating excessive amounts of spicy and fatty foods.
- Overloads of a physical nature that are present over a long period of time.
Quite often, cardiosclerosis also develops as a consequence of such diseases and pathological processes:
- Myocardial infarction and atherosclerotic changes in heart vessels.
- Sarcoidosis. It is characterized by the formation of neoplasms of various types in the heart muscle.
- Hemogromatosis. This pathological condition is accompanied by the accumulation in the myocardium of an excessive amount of microelements with a predominance of iron, which leads to the death of muscle fibers and their replacement with connective tissue.
- Scleroderma.
It should be noted that the cause of cardiosclerosis can be allergies, infectious processes, and in some cases also heredity.
Causes of the disease
Fine-focal cardiosclerosis is secondary in nature, that is, it develops against the background of other diseases. Often the disorder appears in patients suffering from ischemia (CHD).
Pathology is also provoked by:
- heart defects;
- arrhythmia;
- angina pectoris;
- myocarditis;
- rheumatism;
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- intoxication with heavy metals.
The list of reasons can be supplemented by diabetes mellitus, excess weight, alcoholism, heart surgery, constant stress, drug abuse, and age-related changes.
Clinical picture
At first, the formation of cardiosclerosis of the heart does not manifest itself with any pathological symptoms. The growth of connective tissue is insignificant and does not lead to a deterioration in the elasticity of the vascular walls or the functional ability of the heart muscle.
Focal cardiosclerosis, formed as a result of a heart attack, can also occur without visible signs, especially when the affected area is superficial. Impaired functioning of the heart muscle is often accompanied by diseases that cause the formation of cardiosclerosis.
The following pathological symptoms may indicate the process of sclerosis:
- attacks of shortness of breath;
- coughing attacks;
- heart rhythm disturbances of various types;
- increased heart rate;
- rapid loss of strength;
- edematous processes;
- dizziness.
Well, now let’s look at the signs of cardiosclerosis in more detail.
Shortness of breath and cough
This symptom is the main indication of the presence of heart failure accompanying cardiosclerosis. Please note that it begins to appear after several years from the moment when the growth of connective tissue began. Shortness of breath may appear much faster if the cause of cardiosclerosis is myocardial infarction.
The symptom is characterized by the inability to restore the functional rhythm of inhalation and exhalation. In some cases, it may appear in parallel with a cough, palpitations and pain in the chest.
Shortness of breath occurs as a result of the loss of the ability of the heart muscle to perform its pumping function. Congestion in the pulmonary circulation is observed, as a result of slow gas exchange and respiratory dysfunction.
Shortness of breath can be caused by:
- physical load;
- lying position of the patient (blood flow to the heart increases);
- stressful situations.
Please note that it is generally impossible to get rid of this pathological symptom, because it is accompanied by irreversible changes in the heart. With the progression of the pathological process, shortness of breath can bother the patient not only in the presence of provoking factors, but even at rest.
Cough. This pathological symptom, like the previous one, appears as a result of congestive processes in the lungs. There is congestion of the bronchi, an increase in their size, which causes irritation of the cough receptors. In the vast majority of cases, the cough is dry and responds well to treatment.
Rhythm disturbances and increased heartbeat
They are formed if areas of localized cardiosclerosis spread to the conduction system of the heart and lead to damage to the fibers through which impulses are transmitted. All this causes a delayed reaction of parts of the heart muscle to carry out the contraction process, deterioration of blood flow and excessively intense mixing of blood in the heart chamber, and this increases the risk of blood clots.
Violations can manifest themselves in the form of:
- Tachycardia. Characterized by an increase in heart rate that occurs with circulatory failure.
- Bradycardia. It manifests itself as a slow heart rate; in most cases, this symptom is invisible to the patient and is discovered by chance.
- Extrasystoles. This symptom is characterized by the appearance of additional contractions of the heart, which lead to disruption of the overall rhythm. This process can only be diagnosed by electrocardiography.
Arrhythmias accompany cardiosclerosis only if the lesions are small. This symptom can cause a poor prognosis, as the risk of severe complications increases.
Increased heart rate. This symptom of cardiosclerosis is formed as a result of rhythm disturbances or uneven contraction of the heart. The patient may complain of abnormal heartbeat in the abdomen or neck. Examination may show pulsation, which is localized at the xiphoid process.
A feeling of fatigue that appears quite quickly indicates heart failure. The heart loses its ability to pump out the required volume of blood, which can lead to a drop in blood pressure and insufficient oxygen supply to the tissues.
Rapid fatigue occurs not only as a result of physical activity, but also mental stress. There may be a disturbance in concentration and memory disturbances.
Edema and dizziness
Edema is evidence of advanced cardiosclerotic heart disease. They do not appear in all patients and indicate congestive processes in the systemic circulation. This symptom indicates a violation of the functional ability of the right ventricle and the development of stagnation as a result of the loss of the ability to pump blood in the required volume.
The favorite localization of edematous processes are areas of the body where blood flow is slow and blood pressure is low, most often these are the lower extremities. There is expansion and swelling of the veins, which over time turns into edema as a result of fluid entering the soft tissues.
The peculiarity of this symptom is that it first appears only in the morning and disappears during the day. Over time, swelling is present throughout the day.
Dizziness. This symptom, like the previous one, is evidence of an advanced course of the disease; it appears from time to time. This occurs as a result of insufficient oxygen reaching the brain. The body thus tries to defend itself, reduce energy costs and use the oxygen supplied by the heart muscle for as long a period of time as possible.
Symptoms
Atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis is a disease that can last for a long time. If appropriate therapy is not carried out, the pathological process will worsen.
At the initial stages of development, the patient does not experience any manifestations. The diagnosis is usually made incidentally during electrocardiography.
Over the years, the likelihood of atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels increases significantly. Therefore, even if there has never been a heart attack, scars still appear in the heart due to lack of oxygen.
Also read: Mitral regurgitation - what is it?
Pathological processes with development are complemented by new manifestations:
- Initially, the patient often experiences a feeling of lack of air during physical activity. Gradually, it becomes difficult for a person to breathe, even if he walks slowly. The patient begins to get tired quickly, suffers from weakness and cannot fully perform his usual work.
- Painful sensations appear in the left chest. At night they begin to intensify. Manifestations similar to angina attacks may occur. Unpleasant sensations spread to the shoulder blade, the entire arm and other parts of the body.
- I often get headaches, stuffy ears and hear noises. This indicates insufficient oxygen supply to the brain.
- The rhythm of heart contractions is disrupted. The beat frequency increases, and signs of atrial fibrillation appear.
All these symptoms appear already in the presence of serious disruptions in the functioning of the heart. Therefore, it is important to undergo regular examinations to identify problems early in development.
Diagnostics
Every doctor knows that cardiosclerosis is a very difficult disease; in order to prescribe adequate treatment, he, first of all, must make a correct diagnosis; for this, the following is carried out: collection of anamnestic data, with clarification of previous heart diseases (and not only) even during childhood; collection of patient complaints with clarification of the time of appearance of the first pathological symptoms that indicate illness.
After this, the following examinations are prescribed:
- ECG - this study allows you to determine the characteristics of the heart rhythm.
- Angiography. The examination allows you to identify affected areas of blood vessels in which cholesterol plaques and stagnation are localized. To carry it out, a contrast agent is injected into the bloodstream, which makes it possible to determine the patency of blood vessels.
- Biopsy - allows you to take biopsy material for further examination of pathological tissue.
- ECHO-cardiography allows you to assess the functional ability of the heart valves.
- X-ray examination allows you to determine the size of the heart, as well as the stage of progression of the aneurysm.
- Computed tomography is an analogue of an x-ray, but provides a more accurate picture of the condition of the heart and areas of localization of the pathological process.
It is also mandatory to conduct studies, such as a general blood and urine test. These examinations are considered auxiliary and help to determine the factors that caused the formation of cardiosclerosis.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of cardiosclerosis can be carried out either conservatively or surgically. To determine treatment tactics, the provoking factor in the development of the pathological process is first taken into account.
As for drug therapy, the following is considered justified:
- ACE inhibitors (Captopril, Enalapril, Lisinopril), the action of which is aimed at preventing the process of expansion of the heart chambers;
- beta blockers (Bisoprolol, Coverdilol) - help increase cardiac output;
- diuretics (Furosemide) - help reduce the intensity of manifestations of heart failure;
- statins help reduce the amount of cholesterol in the blood;
- cardiac glycosides (Digoxin).
If the disease requires surgical intervention, it can be performed by:
- coronary artery bypass surgery - restoration of normal blood flow through the coronary arteries occurs;
- resection of a cardiac aneurysm, which allows normalizing the contractility of the unaffected myocardium;
- implantation of a pacemaker, it is considered justified to carry out this intervention in the presence of conduction disturbances and an increased level of excitability;
- Heart transplantation is necessary if the changes are irreversible.
Quite often, people use recipes from sources of traditional medicine to treat cardiosclerosis, which, for cardiosclerosis, recommends taking medications made from herbs that have diuretic and antisclerotic properties. However, if you decide to be treated with the help of such prescriptions, you must be careful and be sure to consult your doctor. After all, such self-medication will not only not lead to improvement, but will also cause complications.
Please note that the best results are observed with a combination of traditional and traditional methods of treatment (under the supervision of a doctor).
Treatment
Treatment of diffuse cardiosclerosis should begin as early as possible and be comprehensive. Its main points are aimed at the following goals:
- elimination of ischemia that caused damage to the myocardium by scar tissue;
- improvement of the condition and preservation of the remaining myocardial fibers;
- elimination of signs of heart failure;
- elimination of arrhythmias.
Treatment of the diffuse form of cardiosclerosis can be carried out on an outpatient or inpatient basis. The patient is advised to limit physical activity, give up bad habits and follow a diet.
Some dishes and foods should be excluded from the patient’s diet:
- fried meat dishes;
- foods rich in cholesterol (offal, egg yolks, etc.);
- strong tea;
- natural coffe;
- foods that cause bloating;
- radish;
- turnip;
- garlic;
- onion.
The daily diet should limit the consumption of free liquid and table salt. It is recommended to prepare dishes by steaming, boiling, stewing or baking. Food should be consumed in small portions (5-6 times a day).
For the conservative treatment of ischemia, various drugs can be used, the selection of which can only be carried out by a doctor after a diagnostic examination. To normalize coronary circulation, the following can be used:
- Nitrates (Nitroglycerin, Nitrosorbide). These drugs help reduce the load on the heart wall, reduce the myocardial oxygen demand, and improve coronary blood flow. Such antiangial drugs can be taken to eliminate and prevent an attack.
- Calcium antagonists (Nifedipine, Diltiazem, Veroshpiron). These drugs help lower blood pressure, reduce the load on the myocardium, eliminate spasm of the coronary vessels and help reduce the need for oxygen in the heart muscle.
- Beta-blockers (Anaprilin, Inderal, Nebivolol). These drugs, their dosage and frequency of administration must be selected strictly individually. Beta-blockers help reduce myocardial oxygen demand (especially during physical activity), lower blood pressure and eliminate certain types of arrhythmias.
If it is necessary to reduce blood cholesterol levels, the patient may be recommended to take statins (Rosuvastatin, Simvastatin, Atorvastatin, Lovastatin). These drugs must be taken according to a special regimen and under constant monitoring of laboratory blood parameters.
If necessary, the patient may be prescribed:
- diuretics (Furosemide, Trifas, Britomar, etc.);
- antiplatelet agents (Cardiomagnyl, Aspirin);
- ACE inhibitors (Enalapril, Ramipril, Captopril).
The dosage, medications and regimen of their administration are selected individually for each patient, and their self-prescription can cause a number of undesirable consequences.
For ischemia that cannot be treated with medication, the patient may be recommended surgical treatment:
- coronary artery bypass grafting;
- stenting;
- pacemaker implantation.
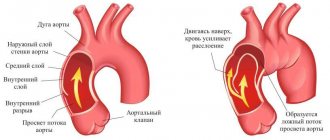
In some cases, diffuse cardiosclerosis can lead to the formation of a cardiac aneurysm. Such a pathology can threaten the patient’s life, and surgery may also be necessary to eliminate it. The essence of this intervention is aimed at excision of the area of protrusion from the vascular wall and its replacement with a special plastic prosthesis or a section of a blood vessel taken from another part of the patient’s body.
Complications
Summarizing the information presented, we can conclude that cardiosclerosis is considered a disease that is accompanied by irreversible changes. There is a disruption in the functioning of the heart muscle and the risk of various complications. Even if you seek help in a timely manner and eliminate the provoking factor, the connective tissue in the myocardium causes negative consequences. They can be mitigated by surgical or conservative treatment, but they cannot be eliminated forever. Most often, cardiosclerosis leads to the formation of such pathological processes and conditions as:
- chronic heart failure;
- aneurysm of the heart muscle;
- various rhythm disturbances;
- thromboembolism;
- a syndrome called “chronic fatigue”.
Kinds
Depending on the characteristics of the spread of the pathological process, atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis is divided into the following types:
- diffuse – foci of sclerosis are located throughout the myocardium;
- focal (cicatricial) – the pathological process is localized in a small area of the myocardium;
- large-focal – scars can reach several centimeters;
- fine focal - characterized by the presence of small scars, the size of which does not exceed 2 mm.
For effective treatment of atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis, it is necessary to limit physical activity and adhere to a diet - table No. 10 according to Pevzner.