Why might there be discharge?
Many processes in the female reproductive system are periodic. The cycle appears almost simultaneously with menstruation. At this time, the endometrium begins to shed and leave the body. In parallel with this, the maturation of the egg occurs. This process is carried out under the influence of estrogens. A month later, ovulation occurs, which is accompanied by the production of progesterone.
Sometimes, due to changes in the amount of hormones in the body, such a secretion appears. Some women are alarmed by the fact that the discharge in the middle of the cycle is brown. The color is affected by hemoglobin, which is part of the blood. Its protein is brown.
If the female secretion begins to change its color, then you should visit a gynecologist. This will help prevent further development of pathology in advance.
Brown discharge can be classified according to its saturation:
- Red-brown. They indicate that the blood was released relatively recently and has not yet clotted. Often, red discharge appears due to microcracks formed in the vagina. They can occur after sexual intercourse.
- Light brown discharge. Occurs due to the use of contraceptives. Sometimes they appear after inflammation or problems with the menstrual cycle.
- Dark brown. They often appear as a reaction to taking hormonal drugs.
Brown discharge mid-cycle
Brown discharge in the middle of a woman's menstrual cycle is not entirely normal, and in some cases completely abnormal. What it can mean and what to do in this case - read on.
It must be said that there is not a single woman who, for one reason or another, does not experience such discharge at least once in her life. In 80 women out of 100, such discharge, if it appears, is insignificant; in the remaining 20 cases, discharge appears unexpectedly or after intimacy and is abundant. During pregnancy, such discharge indicates the likelihood of miscarriage.
Discharge as a sign of disease
If a woman is not pregnant, brown discharge in the middle of her cycle may be a sign of a certain disease in the following cases:
- when there is discharge, and the woman does not use hormonal contraceptives;
- when the discharge causes dryness, burning and itching in the vagina, pain in the lower abdomen, sexual intercourse is painful, there is a fever;
- if a woman who is already in menopause has not had menstruation for more than a year;
- when discharge appears regularly after each act of intimacy.
When can cinnamon discharge be considered normal?
- If brown discharge appears just before menstruation for a few days or hours, which is a sign that your period is approaching;
- if the discharge continues for several days after menstruation, this is how the uterus gets rid of the last drops of blood;
- if a woman takes hormonal contraceptive pills;
- after violent sex in the absence of lubrication, damage to the vaginal mucosa occurs, which creates microtraumas;
- during the very first sex - rupture of the girl's pleura.
Causes of bleeding between periods
There are two groups of brown discharge between cycles: 1 - uterine bleeding, 2 - intermenstrual bleeding.
Uterine bleeding
What discharge can be considered normal?
Normal liquid is odorless and colorless. After your period has ended, the fluid released should be clear. A woman's body begins to prepare for the onset of ovulation. During this period, the liquid becomes more viscous, thick and mucous. Outwardly, it resembles the white of a chicken egg.
After the release of the egg from the follicle, their abundance decreases, and they gradually turn a less transparent white color. Sometimes in the liquid you can notice small clots of curd lumps that have a sour smell. This phenomenon is quite normal if it is not accompanied by vulvar irritation and itching.
If throughout the entire cycle the fluid has not changed in any way, then this phenomenon is considered pathological.
Types of brown discharge
If you find unnatural discharge from the genital tract, then first of all you need to pay attention to its color, abundance and character:
- Dark brown vaginal fluid most often indicates that there is a hormonal imbalance in the body;
- Light brown discharge usually appears as a result of some disease of the reproductive organs. This color indicates that oxidized blood is leaving the body;
- Red-brown secretory fluid indicates mechanical damage to the mucous membranes. This can happen due to intense or first sexual intercourse. Often, a similar phenomenon is observed in women after 45 years of age at the initial stage of menopause.
A qualified gynecologist will tell you more about the causes of unnatural discharge.
Reasons for appearance
Brown discharge in the middle of the cycle does not always appear during its passage. However, this does not mean that they should immediately be classified as pathologies. Often, discoloration occurs due to various physical damage to the vagina. In order to accurately determine the causes of brown discharge in the middle of the cycle, you need to consult a doctor.
Ovulation
During ovulation, the ovarian follicle ruptures and problems with hormonal levels appear. It is because of this that bloody and slightly black discharge is observed. Most women face them. If they last no longer than three days, then they cannot be classified as a pathology.
Pregnancy
Discharge in women appears due to the attachment of the fertilized egg to the lower part of the uterus. This process is completely painless. Sometimes it is accompanied by brown secretion. They should not appear when carrying a baby. If the liquid continues to appear, then you should visit a specialist.
Sometimes the appearance of discharge in pregnant women indicates that there is not enough progesterone in the body. It is because of this that the endometrium begins to be rejected. Another reason for their appearance is ectopic pregnancy. In this case, the fetus does not leave the fallopian tube and therefore does not enter the uterine cavity. Immediate surgery will help correct the situation.
Endometriosis
It provokes periodic spotting in the middle of the cycle. In some cases they take on a dark tint. It is this color that indicates the presence of this disease. The disease is accompanied by the proliferation of cells that are located inside the uterus. This provokes regular bleeding. In the future, they can cause inflammation of surrounding tissues.
This disease is quite serious. It is accompanied by serious complications and even leads to infertility. Signs of the disease include:
- severe pain during urination or bowel movements, often radiating to the lower abdomen,
- discomfort during sex,
- the abundance of menstruation increases,
- stomach pulls a lot,
- menstruation is accompanied by pain.
If these signs appear, you should immediately visit your doctor.
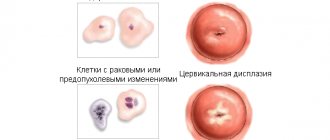
Cervical erosion
This disease is indicated by bleeding that appears between menstruation. They can appear not only in the middle of the cycle. The appearance of erosion should be suspected if blood regularly begins to be released after gynecological examinations or sexual intercourse. To confirm the diagnosis, a gynecological examination is performed using a so-called colposcope. This device will help to study changes in the cervix in detail.
The appearance of formations in the uterus
Often, mucous discharge may indicate neoplasms that have appeared in the genitals. They can be malignant or benign. The latter include uterine cyst and fibroids. Their further development may be accompanied by bleeding in the middle of the cycle. In some cases, they even turn into bleeding. If formations occur, it is necessary to regularly see a doctor.
Brown fluid may also indicate uterine cancer. This disease is very dangerous, as it can spread to other organs. Most often, the disease appears in women over 50 years of age. If the tumor is malignant, then during menopause a brown spotting secretion is formed in the middle of the cycle. Over time, their number decreases.
The appearance of the menstrual cycle
When teenagers start getting their periods, they are quite unstable. Their instability is manifested in the amount of fluid secreted and in the date of their appearance. During such periods, not only regular bleeding appears, but also other spotting brown discharge. This can continue for several years from the moment the cycle begins. However, if this continues further, you will have to consult a specialist.
Amenorrhea
Characterized by the absence of menstruation for six months. This phenomenon is considered normal during lactation or pregnancy of a girl. Amenorrhea can also occur in adolescents during the formation of a cycle. All other cases are considered a deviation from the norm. Amenorrhea is accompanied by a small amount of brown discharge.
Sexual diseases
They appear in the form of discharge, which may have an unpleasant fishy odor. Such diseases can lead to a general deterioration in health.
Vaginal or oral contraceptives
When taking Jess and other contraceptives, dark discharge may occur in the middle of the cycle. Sometimes they turn into bloody discharge. It is not uncommon to see brown fluid appear after using an intrauterine device. If everything is normal, then this should go away within a few months.
Problems with the pelvic organs
Quite often they are associated with the occurrence of inflammatory processes that can occur in the bladder. In addition to discharge, symptoms of inflammation include pain during sex, heaviness in the lower abdomen, and high fever. If these symptoms appear, you should not self-medicate.
All about DISCHARGES... For everyone
Vaginal discharge is normal
Normally, vaginal discharge is light, mucous, and may be slightly cloudy due to the admixture of epithelial cells from the vagina; if you use the same panty liner throughout the day, the discharge on it may be slightly yellowish in color. The nature and amount of vaginal discharge depends on the day of the menstrual cycle: in the middle of the cycle, as ovulation approaches, vaginal discharge becomes similar in consistency to egg white, the discharge is more abundant than usual, more alkaline. The amount of vaginal discharge increases during sexual arousal, especially during sexual intercourse. Normal discharge does not cause discomfort, does not cause unpleasant sensations: itching, burning and irritation of the genitals. If you take a smear with normal discharge, then there will not be an increased number of leukocytes, and the flora will be dominated by rods.
Fresh vaginal discharge has virtually no odor; the smell of discharge appears when bacteria multiply in it.
Transparent, stretchy, mucous discharge , similar to egg white, often abundant - in the middle of the cycle, the period before ovulation is the norm.
Creamy or jelly-like scanty discharge - the second half of the cycle - is normal.
Creamy or jelly-like, increasing discharge - the last days of the cycle - is normal.
Transparent, white or slightly yellowish discharge in clots is normal in the first hours after unprotected intercourse, when sperm enters the vagina.
Abundant white liquid discharge the morning after unprotected intercourse is normal.
Creamy white scanty discharge after sex with a condom or without ejaculation in the vagina - “used” vaginal lubrication is the norm.
Scarlet red bleeding , intensifying - the beginning of menstruation, the first day is normal.
Discharge with blood - scarlet bloody streaks in the middle of the cycle (between menstruation) - happens shortly after ovulation in the middle of the cycle - a variant of the norm.
Liquid whitish light discharge, similar to milk, during pregnancy, usually intensifies with increasing pregnancy - the norm, if it does not irritate the external genitalia and does not have an unpleasant odor.
Ichor, pink discharge like diluted blood, like “meat slop” - lochia after childbirth, normal
Abnormal vaginal discharge - leucorrhoea - has various causes, but most often they are associated with, mainly infectious in nature. Any abnormal vaginal discharge may be a sign of a genital infection and should be seen by a doctor immediately.
Discharge before menstruation
The state of vaginal flora and secretions depends on hormonal changes during different phases of the cycle, so the color and consistency of the discharge may change before menstruation, the discharge may become more cloudy, yellowish or white and more abundant (a feeling of constant wetness), more viscous. But if such discharge persists even after menstruation, especially if these symptoms are accompanied by vaginal itching or pain in the lower abdomen, you should consult a gynecologist.
Brown discharge before menstruation is discharge mixed with blood. Bloody discharge can normally appear a day or two before the onset of heavy menstrual bleeding. If spotting precedes menstruation for more than 2 days, or brown, pink, red-brown discharge appears in the middle of the menstrual cycle, this most likely indicates a disease.
Brown discharge before menstruation can signal: hormonal disorders, the presence of any infections (in particular, endometritis - inflammation of the endometrium), hematological diseases, adeomyosis. Very often, such phenomena accompany endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial polyps.
In particular, brown discharge before menstruation in combination with other symptoms (pain during menstruation, heavy bleeding with clots for more than 7 days) are signs of endometriosis.
Brown discharge mid-cycle may be a sign of progesterone deficiency or polycystic ovary syndrome, such conditions cause infertility and require treatment.
Discharge after menstruation
At the end of menstruation, blood clotting increases, blood is released more slowly and has time to clot; therefore, discharge and blood clots have a darker color and may be brown. If they have no smell, this is normal. If a smell appears, then you need to take a smear and PCR tests for chlamydia, gardnerella, mycoplasma and ureaplasma, herpes, CMV.
If discharge appears a few days after your period or if your period lasts more than 7 days, you should take a pregnancy test to rule out ectopic pregnancy or threatened abortion.
Discharge in diseases
- Constant discharge that does not change during the cycle , with the exception of the period of menstruation, occurs when a woman takes hormonal contraceptives or suffers from infertility and does not have inflammatory processes in the vagina.
- Scarlet spotting a few days before menstruation - cervical erosion, endocervicitis.Scarlet spotting during pregnancy — detachment of the ovum or placenta, threat of termination of pregnancy.Scarlet spotting after sexual intercourse - microcracks in the vagina formed during sexual intercourse, cervical erosion, cervicitis. After an abortion, there may be bleeding, varying in quantity and color. After 1 week Be sure to contact a gynecologist and perform a control ultrasound.
Selection options in Photoshop.
- White mucous discharge or transparent mucous discharge with white streaks at the end of the cycle, before menstruation - cervical erosion, cervicitis (inflammation of the cervical canal). The secretion of mucus is somehow related to the cervix. White curdled or kefir-like discharge , white films or plaque between the labia majora and minora, on the clitoris, usually in combination with a bready or sour-milk odor - thrush (candidiasis). White or slightly greenish, grayish discharge that peels off in films, usually in combination with a fishy odor - vaginal dysbiosis (gardnerellosis)
- Bubbling yellow or green discharge is a sexually transmitted infection (trichomoniasis, etc.). Yellowish or greenish copious discharge is an acute bacterial infection in the vagina, acute adnexitis (inflammation of the ovaries), acute salpingitis (inflammation in the fallopian tubes). Yellow or greenish scanty discharge - bacterial infection in the vagina, cervical erosion, chronic adnexitis (inflammation of the ovaries), chronic salpingitis (inflammation in the fallopian tubes) Purulent discharge green , thick, combined with mucus, aggravated by tension, after defecation - purulent cervicitis
- Brown dark spotting bloody discharge at the end of the cycle before menstruation (daub) is a pathological process in the uterus (endometriosis, polyp or endometrial hyperplasia, etc.) Brown spotting bloody discharge (daub) for a long time after menstruation is a pathological process in the uterus (endometriosis, polyp or endometrial hyperplasia, etc.) Brown spotting during pregnancy, including in the early stages (daub) is an old detachment of the ovum or placenta, which happened several days or even a week ago. Brownish discharge (spotting) in the first months of taking hormonal contraceptives is normal.
- Ichor, pink discharge like diluted blood , like “meat slop”, but with an unpleasant odor, usually before and after menstruation - chronic endometritis, chronic endocervicitis. Liquid watery discharge that takes on a dirty color on the pad, before and after menstruation - chronic endometritis, chronic endocervicitis.
- Discharge in large clots during menstruation - bending of the cervix, blood clotting disorder - tendency to form blood clots, hypovitaminosis of B vitamins, pathological process in the uterus (polyp, endometriosis, fibroids). Also, similar discharge occurs if a woman has an intrauterine device.
The most common colored discharge (leucorrhoea), their diagnosis and treatment:
- Brown discharge
Any brown discharge is bloody discharge. If there is severe or prolonged bleeding, it is necessary to do a biopsy of the endometrium (uterine lining) to rule out endometritis (inflammation of the uterus) or other pathology of the uterus.
Excessive bleeding during menstruation - An ultrasound is needed to assess the condition of the internal genital organs. Such bleeding may be symptoms of uterine fibroids or endometriosis, then if the thickness of the endometrium (uterine mucosa) is normal, curettage (as this procedure is called) may not be necessary. If the cause of bleeding is hypertrophy (increase in thickness) of the endometrium, endometrial or cervical polyps, then curettage must be performed. This will stop the bleeding and allow the procedure to be performed to rule out a more serious pathology.
- White discharge
Infection or inflammatory process. The diagnosis is made based on a smear and ultrasound.
- White discharge with a sour odor
Thrush (candidiasis). Associated symptoms: itching, discomfort in the genital area - but these signs may not be present. The diagnosis is made on the basis of a gynecological examination based on characteristic discharge and smear results.
- Yellow, yellow-green vaginal discharge
Bacterial infection. Treatment based on smear results.
- Foamy vaginal discharge
Trichomoniasis. Diagnosis is made based on a smear.
Discharge during pregnancy
Bloody or brown discharge during pregnancy is a very unfavorable symptom. This is a sign of a threatened miscarriage. Other diseases have nothing to do with it. There may be increased discharge on the days of expected menstruation; the color of the discharge may be yellowish. Limit sexual activity during this period to avoid the risk of miscarriage.
White discharge during pregnancy is most often a sign of thrush.
Discharge after childbirth
Normally, spotting after childbirth goes away within 3 weeks, or a maximum of a month. Otherwise, an inflammatory process in the uterus may be suspected, which requires examination and treatment.
Selection in Frame mode
Discharge after IUD insertion
Bloody discharge is a complication of the IUD and usually stops after 2-3 weeks. Scanty bleeding during the intermenstrual period is also a side effect of this method of contraception. If a gynecological examination and ultrasound do not reveal any pathology in the location of the IUD in the uterus, then blood loss can be reduced by prescribing gestagens or prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors.
The IUD quite often leads to heavy, prolonged menstruation with large blood loss. If anemia (anemia) develops, the IUD is removed. If you feel well, you can try drinking decoctions of nettle, water pepper, yarrow, and cinquefoil 2-3 days before the start of menstruation, 50 ml 3 times a day; pure extract from water pepper, red viburnum, 40 drops 4 times a day - until the end of menstruation, massage the nipples of the mammary gland for 3 minutes 3 times a day, after consultation with a doctor - dicinone and cotarnine.
Discharge after sexual intercourse
Contact bleeding (after sexual intercourse) can be a consequence of pathology of the cervix (discovered during a gynecological examination) or pathology of the uterus itself - polyps, hyperplasia, fibroids, etc. To find out the reasons, it is necessary to do an ultrasound scan at different periods of the cycle; functional diagnostic tests may be required.
Best posts on this topic:
Treatment
You should seek medical help if spotting does not go away for several days, and at the same time there is a feeling in the lower abdomen. In order to establish the cause of their appearance, you should undergo special examinations:
- PRC diagnostics or serological study:
- Ultrasound,
- hysteroscopy, during which the uterine cavity is examined,
- taking tests.
The results obtained will help prescribe the correct treatment. If all of the above examinations fail to identify pathology, then therapeutic therapy will not be necessary.
The following medications may be prescribed to treat the pathology:
- antigonadotropins,
- gestagens,
- antiestrogens,
If dark-colored discharge is accompanied by inflammatory processes, then a comprehensive solution is prescribed in which the following medications must be taken:
- vitamin complex,
- anti-inflammatory:
- antibiotics,
- oral contraceptives.
The choice of more effective and optimal therapy directly depends on the characteristics of the pathology and the patient himself.
Is there discharge before ovulation?
As soon as menstruation ends and a new phase of egg maturation begins, thick cervical mucus clogs the cervical canal, thereby protecting it from penetration by pathogenic organisms and sperm. During this period, in the absence of pathology, there should be no discharge.
When the follicle grows in the ovaries and the egg matures under the influence of increased estrogen hormone, the contents of the cervix gradually begin to liquefy and discharge may appear. But while they are scanty and thick, sperm cannot move and die as unnecessary, because the egg is not yet ready to merge with one of them.
Sometimes women notice brown discharge before ovulation. High levels of progesterone provoke rupture of the follicle, as a result of which the mature egg leaves it. These discharges are normally very slight, odorless, and not accompanied by pain or itching.
It is important to know that the duty of the born egg is to reach the fallopian tube, moving towards the sperm. She retains her ability to fertilize for a day, sometimes longer, but usually dies on the 2-3rd day. If a woman needs to get pregnant, she should try to use the time before ovulation, because sperm retain their vital activity and mobility for up to 5 days.
Prevention
In order to avoid problems with the appearance of fluid, you need to constantly monitor your health. It is recommended to adhere to certain recommendations:
- Drawing up and maintaining a daily routine.
- Reduce the amount of physical activity.
- Preparing a proper diet.
- Walking outside, regular gymnastics and fitness classes.
- You should take care of your body and not expose it to malnutrition or lack of sleep.
- Choosing the right sexual partner. It is recommended to avoid casual relationships.
Pathological discharge during pregnancy
If the brown discharge is not accompanied by pain, it probably does not mean anything bad:
- Period. Spotting before and after menstruation is normal. A couple of days before your period, the accumulated dirt comes out. At the beginning of the cycle, remnants of the endometrium emerge from the uterus. The mucus has a light brown tint. The process lasts no more than 3 days.
- Ovulation. In the middle of the cycle, the follicle ruptures, in which an egg is formed. Because of this, vaginal secretions change color to light brown. The process continues for up to 72 hours.
- Adaptation to hormonal agents. In the first 3-4 months of taking oral contraceptives, the body gets used to hormonal changes. A similar process is observed after discontinuation of medications.
- Puberty. In the first 2-3 years, girls' menstrual cycle normalizes. During this period, periods are weak and irregular.
- Beginning of sexual activity. After defloration, several sexual acts are accompanied by minor bleeding. Because of this, the mucus takes on a brownish tint.
- Pregnancy. Attachment of the fertilized egg to the wall of the uterus causes rupture of blood vessels. In the first hours after this, red-brown discharge appears in women. At later stages the phenomenon is dangerous. It indicates placental abruption, threat of miscarriage or premature birth.
- Postpartum period. After childbirth, hormonal levels normalize, and the body begins to prepare for a new fertilization. The formation of the menstrual cycle occurs. Discharge after childbirth is spotting and irregular.
- The beginning of menopause. In middle-aged women, the endometrium atrophies and comes out with small amounts of blood. The process does not depend on the menstrual cycle and is accompanied by hot flashes, sweating and mood swings.
- Lack of personal hygiene. Lack of cleanliness in the intimate area leads to the growth of pathogenic microflora and changes in the acid-base balance. As a result, the color of the vaginal secretion changes.
- Injuries. Due to lack of lubrication during sexual intercourse, microcracks appear in the vagina. Damage also occurs after abortion and inaccurate gynecological examination.
Pathological processes in the body, accompanied by bleeding, occur against the background of pain and other unpleasant symptoms:
- Colpitis. Inflammation of the vaginal mucosa. Characterized by blood in the discharge. Associated symptoms: itching and burning; lower abdominal pain; hyperemia of the mucous membranes; painful urination.
- Cervical erosion. The formation of ulcers and erosions on the uterine lining, which bleed after mechanical damage. Mucus mixed with blood is released, pain appears in the lower abdomen during sexual intercourse.
- Ectopic pregnancy. Appears after some delay in menstruation. It involves the attachment of the fertilized egg to the wall of the fallopian tube. The first symptoms are spotting dark brown discharge in women and severe pain in the lower abdomen.
- Inflammation of the urinary system. Infections of the kidneys, bladder and urethra are accompanied by pain in the lower back and lower abdomen. Patients suffer from a frequent urge to urinate and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. Blood is excreted in urine. A brown tint also appears in vaginal mucus.
- Endometrial pathologies. Diseases affecting the inner layer of the uterus are accompanied by the growth of the endometrium. The tissues peel off or form polyps. During the intermenstrual period, discharge mixed with blood appears. Menses are long and heavy, with clots. Sometimes there is pain in the abdomen.
- Uterine fibroids. Benign tumor of the muscular layer of the reproductive organ. Its characteristic intermenstrual bleeding causes brown vaginal discharge. Menstruation is heavy and painful. The cycle is broken. A large tumor puts pressure on the bladder and intestines, causing constipation and a frequent urge to urinate.
Brown discharge in women is often not a sign of pathology. If they are short-lived and not accompanied by pain, there is no need to worry. The regular appearance of mucus with a brown tint and pain should alert you. In this case, you should not delay your visit to the gynecologist.
Brown discharge is a natural secretion mixed with blood, which indicates the pathological nature of the discharge. Bloody periodic discharge is the norm for a healthy woman of reproductive age. Normally, the color of menstrual discharge varies from bright red to dark shade, which is due to the presence of enzymes in it.
Menstrual bleeding lasts from 3 to 8 days in a healthy woman. The appearance of bloody discharge (brown discharge) in any other phase of the cycle is a deviation from the norm. Brown discharge appears in 80% of women. Depending on the reasons causing uncharacteristic discharge, they speak of a physiological norm or a pathological disorder.
Brown discharge in girls in the middle of the menstrual cycle is considered normal in the following cases:
- The use of various hormonal contraceptives (oral, intrauterine devices, patches);
- Possible injuries to the walls of the vagina or cervix (during personal hygiene, aggressive sexual intercourse);
- At the first sexual intercourse;
- On the eve of menstrual bleeding (in some cases, brown discharge appears several days before the expected menstruation, which only indicates the scarcity of menstrual flow, during which the blood has time to clot);
- After the end of menstrual bleeding for several days.
Brown discharge in girls in these cases is a normal variant due to hormonal changes, but the amount of discharge, its consistency, and smell should also be taken into account. If the discharge acquires a brown tint, becomes abundant, has a heterogeneous consistency, and is characterized by an unpleasant odor, then in such cases a pathological process occurs.
Brown discharge that appears during the period of ovulation (usually between days 11 and 19 of the cycle) is also considered a normal variant. Discharge may appear during egg implantation, and the discharge may be accompanied by stabbing pain in the lower abdomen. Such discharge is short-term and spotting. In this case, they talk about implantation bleeding.
Brown discharge in women is a sign of pathology in the following cases:
- The appearance of pathological discharge in the middle of the cycle if the woman does not take hormonal contraceptives;
- Brown discharge during menopause in the absence of normal menstrual bleeding for 1 year or more;
- Regular occurrence of bleeding after sexual intercourse;
- Discharge accompanied by pain, itching, burning, and increased body temperature.
In case of any pathological discharge, it is necessary to consult a doctor for a full examination, since brown discharge in women is a symptom of various gynecological diseases, which, if not properly treated, can result in infertility, the development of benign and malignant neoplasms.
Brown discharge, which is essentially natural vaginal discharge mixed with blood, is divided by gynecologists into the following types:
- Intermenstrual bleeding;
- Uterine bleeding.
When diagnosing intermenstrual brown discharge, the causes may be:
- The use of hormonal medications that affect the menstrual cycle;
- Mental shock (emotional outbursts, shock, states of constant stress);
- Hormonal imbalances of various etiologies;
- Injuries to the genital organs, some types of gynecological procedures;
- Inflammatory processes, gynecological diseases, STDs;
- Intrauterine device.
Determining the causes of pathological discharge is necessary to prescribe effective therapy.
When diagnosing uterine brown discharge, the reasons may be:
- Tumor processes of the uterus and appendages;
- Pathological processes of the endometrium (endometritis, endometriosis);
- Cervical erosion;
- Cystic formations of the ovaries.
Brown discharge after menstruation is normal in the following cases:
- Scanty spotting, not accompanied by itching or burning;
- No pain, symptoms of inflammation, fever;
- The amount of discharge gradually decreases;
- The duration of such discharge does not exceed 3 days, and in total with the period of menstrual bleeding, menstruation lasts no more than 8 days.
Brown discharge after menstruation is a residual phenomenon, the removal of excess blood from the uterus. The discharge acquires a brown tint due to the fact that blood clotting increases at the end of menstruation.
If brown discharge after menstruation appears a few days after menstrual bleeding has completely stopped, then the following examinations must be carried out:
- Pregnancy test, ultrasound to exclude ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage;
- Smear, PCR analysis for the presence of chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, gardnerella, CMV, herpes virus.
Brown discharge during pregnancy is considered a pathology. Normally, discharge may appear during implantation of the fertilized egg, when the integrity of the endometrium is disrupted for a period of 1-2 weeks. Spotting brown discharge may also appear during pregnancy in the first trimester on the days of expected menstruation. If you have any brown discharge, you should consult a doctor.
Causes of brown discharge during pregnancy:
- Low levels of progesterone, which provokes endometrial rejection and poses a threat of miscarriage;
- Ectopic (tubal) pregnancy;
- Placental abruption, previa.
Any brown discharge during later pregnancy poses a risk of miscarriage.
To suspect that bleeding or spotting are pathological phenomena, a woman must clearly know what her cycle should be like. Of course, every experienced representative of the fair sex knows how many days between menstruation is the norm for her. How many days there should be between menstruation is an individual concept.