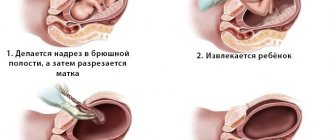
There are many indicators for carrying out a surgical operation called cesarean section, in which the fetus is removed from the mother's womb through an incision in the abdominal wall of the uterus, namely:
- health of the expectant mother;
- problems during pregnancy;
- condition of the fetus.
There is also more than one method of anesthesia for it (today, general, epidural and spinal anesthesia are used).
In most foreign countries, births by cesarean section are performed under epidural or spinal anesthesia, but attention should be paid to the fact that the rate of use of the latter is constantly growing and often dominates over epidural.
Each method is “endowed” with its own advantages and disadvantages, and, therefore, indications and contraindications as well (the doctor must take all this into account when choosing a method of pain relief). Today we will talk in more detail about spinal (or spinal) anesthesia.
Reasons for prescribing a caesarean section
Up to 20% of babies nowadays are born by caesarean section. Of this number, 2/3 of births were not initially planned surgically.
A planned caesarean section is prescribed for a number of diseases in the mother, so as not to significantly risk her health.
Emergency surgical delivery can occur for several reasons:
- problems during natural childbirth, if this increases the risk to the health and life of the mother and child;
- if a particularly large fetus is predicted;
- with a breech baby;
- with a combination of different factors (for example, a narrow pelvis in a woman in labor + a moderately large size of the fetus according to ultrasound).
During pregnancy, the expectant mother is under the supervision of doctors from the antenatal clinic and undergoes the necessary examinations in a timely manner. This is done to identify and prevent risks associated with pregnancy and childbirth, including possible indications for cesarean section.
Types of anesthesia for caesarean section
Meeting a child brings a lot of different feelings: fatigue, pain, but above all joy, pride, happiness. In order for a caesarean section to be carried out with a minimum of negative impressions, doctors study the patient’s history and determine the type of anesthesia that will be preferable for her during the operation.
There are 3 types of anesthesia that are used for caesarean sections:
- General. During the effect of general anesthesia, the expectant mother sleeps. She is in this state, including at the time of the birth of the baby. The child is brought to her after the operation, and then their acquaintance will take place.
- Epidural. This is the injection of an anesthetic drug through a very narrow plastic tube (catheter) into the epidural space in the spine. The dura mater surrounds the spinal cord and nerve roots. The epidural space runs along the spinal trunk, enveloping the dura mater. An anesthetic is injected there in order to block the transmission of pain impulses along the nerve endings of the spinal cord, which means it minimizes pain.
- Spinal. This is the most popular type of anesthesia for caesarean sections.
As you know, epidural (or otherwise, peridural) anesthesia is also used for natural delivery. However, during surgery, the dose of drugs is much higher.
Let us consider in detail the features of spinal or neuraxial anesthesia for cesarean section.
Description
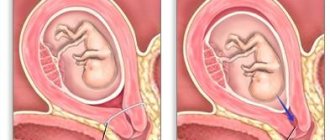
If during an operation it is necessary to deprive the lower part of the human body of sensitivity, then spinal anesthesia is performed. The essence of this method is to inject an anesthetic into a certain area near the spinal cord (in the back - that’s why this method came to be called that way). This is the subarachnoid space, which is located between the spinal cord and the meninges, it is filled with cerebrospinal fluid - cerebrospinal fluid.
A huge number of large nerves pass through the cerebrospinal fluid; the transmission or pain signals to the brain must be blocked. Spinal anesthesia is performed in the lumbar region, the area below the lower back is numbed. The anesthesiologist should pass the needle to the spine, the ligaments between the vertebrae, the epidural and the meninges, then inject the selected anesthetic.
There are numerous reviews of caesarean section with spinal anesthesia.
View gallery
Regional anesthesia
Epidural and spinal anesthesia are classified as so-called regional anesthesia (different from general anesthesia). Most doctors prefer to prescribe regional anesthesia for cesarean section unless there are contraindications.
What is common between epidural and spinal anesthesia?
Many people outside the medical profession believe that the types of regional anesthesia are the same. This is not true, although they have a lot in common:
- The specialist administers anesthesia through an injection in the back.
- The anesthetic drugs are the same: lidocaine, bupivacaine, ropivacaine and other anesthetics.
- The mother can see the baby soon after his first cry, as she is conscious.
- Regional anesthesia requires significantly fewer drugs than general anesthesia, which means the risk of side effects or their severity is reduced.
The choice of type of anesthesia ultimately remains with the doctor.
Differences between spinal anesthesia and epidural
There are fundamental differences between epidural and spinal anesthesia.
- With spinal anesthesia, the needle is inserted into the subarachnoid space, that is, deeper than with epidural, below the level of the spinal cord, into the cerebrospinal fluid.
- The needle for administering the drug during neuraxial anesthesia is thinner than during epidural anesthesia.
- Spinal anesthesia works faster than epidural.
- A catheter is placed for epidural anesthesia, but not for neuraxial anesthesia.
In general, spinal anesthesia is considered easier to administer than epidural anesthesia.
How to administer pain relief before caesarean section
Epidural anesthesia is most often performed in a sitting position, and spinal anesthesia - in a position lying on your side, bending your knees to your stomach, while clasping them with your hands.
Is it painful to have an epidural?
Before inserting the puncture needle, the injection site is first anesthetized, so the procedure of immersion in anesthesia is almost painless. When injecting into general anesthesia, they do not first anaesthetize, but only treat the needle entry site with an antiseptic.
How to numb the puncture site
Before inserting a needle into the epidural space, the doctor first performs local anesthesia on the skin and subcutaneous fat layer at the injection site. The anesthetic is injected with a separate syringe using a thin needle.
Administration of anesthetic
For spinal and epidural anesthesia, the needle is usually inserted between the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebrae. The difference between these types of anesthesia is that with spinal, a smaller amount of anesthetic is injected, and the needle penetrates a little deeper and enters the spinal space.
A catheter is inserted through a needle into the epidural space under the same anesthesia, which remains for the entire duration of delivery. Through it, you can gradually and slowly introduce an anesthetic drug, thereby maintaining a stable concentration in the blood. The duration of action depends on the amount of anesthetic administered through the catheter. Spinal anesthesia is performed with one injection, and the effect lasts approximately two hours.
It is necessary to carefully plan the surgical intervention and anticipate possible complications that may prolong the duration of the cesarean section.
Time of action
With epidural anesthesia, as with general anesthesia, the anesthetic can be injected into the catheter as needed, so the duration of action depends on the progress of the operation and the amount of substance injected.
For spinal anesthesia, the drug is administered once, its effect lasts from one and a half to four hours, this time depends on the selected anesthetic. After the operation, sensitivity in the lower part of the body returns after 3-4 hours, and the woman is taken from the operating room on a gurney to the ward. It is necessary to remain in a horizontal position for several hours to prevent complications.
Monitoring blood pressure and heart rate during surgery
Monitoring these parameters throughout the operation is of great importance, since pressure fluctuations in either direction can cause complications during cesarean section. Before the baby is removed from the uterine cavity, blood pressure numbers may be slightly elevated, and after birth, a redistribution of load and blood flow occurs in the body, and the pressure decreases.
The process of spinal anesthesia
In the operating room, the expectant mother is put on a sterile shirt, shoe covers, and a cap and taken to the table. First, a catheter for an IV is placed in the arm. Next, the anesthesiologist asks the patient to practically curl up, which, of course, can be problematic due to a large belly. Spinal anesthesia is administered while lying on your side or sitting.
First of all, the injection site is determined by palpation (the area between 5.4 and 3 vertebrae), and it is treated with an anesthetic spray. The expectant mother feels cold on her skin. The area intended for spinal anesthesia is lubricated with povidone iodine and then the needle is slowly inserted into the subarachnoid space. Soon, a mandrin is removed from the needle - a conductor that closes its lumen. If cerebrospinal fluid drips into the cannula, everything is done correctly and the drug can be administered. After anesthesia, the injection site is covered with a sterile bandage.
Then the patient is helped to lie down on the table, and she almost immediately feels a tingling sensation in her legs and a spreading warmth, a feeling of heaviness. Pretty soon (after about 10 minutes) her lower torso stops feeling anything. A pregnant woman cannot move her toes or roll over. The effect of spinal anesthesia is certain. However, surgeons have their own ways of checking whether the anesthesia has worked.
Preparations for spinal anesthesia
When performing regional spinal anesthesia, two groups of drugs are used.
- Local anesthetics. Lidocaine, bupivacaine, ropivacaine and other drugs provide precisely the analgesic effect.
- Adjuvants. These are additives to anesthetics, such as: adrenaline, fentanyl, morphine, clonidine and others. They lengthen the duration of the block and enhance the effect of anesthetics, which allows the latter to be used in smaller doses. Also, auxiliary drugs regulate the vital functions of the body during a cesarean section and alleviate the patient’s condition.
Before the operation, doctors warn the woman so that she informs them about a possible deterioration of the condition, then they introduce additional drugs into the IV. After the caesarean section, the mother spends a day in the intensive care unit under the supervision of medical staff.
Indications for spinal anesthesia
There are several main reasons why doctors prefer to perform neuraxial anesthesia for cesarean section - this is an advantage over general anesthesia. So, spinal anesthesia:
- Safer for mother and child.
- When performing an operation with this type of anesthesia, the mother’s relatives may be present during the birth.
- The woman is conscious and does not feel severe drowsiness during cesarean.
- She will see the newborn baby soon after it is delivered, and in the operating room it can be put to the breast.
- The baby is lucid at birth.
Spinal anesthesia is one of the inexpensive and effective methods of pain relief for cesarean section.
Which anesthesia is preferable?
There is no type of pain relief that does not have contraindications and disadvantages. Absolutely every anesthesia listed above has both pros and cons. But after analyzing the above about anesthesia during a cesarean section, we can conclude that the most optimal option is spinal anesthesia.
It would not be superfluous to add that the material in this article is for general development only. Under no circumstances should you use the acquired knowledge during childbirth, or argue with anesthesiologists after surgery. After all, when choosing a method of pain relief, adjustments are made for the current situation.
Contraindications to spinal anesthesia
The use of any drug or medical procedure for a pregnant woman may be questioned by her doctor. If this concerns such a serious topic as the method of birth and the type of anesthesia, possible contraindications are taken most seriously. Here are some of them:
- The patient's categorical refusal of regional anesthesia. There are impressionable women who are afraid and do not want to be conscious during surgery.
- Allergy to anesthetics.
- Skin infections and severe irritation at the intended injection site.
- Intracranial hypertension.
- An emergency situation when there is no time to prepare and perform spinal anesthesia.
- Anomalies of the female spine.
- Risk of bleeding, coagulopathy.
If there are contraindications to regional anesthesia, the woman is given general anesthesia.
Video: Spinal anesthesia
Contraindications for epidural anesthesia
As we noted earlier, there are contraindications in the presence of which the use of this type of regional anesthesia is impossible. Contraindications are:
- There are purulent lesions in the adjacent area where the catheter should be inserted;
- Presence of acute infectious diseases;
- Abnormal position of the baby in the uterus;
- Pathology of blood clotting;
- There are abnormal displacement of the vertebrae or injuries to the spinal column, as well as inflammatory diseases of the spine;
- Presence/suspect of bleeding in a woman in labor;
- Allergic reactions to the anesthetics used;
Side effects of spinal anesthesia
Since cesarean section operations began to be performed under regional anesthesia, many rumors have developed that this type of anesthesia has a detrimental effect on the future health of the mother and child. Of course, surgery is always a risk. But the negative views of the majority are greatly exaggerated. Still, doctors do not deny that there are some side effects:
- Decreased blood pressure (temporary reaction, corrected with medications).
- Skin itching during surgery (treatable).
- Tingling or numbness in the legs (occurs only in some patients and goes away a few weeks after birth).
- Pain in the back (lasts several days) or hematoma at the injection site (also resolves over time).
- Headache, nausea (temporary reaction, can be corrected with medication).
Spinal anesthesia does not cause chronic pain, and some of the consequences of a cesarean section are comparable to the consequences of a natural birth.
Nowadays, caesarean section operations are performed mainly under spinal anesthesia, which is considered the safest, fastest and most effective.
When choosing a method of pain relief for a patient during surgery, doctors decide the issue individually, in a way that is best for mother and baby.
Complications of epidural anesthesia
Unfortunately, epidural anesthesia can have a number of undesirable consequences and complications for the health of the mother and her baby. In most cases, the occurrence of complications during epidural anesthesia is caused by errors by the anesthesiologist during the procedure. What consequences may there be:
- The appearance of persistent headaches. This consequence can develop against the background of a violation of the integrity of the nerve structures or damage to the dura mater with a needle. Also, as a result of this, pain can occur in the lower extremities and back;
- Spinal cord injury. This problem occurs extremely rarely, since the spinal cord is located somewhat further and getting into it, intending to make a puncture in the epidural area, is quite problematic. But if the hands are hooks...;
- Problems with urination. As a rule, this consequence goes away on its own after some time;
In addition, there may be complications for the child:
- Since natural blood circulation in the placenta is disrupted, the child may develop heartbeat disturbances and, as a result, hypoxia;
- Sometimes in the process of pain relief, narcotic substances are used, which can cause the child to develop a respiratory disorder, which can subsequently be eliminated only by ventilation of the lungs with the possibility of damage to the respiratory tract;
In any case, it should be understood that any surgical intervention in the human body cannot remain without consequences. Often, the consequences are eliminated by the woman’s body on its own, but this does not mean that all this is absolutely safe. Therefore, the reviews that you can find on the Internet are both positive and negative.
As an example, we will give several real reviews from mothers who were “lucky” to encounter this process during a caesarean section.