A hard belly or stiff abdominal muscles may be due to digestive problems or a symptom of abdominal disease. If the reason lies in errors in nutrition, then there is no need to worry, since, in all likelihood, this is a banal gas formation that will go away after some time.
But if the syndrome is accompanied by pain in the epigastric region, nausea, vomiting and fever, then it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor, since a hard stomach is often an alarming symptom of pathologies of internal organs.
Flatulence
The cause of hardness in the abdominal muscles is often increased accumulation of gases. Flatulence or gas formation is often a consequence of the fermentation process in the intestines, which can be caused by overeating, eating stale foods, carbonated drinks, baked goods or vegetables containing large amounts of fiber and starch. In some cases, discomfort can be caused by eating food too quickly, resulting in air entering the gastrointestinal tract.
About 500 ml passes through the digestive tract of a healthy person during the day. gases With their increased formation, the intestines become distended, which negatively affects the digestion process. Associated symptoms will be bloating, a feeling of heaviness, nausea, belching, and sometimes heartburn.
How to behave during a hardening of the abdomen?
Having discovered such a symptom, the expectant mother should not worry. You need to immediately lie down, relax and listen to the sensations. Analyze what was done wrong. If it is simple fatigue, you need to lie down and limit heavy loads in the future. Another reason is that training contractions may begin. Already from the second month, the body begins to prepare the uterus for childbirth, but this is an exclusively individual process and does not apply to every pregnant woman.
Attention! When, during pregnancy, the tummy hardens in later stages and the muscles begin to contract at the same time interval, it means that premature labor begins.
If hypertension is chronic, you cannot do without treatment. The doctor may prescribe sedatives and hormonal pills. It is very important to maintain bed rest. In any case, at the slightest disturbance in the body, a woman expecting a child is simply obliged to immediately seek help from a doctor.
Peritonitis
Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum that occurs as a result of a ruptured appendix, perforation of an ulcer, inflammation of the abdominal organs, internal bleeding and many others. Inflammation of the peritoneum has a toxic effect on the body. Accompanied by pain, nausea, vomiting, fever and muscle tension in the anterior abdominal wall. Severe form of peritonitis is fraught with the development of complications and poses a threat to human life. Peritonitis is treated by surgery.
Why does this confuse the expectant mother?
It is inherent in female nature itself that, being pregnant, the expectant mother in every possible way protects her baby from external influences and irritants on an instinctive level. That is why an attempt to touch the belly may seem to a woman during pregnancy as an invasion of her personal space, a kind of threat to the unborn baby, which can undoubtedly cause irritation or even anger.
Some believe that during a period of increased sensitivity you can feel someone else's energy. Thus, the energy of the hands of unfamiliar people can have a bad effect on the biological field of the baby and his mother. This is the basis of many folk superstitions.
That is why, before touching the expectant mother’s belly, think about whether you know her well enough to break into her personal space, and be sure to ask permission. Girls in this position are especially vulnerable and fragile, so protect them from anxiety and unnecessary worries.
Intestinal obstruction
Intestinal obstruction is a condition in which the movement of intestinal contents is disrupted. The syndrome is caused by mechanical blockage or impaired motility due to the presence of fecal stones, neoplasms, hernias, congenital pathologies, inflammatory diseases of the abdominal organs, strokes and poisoning with heavy metal salts. Intestinal obstruction leads to intoxication of the body. The most pronounced symptoms are cramping pain, nausea, foul-smelling vomiting with a putrid odor, headache, weakness, bloating, tachycardia and decreased blood pressure.
Why is my stomach hard during pregnancy?
The main reason why the stomach is hard during pregnancy is the threat of miscarriage. This condition is divided depending on the gestational age into 2 concepts - threatened miscarriage (risk of termination of pregnancy before 22 weeks) and threatened premature birth (termination of pregnancy for a period of 22 to 37 weeks).
The reasons for a hard belly during pregnancy can be very diverse. Let us list the main causative factors:
— infection (most often we are talking about urogenital infection);
- hormonal disorders (can cause miscarriage up to 30 weeks);
- isthmicocervical insufficiency, which is manifested by a certain opening of the cervix, which disrupts its obturator function;
- malformations of the uterus and others.
Regardless of the impact of one reason or another, the feeling of a hard abdomen during pregnancy is associated with increased uterine tone, that is, the longitudinal muscle fibers are in a state of contraction, which leads to the opening of the circular fibers of the cervix. As a result, this leads to structural changes in the cervix, during which it is not possible to maintain pregnancy.
In some cases, the symptom of a hard belly during pregnancy may be accompanied by premature rupture of amniotic fluid, and the shorter the period, the less chance of maintaining the pregnancy. As a rule, this condition is associated with exposure to an infectious factor.
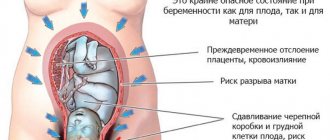
Another reason why the stomach becomes hard during pregnancy is premature placental abruption, which can occur in the second half of pregnancy. This is a condition in which placental abruption occurs before the afterbirth period, as is normal. The main cause of premature placental abruption is vascular pathology. It can occur with gestosis (a complication of pregnancy, which is accompanied by arterial hypertension, edema and the appearance of protein in the urine), arterial hypertension, autoimmune pathology, etc.
Let's talk about how to confirm the diagnosis of threatened miscarriage and premature abruption of a normally located placenta, which occurs in the second half of pregnancy.
Signs indicating abruption of a normally located placenta:
- bloody discharge from the genital tract, but may be absent with the formation of a retroplacental hematoma;
— ultrasound criteria for placental abruption.
Diagnostic signs of threatened miscarriage:
- vaginal examination data indicating shortening and dilatation of the cervix;
- ultrasound confirmation of the diagnosis (cervicometry, which also reveals the presence of structural changes in the cervix).
Treatment for a hard belly during pregnancy depends on the specific diagnosis that was made. Treatment of threatened miscarriage should be comprehensive and depend on the stage of pregnancy. If possible, it is necessary to identify the cause that led to the development of this condition.
If you are 20 weeks pregnant and your stomach is hard, then the main groups of drugs that are used to treat a threatened late miscarriage are antispasmodics (no-spa, papaverine), magnesium sulfate, suppositories with indomethacin (from 16 weeks onwards). All of these medications for uterine hypertonicity are used up to 22 weeks of pregnancy.
Treatment of threatened premature birth (from 22 weeks to 37 weeks) - calcium channel blockers (nifedipine, verapamil), magnesium sulfate, adrenomimetic drugs (ginipral), antispasmodics. All of these medications relieve the reasons why the lower abdomen becomes hard during pregnancy.
Also during these periods (22-34 weeks), the symptom of a hard abdomen during pregnancy is accompanied by the prescription of glucocorticoids (prednisolone, dexamethasone, betamethasone), which accelerate the maturation of the fetal lungs.
To treat premature abruption of a normally located placenta, it is necessary to use the following drugs in the presence of conditions for maintaining pregnancy - magnesium sulfate, antispasmodics, dicinone, tranexam, glucocorticoids for the birth of a viable child by accelerating the maturation of the fetal lungs.
If signs of massive obstetric hemorrhage appear, surgical delivery is indicated to preserve the life of the fetus and the pregnant woman. With a mature birth canal, childbirth can be carried out through the natural birth canal using early opening of the membranes (early amniotomy).
If you are 37, 38, 39, 40 weeks pregnant, a firm belly indicates that labor is imminent. And in these cases, it is better to play it safe and see a doctor as soon as possible. Obstetrician-gynecologist Marina Slavina
Attention! The Site Administration does not provide any medical services. All materials are for informational purposes only. The same applies to the advisory section. No online consultation will ever replace face-to-face medical care, which is provided only in specialized medical institutions. Self-medication can cause irreparable harm! For any diseases or ailments, please contact your doctor!
Read along with this article:
- No-spaIn what cases is no-spa prescribed to pregnant women...
- If your belly is small during pregnancy, the causes of a small belly during pregnancy may be...
- TranexamTranexam is indicated for pregnant women for vaginal...
Add a review
Appendicitis
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, caused by stagnation of intestinal contents due to kinking of the appendix, mechanical blockage or infectious diseases. Symptoms of inflammation are sudden pain in the right lower abdomen, hard muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, nausea, vomiting, defecation disorder, and gas formation. The development of appendicitis can be complicated by an abscess or thrombophlebitis of the abdominal cavity. Treatment of inflammation involves surgery.
Abdominal circumference
Abdominal circumference during pregnancy by week is one of the important and monitored indicators. It is calculated according to the gestational age and compared with tabular indicators. Abdominal circumference is measured starting at 20 weeks.
| Duration (week) | Abdominal circumference (cm) |
| 20 | 70-75 |
| 22 | 72-78 |
| 24 | 75-78 |
| 26 | 77-82 |
| 28 | 80-85 |
| 30 | 82-87 |
| 32 | 85-90 |
| 34 | 87-92 |
| 36 | 90-95 |
| 38 | 92-98 |
| 40 | 95-100 |
Such values make it possible to estimate the rate of intrauterine development of the baby.
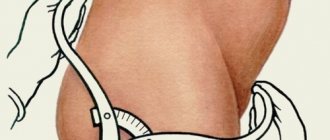
During each routine examination, the doctor determines the regularity of fetal development in the uterus. To do this, the woman must lie down on the couch. The gynecologist, using a measuring tape, determines the length from the edge of the symphysis pubis to the prominent area of the uterine fundus. In this way, the height of the uterine fundus is measured.
Such manipulations allow you to control the increase in centimeters in the abdominal area. On average, starting from week 20, a pregnant woman’s belly increases by 1 centimeter per week. The abdominal circumference by week of pregnancy must be compared with the height of the uterine fundus. Normally, these indicators should correspond to the established deadline.
Ectopic pregnancy
In women, a hard belly may be due to the presence of an ectopic pregnancy, which in the early stages has symptoms of the usual: drowsiness, nausea, delayed menstruation, breast tenderness. At week 4, cramping pain appears below the navel, painful urination and defecation, and spotting.
If you do not see a doctor in time, then over time the fallopian tube will rupture and internal bleeding will occur.
Excessive blood loss is characterized by a drop in blood pressure, weak pulse, pale skin and hardness of the anterior abdominal wall. An ectopic pregnancy poses a threat to a woman’s life, so at the slightest sign it is necessary to seek medical help.
The stomach gets hard during pregnancy - why?
Many expectant mothers are faced with the fact that during pregnancy, the stomach hardens at different stages, which naturally causes concern. What kind of state is this in a pregnant woman’s body when her stomach gets hard?
This condition is called or. - This is a muscular organ that is normally relaxed, but when muscles contract, for various reasons, it becomes tense.
What factors can cause this condition?
Stressful situations, physical activity, physiological processes in the body, as well as hormonal changes can lead to increased tone.
During what periods of pregnancy can hypertension occur, and what are the consequences?
The uterus can be in good shape at any stage of pregnancy - there is nothing wrong with this phenomenon, because any muscles in the body contract. In the first half of pregnancy, the uterus rarely comes into tone; tension occurs for a couple of minutes, and then releases. If there is no pain and no discharge (especially bloody), then there is no cause for great concern. In this case, you need to reconsider your daily routine, be less nervous, and rest more.
There are sources that say that if you relax the facial and neck muscles, then the muscles of the uterus will return to normal. An exercise in which you should get on all fours, then raise your head and bend your lower back for a few seconds, maintaining even breathing, and then lower your head and arch your back up for 5 seconds can also help to relax the uterus. You should also avoid poses or movements that will automatically cause abdominal muscle contractions. For example, you should not sleep on your back, or when you roll over onto your back, bend your knees.
Please note that indigestion, in particular constipation, standing for long periods of time, or sedentary work, can cause similar symptoms.
If there is increased tone, the doctor may prescribe "", it can be taken without fear, but only from 12 to 37 weeks of pregnancy.
If your stomach becomes hard during pregnancy, the pain is severe and discharge appears, be sure to contact your gynecologist, as this may be a threat of miscarriage and emergency measures must be taken.
In the second half of pregnancy, the uterus can tone more often than in the first half of the term, up to 10 times a day; this condition is called Braxton Hicks contractions, or training contractions. They also should not cause you to panic unless they are accompanied by pain or discharge.
If your stomach becomes hard during pregnancy, and your doctor diagnoses uterine hypertonicity, then you have the power to choose how to cope with this condition - yourself or with the help of doctors. The main thing is not to hang your nose and think about beautiful things.
Share with your friends!
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. In the chronic form of the disease, bloating occurs after every meal. This is due to insufficient secretion of digestive enzymes. Disruption of the digestive process leads to gas formation, rumbling in the stomach, nausea, frequent vomiting, and fever. Accompanying symptoms with pain localized in the left side of the abdomen and muscle hardness upon palpation suggests an acute attack of pancreatitis.
When to urgently seek help from a doctor
Many patients do not rush to consult a hospital if the pain is not too intense. When the acute phase begins, the disease often progresses with complications. Particularly dangerous symptoms include:
1 frequent nausea and severe stomach pain;
2 pains in the right hypochondrium, accompanied by fever and attacks of nausea;
3 change in skin color in the area where the pain is located;
4 spotting or copious uncharacteristic discharge of blood from the vagina;
5 prolonged diarrhea with bloody inclusions.
If severe symptoms appear, you should not randomly take painkillers, which will only complicate the diagnosis.
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder. The disease is most often caused by cholelithiasis. At risk are people who are overweight and lead a sedentary lifestyle; genetically predisposed; those suffering from endocrine diseases and diseases of the cardiovascular system; leading an unhealthy lifestyle. The pathology is accompanied by acute cramping pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, bitter taste in the mouth, gas formation, bloating, yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes.
What affects belly size?
When carrying out measurements, specialists are guided by generally accepted standards, but at the same time take into account the fact that indicators may differ significantly in each case.
Among the list of factors influencing changes in abdominal circumference are the following:
- the physique of the expectant mother;
- speed of weight gain - many pregnant women have an increased appetite;
- fruit size;
- presentation;
- amount of anatomical fluid.
In mothers who are prone to being overweight, roundness may not be noticeable until the very moment of childbirth, while girls with a narrow pelvis and a fragile physique are faced with a change in abdominal volume at the very beginning of the second trimester. The volume of the abdomen during multiple pregnancy increases quite quickly, so an interesting position can become noticeable to others much earlier.
The size of the abdomen may not increase systematically, but in leaps and bounds. Experts begin to monitor the dynamics of the increase in centimeters in the abdominal circumference not immediately, but, as a rule, from the 17th to 20th week of pregnancy.
Tumor
Intestinal tumors of various origins lead to destruction of the intestinal walls. At the initial stages, the pathological process is accompanied by mild episodic pain. Over time, the pain syndrome increases and is not suppressed by analgesics, accompanied by lack of appetite, weight loss, weakness, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, and defecation disorders. There may be blood, mucus and pus in the stool. In this case, the abdomen is hard and painful on palpation.
Treatment of any disease of the digestive system must begin with a review of the diet and diet. So, with increased gas formation, it is necessary to give up foods containing starch and fiber, carbonated drinks, fatty and heavy foods.
If you have a disease, the symptom of which is a hard stomach, you should contact a medical facility. Only a doctor can prescribe the necessary treatment. Self-medication and unsystematic use of medications can worsen the condition and lead to serious consequences.
Causes of a bloated and hard belly in men
The effect of muscle fiber stiffness has more than one factor that causes this phenomenon. The causes of a hard belly in men can be caused by systemic disorders of the internal organs. A feeling of fullness appears after overeating, drinking too much sweets, or carbonated drinks. No action is required, just moving around is enough for the condition to improve.
Important! A constantly swollen belly can be a sign of lumbar lordosis - a forward-facing curve. The bulge appears due to excess weight - the spinal defect is diagnosed by examination by a specialist, who will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Dysbacteriosis
The intestinal microflora is populated by many bacteria necessary for the normal functionality of the gastrointestinal tract. Due to the use of antibiotics, poor nutrition, and stress, bacterial balance is disrupted. Food that enters the stomach is not digested, rots and causes fermentation. The result is a hard, bloated belly. Failure to treat dysbiosis will lead to pathological consequences for the entire body, one of which is toxic poisoning by fermentation products.
To avoid this, you should adjust your diet, take probiotics and for some time go on a diet limiting sweets, fatty and other foods that cause discomfort.
Intestinal blockage
Erosion on the penis: causes, symptoms and treatment
The first symptom is pain in the abdomen. There may be a feeling of hardening in some part of the intestines, stool retention occurs, and gases do not pass away. Painful sensations of varying intensity and character increase and are localized. The result is a hard, elastic stomach, the causes of blockage are different: from poor nutrition to pathological changes in the functioning of internal organs.
If constipation does not go away for a long time, home remedies (enemas) and medications do not help, you should consult a doctor. It will require examination and identification of the provoking factor, then prescribed treatment.
Peritonitis
This disease is caused by inflammation of the peritoneum, which is what causes a tight stomach in men. The membrane lining the insides becomes inflamed with advanced appendicitis, inflammatory processes in the intestines and other pathologies. The contents of the internal organs enter the peritoneum, which leads to peritonitis.
Appointment with a urologist: preparation for examination, diagnosis and treatment measures
The rapid absorption of substances into the mucosal tissue causes the immediate spread of infection through the blood; the lack of immediate help threatens sepsis. Signs of peritonitis:
- the stomach is very hard, dense, the skin is stretched tightly;
- vomiting appears, but unlike poisoning, vomiting does not bring relief, but aggravates the patient’s condition;
- body temperature rises;
- there is a constant feeling of thirst;
- weakness sets in;
- heart rate increases;
- I sweat more than usual.
There is no home treatment for peritonitis. Urgent surgical care is required, otherwise the patient will not survive 24 hours.
Fundal height of the uterus
An increase in the size of the uterus occurs throughout the entire gestation period:
- In the 1st trimester of pregnancy, up to the 12th week inclusive, the entire uterus is located in the small pelvis, despite the fact that already at this stage its dimensions are proportional to the newborn’s head.
- Starting from the 12th week, the uterus is palpated in the lower abdomen, a couple of centimeters above the pubic bone. As the period increases, it rises.
- At week 16, the fundus of the uterus is localized in the middle part of the space between the pubic bone and the navel.
- At week 20, the tummy often becomes noticeable to others, the bottom is 2 cm below the navel.
- At 24 weeks, the fundus of the uterus is at the level of the navel.
- At week 28, the fundus of the uterus is 2 cm above the navel.
- At 32 weeks, the fundus of the uterus is centered between the navel and the extreme part of the sternum.
- The highest level of the uterine fundus is at 38 weeks of pregnancy. The uterus rises to the level of the costal arches. The navel protrudes.
- By week 40, the height of the uterine fundus becomes smaller as the fetus turns over and prepares for the birth process. The uterus passes into the pelvic area and descends.