A stable monthly cycle is the main sign of good health of the female reproductive system. Menstruation should not cause a woman great discomfort, cause loss of productivity, or a deterioration in the quality of life for several days. Severe pain, weakening of the body, temperature before menstruation may indicate developing diseases and other problems of the reproductive health organs. If its level reaches 37 degrees, there is no reason to worry, but in other cases you should find out why its level is increasing. A woman should know whether there may be a temperature before menstruation, which causes hyperthermia.
What are normal temperature readings before menstruation?
For most women, a temperature of 37 before menstruation is normal. It does not affect the quality of life and does not worsen the general condition. This increase has a simple explanation and is associated with cyclical changes that occur in the body every month. This reaction does not occur in all women; it is an individual reaction before menstruation.
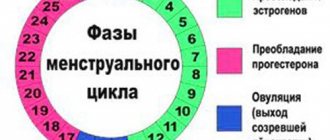
Before the onset of menstruation, the hormonal background changes - progesterone levels increase. Blood is actively flowing to the ovaries, the temperature may rise, this is normal. With the onset of menstruation, the elevated levels begin to return to normal. After 2-3 days the temperature should be 36.6.
Low-grade fever before menstruation may increase 2-4 days before bleeding appears. This is observed in sensitive women. This reaction is individual. When menstruation begins, the hormonal balance is equalized and the indicators return to normal.
In some cases, the indicator may rise above the normal level 10 days, a week before menstruation. This does not always mean that there are problems or illnesses. This is an individual reaction of the body that does not require drug therapy. If a woman is worried about other uncomfortable symptoms, she should consult a gynecologist.
If the usual indicators increase, it is better for a woman to check what the temperature was 2-3 days before the start of menstruation, and how it changed after it began. If she returns to normal, then there is no reason to worry.
How to feel better
The temperature before menstruation does not immediately indicate pathology, but if you are depressed, you can improve your health in the following ways:
- Move more. Physical exercise reduces malaise and improves your mood.
- Cold and hot shower. The water should be no more than 30 degrees. This procedure will relieve fatigue and invigorate.
- Proper nutrition. Before the onset of menstruation, you need to eat more food of plant origin; vegetables and fruits will have a good effect. You can't drink alcohol.
- Maintaining a sleep and rest schedule. You need to be able to take time for yourself, and not just work. You should not visit gyms and saunas before menstruation.
- It will be good to give up coffee or at least reduce its consumption.
Physiological reasons
An increase in temperature before menstruation, observed in many women, is a normal reaction of the body to monthly hormonal changes. Progesterone is produced in greater quantities than usual, affecting thermoregulation. This provokes an increase in the usual indicators to 37 degrees.
The physiological cause of hyperthermia is the abundant blood flow to the ovaries before menstruation. This condition is normal and should not cause concern if the indicators return to normal with the onset of menstruation.
Women suffering from PMS experience an increase in temperature in the second phase of the menstrual cycle, which occurs after ovulation. The condition persists until the onset of menstruation. On average it is 10 days. If, apart from an increase in temperature, there are no alarming symptoms, then there is no cause for alarm.
If you experience nausea, severe pain in the lower abdomen, vomiting and an increase in temperature during the menstrual cycle up to 38 degrees, then you need to consult a specialist. Timely diagnosis will help avoid possible problems in the future.
It should be remembered that deterioration of the condition before menstruation can be triggered by physical activity. Gynecologists recommend giving up active sports during this period. Strength exercises and abdominal pumping should be postponed until the end of menstruation.
What does it mean that there is no increase in BT after ovulation?
High temperatures, indicating ovulation, persist until menstruation. However, when creating graphs, you may encounter a situation that differs from the generally accepted norm. For example, menstruation has not yet begun, but the indicators are getting lower. The answer to the question why after ovulation the basal temperature does not rise, but rather drops sharply, can only be given by a gynecologist. He should show off his schedule.
Low basal temperature after ovulation is a signal of serious reproductive problems. If the values do not reach the optimal 37 degrees, then it is almost impossible to conceive a baby. There are no suitable conditions for the egg, it will not survive.
The reasons for a sharp drop in temperature usually lie in ovarian dysfunction. This disorder leads to progesterone deficiency. And without it, the birth of a new life is unlikely, because the sex hormone is necessary for subsequent pregnancy. Is it possible to correct the condition in a particular case? The doctor will answer. Hormone replacement therapy increases the chances of becoming a mother.
A pronounced drop in organ temperature may indicate the release of a defective egg. If this is recorded once, and the schedule is stable for several cycles, then there is no need to panic: sometimes follicles produce non-viable eggs. But it is very advisable to see your doctor. The repetition of the phenomenon in each cycle indicates reproductive pathologies and infertility.
PMS
One of the main causes of increased body temperature is PMS - a set of symptoms before the onset of menstruation that begin to disturb a woman 2-10 days before the first discharge begins. Hormonal changes also affect the work and condition of a woman’s cardiovascular and nervous system. In combination, this is manifested by the presence of uncomfortable symptoms that worsen the woman’s general condition.
Common symptoms of premenstrual syndrome can be identified:
- Increased temperature before menstruation, periodic chills.
- Changes in mood, depression.
- Unstable psycho-emotional background.
- Headache.
- Elevated blood pressure levels.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- The appearance of edema.
- Swelling of the mammary glands.
- Increased flatulence.
This period negatively affects the woman’s general condition and performance. Many people show harshness and aggressiveness. Taste preferences and sensitivity to smells may change for several days. There is increased sweating. Such symptoms are clearly manifested in approximately 25% of women.
During this period, body temperature can rise to 37.4 degrees, as soon as menstruation begins, after 1-2 days the condition returns to normal. Experts note that the unpleasant symptoms of PMS in addition to hyperthermia can be triggered by problems with the functioning of the organs of the reproductive system. To protect yourself from possible consequences, it is better for a woman to undergo a doctor’s examination and take the necessary tests.
Significantly elevated temperature during pregnancy - fever
A temperature above 38°C is a fever and is an undesirable condition for pregnant women. That's why
The expectant mother needs to drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration at elevated temperatures. A significantly elevated temperature during pregnancy is dangerous because
Temperature increases during pregnancy for two reasons:
First, the production of progesterone (pregnancy hormone) increases, which affects the thermoregulatory center located in the brain.
Secondly, with the onset of pregnancy there is a weakening of the immune system - immunosuppression.
A pregnant woman is susceptible to various infections, ranging from ARVI and influenza to pyelonephritis, pneumonia and other diseases. A rise in temperature during an infection means that the body is actively fighting off harmful agents.
Pregnancy
Body temperature may increase if a woman becomes pregnant. Hormonal changes begin in the body, affecting the process of thermoregulation, and as a result, hyperthermia is observed. When conception has just occurred and the woman does not yet know that a new life is developing inside her, the thermometer may show 37 degrees. Basal temperature readings will be more accurate. It is measured in the rectum, vagina, and mouth. The second sign is a delay or the appearance of spotting. You should take a pregnancy test and consult a gynecologist.
During this period, indirect signs of pregnancy are also observed:
- Dizziness.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Swelling of the mammary glands.
- Change in taste preferences.
- Acute reactions to familiar smells.
Some may experience slight bleeding. Girls mistakenly believe that this is menstruation. Such discharge has a different character - it is scanty and ends in about 2 days. The discharge shows that the fertilized egg has been successfully implanted into the uterine wall, where it will develop throughout the entire period of pregnancy.
How to measure basal temperature
Correctly constructing a BT schedule requires strict adherence to all recommendations of gynecologists. Any deviation distorts the indicators, which can lead to ambiguous interpretation by the doctor.
Algorithm of actions when measuring basal temperature at home.
It is justified to use methods to lower the mercury column if the temperature is above 38 degrees at the beginning of pregnancy, in the later stages - after 37.5. When using products, always consult a doctor who will prescribe safe treatment. Self-medication is dangerous for the health of the baby who will soon be born. Medications that can be prescribed to pregnant women:
- Paracetamol;
- Panadol;
- Viburkol (homeopathic suppositories).
Pregnant women should not take medications such as aspirin. If hyperthermia is caused by infectious diseases, then treatment of the cold is necessary. Doctors recommend using non-drug methods that do not cause side effects:
- In case of hyperthermia associated with vasodilation, it is necessary to ventilate the room and place a damp compress on the forehead. Do not use alcohol, vinegar, or cold water.
- If hyperthermia occurs due to vascular spasm, and the hands and feet are cold and dry, then warming the body and drinking plenty of hot drinks will help.
Possible pathologies
Body temperature can rise not only before the onset of menstruation, which is often the norm, but also as a sign that there is a developing disease in the body. Normally, the body temperature before menstruation rises a few days before the onset of discharge and stops at 37 degrees. The condition normalizes with the arrival of menstruation. If the indicator reaches 38 degrees and persists for a long period, you should consult a doctor for an examination and necessary diagnostics.
Experts have identified a number of diseases that hyperthermia can signal:
- Inflammation of the appendages. The main symptom of the development of pathology is a temperature of 37.5 – 37.7 degrees. The indicator remains at this level during menstruation and may remain after it. This manifestation is the main sign of a developing inflammatory process.
- Inflammation of the uterus (endometritis). The disease is characterized by the same body temperature before and after menstruation - 37 degrees. The condition may be accompanied by bloating and diarrhea. The combination of symptoms clearly indicates endometritis.
- Infectious diseases of the vagina. Pathogenic microbes can enter the vagina during menstruation, causing the development of diseases and an increase in BT levels.
- The presence of inflammation in the intestines is characterized by an increase in BT to 38 degrees. The indicator stops at this mark before menstruation and remains after it. Additional symptoms are diarrhea, dry mucous membranes and skin.
- An increase in temperature up to 39 degrees is observed with an ectopic pregnancy. A woman needs to see a gynecologist, undergo an examination, the necessary diagnostics, and donate blood for hCG. The same condition is typical when a normal pregnancy is terminated.
- An increased BT level may indicate an insufficient amount of progesterone in the body. This condition causes the second phase of the menstrual cycle to shorten. It can last 10 days or less. The condition is dangerous for women and can cause infertility.
A woman should clearly know why her temperature rises before her period. When is this condition normal and does not pose a threat to her health, and when should it be a reason to see a doctor.
How to distinguish pathological from physiological fever
In case of infection with pathogenic microorganisms, the expectant mother feels tired, unwell, loss of appetite, chills or fever.
Elevated temperature during illness reaches higher numbers (38.0-38.5 degrees). Temperatures above 38 degrees are especially dangerous.
Since this temperature affects the development of the fetus and causes the following pathological conditions:
- malformations of the central nervous system
- mental retardation
- child's muscle hypotonia
- underdevelopment of some parts of the body
- facial defects (cleft lip, cleft palate)
- microcephaly
- syndactyly (fusion of fingers)
In cases where the temperature drops to 36.4 or lower during the period up to 14 weeks of pregnancy, this may indicate a threat of miscarriage.
Why is it important to monitor your temperature?
Body temperature indicators before, during and after menstruation are important factors in determining the state of the entire reproductive system. Women planning pregnancies must monitor them and keep a schedule, measuring their basal body temperature daily in the mouth, vagina or rectum. To measure indicators, a regular thermometer is used. So a woman has the opportunity to monitor the temperature of the mucous membranes, knowing when ovulation and menstruation will occur. Normally, BT levels can range from 36.9 to 37.2 degrees. They are at this level during pregnancy.
If the temperature rises during the monthly cycle, the woman needs to come to the gynecologist, undergo an examination, and take tests. Timely diagnosis and establishment of the cause of this condition will protect you from unpleasant consequences. It should be remembered that a long-lasting high temperature is a symptom of a developing disease that cannot be ignored so as not to aggravate the condition.
Basal temperature indicators are individual for each woman, but you need to know about the average values in order to monitor your condition and be able to see alarming symptoms. Self-control and attentive attitude towards yourself will help maintain the health of the reproductive system, protect you from unpleasant diseases and their possible consequences.
Low or increased t of certain parts of the body
Most often, problems with a woman’s hormonal levels arise due to a lack of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormone of the pituitary gland or estrogen, which subsequently becomes the cause of disturbances in the 2nd phase. In this case, low rectal temperature will be noted even after the ovulatory period.
Based on deviations from the norm in the graphs, the following problems can be preliminarily diagnosed::
- if BT rose in the second part of the cycle (by 0.1 - 0.3 divisions), then this indicates a decrease in progesterone and estrogen;
- absence of premenstrual drop in indicators and a short second period (up to 10 days) with maintaining a temperature difference of 0.4 degrees - a two-phase cycle with a lack of progesterone;
- a monotonous line throughout the entire cycle and a temperature of 36.9 after ovulation (without sudden jumps) – absence of an egg, anovulatory cycle;
- a chaotic curve with sharp discrepancies in values – exposure to excess estrogen or other factors;
- temperature exceeds 37.5 degrees – an inflammatory process.
Help : a maximum of 2 anovulatory cycles per year in a healthy woman is an acceptable norm.
Pathological causes and associated symptoms
Fever is a nonspecific symptom that appears in response to inflammation or other biochemical processes occurring in the body. The following types are distinguished: subfebrile (37-38 C), febrile (38-39 C), pyretic (39-41 C) and hyperpyretic (more than 41 C).
Premenstrual syndrome is a symptom complex that occurs in the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle and is characterized by somatic, neuropsychic, vegetative-vascular and metabolic-endocrine manifestations.
It occurs 2-10 days (on average a week) before menstruation and goes away in the first days after its onset. Before menstruation, only low-grade fever can be considered physiological norm. It is usually accompanied by the following PMS symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- discomfort in the lower back;
- weakness;
- chills;
- anxiety, irritability, tearfulness, sudden mood swings, headaches;
- decreased/increased appetite, constipation/diarrhea, nausea;
- pain and swelling in the mammary glands;
- acne, swelling.
This reaction is not typical for everyone; in some women everything is completely asymptomatic or the symptoms are isolated and mildly expressed.
Usually the temperature rise is in the lower range of subfebrile temperature, that is, on average up to 37.1 C. If the temperature rises to 38 C, then this indicates a possible inflammatory process of the pelvic organs.
In inflammatory diseases, pain below becomes severe and sometimes unbearable, simulating acute surgical pathology, for example, appendicitis. The indicator exceeds 38 C, which is due to body intoxication syndrome, which is not normal and poses a threat to a woman’s life.
The temperature before menstruation may increase due to the development of various diseases of the reproductive system. It is imperative to consult a doctor in the following situations:
- the discharge contains clots of pus;
- the temperature rose sharply above 38 degrees;
- periods are short and scanty (protracted and heavy);
- the temperature does not decrease after the start and end of menstruation.
Endometritis (inflammation of the uterine mucosa) is the most common cause of fever before menstruation to 37 degrees or higher. Associated symptoms of the disease:
- periodic nagging pain in the uterine area;
- purulent discharge at any period of the cycle;
- Possible problems with urination.
Inflammation of the appendages (fallopian tubes and ovaries), called adnexitis, is accompanied by chills, sweating, acute pain in the lower abdomen (to the right or left of the uterus), radiating to the lower extremities.
Endometriosis, cystitis
With endometriosis, the tissue that lines the walls of the uterus grows beyond the endometrial layer. The pathology usually occurs between the ages of 25 and 30 years, accompanied by pain of a cyclic nature, intensifying before the onset of the menstrual cycle, pain during bowel movements or urination.
Endometriosis nodes grow into the ovaries, vagina and rectum, with each cycle the tissue is affected deeper. The reflux of menstrual blood into the abdominal cavity and its accumulation provokes the occurrence of an inflammatory process and an increase in temperature. If left untreated, there is a high probability of formation of adhesions and the development of infertility.
Cystitis is accompanied not only by elevated temperature (up to 38 degrees and above). Characteristic signs of the disease are pain and cramping when urinating, frequent and unproductive urges. As a rule, the chronic form of the disease worsens before a new cycle.
A pathological condition in which a fertilized egg does not attach to the wall of the uterus is called an ectopic pregnancy. In this case, the fetus may begin to develop in the ovary, abdominal cavity, or fallopian tube.
Regular measurement of BT allows timely detection of ectopic pregnancy and prevent possible consequences of the pathology. In the first phase of the cycle (follicular), BT fluctuates between 36.2-36.6 degrees. In the ovulatory phase it increases to 37.2. Subsequently, the indicators change as follows:
- upon implantation of a fertilized egg into the walls of the uterus (7-10 days after ovulation), BT decreases slightly;
- with an ectopic pregnancy, the BT value will be similar to the follicular phase.
Also, one of the signs of pathology is one line in a pregnancy test in the absence of menstruation and the woman is confident in conception. In this case, it is necessary to undergo an urgent examination.
At 6-8 weeks after conception, body temperature may rise to 40 degrees and acute cramping pain in the abdomen. This requires emergency surgical care and further long-term treatment.
Other reasons
In addition to all of the above reasons, an increase in temperature before the onset of menstruation can be caused by:
- intestinal infections, acute respiratory viral infections (in this case, the diseases coincidentally coincide in time with the beginning of the cycle);
- insufficiency of the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle;
- characteristics of the body (even healthy women may periodically experience a rise in temperature before menstruation).
DETAILS: Gymnastics in bed (Tibetan, exercises, exercises) while lying down after sleep
BT for ectopic and frozen pregnancy
Gradual decline
Anembryonia (death of the embryo) is accompanied by a decrease in rectal indicators. The development of pathology is most often observed at the early stage of the formation of the fertilized egg.
The process of non-developing pregnancy occurs gradually. For some time, hormones continue to be produced by inertia by the cells of the chorionic membrane. Therefore, even against the background of fetal fading, signs of pregnancy persist.
If the graph shows that BT drops simultaneously with the appearance of unpleasant symptoms (abdominal pain, toxicosis and chest tension disappear), then you need to urgently run to a specialist.
A characteristic sign of a frozen pregnancy is when the basal temperature drops below the critical level of 37°, that is, it returns to the levels preceding conception.
There are cases when fetal development proceeds normally, without the manifestation of alarming symptoms. In this case, signs of anembryonia in the form of increased BT and malaise occur suddenly.
A high temperature of up to 37.8° or more during pregnancy may appear due to the development of sepsis against the background of fetal decomposition. Therefore, any fluctuations in values require medical attention.
It is difficult to recognize an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages using a BT schedule. Normally, gestation should occur against a background of elevated temperatures.
Signs of ectopic pregnancy most often appear in the 5th week and later. BT rises above 37.8°, accompanied by dark brown discharge, severe pain in the abdominal area and other unpleasant symptoms.
The condition threatens life and health and therefore requires immediate hospitalization.
Every woman has this picture