Methods for calculating gestational age
The main method for determining the duration of pregnancy is the method used by the gynecologist at the antenatal clinic, or the obstetric method. He calculates the gestational age from the first day of the last menstruation and prescribes routine instrumental and laboratory tests based on this date.
The embryonic counting method takes the date of ovulation as a starting point and lags behind the obstetric period by about 2 weeks. Women may believe that their pregnancy began on the day when the expected menstruation did not arrive. To avoid confusion when communicating with your doctor, it is recommended to adhere to the obstetric method.
What happens to the fetus at this stage?
According to the obstetric method, at 4 weeks the zygote, or fertilized egg, begins to rapidly divide. It produces many cells with different structures and functions. Actually, it is not yet a fruit. The collection of cells is called a morula, or blastocyst. In shape, it resembles a multi-chambered berry, not yet attached to the endometrium of the uterus. It is difficult to name the exact parameters of the blastocyst, since it is continuously growing.
Approximate parameters of the future embryo:
- Weight – 0.5 mg;
- Height – 0.36-1 g.
In figurative language, it is comparable in size to a poppy seed.
If we calculate the gestational age using the embryonic method, at week 4 the embryo has already established itself in the uterine cavity and continues intensive development.
At this stage, it is a germinal disc and consists of 3 layers:
- Primary ectoderm is the basis of skin, hair, tooth enamel, eye lenses, nervous system cells;
- Mesoderm is the basis for the formation of future organs, skeleton, muscle tissue, circulatory, excretory and reproductive systems;
- Endoderm is the basis of the respiratory and digestive systems, liver, thyroid and pancreas.
The future fetal head currently looks like a small droplet. The placenta has already begun to form. While it is still very primitive, it consists of 2 layers. The tissues of the future placenta are already connected to the tissues of the uterus, which makes it possible to provide the embryo with nutrition and oxygen.
The following extraembryonic organs are responsible for nutrition:
- The chorion is a prerequisite for the real placenta, which will form until the 12th week; from the 4th week, a vascular network begins to form at the point of contact of the embryo with the endometrium of the uterus;
- Amnion is a kind of “packaging” of the embryo, a prerequisite for the amniotic sac, which protects the fetus from physical impact and drying out;
- The yolk sac is a supply of nutrients for the embryo, the basis of hematopoiesis until 7-8 weeks of pregnancy.
Without the yolk sac, the existence of an embryo is impossible; if its functions are impaired or there is congenital pathology, a miscarriage occurs. When performing an ultrasound, the doctor determines the quality of pregnancy and the viability of the embryo based on the condition of the yolk sac.
According to research, it turned out that male genes are responsible for the formation of extra-embryonic organs. We can say that the function of protection and provision is inherent in a person even before birth.
By the end of 4 weeks, blastogenesis, the initial stage of embryonic development, ends.
What causes nagging, aching pain during pregnancy?
The stomach feels tight due to the implantation of a fertilized egg into the wall of the uterus. But by week 4 you should feel better.
If this does not happen, look for pathology:
- infectious and inflammatory condition of the urinary system – pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis;
- sexually transmitted infections – chlamydia, gonorrhea;
- ectopic pregnancy - the zygote does not reach the uterus, but is embedded in the wall of the tubes;
- inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract - duodenal ulcer, colitis;
- increased gas formation in the intestines, impaired stool formation (constipation, diarrhea);
- use of certain medications, especially if they are not prescribed by a doctor (hormones, antibiotics);
- increased uterine tone with the risk of sudden termination of pregnancy, miscarriage, premature birth;
- severe form of toxicosis with severe dehydration;
- diseases of the circulatory and coagulation systems with the risk of blood clots.
It is important for a pregnant woman to reduce the load. If she works for a long time, stands on her feet, or carries heavy things, there is a threat to the fetus.
The uterine muscles are strong, but under the influence of excessive loads they contract. This causes a dull soreness that appears in the late afternoon, but goes away in the morning after the woman has rested.
Minor discomfort develops into pathology, so the doctor will suggest bed rest. For the entire period of the threat, the patient should lie down and not make any effort.
How does a woman feel at 4 weeks pregnant?
If the pregnancy was unplanned and the woman does not suspect that she is pregnant, it is possible that she does not experience any changes in well-being. But this does not happen often; in most cases, the woman’s mental state changes, she becomes extremely emotional, touchy and whiny, irritable.
Additional sensations:
- The perception of the smells and taste of familiar food has changed;
- The figure became somewhat heavier due to hormonal changes;
- Swelling of the limbs appeared;
- Nausea occurred, and in some cases vomiting (early toxicosis);
- Nagging pain appeared in the lower back and lower abdomen;
- Increased frequency of urination;
- Vaginal discharge takes on the character of thick mucus;
- Increased sensitivity of the mammary glands appeared.
It is quite possible that due to early toxicosis the woman will not recover, but, on the contrary, will lose weight. There is no need to worry about this if there are no other symptoms other than loss of appetite.
Lower abdomen hurts
Often the lower abdomen feels tight even before pregnancy is known. At this time, implantation begins, in other words, after conception, the egg begins its journey through the fallopian tube and is implanted into the uterine wall.
Symptoms begin, which can occur before menstruation, when the lower abdomen pulls.
As a rule, there are distinctive features, since there are symptoms, but the period never comes, and the abdominal pain remains.
When the pregnancy reaches 4-5 weeks, the lower abdomen pulls and the intensity of this phenomenon intensifies, which makes women worry and be wary.
Symptoms may vary in strength and duration.
In some cases, abdominal pain will be nagging, dull or sharp.
Discomfort appears almost constantly, even if the woman does not move, but simply lies or sits. There are many reasons for this phenomenon.
Condition of the uterus and endometrium
The size of the uterus at the 4th week of pregnancy practically does not increase; it is still located within the boundaries of the small pelvis. Its structure changes - the uterus becomes swollen, the tissues in the isthmus area soften, which gives it slight mobility. Both the uterus and its cervix become bluish due to the influx of blood. A mucous plug begins to form in the cervical canal, protecting the fetus from bacterial infection from the outside.
The endometrium thickens, its structure changes - new blood vessels sprout, the number of glandular cells increases, which subsequently transform into the placenta. At this stage, such changes ensure the viability of the embryo, its respiration and nutrition. Due to the large number of blood vessels, the endometrium becomes bluish in color. Its thickness at 4 weeks, calculated using the embryonic method, is about 2 cm.
Causes
Many women wonder why the lower abdomen feels tight in the third week of pregnancy.
Painful discomfort in this area may not in all situations indicate a pathological process; it is often associated with changes in physiology characteristic of fruiting.
Directly at this stage, the stress on the woman’s body increases significantly, and a restructuring of many internal organs occurs.
Provoking factors of discomfort in the lower abdomen or lumbar region, when pregnancy is 3 weeks old, can be divided into 2 groups - physiological and pathological.
It is necessary to roughly know their main differences, since if physiological ones do not in any way pose a threat to the life of the pregnant woman and the fetus, then pathological ones can lead to irreversible consequences.
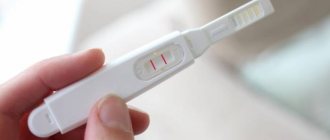
Pregnancy confirmation methods
By the end of the 4th obstetric week, it is already possible to confirm or deny pregnancy.
Methods used:
- Test strips for determining pregnancy may not show a positive result, although pregnancy is already present due to the low concentration of hCG in a woman’s urine, it is quite possible that after 2-4 days the result will change;
- A blood test for hCG - at this stage of pregnancy gives a 100% result, since the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood indicates fertilization has taken place;
- Ultrasound - at the end of the 4th obstetric week, with high-precision equipment, you can see a thickened endometrium and a black dot on it - an attached embryo.
Ultrasound at 4 weeks according to the embryonic method is performed using a transvaginal sensor. At this stage, the existing pregnancy is clearly visible.
What you can see:
- Dilated blood vessels of the endometrium, giving the embryo the opportunity to nourish itself;
- The fetal sac is in the form of a black circle with a diameter of several millimeters;
- The yolk sac is in the form of a small ring with a diameter of 2-3 mm.
The embryo itself will be visible on the yolk sac in another week. Ultrasound examination at this stage of pregnancy is carried out exclusively for medical reasons - to exclude hydatidiform mole or ectopic pregnancy.
Diagnosis of pathologies
It is necessary to begin the examination by visiting a gynecologist and conducting an examination. Then the doctor may prescribe various tests and instrumental examinations.
In a normal pregnancy without pathological signs, an ultrasound scan at 3 weeks is not necessary. It is required only to confirm that ovulation has occurred. In other cases, it will not be possible to obtain any information through this examination method.
If an ectopic position of the egg is suspected, it will be quite informative: the image shows that the fetus has attached itself to the tube and has not passed into the uterus. For an accurate examination, the transvaginal ultrasound method is used.
X-rays, MRIs and other instrumental examinations at 3 weeks of pregnancy are used only in rare cases.
Hormones at 4 weeks
The chorion (embryo membrane) produces hCG - human chorionic gonadotropin. It prevents the rejection of the embryo, which represents a symbiosis of its own and foreign cells for the body, produces steroids, determining the sex of the unborn child, and supports the functioning of the corpus luteum. HCG levels increase daily until 7-8 weeks of pregnancy, then they begin to decrease.
Before the formation of the placenta, the corpus luteum produces progesterone, which plays an important role in the normal course of pregnancy.
Functions of progesterone:
- Ensuring the growth of the uterus;
- Reducing the frequency and intensity of uterine contractions, preventing miscarriage;
- Growth of subcutaneous tissue to nourish the embryo;
- Prevention of rejection of a foreign organism;
- Development of individual fetal tissues;
- Preparing the mammary glands for breastfeeding.
The average amount of progesterone in the blood of a pregnant woman at week 4 is 18 nmol/l. Before the study, physical and mental stress and taking hormones are not recommended.
When to see a doctor?
If you feel normally, you can still postpone a visit to the doctor. If the test result is positive and there is nagging pain, signs of early toxicosis, or atypical discharge, you should consult a doctor.
Possible actions of a gynecologist if a woman feels well at the 4th obstetric month:
- Taking anamnesis;
- Visual examination, examination on a gynecological chair;
- Prescription of vitamin-mineral complexes containing, among other components, folic acid.
Signs of disease and a history of miscarriages require specific treatment. Women who have problems conceiving and become pregnant using IVF or ICSI are under the supervision of a doctor from the first days of pregnancy.
Watch a video that will tell you why you need to do a genetic analysis, what happens in the female body, about hereditary diseases - cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, Down syndrome and screening for chromosomal pathologies:
Urolithiasis
The fifth week of pregnancy is characterized by various exacerbations, including those of the urinary system.
This is caused by anatomical features, as well as the fact that the uterus is very close to the bladder.
Even in normal conditions, many women suffer from urinary diseases. As a rule, pathologies that cause pain in the lower abdomen and problems with urine excretion include:
- Cystitis.
- Pyelitis.
- Pyelonephritis.
After conception, doctors keep women with such pathologies under close control, since pregnancy may be at risk.
As soon as the 3-5th week of pregnancy begins, with cystitis, the lower abdomen pulls, and a frequent urge to urinate appears, but this may be the norm, because the uterus begins to put pressure on certain organs.
To determine the disease in more detail, it is important to know the main symptoms of cystitis:
- The abdomen begins to ache a little above the pubis and at the very bottom, and the pain can be dull or sharp. During pressing, the sensations become stronger.
- An increase in urination begins, some even have the urge every 10 minutes.
- There is discomfort when urinating, especially at the end.
- In some cases, drops of blood can be seen in the urine, which indicates hemorrhagic cystitis.
- Sometimes you can notice an increase in temperature, although cystitis may not change it.
- Urine becomes cloudy.
Cystitis often appears as a result of bacterial infection, and the disease must be treated with antibiotics, which are largely prohibited during pregnancy.
Without providing the necessary therapy, a woman begins to develop pyelonephritis - inflammation of the kidneys.
With kidney inflammation, the pathology can cause organ failure and often occurs in a chronic form.
While carrying a child, this disease is very dangerous, since the load on the body increases, and the kidneys may completely fail to function.
The main symptoms of the disease include:
- Severe pain in the lumbar region, pain in the lower abdomen.
- A high fever appears.
- Chills.
With an exacerbation of a chronic disease, the symptoms will not be so obvious, but fever and pain will accompany the woman.
When the kidneys become inflamed, general intoxication begins, which causes harm to both the child and the mother. The disease is especially dangerous in the early stages, when all the organs of the fetus are formed.
Treatment can only be done with antibiotics. In some cases, doctors select a variety of medications that will not harm the child’s development, but will relieve inflammation and kill pathogens.
Abdominal and lower back pain at 4 weeks
Low-intensity pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, without abnormal discharge and increased body temperature, is the norm at 4 weeks of pregnancy. Such sensations are caused by hormonal changes in the body; they pass quickly and without consequences. Intense pain accompanied by bloody discharge may be signs of the following pathologies:
- cystitis, pyelonephritis – urination disorders and hyperthermia are added;
- Constipation, flatulence;
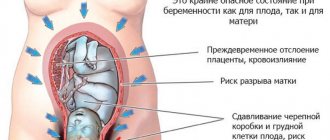
- Ectopic pregnancy - sensations often occur on one side;
- Threatened miscarriage or frozen embryo - accompanied by bloody or sanguineous vaginal discharge;
- Surgical pathologies (appendicitis).
The appearance of such symptoms is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
Pathological causes
There are a large number of diseases during which the stomach may hurt. Some of them accompany pregnancy or are provoked by it.
If there is the slightest suspicion of a pathological nature of pain, you should immediately contact a specialist.
However, the choice of treatment by specialists regarding the continuation of pregnancy at 3 weeks remains controversial.
In accordance with Western recommendations, at this stage the body begins to reject embryos with genetic and chromosomal abnormalities.
But, given the amount of effort women put into getting pregnant, many specialists prefer to prescribe hormonal therapy and maintain the pregnancy.
In addition, we should not forget that in the early stages, pathological discomfort is not only a threat of miscarriage.
It also indicates other pathological processes:
- An incipient miscarriage or abortion is in progress.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Uterine fibroids.
- Diseases of the urinary system.
- Stomach diseases.
- Acute surgical pathological processes.
Vaginal discharge at 4 weeks
Normally, at this stage of pregnancy there should be clear, thick mucous discharge from the vagina. It is possible to add a small amount of brownish discharge - a sign of egg implantation into the endometrium of the uterus. If the color of such discharge becomes dark brown, it is accompanied by abdominal pain and an unpleasant odor - this is a sign of an ectopic pregnancy, an incipient miscarriage, cervical erosion, or bacterial infection of the vagina.
There should normally be no bloody discharge during this period. Menstruation will no longer begin, since this process is regulated by the woman’s hormones.
Possible causes of bloody vaginal discharge:
- Sexual intercourse;
- Gynecological examination in mirrors;
- Cervical erosion;
- The onset of spontaneous abortion;
- Ectopic pregnancy.
All atypical bleeding of any intensity requires immediate medical consultation. During a miscarriage, the discharge may be accompanied by fever, spasmodic pain, and contain tissue particles. With an ectopic pregnancy, a woman may lose consciousness from intense pain, her skin turns pale, and she feels dizzy.
Fever and cold at 4 weeks
A slight increase in basal and general temperature to +37.3°C is the norm at this stage of pregnancy, if it is not accompanied by signs of a viral infection. The reasons for this symptom may be hormonal changes in the body, acceleration of metabolism, decreased immune response, as a prevention of embryo rejection.
Against the background of decreased immunity, a pregnant woman may develop an infectious disease at 4 weeks - ARVI, influenza, cystitis, pyelonephritis. Then the body temperature rises to +38°C-+39°C. In this case, there is a danger for the proper development of the embryo, the risk of miscarriage.
Prevention of colds during pregnancy:
- Avoid places where there are a lot of people;
- Do not contact people with infectious diseases;
- Ventilate the premises more often;
- Maintain a routine of walks in the fresh air, a routine of sleep and rest;
- Eat right, taking vitamins in the form of fresh vegetables and fruits.
You should not self-medicate colds. Only a doctor can choose the right medications based on pregnancy.
The biggest mistake when self-medicating during pregnancy is taking antibiotics. There are a limited number of antibacterial drugs suitable for treating pregnant women, and week 4 is not the best time to use them. During the formation of the most important organs of the fetus, antibiotics can exhibit a teratogenic effect and cause deformities and developmental pathologies in the unborn child.
Nutrition at 4 weeks of pregnancy
The basic requirements for creating a diet for a pregnant woman are a balanced diet rich in nutrients. Now you should not eat canned food, fast food products and semi-finished products.
The best dishes to introduce into the diet are vegetables and fruits, dairy and fermented milk products, fatty fish - salmon, trout, salmon. It is advisable to eat familiar food, avoiding exotic dishes. Steaming, boiling in water, and stewing foods is encouraged. Fried and smoked foods are not included in the diet of a pregnant woman.
It is completely unacceptable to consume alcohol in any form - beer, homemade wine, low-alcohol cocktails. The woman and her unborn child now share a common circulatory system, and everything she eats and drinks ends up in the blood of the embryo.