Hello friends! Lena Zhabinskaya is with you! Doctors who come to examine babies in the maternity hospital always feel their heads. What are they looking for there? Fontana in newborns. The small, soft, pulsating area is of great interest to physicians.
It allows them to judge not only the state of health of the baby immediately after his birth, but also the quality of his nutrition and the rate of growth and development in the future.
By the way, its functions do not end there. What is this area and what is it for? Let's find out today.
General information
The process of giving birth to a baby is so meticulously “thought out” by nature that it provides for all the moments so that the child can be born healthy. In order for the small body to pass through the mother’s birth canal, its head takes on an oblong shape and is slightly flattened on the sides. The baby has gaps between the bones of the skull, which are filled with plates of connective tissue. These gaps are called fontanelles , and parents have a lot of different questions about them.
However, most of them - and there are six fontanelles after birth - quickly overgrow. Therefore, parents often simply do not notice that there were so many of them. But the main one - the frontal or greater fontanel (abbreviated as BR) remains for a longer period. After all, its function is also to provide shock absorption, protecting against injuries and fractures during a fall. We will discuss in the article below when the crown of a newborn becomes overgrown and how this process occurs.
Baby's skull bones during childbirth
In most natural births, the baby passes through the birth canal head first , which is the majority of his body. Nature designed the bones of the skull to be tiny that they are flexible and mobile and do not grow in the womb until the end.
They may even overlap where the fontanel is to make it easier for the head to pass through the birth canal. The brain is protected because it is located between two halves - the brain chamber and the cerebrospinal fluid . This system is cushioned, pressure, brain compression and overlap do not matter. When the head passes, then all other parts of the body easily go well directed.
When does the fontanelle close up in newborns?
Young parents often worry whether everything is going well and are looking for information about when the large fontanelle closes up. The older the baby gets, the more worried parents become about this. But in fact, even after the baby is one year old, and the crown remains, there is no need to worry. After all, in children this process is normally completed before the age of 1.5 years. But if you are still overcome by a certain concern that the process is progressing late, it is better to visit a doctor who will help determine when the child’s fontanelle closes up in a particular case.
After all, we can talk not only about a disease, but also about a certain developmental feature. Therefore, sometimes the answer to the question of at what age a child’s fontanelle closes up is not so categorical. In any case, when visiting a doctor with the baby, the mother should ask him all the questions about how long the child’s fontanel should heal.
What should the crown be like?
The doctor evaluates the characteristics of the fontanel immediately after the child is born, as well as every time during monthly examinations. The pediatrician must pay attention to the size of the crown, the rate at which it decreases, and the density of the bones surrounding it.
What size should a healthy baby's fontanel be? In a full-term baby, its dimensions are 2.5-3 cm. The doctor determines this by palpating the skull and taking measurements between opposite sides of the diamond.
In premature babies, these dimensions are larger - about 3.5 by 3.5 cm. But if a large baby was born at 41-42 weeks, then the crown may be smaller. Interestingly, a baby at the age of 1 month may have even more BR than at the time of birth. The thing is that during this period the brain is actively growing, and therefore the bones diverge a little.
Therefore, it is difficult to determine exactly what kind of BR a baby should have at a certain age. However, in some sources you can still find certain indicators:
- at three months – 1.8-2 cm;
- in six months - 1.8-1.6 cm;
- at nine months - 1.3-1.4 cm;
- in one year - 0.4-0.8 cm.
But it should be understood that these indicators are just a rough guide. This is due to the fact that:
- the size of the fontanelle is initially different for all children;
- the way the fontanel tightens in children does not depend on its size; A large one can last for a year, a small one sometimes does not heal until a year and a half later.
But it is very important to ensure that the fontanelles are at the level of the cranial bones and are not too tense. It is possible that the spring will sink or swell a little, and its pulsation is also possible.
It is also important that the parietal and frontal bones surrounding the crown are dense, and there are no areas of softening noted on them.
What does a pulsating fontanel signal?
Ripple deserves a separate discussion. This is the norm. You can see how in some children the fontanel does not move, while in others it trembles rhythmically. The reasons for this are the structural features of the infants’ skull and hereditary characteristics. Under the surface of the fontanel there is a cerebrospinal fluid pathway—the place where intracerebral fluid “leaks.” If a newborn has cried or sucked for a long time or moved actively, then his blood flow increases and the pulsation of blood vessels becomes noticeable. There are many vessels under the cerebrospinal fluid, they are quite large and seem to push the cerebrospinal fluid from below. In response, it begins to tremble rhythmically. At elevated temperatures, similar processes occur and pulsation can also be seen. If parents are very concerned about this, then you can draw the pediatrician’s attention to this feature of the baby.
If the fontanel does not close, what should you do?
You need to visit a doctor and consult with him if the fontanel has not closed by 18 months. This condition may be normal for the baby. However, we can also talk about certain pathologies.
| Disease | What does a fontanel look like? | What research is needed? | How to proceed? |
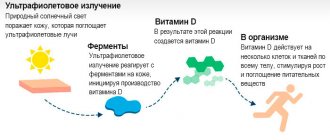
| Rickets | Lack of calcium leads to softening of bones, including the skull. The BR remains open for a long time, the edges of the bones are soft to the touch. The child becomes lethargic, often sweats during sleep, and the back of his head becomes bald. Bone growths appear on the wrists and ribs, and curvature of the lower leg is noted. | An examination by a pediatrician, a urine sample according to Sulkovich, and a blood test for phosphorus, calcium, and alkaline phosphatase are necessary. | The use of therapeutic doses of vitamin D . |
| Congenital hypothyroidism | BR does not heal for a long time due to a deficiency of thyroid hormones, which regulate, among other things, bone growth. Constipation is a concern , the voice becomes nasal, and umbilical hernias . The fontanel does not last long. | It is necessary to consult with a pediatrician and pediatric endocrinologist, conduct a blood test for TSH, T3 and T4, and an ultrasound of the thyroid gland. | Thyroid hormone replacement therapy is carried out. |
| Achondrodysplasia | A disease of bone tissue that impairs growth. The skeleton becomes disproportionate, the head becomes massive and wide, the limbs become short. The fontanel does not last long. Genetic consultation is required. | A PCR X-ray of the skull is performed to determine the gene mutation. | The growth hormone somatotopin . |
| Hydrocephalus | Due to increased cerebrospinal fluid pressure, the cranial bones cannot “come together”. The fontanelle rises above the bones, the head circumference increases. Possible manifestations of seizures, hearing and vision impairment, and developmental delays. | Observation by a pediatric neurologist, EEG, MRI, and ultrasound of the brain are indicated. | Anticonvulsants, diuretics, and nootropics are prescribed. Sometimes shunting is indicated. |
What to do if the fontanel overgrows very quickly?
If the baby has a very small fontanel, parents need to show the child to specialists - a pediatrician, endocrinologist, neurologist. Sometimes there are cases when the fontanel in a newborn heals already at 3 months. This happens rarely - in about 1% of cases. If the baby’s other indicators are normal, then we are not talking about deviations.
However, in some cases, too small BR may be evidence of pathology. The table below shows possible conditions in which the baby's fontanelle is too small.
| Disease | What does a fontanel look like? | What research is needed? | How to proceed? |
| Craniosynostosis | The sutures of the skull and fontanelles fuse very early and quickly. Possible deformation of the skull, jaw, and secondary hydrocephalus. | An MRI, CT scan of the head, and radiography of the skull are performed. | Surgical cutting of sutures. |
| Increased function of the parathyroid glands | Due to impaired calcium and phosphorus metabolism, the calcium content in the blood increases. The baby's BR closes early, pain in the bones bothers him, the kidneys and gastrointestinal tract are affected, and arrhythmia . | A blood test is performed for phosphorus and calcium, and the content of parahormone in the blood is determined. X-rays of the skull bones and ultrasound examination of the thyroid and parathyroid glands are also performed. | Surgical methods of treatment. |
| Microcephaly | Due to abnormal development of the brain, the bones of the brain part of the skull stop growing, but the growth of the facial bone continues. The brain remains underdeveloped. Developmental delay is noted. | The child is observed by a neurologist, electroencephalography and ultrasound of the brain are performed. Genetic consultation is important. | Symptomatic treatment. |
Developmental disorders
The rate of bone fusion in the area of the fontanel and the condition of its edges can tell a pediatrician and/or neurologist a lot. Possible developmental abnormalities that doctors can diagnose based on the condition of the fontanelle:
- rickets most often occurs in premature infants with vitamin D and calcium deficiency;
- hypothyroidism - insufficient production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland affects the slow closure of the fontanel;
- Down syndrome - a large fontanel of too large size may be one of the symptoms;
- excess calcium in the body is characterized by small fontanel sizes in a newborn and can cause the development of microcephaly and craniosynostosis.
Protruding fontanel
Most often it speaks of increased intracranial pressure, which can occur against the background of diseases such as encephalitis, meningitis, hydrocephalus. brain tumors. You need to urgently consult a doctor if your baby has a bulging fontanel accompanied by the following symptoms:
- vomit;
- convulsions;
- strabismus;
- loss of consciousness;
- the fontanel protruded as a result of the fall;
- The fontanelle has been bulging for a long time.
Sunken fontanel
The fontanel in a newborn becomes sunken due to dehydration due to high fever, vomiting, and diarrhea. Drink plenty of fluids and consult a doctor to treat the disease that caused dehydration.
What to do if a child’s fontanel is too large?
A fontanel is considered too large if its size exceeds 3.5 cm. But for immature or premature babies this may be the norm. In such cases, the child’s large fontanelle closes before one and a half years. Often, at the age of 3 months or older, the BR begins to actively decrease, and by this age it gradually closes.
In other cases, it is necessary to consult a pediatric neurologist, conduct an ultrasound of the brain and other necessary studies to exclude hydrocephalus and increased intracranial pressure .
How to measure a fontanelle?
During each routine examination, the pediatrician must palpate and measure the crown of the head - this allows one to obtain minimal information about the rate of development of the brain and the baby as a whole.
Table of average crown sizes by month
| Age (months) | Size(cm) |
| From birth to 1 month | 2,6–2,8 |
| 1–2 | 2,2–2,5 |
| 2–3 | 2,3–2,4 |
| 3–4 | 2,0–2,1 |
| 4–7 | 1,6–1,8 |
| 7–8 | 1,4–1,6 |
| 8–9 | 1,4–1,5 |
| 9–10 | 1,2–1,4 |
| 10–11 | 0,9–1,2 |
| 11–12 | 0,5–0,8 |
Important!
To measure the fontanel yourself, place 2-3 fingers on the crown, with the width of 1 finger equal to 1 cm. Measurements should be taken from corner to corner of the diamond.
Why does the fontanelle pulsate in a baby?
Since the brain is actively supplied with blood, and its vessels are located close to the heart, when the blood flows there is strong pressure and, accordingly, tremors.
This pulsation is transmitted to the cerebrospinal fluid, to the membranes of the brain and the plate that covers the BR. Therefore, if the fontanel pulsates a little at 3 months or at another age, this is normal. But if the BR pulsates very strongly in a child, this may indicate developing diseases. But in this case, as a rule, there are other unpleasant symptoms - intoxication, dehydration, fever, vomiting, etc. In such a situation, you need to consult a doctor, establish a diagnosis and carry out the correct treatment.
What does it mean if a baby’s fontanelle has sunk?
When the BR drops, this is evidence that the baby is malnourished or his body is dehydrated. A sunken fontanel in a child due to loss of fluid can be observed:
- in extreme heat;
- due to overheating if the child is wrapped up too tightly;
- as a result of elevated temperature or intoxication of the body;
- after severe vomiting or diarrhea .
It is very important to immediately replenish fluid loss. If the baby is overheated, he should be cooled and given fluids. In case of intestinal infection manifested by severe symptoms, treatment is carried out in a hospital.
If the fontanel protrudes, what does it mean?
Bulging (elevation above the bone level) of the fontanel may be evidence of increased intracranial pressure - a symptom characteristic of meningitis , encephalitis , tumors, and intracranial bleeding. There are other possible reasons for this phenomenon.
Parents should be very careful and call emergency help if, in addition to the bulging fontanel, the following signs are observed:
- elevated temperature;
- diarrhea and vomiting in an infant;
- disturbances of consciousness;
- bulging after head injury;
- strabismus;
- convulsions.
In the absence of such symptoms and the bulging continues for a long time, you should also contact a specialist. In such a situation, an ultrasound of the baby’s brain may be needed. Whether this is normal or not will be determined by the results of the examination.
conclusions
Despite the fact that normally the process of closing the BR is completed by one and a half years, sometimes certain deviations can occur in healthy children. Therefore, the answer to the question of when a child’s fontanelle should close is not always clear. Parents should be wary of the situation when the fontanel closes in infants under 3 months. If parents have certain doubts about the process taking place, about when the child’s fontanel closes, it is better to ask a pediatrician.
The process of closing the BR occurs faster if the baby is well fed and quickly gains weight. Most often, in breastfed children, closure occurs faster.
Physiological features of fontanelles
Yes, this is not a mistake. In addition to the largest frontal crown, there are 5 more small fontanelles, the existence of which many parents are not even aware of. The vertex connects the frontal and parietal plates of the skull; it is diamond-shaped and varies in size from 22 to 35 mm.
At the back of the head there is a posterior fontanelle that connects the pair of parietals and the occipital bone. It resembles a triangle with dimensions of 5 mm. Germination occurs quickly - within 2 months after birth. There are often cases when a baby is born without it - this is a variant of the norm.
The smallest are the paired temporal wedge-shaped and paired mastoid, located behind the ears of the newborn.