Sulfur poisoning is one of the types of intoxication of the body, which can be progressive and provokes serious consequences in the form of mental disorders, Parkinson's disease and death. That is why you need to have information about the dangers of a chemical substance, first aid for those affected by its effects, treatment and prevention of negative effects on the body.
Briefly about the substance
The opinion that it can negatively affect only those who work in the chemical industry is erroneous. Anyone can be harmed by sulfur and its compounds, as they are used in various industries:
- as part of preparations for disinfection;
- as components of insecticides;
- in the production of acids and sulfites;
- for the production of bleaches in the textile industry;
- in the production of explosives;
- as part of food preservatives.
That is, a person in everyday life can often encounter sulfur and accidentally become a victim of its toxic effects.
About the causes of sulfur poisoning
It is worth taking into account that the dioxide of the above substance is a component of urban smog, which is formed after emissions into the air from industrial enterprises. By being forced to inhale it, the body is slowly poisoned. This is why sulfur is dangerous for people living near such industries.
However, it is not always used in its pure form. More often there are its combinations with other chemical elements, for example, hydrogen sulfide, sulfuric acid, carbon disulfide, dioxide. The latter is nothing more than sulfur dioxide, also called sulfur dioxide.
Considering such a number of compounds, one can understand why cases of intoxication due to the substance are not uncommon. This happens when:
- Inhalation of gases that are formed when a substance burns. Statistics show that the inhalation route is most often the mechanism due to which sulfur vapor poisoning occurs.
- Destruction of field pests with insecticides. These are special checkers and other preparations containing a chemical element.
- Fires, industrial emergencies. Force majeure circumstances occur in industrial enterprises when safety rules are not followed.
- Prolonged stay near sewers, where hydrogen sulfide is the result of protein rotting. It has a characteristic smell of rotten eggs. This is what sulfur smells like.
- Suicide attempts involving ingestion of derivatives of a chemical element.
What is the clinical picture of sulfur poisoning?
So, it is important to know how to recognize intoxication with a chemical element, sulfuric acid poisoning. Symptoms of sulfur poisoning are a number of characteristic signs of trouble in the body and negative changes. They differ depending on the specific substance causing the problem.
Sulfur dioxide poisoning is characterized by damage to the respiratory tract. This is manifested by sneezing, coughing of varying intensity with the release of blood, wheezing, nausea, itching of the mucous membranes of the visual apparatus and their hyperemia. Possible nosebleeds and fogginess, a jump in body temperature. When severe sulfur dioxide poisoning occurs, toxic pulmonary edema can lead to death.
As for hydrogen sulfide intoxication, it first manifests itself as dizziness and pain in the eyes, then blepharospasm, convulsions, and in severe cases - collapse, apoplexy. The lethal volume of the substance is only 1.2 mg/l. Carbon disulfide intoxication has the following symptoms:
- feeling of slight intoxication;
- inappropriate behavior;
- overexcitement;
- psychotic outbursts;
- inability to open eyes.
When it comes to a chronic form of intoxication, the signs of sulfur poisoning are prolonged pain in the head, weakness and poor sleep, sweating and irritability. As intoxication progresses, depression, intimate disorders, encephalopolyneuritis develop, and memory deteriorates. Symptoms of Parkinson's disease may appear. It should be noted that the harmful effects of carbon disulfide primarily affect the central nervous system.
About first aid and treatment of intoxication
To avoid deterioration in well-being and sad health consequences, you need to know what to do in case of sulfur poisoning. If you suspect him, you need to immediately call a medical team or call an ambulance. Further, before the arrival of specialists, first aid for sulfur poisoning consists of evacuating the victim from the contaminated area, and, if possible, administering oxygen inhalations. When the substance gets on the skin, it is necessary to immediately wash it with plenty of water, or better yet, with a solution of sodium bicarbonate. After contact with dangerous compounds, eyes are washed with water, then instilled with 0.5% Dicaine.
If a person has inhaled harmful fumes, he needs to instill vasodilating nasal drops before the arrival of specialists. And when it comes to ingesting substance compounds, you need to force the person to drink a lot of warm water and thus provoke vomiting.
It is important to carry out all of the above as soon as possible, and then entrust the treatment of sulfur poisoning to doctors. They take comprehensive actions, eliminating intoxication and cleansing the victim’s body. In therapy they use:
- Probe cleansing of the stomach.
- Amyl nitrite is used as an antidote to hydrogen sulfide.
- Atropine is used when sulfur poisoning occurs.
- Diuretic medications are prescribed to speed up diuresis.
- Relieve a severe cough with Codeine.
- Vitamin B6 and Encephabol are prescribed to improve blood flow to the brain.
- Calcium gluconate is administered intravenously for hydrogen sulfide damage.
The victim remains in the hospital until his condition stabilizes. After discharge, treatment can continue on an outpatient basis. Read what to do in case of hydrochloric acid poisoning here.
About possible consequences
They depend on the severity of the injury, the state of the victim’s defenses, and his age. Poisoning with sulfur oxide and other sulfur compounds can have extremely serious consequences. We are talking about mental disorders, persistent VSD, encephalopathy, toxic parkinsonism, a significant decrease in visual acuity or its complete loss, diseases of the nervous and respiratory systems. The most dangerous outcome of intoxication is the death of the victim. In most cases, this happens when qualified assistance is not provided in a timely manner.
Prevention of lesions
By following a number of measures, you can avoid the negative effects of sulfur compounds on the body. Here are the main recommendations:
- Use of personal protective equipment when in contact with derivatives of the substance.
- Strict adherence to safety precautions in chemical production and regular medical examinations in order to prevent chronic intoxication.
- Prohibition of staying in rooms with fumes of sulfur gases.
- Follow instructions for working with insecticides in the field and in the garden.
- Taboo on self-medication with drugs that contain a chemical element.
By exercising forethought and caution, long-term therapy after intoxication with a toxic substance can be avoided.
Sulfur compounds are an intermediate or by-product of a number of industrial and natural processes. Their danger lies in the fact that they are capable of causing severe, sometimes progressive poisoning. Most often, sulfur dioxide is found in urban smog, which forms after frequent emissions from city-forming industrial enterprises.
Chronic sulfur poisoning is typical for workers in textile industry enterprises producing viscose, silk, and cellophane. Sulfur compounds are also used in the chemical industry, as well as in agriculture in the form of insecticides.
Contact with sulfur in any form can result in severe poisoning. A lethal dose for humans is 1 gram of carbon disulfide if ingested; if we talk about the concentration of sulfur in air masses, then 10 ml is sufficient.
Sulfur residues accumulate in the bulk of the kidneys and liver, and naturally do not leave their mark on these organs.
The presence of sulfur compounds in the air, in particular hydrogen sulfide, can be determined by the presence of the characteristic smell of rotten eggs. It is noteworthy that a concentration of the substance in air masses from 0.02 to 0.2 ml can cause poisoning, and 1.2 mgl can lead to death.
Why is sulfur oxide dangerous?
Strong poisons include sulfur oxides: dioxide and trioxide. These are toxic gases that, even when inhaled in low concentrations, lead to painful effects. The reagents have a destructive effect on many organs:
- inflammation of the upper respiratory tract;
- damage to lung tissue;
- mucous membranes of the eyes;
- circulatory system;
- digestive organs;
- nervous structure.
Sulfur dioxide is especially dangerous when it interacts with sulfuric acid salts, which can accumulate in the respiratory system. Such contact can provoke serious diseases leading to destruction.
Poisoning with the reagent leads to both local and general toxic syndrome. Above a concentration of 1.2 mg/l, cellular respiration is blocked and tissue redox functions are inhibited. This leads to oxygen starvation and death.
In cases of sulfur oxide poisoning, dangerous symptoms include loss of smell. People working in production may not feel the gas and thereby limit their ability to leave a place with a polluted atmosphere in time.
In everyday life, sulfur poisoning most often occurs. Gas entering the eyes can cause blindness. If you stay near a toxic substance for a long time, you can suffer suffocation and pulmonary edema.
On city streets there is danger from a suffocating veil of smoke, which includes sulfur dioxide. Chad produces industrial enterprises, factories and oil depots. Sometimes it falls to the ground in the form of acid rain. In this regard, severe and sometimes progressive poisoning may occur.
Toxic reagents can form in sewers. Therefore, prolonged exposure to such systems can lead to intoxication of the body.
Signs of poisoning
The clinical picture varies depending on the degree of toxic gases entering the body. Sulfur compounds disrupt the neuroendocrine and vegetative-vascular processes and therefore cause certain symptoms.
Acute form
An acute form of poisoning appears almost instantly. The main symptoms include the following ailments:
- dizziness;
- runny nose;
- wet wheezing;
- cough;
- nausea;
- sore throat;
- vomiting with bile;
- pain in the chest, head, nose;
- burn of the mucous membranes of the eyes;
- conjunctivitis;
- profuse lacrimation;
- formation of blisters on the skin.
In case of severe poisoning with sulfur compounds, symptoms appear that threaten the life of the victim:
- loss of consciousness;
- lack of response to external stimuli;
- breathing problems;
- convulsions;
- acute emphysema;
- suffocation;
- paralysis;
- coma;
- collapse;
- apoplexy.
The nervous system suffers from poisoning. The patient experiences an unstable emotional state, increased motor activity, develops auditory hallucinations, and a mental disorder. Abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract include pain in the esophagus and discomfort in the stomach. Paralysis of the respiratory or vasomotor center leads to death.
Chronic
Most often, people who work for a long time in production where they use the reagent are poisoned. Regular exposure to low doses of hydrogen sulfide leads to the following chronic symptoms:
- dystrophic change in the liver;
- kidney dysfunction;
- decreased diuresis;
- yellowing of the skin;
- development of heart failure;
- wheezing;
- dyspnea;
- cough with foam.
The victim has an abnormal heart rhythm and pulse, wheezing is heard in the chest, and asthenovegetative syndrome manifests itself. The chronic form is expressed in impaired sensitivity, weakness in the limbs, and progressive loss of body weight. In women, the menstrual cycle is disrupted.
What is forbidden to do in case of poisoning
In addition to the mandatory principles in case of poisoning, you should also know what should not be done in this case:
- drink sparkling water;
- induce vomiting in an unconscious patient;
- take a laxative and induce a gag reflex in case of poisoning with alkali, acids, petrochemical products;
- cause vomiting in a pregnant woman;
- give alkali in case of acid poisoning and vice versa;
- provoke vomiting in the presence of convulsive syndrome, heart pathologies.
Plisov Vladimir, medical observer
10, total, today
( 190 votes, average: 4.64 out of 5)
Respiratory failure: classification and emergency care
Alcohol poisoning: drugs and traditional medicine
Related Posts
First aid algorithm
Having discovered the first symptoms of sulfur poisoning in a victim, you must immediately provide him with emergency assistance. First of all, everyone should be evacuated from the contaminated area. If the compound gets into your eyes, you should rinse them with clean water and then drip them with an anesthetic, for example, Tetracaine or Dicaine. Exposed areas of skin should be thoroughly cleaned with a solution of baking soda or running water.
If the victim has inhaled toxic fumes, it is recommended that he drip his nose with nasal drops with a vasodilating effect. To replenish the body with pure oxygen, you can perform oxygen inhalations. The antidote Amylnitrite may be suitable for this. You need to put a few drops on a handkerchief or a piece of gauze and bring it to the patient so that he can inhale the medicine.
If the victim begins to have convulsions, an intravenous or intramuscular injection of Diazepam can be given. The dosage is selected according to the instructions for the drug. The sedative effect occurs within a few minutes.
In case of poisoning, the patient needs to thoroughly cleanse the stomach. The victim should drink as much clean water as possible, trying to provoke vomiting.
The main help in eliminating symptoms can only be provided by professionals, so you need to call them immediately.
Pharmacy drugs
For vomiting and poisoning
- Furazolidone and Nifuroxazide. The first medicine is cheaper, but it is recommended for use only by adults. The second option will be a little more expensive, but it can even treat children. The course of therapy is no more than 10 days.
- Cerucal (can be replaced with Metoclopramide).
- Buscopan - children under 6 years of age should not use this product.
- Domperidone - suitable for patients whose weight exceeds 35 kg.
For nausea and poisoning
- Sumamed is an antibiotic. Its action is aimed at destroying pathogenic bacteria, blocking their growth and development. Available in tablet, powder or drop format. Helps quickly cure poisoning.
- Xylocaine spray. Not only reduces pain, but also eliminates the urge to vomit.
- Motilium - helps reduce pain and get rid of vomiting of any origin.
In case of poisoning with tablets
- Activated carbon – has the ability to absorb more than 200 types of toxins. The first time, take 20 tablets at a time, and then take 10 tablets three times a day.
- Smecta is a natural-based drug. Several times stronger than activated carbon. Dissolve the sachet from one sachet in 100 ml of water. Drink three times a day for five days.
- Polyphepan is a medicine made from wood. The daily intake is calculated based on the person’s weight. The entire portion is distributed 3-4 times throughout the day.
For food poisoning
Food poisoning is treated with the following drugs:
- You can use activated carbon or Polysorb as sorbents.
- Regidron is a drug aimed at combating dehydration.
- No-shpa or Nimesil. These medications help relieve spasms.
- Pancreatin or Linex. Means that help normalize intestinal microflora.
For alcohol poisoning
- Enterosgel is a sorbent that is recommended for use specifically for alcohol intoxication.
- Anestezin is a drug whose action is aimed at stopping the urge to vomit.
- Biotredin not only reduces the symptoms of poisoning, but helps fight moderate alcoholism.
- Limontar – helps cure poisoning, improves appetite.
- Zorex - fights the remnants of alcohol in the body and the breakdown products of alcoholic beverages.
Therapy
After sulfur poisoning, after studying the victim’s symptoms, doctors prescribe appropriate treatment. In such cases, complex therapy is prescribed:
- if poison enters the stomach, the patient is given a gastric tube;
- to accelerate the excretion of chemical compounds in the urine, the patient is prescribed diuretics;
- for symptomatic treatment, as well as improving blood supply to the brain, doctors prescribe vitamin B6, Encephabol;
- to relieve pulmonary edema, calcium chloride or gluconate is used intravenously;
- oxygen pillows are used;
- prescribe medications to improve the functioning of the peripheral and central nervous system;
- Glucocorticoids will help restore carbohydrate, protein, fat and mineral metabolism;
- Antibiotics will help kill bacteria.
Any burns that appear are carefully washed and treated. If the patient's condition is serious, strong narcotic analgesics are used. After treatment, the patient remains in hospital for about a week under medical supervision. But even after this time, the victim must be registered with medical staff and constantly undergo examinations. This is done in order to prevent many ailments that occur after sulfur poisoning.
Consequences
Poisoning with sulfur compounds does not occur without consequences for the patient. This applies to all organs of the body:
- partial or complete loss of vision when sulfur gets into the eyes;
- rhinitis, tonsillitis, tonsillitis and other chronic respiratory diseases;
- destruction of the digestive system;
- Parkinson's disease;
- encephalopathy;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
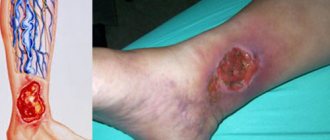
- post-burn marks and scars.
To avoid dangerous situations, it is necessary to carry out preventive work. Work with chemical compounds in ventilated areas and with good ventilation. Before any manipulations with reagents, you need to wear protective clothing, shoes, goggles, gloves, and a respirator. All workers in hazardous industries must undergo regular medical examinations, where specialists are able to detect the initial stage of chronic poisoning in time.
It is recommended to use harmful substances in everyday life, strictly following the operating instructions. If possible, it is better to replace drugs with sulfur with similar products without toxic compounds.
Under no circumstances should medications containing sulfur compounds be used in home treatment. You should try to avoid places with high concentrations of toxic gas.
People encounter toxic chemicals everywhere, both at work and at home. Poisoning can occur at any time if you do not take safety measures. Remember that it is better to prevent the onset of symptoms than to treat the terrible outcome of poisoning.
There is a misconception that only employees of industries where this element and its compounds are used can get sulfur poisoning. But practice shows that this often happens in everyday life.
Sulfur is an element of the periodic table, a non-metal. It and its compounds are used in various fields:
- in chemistry (production of sulfuric acid, sulfites, thiosulfates, acids, etc.);
- in agriculture to destroy pests and fungi;
- in industry (lead batteries, dyes);
- for the manufacture of explosives, sparklers, matches, black powder;
- in the food industry as a preservative E220;
- in the textile industry for bleaching fabrics (silk, wool);
- in disinfectants, etc.
In other words, you can encounter sulfur anywhere, which means there is a risk of being poisoned by it or its compounds.
How can you get poisoned?
Sulfur in its pure form is not used everywhere; more often, its compounds play the “main roles”: hydrogen sulfide, sulfuric or sulfurous acid, carbon disulfide, sulfur oxide and dioxide (also known as sulfur dioxide, sulfur dioxide or sulfur dioxide) and many others.
You can be poisoned by sulfur compounds in different situations:
- when inhaling toxic gases resulting from the combustion of an element (the inhalation route is the most common);
- when inaccurately treating pests of gardens and vegetable gardens with insecticides containing sulfur (smoke bombs, etc.);
- in case of non-compliance with safety precautions in production where sulfur is used;
- in case of accidents, fires at work;
- during combustion of petroleum products, during which sulfur oxide is formed;
- when inhaling hydrogen sulfide (when living or staying for a long time near sewers, where as a result of the process of rotting protein, this gas is formed with the characteristic smell of rotten eggs);
- when intentionally ingesting liquid sulfur derivatives (suicide attempt), etc.
Getting the compound on your skin is no less dangerous. For example, sulfuric acid instantly causes severe burns, immediately “eating” the skin layers deep inside. Accidental exposure of gases or liquids to the eyes will result in irritation (mild) or cell death and vision loss (severe).
First aid and treatment of poisoning with sulfur compounds
Atropine acts as an antidote to sulfur; it is used, as a rule, for intoxication with vapors of the substance.
In case of poisoning with any sulfur compounds, first of all, it is necessary to immediately remove the victim to fresh air. To wash your eyes, mucous membranes, rinse your nose and throat, you can use a 2% soda solution (about half a teaspoon per 200 ml of water).
Carbon disulfide
- If the patient's condition is severe, before the ambulance arrives, a solution of glucose with ascorbic acid, vitamin B6 (5 ml, 5% solution), and glutamic acid (20 ml, 1% solution) can be administered intravenously.
- As described above, carbon disulfide is distinguished by its effect on the central nervous system, which requires specific treatment aimed at normalizing metabolic processes in the brain and suppressing increased nervous excitability through tranquilizers.
- In case of chronic poisoning, patients need complex treatment under strict medical supervision.
Sulphur dioxide
- To reduce eye irritation, drop a solution of Levomycetin (0.25%) and put sunglasses on the patient.
- To ease breathing and reduce inflammation, vasoconstrictors (for example, Farmazolin) should be instilled into the nose.
- The development of subsequent infections (against the background of an affected nasopharynx) is prevented by the use of an aerosol of antibiotics with sulfonamides in a novocaine solution.
- Prevents pulmonary edema by intravenous administration of calcium chloride with glucose (20 ml, 40% solution) with ascorbic acid (1 ml, 5% solution).
- If laryngeal spasm develops, atropine sulfate (1 ml, 0.1% solution) is injected into a vein.
Symptoms of poisoning
The clinical picture will vary depending on the type of sulfur compounds or their concentration:
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
The specific smell of this compound, reminiscent of rotten eggs, is deceptive: after a few breaths it is no longer noticeable, as a result of which you can inhale the gas to the point of death. At first a person feels:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- pain and severe burning in the eyes;
- lacrimation;
- vomiting, diarrhea;
- cough, pressing chest pain, shortness of breath;
- overexcitement;
- A distinctive symptom develops - blepharospasm.
In cases of severe sulfur poisoning, the symptoms are much more serious: convulsions begin, collapse, coma, toxic pulmonary edema and instant death (apoplexy) are possible.
Acute intoxication with hydrogen sulfide occurs when 0.01–0.2 mg/l enters the body; the lethal dose is negligible and amounts to only 1.2 mg/l.
Carbon disulfide (CS2)
Skin contact with this liquid, which has the smell of ether, leads to the appearance of irritation, redness and blisters with serous contents inside.
Carbon disulfide vapor poisoning causes mild, moderate and severe stages of acute poisoning:
- with a mild degree of poisoning, the patient seems to be drunk, inappropriate behavior and overexcitation are observed (with help, it disappears without a trace);
- moderate severity is characterized by the addition of psychotic outbursts, convulsions, runny nose, lacrimation, inability to open eyes due to severe pain (this stage also does not threaten serious consequences in the future);
- Severe poisoning is similar to the state of a person under chloroform anesthesia; further mental disturbances are possible.
Chronic intoxication:
- persistent headaches;
- sleep disorders;
- sweating, weakness, mood swings, irritability;
- VSD, polyneuritis.
As chronic carbon disulfide poisoning progresses, encephalopolyneuritis, encephalopathy, memory loss, lethargy, and depression develop. Arterial hypertension, sexual dysfunction, digestive disorders and liver function disorders are also observed. Possible development of Parkinson's disease.
The main harmful effects of carbon disulfide are on the nervous system. It is she who suffers from poisoning with this compound more than others.
The lethal dose of carbon disulfide when swallowed is 1 g; when its vapor is inhaled, it is more than 10 mg/l.
Sulfur dioxide (SO2)
Sulfur dioxide poisoning (sulfur dioxide, sulfur dioxide or sulfur dioxide) mainly affects the respiratory tract. Symptoms of sulfur dioxide poisoning look like this:
- respiratory tract irritation;
- sneezing and coughing (sometimes with bloody sputum);
- shortness of breath with wheezing;
- sometimes vomiting with nausea;
- irritation and itching of the mucous membranes of the eyes and respiratory tract;
- hyperemia and inflammation of the eyes;
- chest pain;
- nosebleeds;
- acute bronchitis;
- fog, fatigue;
- temperature.
Severe sulfur dioxide poisoning can result in suffocation, toxic pulmonary edema and death.
In domestic conditions, sulfur dioxide poisoning is possible when using smoke bombs containing this component. Failure to comply with safety precautions when working with them, in the worst case, can result in blindness (if the eyes are damaged by sulfur smoke), pulmonary edema and death.
Causes of bloating
Among the main causes of bloating in adults, it is worth noting both completely harmless ones, like basic food poisoning, and very serious ones. These include:
- Chronic pancreatitis. The disease is characterized by disruption of the pancreas and its loss of the ability to produce enzymes necessary for the proper functioning of the intestines, as a result of which flatulence begins every time after the next meal.
- Intestinal problems. A rather rare, but still occurring disease is irritable bowel syndrome, which begins to malfunction, loses its motor function and leads to a person feeling bloated, discomfort, and even slight but constant pain.
- Dysbacteriosis. A weakened immune system is unable to fight attacks from bacterial viruses, which can result in a disruption of the intestinal microflora, provoked by harmful microorganisms that decompose inside the intestines and release methane, hydrogen sulfide and ammonia, causing bloating.
- Negative reaction to lactose. Not every intestine absorbs milk lactose; in many patients being treated for bloating, this problem was discovered, caused by an insufficient amount of enzymes in the body necessary for the absorption of lactose.
- Lack of intestinal patency. The presence of parasites or a well-hidden tumor in the intestines can cause obstruction of gases that accumulate inside and cause many unpleasant symptoms, ranging from bloating to diarrhea.
If you observe any signs of bloating, do not panic; it is likely that your stomach is filled with gas for one of the following reasons. This may happen due to:
- Drinking carbonated water in excess quantities. If bloating occurs for this reason, there is no need to worry too much, it will go away on its own, since in a healthy body the elimination of gases is a normal physiological process.
- Too fast food. The rate of food consumption directly affects the formation of gases in the intestines and possible flatulence, which consequently causes discomfort. Together with poorly chewed pieces of food, a person swallows a large amount of air, which becomes the cause of a bloated abdomen.
- Fermentation in the intestines caused by certain foods. Potatoes, buns, brown bread and legumes contain a large amount of fiber that is easily digestible by the body, as well as carbohydrates and starch, which contributes to their rapid fermentation. It is fermentation that causes bloating.
- Food variety. Eating the same food every day is harmful, but you also shouldn’t mix completely incompatible foods with each other. So, it is best to eat fruits and berries several hours before a heavy lunch or dinner, otherwise diarrhea may develop, accompanied by bloating.
A swollen belly in adults is not often noticed; sometimes a person can pass in this state for several hours, complaining of incomprehensible symptoms.
How to help the victim
In case of intoxication with sulfur and any of its compounds, first aid should begin with calling an ambulance, especially if the signs of poisoning clearly indicate a severe form. After this you immediately need:
- evacuate the victim from the contaminated area;
- if possible, it is advisable to do oxygen inhalations;
- when the compound gets on the skin, thoroughly rinse the affected area with plain water or soda solution;
- in the eyes - rinse with water and drop Dicain 0.5%;
- for a person who has inhaled vapors, instill nasal drops with a vasodilating effect;
- if swallowed, clear the stomach by giving the poisoned person plenty of warm water to drink and inducing vomiting.
There is no need to do anything else, as further only professional actions will be required to eliminate the symptoms of poisoning and prevent the consequences as much as possible.
Therapy
If assistance for poisoning with sulfur or its compounds was provided on time and correctly, this will significantly facilitate the task of doctors and speed up the recovery of the victim.
Treatment of such poisonings is always complex, including a number of measures:
- cleansing the stomach through a tube (when the chemical gets inside);
- antidote Amyl nitrite inhalation (to hydrogen sulfide);
- antidote Atropine (to sulfur vapor);
- oxygen therapy;
- diuretics to force diuresis (accelerates the excretion of sulfur in the urine);
- for seizures - Diazepam intravenously;
- for irrepressible cough - Codeine orally;
- to improve blood supply to the brain and metabolism - Encephabol and vitamin B6;
- for hydrogen sulfide poisoning - intravenous calcium gluconate or calcium chloride in a volume of 10 ml;
- drugs to eliminate bronchial irritation;
- means for improving the activity of the peripheral and central nervous system;
- glucocorticoids;
- antibiotics.
Before starting treatment, a chest x-ray is sometimes taken as an additional diagnosis of poisoning. The image usually shows diffuse small infiltrates in the lungs or pulmonary hypertension.
Symptoms and treatment are always closely related, since poisoning with each compound requires individual procedures and the prescription of special antidotes and medications.
The poisoned person remains in the hospital until he is completely stabilized, then he is discharged home for outpatient treatment.
Indications for hospitalization in case of poisoning
Most household poisonings do not require hospital treatment, but in severe cases it is necessary, especially when there is a threat to the patient’s life. In particular, hospitalization is necessary in such cases of poisoning:
- a child under 6 years old (children of this age cannot always drink the right amount of liquid, which often ends in dehydration);
- poisoning by mushrooms, plants, acids, meadows, household chemicals;
- pregnant woman at any stage of gestation;
- severe poisoning (diarrhea more than 10 times a day, incessant vomiting, bloody stools, rapidly increasing weakness, high body temperature for 2 days or more).
Consequences
Most often, even mild poisoning with sulfur vapor leads to complications. And if the intoxication is severe, the consequences will be extremely serious:
- mental disorders (as a result of carbon disulfide poisoning);
- encephalopathy;
- persistent VSD;
- decreased visual acuity or loss of vision;
- Chronical bronchitis;
- Parkinson's disease (toxic parkinsonism);
- decreased performance, “occupational” diseases of the respiratory and nervous system.
The worst consequence of severe poisoning with sulfur compounds is death. But if the victim manages to be handed over to the doctors, the doctors will do everything to prevent this from happening. However, a complete recovery, unfortunately, is not always possible.
Have you ever had sulfur poisoning?
- No, it wasn't 45%, 136 votes
136 votes 45%
136 votes - 45% of all votes
- Yes, it was 33%, 101 votes
101 votes 33%
101 votes - 33% of all votes
- Currently there are symptoms of intoxication 22%, 67 votes
67 votes 22%
67 votes - 22% of all votes
Total votes: 304
09.10.2017
×
You or from your IP have already voted.
How to get rid of food poisoning
In most cases, cases of food poisoning resolve on their own. The goal of most traditional treatments is to prevent dehydration. Nausea and vomiting cause many people with food poisoning to lose a lot of fluid and experience additional health problems as a result of dehydration. Your doctor will likely recommend that you rest and increase your fluid intake through soups, broths, juices and water.
In more extreme cases, especially when signs of food poisoning include a fever or additional infections, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics. However, in the absence of these signs, it is necessary to give the body a chance to heal on its own.