All expectant mothers gain weight as their belly grows - this is a completely normal reaction of the body to the child’s growth and body changes. The weight you gain during pregnancy is a source of nutrition and all the necessary substances for the proper growth and development of your unborn child. This extra weight is stored as fat to prepare your body for breastfeeding after pregnancy.
However, many women gain more or less weight during pregnancy. Being underweight or overweight can cause some problems. And while women often encounter excess weight, underweight is less discussed. But today, in pursuit of slimness, women are ready to go on a diet even during pregnancy, just so as not to gain excess weight and spoil their figure.
Let's talk about how this can affect your health and your baby's development, and identify ways you can try to gain or lose weight.
What does being underweight mean during pregnancy?
How to determine how much can be added during the period of bearing a baby?
Body mass index, or BMI, is often used as a screening tool to determine weight groups. This indicator distinguishes underweight, normal or healthy weight, overweight and obesity. If you're in a weight class that means you're underweight, don't panic. This may not always be the cause of serious health problems. Lack of weight gain may be due to your pre-pregnancy weight or poor nutrition. It may also indicate that your body is not storing enough fat.
Some women find it difficult to gain weight during the early stages of pregnancy. They may even lose weight during the first trimester due to morning sickness with nausea and vomiting. This is not a dangerous sign, since the baby at this time consumes as many calories or nutrients as in late pregnancy.
Additionally, women with eating disorders such as anorexia or bulimia nervosa have a harder time gaining or maintaining a healthy weight range. In addition, lifestyle, activity, health status and other factors may influence. We wrote about why a woman’s taste preferences change during pregnancy here.
A little anatomy
Normally, the uterus looks like the picture below. She has appendages (tubes, ovaries) extending into the organ cavity, body and neck.
A girl's reproductive organs are formed during the period from 6 to 32 weeks of intrauterine development. According to experts, abnormalities in the development of the uterus most often occur at this time, under the influence of various unfavorable factors that disrupt embryogenesis (organ formation).
There are many types of developmental anomalies. The organ may acquire the shape of a saddle (saddle-shaped), have two horns, one of which is not developed, or two uteruses are formed.
Duplication of the uterus
At approximately 6 weeks of embryo development, the formation of two canals occurs, which form the prototype of the reproductive system. These channels touch the walls, and at week 8 the partitions between them resolve. The fusion and formation of the reproductive organs occurs.
By approximately 24 weeks of fetal development, the reproductive system acquires its anatomical structure. That is, it is already possible to distinguish between the tubes, the body of the uterus and the cervix. If during this period embryogenesis was affected by unfavorable factors (disease, genetic failure, alcohol, etc.), then the process of fusion of the paramesonephric canals is disrupted. As a result, a number of uterine anomalies are formed.
The organ takes on a bicornuate shape with various variations of changes.
- An anomaly in which two horns are formed, connected by a common uterine cavity, there is one cervix and one vagina. In this case, the channel merging began, but did not end. A common cavity has formed, which can be divided by a partition, partially or completely.
- Pathology in which two separate (separate) organs are formed. Each uterus has its own cervix, but one common vagina.
- The formation of two separate horns occurs, while doubling of both the cervix and vagina is observed.
- The formation of two horns is observed, while one of the horns is underdeveloped.
All of these anomalies are associated with one term - bicornuate uterus. It is noted that the ovaries and fallopian tubes, with uniform development of the horns, are complete, and ovulatory functions are not impaired. Menstrual function, the ability to conceive and bear children are fully preserved.
How much weight should you gain during pregnancy if you are underweight?
In this case, there is no universal solution.
You should consider your BMI, pre-pregnancy weight, daily activities, food intake, etc. As a general guideline, there are weight gain options for pregnant women depending on their starting weight.
- Underweight (BMI <18.5) we gain from 13 to 18 kg;
- Normal weight (BMI from 18.5 to 24.9) – from 11 to 16 kg;
- Overweight (BMI from 25 to 29.9) – from 7 to 11 kg;
- Obesity (BMI 30 or more) – from 5 to 9 kg.
If you are expecting twins, experts recommend the following weight gain indicators:
- Normal weight (BMI from 18.5 to 24.9) – from 17 to 25 kg;
- Overweight (BMI from 25 to 29.9) – from 14 to 23 kg;
- Obese (BMI 30 or more) – about 11 to 19 kg.
Your doctor may recommend a different weight gain regimen that suits your body. In this case, follow the recommendations for increasing body weight that the specialist talks about.
Recommendations suggest that women who are in their second and third trimesters and have a low BMI (<18.5) should try to gain 1 to 1.3 kg each week until they are within the normal weight range.
Discuss with your doctor the specific dynamics of weight gain and diet and exercise patterns, not only during the first visits, but throughout your pregnancy. You can develop a diet plan to meet your nutritional needs for continued weight gain throughout the trimesters.
Complications of pregnancy
Pregnancy does not always go smoothly. Complications include:
- Nausea and excessive vomiting during pregnancy;
- Frozen pregnancy;
- Threat of miscarriage;
- Varicose veins of the lower extremities;
- Varicose veins of the vagina;
- Late toxicoses: nephropathy of pregnancy, preeclampsia and eclampsia;
- Fetal hypoxia;
- Lower back pain;
- Anemia (anemia) in the mother;
- Immunological conflicts and Rhesus conflict between mother and fetus;
- Fetoplacental insufficiency;
- Feto-fetal transfusion syndrome;
- Preeclampsia
A separate type of complicated pregnancy is ectopic pregnancy. In this case, fetal development is impossible, and sooner or later it ends in miscarriage.
In most cases, with timely detection, modern medicine is able to prevent and reduce undesirable consequences to a minimum.
Smoking and pregnancy
According to some data, maternal smoking increases the risk of newborn death by 20-35%[9]. According to other data, smoking increases the risk of death of a child in the first four weeks of his life by 40%[10]. Women who smoke are more likely than non-smokers to experience pathologies during pregnancy and childbirth[11].
Passive smoking also harms the pregnant woman and the fetus. Thus, non-smoking wives of smoking husbands are more likely than others to experience toxicosis in early and late pregnancy[12].
The effect of smoking at different stages of pregnancy[13]
| Term | Influence |
| 1st trimester | Dangerous, it occurs against the background of the formation of all the main organs of the human body. May lead to spontaneous miscarriage. There is a risk of fetal death. |
| 2nd trimester | Periodically aggravates toxicosis. The child develops worse and gains less weight. There is a risk of premature birth. |
| 3rd trimester | Dangerously, the likelihood of developing preeclampsia increases compared to the average. Negative infant mortality rates. |
Does being underweight pose risks for you or your baby?
It is important to gain weight steadily and smoothly during pregnancy, especially in the second and third trimesters.
Being underweight can have a negative impact on your unborn baby. Some studies have shown that if a woman is underweight during pregnancy, complications such as low birth weight (less than 2.5 kg) or premature birth (before 37 weeks) may occur. Children born to underweight mothers (BMI <18.5) may be small for their gestational age (gestational age), that is, such children are smaller in height and weight, and weaker than healthy babies. Can being underweight cause a miscarriage? Although being underweight during pregnancy has been associated with an increased risk of miscarriage, the results of several studies have been equivocal or equivocal. However, you should not take risks and adhere to a strict diet during pregnancy.
Diagnosis
Despite the absence of symptoms, it is not difficult to diagnose placental insufficiency. At each visit to the doctor, the gynecologist measures the volume and girth of the abdomen and listens to the heartbeat.
If external data does not change, and the fetal heart rate changes up or down, the child may not have enough strength for full growth and development. He experiences hypoxia.
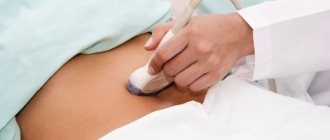
It is possible to confirm or refute the diagnosis using ultrasound and Dopplerography.
Diagnostic measures of the HDN include:
- examination by a gynecologist;
- Dopplerography (allows you to evaluate the speed of blood flow and identify areas with possible disturbances);
- Ultrasound of the fetus and child's place to detect changes (delayed development, premature aging, membrane width, presence of infection or genetic abnormalities);
- laboratory testing (coagulogram, hormone and D-dimer analysis);
- Fetal CTG.
Ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound are performed three times during the gestation period (in the case of a normal pregnancy) - at the end of the first trimester, and in the middle of the II and III trimester.
Diagnosis of disturbances in the MPP of blood flow is necessary to identify the extent of the pathological process. There are the following degrees of GDN:
- Grade 1 is diagnosed with primary changes in one of the vascular systems. It can be corrected with medications and is not an indication for early delivery. It is represented by two subspecies: “a” and “b”. At grade 1a, initial disorders of hemodynamic changes develop without signs of hypoxia. 1b is characterized by a change in the symbiosis “fetus and placenta”. The phenomenon is common and is diagnosed in 80% of patients. Grade 1 can be treated and pregnancy has every chance of further prolongation;
- Grade 2 is accompanied by impaired blood flow in the fetal aorta, uterine and umbilical arteries. The level of essential substances is significantly reduced. The fetus experiences acute hypoxia. The degree of the pathological process is unstable, because it can quickly move to the extreme - third stage. If there is no therapeutic effect during treatment, early delivery is indicated.
- Grade 3 is a severe and dangerous form of placental insufficiency. Treatment is not carried out, but an emergency caesarean section is performed to save the baby’s life, however, practice shows an unfavorable prognosis for childbirth. Critical changes affect the fetal brain and heart muscle.
Treatment of the pathology is carried out conservatively, using oral and parenteral methods. Preference is given to vitamin therapy and anticoagulants.
Bed rest is recommended for pregnant women. Additional therapy is procedures for oxygen saturation (oxygen cocktails, pressure chambers).
The main goal when blood flow in the placenta is disrupted is to prolong pregnancy until 37 weeks. Self-medication is strictly unacceptable.
To avoid negative consequences, pregnant women should not neglect medical prescriptions and visit an ultrasound specialist on time.
In the case of primary symptoms, it is necessary to begin treatment as quickly as possible, otherwise disturbances in the uteroplacental-fetal blood flow will progress to a more severe stage.
There should also be no less effort on the part of the pregnant woman. You should review your diet, monitor your weight gain, and stop drinking alcohol and nicotine.
Eat more vegetables and fruits, walk in the fresh air.
How to make sure you are getting adequate nutrition?
You can get adequate nutrition by following your doctor or dietitian's recommendations for prenatal foods and vitamins.
A woman's body undergoes physical and hormonal changes throughout pregnancy. Therefore, it is important to meet the nutritional needs of your own body and that of your unborn child by eating a healthy and balanced diet. Read about your estimated daily calorie needs in the first, second, and third trimesters based on your BMI. For underweight women, they will be slightly higher than standard in order to gain normal body weight. In general, the first trimester requires practically no extra calories: only the physiological norm of calories. Then you need to add an additional 400 calories per day in the second trimester and approximately 400-600 calories per day during the third trimester.
Recommended calorie limits are very approximate. Every woman has different nutritional needs. Therefore, only your OB/GYN will advise you on how much weight you should gain during pregnancy.
How to get pregnant after BCB
If everything is more or less clear with the nature and etiology of biochemical conception, then further actions raise a lot of questions, or, more precisely, the period that must be waited before planning a new pregnancy. Doctors say that there is no need to wait, since a normal pregnancy can occur in the next cycle. Moreover, the probability that the patient will successfully become pregnant, carry her to term and give birth to a healthy baby is quite high.
In fact, you should not treat biochemical pregnancy as a death sentence. If the first attempt at successful pregnancy fails, it is not at all necessary that history will repeat itself in the next cycle. Examination and therapy may be necessary if the patient monthly experiences a phenomenon such as biochemical conception. By the way, the patient’s partner also needs to be examined so that the doctor can most accurately determine the true cause of miscarriage. It is treated with hormonal drugs that help the uterus and the body as a whole prepare safely for pregnancy.
A healthy diet with enough protein and limiting sugar reduces the risk of BCB. When planning a new pregnancy after a biochemical pregnancy, you need to monitor your condition, diet, daily routine and menstrual cycle, regularly see a gynecologist and treat infectious pathologies in a timely manner.
Nutrient intake during pregnancy
Your diet should contain adequate amounts of both macronutrients (essential nutrients) and micronutrients.
The expectant mother needs proteins, carbohydrates, essential and healthy fats such as omega-3 (DHA), vitamins and minerals (folate, iron, vitamin D, calcium, etc.) that the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends to all pregnant women Consume 30 to 60 mg of elemental iron and 0.4 mg of folic acid per day. If a pregnant woman has calcium deficiency, a daily calcium supplement of 1.5-2 g is recommended.
You can get nutrients from dietary sources such as fruits, vegetables, meat and dairy products.
Every woman today may need additional supplements, taking into account the quality of food and the provision of all necessary substances before conception. The doctor will recommend the necessary vitamin and mineral complexes.
Pregnancy against the background of extragenital pathology
In the structure of extragenital pathology (extragenital diseases) in pregnant women, the first place is occupied by pathology (diseases) of the cardiovascular system (80%), including congenital and acquired heart defects (including rheumatic heart defects), conditions after cardiac surgery, arterial hypertension, hypertension.
| This section of the article has not been written. According to the plan of one or more Wikipedia contributors, a special section should be located in this place. You can help by writing this section. This mark was set on September 30, 2020 . |
How to prevent weight loss during pregnancy?
Your ideal goal is to have a healthy BMI and normal weight before planning a pregnancy.
In other words, you need to gain weight at least to the lower limit of normal weight. By the way, it is a known fact that against the background of weight deficiency, infertility is possible due to inhibition of hormone synthesis and ovarian function. However, if you become a mom while underweight and extremely thin, your goal should be to gain a healthy average weight throughout your pregnancy. Women who are underweight usually tend to eat a low-calorie, low-protein diet throughout their pregnancy. Therefore, doctors urge you to follow the following recommendations.
Don't skip meals. Breakfast is the most important meal of the day. You can add proteins to your dishes, use healthy fats (vegetable oils and butter). Consume healthy snacks such as fresh fruit smoothies and dried fruits between meals. Include foods high in good fats such as nuts and avocados. Add foods such as honey, cheese and yogurt. Eat fresh fruit or drink sugar-free fresh juices from oranges, carrots and apricots to get enough vitamins.
Avoid junk food. Remember to take your special, prenatal vitamins and supplements as recommended by your doctor.
You can keep a weekly chart to track your weight gain during pregnancy. This will help you know when you are exceeding the normal allowance limits.
HCG during biochemical pregnancy
During any pregnancy, the level of the hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) begins to increase even when there are no other signs of pregnancy, and even an ultrasound examination is not able to “see” it. Biochemical in this regard is no exception: the fact of its occurrence can be indicated by hCG exceeding the mark of 5 units. If the blood test for hCG shows a result of 5-6 mU/ml or higher, but neither an ultrasound, nor an examination by a gynecologist, nor a pregnancy test confirmed that conception has taken place, and a repeated blood test for hCG shows a decrease in the concentration of this hormone, then doctors mean biochemical pregnancy in this cycle.
If, against the background of a dynamic increase in hCG, the gynecologist or uzologist ascertains the presence of a fertilized egg in the uterus, then we will be talking about a normal physiological pregnancy, even if it is interrupted.
Biochemical pregnancy has no continuation, since it always ends in an arbitrary miscarriage. Otherwise, if the delay continues further, a repeat hCG analysis also turns out to be positive, and other facts confirming pregnancy are added to it, which no longer speaks of a biochemical, but of a normal pregnancy.
Tips to gain weight during pregnancy
Weight gain during pregnancy can depend on several factors, including daily diet, pre-pregnancy weight, metabolism, physical activity level, or any existing medical condition.
In addition to following the measures mentioned in the previous section, the tips below may come in handy when you are trying to gain those extra healthy pounds: Make your healthy food enjoyable by including some condiments, sauces, etc. For example, instead of eating boiled vegetables or puree, you can add spinach or broccoli soup to your diet.
Eating small, high-calorie meals can help you gain weight. Focus on nutrition, not quantity. For example, a boiled egg, a piece of pasteurized cheese or yogurt can give you those extra calories and also help with pregnancy-related problems such as nausea and heartburn.
Bring healthy snacks with you. Whether you're traveling for work or pleasure, be sure to pack healthy snacks like a banana, orange or apple, as well as dried fruits or nuts to boost your nutrient intake. If you find it difficult to eat food, you can drink these calories. You can make smoothies with yogurt or milk and add protein powder (as recommended by your doctor). You can use vegetables as well as fruits to make these smoothies.
Treat yourself to your favorite (even unhealthy) food, but only occasionally. However, do not forget about physical activity and try to move more so that your weight does not go overboard.
A well-balanced diet is all you need. Weight gain doesn't happen overnight, and you need to eat right every day. As you reach your target weight, you should adjust your diet again to maintain your target body weight.
Planning a pregnancy
Main article: Family planning
Additional information: Symptothermal method and Contraception
Family planning
(English: family planning) is one of the main ways to solve the global demographic problem of stabilizing the Earth's population[2]. The most commonly used methods allow a couple to engage in satisfying sexual intercourse on a regular basis while reliably reducing the woman's chance of an unwanted pregnancy, at least until the couple decides that one should occur. Because of this, family planning includes methods that either prevent fertilization or act after fertilization to prevent implantation of the embryo.
Currently, there is an effective possibility of planning pregnancy. One of the most effective natural methods of family planning is the symptothermal method, but it is inferior to hormonal contraception in effectiveness and does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases like a condom.
When planning a pregnancy, it is important to determine the day of ovulation. After all, the point is that the egg (unfertilized) dies a day after ovulation, so the fertile period in the menstrual cycle begins 2-3 days before ovulation (sperm are active up to 3 days) and ends one or two days after ovulation. And the most favorable days for conception are the day before ovulation and the day of ovulation.
So, a surge in the level of luteinizing hormone means the beginning of the most favorable time for conception.
Literature
- Pregnancy // Encyclopedic Dictionary of Brockhaus and Efron: in 86 volumes (82 volumes and 4 additional). - St. Petersburg, 1890-1907.
- Joanna Stone, Keith Eddleman, Mary Murray.
Pregnancy for dummies = Pregnancy For Dummies. - M.: "Dialectics", 2010. - P. 272. - ISBN 978-5-8459-1690-7. - Kovalenko N.P.Professor, Doctor of Psychological Sciences.
“On the Good Path to a Successful Childbirth” = “On the Good Path to a Successful Childbirth.” — M. Archived copy from February 13, 2010 on the Wayback Machine - Kovalenko N.P.Professor, Doctor of Psychological Sciences.
"Psychoprophylaxis and psychocorrection during pregnancy and childbirth." — M. Archived copy from February 13, 2010 on the Wayback Machine - Kovalenko N.P.Professor, Doctor of Psychological Sciences.
"Perinatal psychology". — M. Archived copy from February 13, 2010 on the Wayback Machine - Kovalenko N.P.Professor, Doctor of Psychological Sciences.
“Scientific collection on perinatal psychology of the Russian Association of Perinatal Psychology and Medicine from 2001-2008” (annually) edited by Kovalenko N.P. - M. Archived copy dated February 13, 2010 on the Wayback Machine - Katherine Crum, Teri Stuffer Drenth.
Physical education during pregnancy for dummies = Fit Pregnancy For Dummies. - M.: “Dialectics”, 2007. - P. 362. - ISBN 0-7645-5829-3. - G. M. Savelyeva, V. I. Kulakov.
Obstetrics. - M.: Medicine, 2000. - P. 816. - ISBN 5-225-04549-9. - V.E.
Radzinsky. Early pregnancy. - M.: Media Bureau Status Present, 2009. - P. 479. - ISBN 978-5-91785-001-6.