Carrying out ultrasound with Dopplerometry during pregnancy allows you to obtain more information about the state of health of the fetus and the maternal body; the characteristics of blood flow in the vessels of the fetus, uterus and placenta are assessed. The method is based on the use of standard ultrasonographic scanning together with measurement of the speed and nature of blood flow in the vessels of interest to the doctor.
Fetal Doppler has several modes that are used in certain situations. The introduction of ultrasound with color Doppler mapping (CDC) into gynecological and obstetric practice has made it possible to more reliably examine the fetal heart, diagnose premature placental abruption and other pathological conditions that occur with changes in the vascular bed.
What is the essence of Doppler ultrasound during pregnancy?
Doppler is a type of ultrasound examination based on the Doppler effect.
In ultrasound, this effect is widely used to study moving structures - in particular, blood flow in vessels. Using ultrasound machines equipped with this mode and high-frequency sensors, the following important hemodynamic parameters can be studied:
- The nature of the blood supply to an organ or tissue - the characteristics of the course of blood vessels and their branching.
- Direction of blood flow: the vessel in which blood moves towards the transducer is colored red (corresponds to arteries of different sizes), but if from the sensor, it is colored blue (venules and veins).
- The completeness of the lumen of the vessel. Atherosclerotic plaques, fixed and floating thrombi, and aneurysms are detected.
- The relationships of blood vessels with each other and with respect to internal organs and structures.
- Using the programs installed on the device, for the completeness of the study, it is necessary to determine part or all of the given indicators: pulsation index (PI), resistance index (RI), maximum and linear blood flow velocity. It is these Doppler indicators that are used to assess uterine blood flow and the state of fetal hemodynamics.
- It is possible to graphically display the velocities and peaks of blood movement in the vessels in the form of a blood flow curve, which is also called Dopplerography. Each vessel has its own curve characterizing normal values.
How is Doppler testing performed?
Doppler measurements are performed in the ultrasound room. In order to undergo this test, there is no need for additional preparation of the body; you only need to come for diagnostics at the appointed time.
In diagnosis, a transabdominal sensor is used, which transmits ultrasonic waves to the device monitor. The patient lies down on the couch and exposes her stomach.
The doctor applies a special gel that improves wave conductivity. A pregnant woman does not feel any pain during this research procedure.
Doppler testing time is no more than 30 minutes. If the pregnant woman does not have any pathologies, then the average procedure time is 10 - 15 minutes.
The Doppler conclusion includes the following indicators:
- Normal blood speed in the bloodstream;
- Disturbances in the placenta - GDN IA;
- Pulsation indicator;
- Resistance index.
Doppler study
Examined structures on Doppler ultrasound
In obstetrics, several main vessels are used for measurement and evaluation:
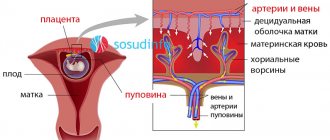
- Uterine arteries. Doppler ultrasound of the uterine vessels is a very important indicator characterizing the primary link of the mother-fetus system.
- Arteries and vein of the umbilical cord. The blood flow in these vessels shows the quality of work of the secondary link of the “mother-fetus” system, which supplies nutrients and oxygen from the pregnant woman to the unborn child.
- The middle cerebral artery is a large vessel of the brain that supplies a large number of structures and segments. It is very important to assess the speed of blood flow in this vessel in the presence of a conflict in the Rh system or blood groups, fetal anemia, or suspected developmental defects.
- The fetal aorta is a major vessel emerging from the mouth of the left ventricle and giving rise to a large number of arteries that supply blood to the internal organs of the child. At the same time, blood flows in the chambers of the heart are measured, which makes it possible to more reliably diagnose the presence of congenital heart disease in the fetus.
- At short stages of pregnancy - within 10-14 weeks, you can measure the indicators of the so-called venous duct. Blood flow in this structure is one of the indirect markers of fetal genetic abnormalities.
So, having measured the indices and blood flow velocities in these vessels, the doctor must correlate their indicators with the data of special tables and diagrams developed by ultrasound diagnostic specialists. Doppler measurements are extremely variable indicators, since they depend on the following factors:
- gestational age is one of the most important criteria, since the difference in fetal blood flow is assessed at intervals of up to one week;
- number of fetuses and placentas, respectively;
- maternal blood pressure and hemoglobin levels;
- the future mother in labor has a bad habit such as smoking;
- use of any medications;
- uterine tone.
The umbilical cord has 3 vessels, what is it, what is the threat of 2 vessels?
You are here: Home > Articles > Pregnancy and childbirth > Pregnancy
June 5, 2020 | views: 24,988
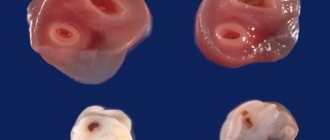
How many vessels should the umbilical cord have - a “conductor” connecting the fetus with the mother during pregnancy, a supplier of nutrients and oxygen. Dopplerometry of the umbilical cord vessels is among the studies required for women who are preparing for motherhood. The procedure is carried out at 21 weeks, with its help the number of arteries is determined. The study allows you to timely identify abnormalities in the development of the embryo and take the necessary measures.
If, in the results of Dopplerometry, the expectant mother discovers that the umbilical cord has 3 vessels - what does this mean? If 2 vessels are diagnosed in the umbilical cord, what threat does this pose to the embryo?
The structure of the umbilical cord is normal
To understand why the umbilical cord has 3 vessels and what this means, you need to understand its structure. This is the name given to a kind of “rope” that ensures the connection between the embryo and the mother’s body and the interaction of the circulatory systems. The formation of the connecting element is completely completed by approximately 12 weeks. The length of the formation is 40-70 cm, “used” before the birth of the child. Normally, it is adjacent to the middle part of the placenta; there are exceptions (for example, membrane attachment).
How many vessels should there be in the umbilical cord? The norm is 2 arteries and one vein – 3 vessels. The vein serves as a conductor through which oxygenated blood penetrates the baby’s circulatory system from the woman’s body. Nutrients also leak into the vein through the vein. Arteries are used to remove waste products. 3 vessels in the umbilical cord during pregnancy indicate no cause for concern.
The structure of the umbilical cord - pathology
The norm that the umbilical cord must meet is 3 vessels, what this means can be read above. However, sometimes there is a deviation from this rule - two vessels in the umbilical cord. Expectant mothers are forced to face the medical verdict “EAP”, which stands for “single artery” of the umbilical cord, in about 0.5% of cases. The risk increases when it comes to multiple pregnancies, reaching 5%. The threat increases if a woman suffers from diabetes.
2 vessels in the umbilical cord - what does this mean, if there is a reason for concern? One of the arteries may be absent immediately, or its functionality may be impaired while waiting for the baby. EAP does not belong to the category of diagnoses that are fatal to the fetus, but requires additional research.
2 vessels in the umbilical cord - danger
So, the umbilical cord has 2 vessels - what does this mean for the baby? In approximately 90% of cases, EAP pathology is an isolated abnormality and does not turn into a threat to the fetus and mother. Despite the increasing load placed on the vessel, its functioning is not impaired. A small baby is born in about 13% of cases.
The umbilical cord vessels (2 or 3) are not of significant importance at the stage of childbirth. The main thing is that the specialist and junior medical staff attending the birth are aware of the presence of pathology. Labor management tactics, selected specifically for such a case, guarantee that there is no danger for the woman in labor and the fetus.
2 vessels in the umbilical cord - what are the dangers of deviation from the recognized norm during the birth process? If it is carried out incorrectly, hypoxia of the embryo is possible (lack of oxygen, complete interruption of its supply). To avoid danger, the doctor may choose a caesarean section. It is also necessary to cut the umbilical cord as carefully as possible - there is a risk of disrupting blood flow.
The umbilical cord has 2 vessels - what does this mean according to doctors? In such situations, obstetricians-gynecologists necessarily insist on additional examination, which is prescribed to the pregnant woman.
2 vessels in the umbilical cord - examination
It’s great if there are 3 vessels in the umbilical cord. However, timely diagnosis of deviations from this norm allows one to avoid risk even with one artery. The gynecologist must prescribe an additional examination to the woman to make sure that there are no other genetic pathologies that develop against the background of the disorder.
The number of vessels in the umbilical cord, normality or pathology - these questions can be clarified already by the 20th week, when the pregnant woman can undergo Dopplerometry. Most often, the umbilical cord has 3 vessels at 20 weeks. If, as a result of the study, it is determined that the number of arteries is not normal, Doppler testing is indicated for the expectant mother until birth. The procedure will provide control of blood flow in the vessels and will allow recording deviations.
Knowing how many vessels there should be in the umbilical cord, when diagnosing a disorder, it is worth consulting with a geneticist. An examination carried out by this specialist will help to reject the assumption of chromosomal abnormalities. A pregnant woman is advised to test blood obtained from the umbilical cord (cardocentesis). An ultrasound of the embryo's heart is required to exclude heart pathology - up to 22-24 weeks. Prevention tools - ultrasound of organs (each), cardiotocography (CTG).
2 vessels in the umbilical cord - is it necessary to terminate the pregnancy?
How many vessels are in the umbilical cord is a question, the answer to which is absolutely unimportant for the future life of the child. The diagnosis of EAP only indicates the need for additional examinations. A threat arises only when other chromosomal abnormalities that can harm the fetus are attached to a single artery.
5 comments on this post
- Nnn
May 20, 2020 at 6:29My youngest son had two vessels instead of three... She carried it normally, although she often went for ultrasounds to monitor the baby’s development. Everything went well, she also gave birth without complications. The weight was 3.900. He grew and developed well... But! When he began to grow up, it was as if he had developmental delays. He only spoke when he was 4 years old. Now he is 7. He has bad memory. They tried to go to different clubs, he can’t do it, he can’t remember anything... He can’t even do simple poems, addition and subtraction don’t work either... He’s absent-minded, he always has to be reminded of everything, he even forgets his briefcase, he also constantly stumbles and falls... Not I know if this is somehow connected with his intrauterine development, but he’s the only one I have….
- Oksana
Mar 21, 2020 at 18:47I was observed by a doctor throughout my pregnancy and gave birth on my own, quickly and without complications. Weight and height are good. The child is very active, has a good memory, at the age of 6 he reads, writes, and counts; his son’s development is simply excellent. She is ahead of her peers, which I am very happy about, because I read that children with two vessels, on the contrary, lag behind... but there is one thing... vision fails -5, -7 and a whole bunch of diseases associated with the eyes. We get treatment and go for procedures, but in general everything is fine with health, I rarely get sick.
- Madina
Oct 29, 2020 at 18:14My daughter also had 2 vessels, she gave birth on her own, the birth went well, her height was normal, but her nails were too short, and today she is three years old and her nails still don’t grow, but only along with her fingers, we don’t cut them, on her toes nails are not beautiful, deformed((((
- Anna
Jun 25, 2020 at 3:57My daughter had two vessels in her umbilical cord. She is already 8 years old, an excellent student, good memory, 100% vision, generally excellent health, tall, does not lag behind in anything, but on the contrary, at school she took part in all the clubs you can, and she entered art school. The doctors told me that 2 vessels do not affect what kind of child will be born, this is a variant of the norm!
- Elena
Oct 25, 2020 at 8:16The number of vessels only affects the nutrition of the fetus. Vision, memory, and mental abilities do not depend on the number of vessels and arteries. I have a 5-year-old son, a completely healthy and active child, although there were 2 vessels. And this happens much more often than 0.5%, I only have 2 friends and everything is fine.
Leave your comment: Cancel
Indications for the procedure
When performing an ultrasound scan in the Color Doppler mode, the diagnostician must know what goals the attending physician pursued when referring the woman for such an ultrasound, as well as be aware of her previous results and the presence of aggravating pathology.
- Common pathologies and conditions during pregnancy, in which ECHO scanning is performed only with Doplerometry.
- A certain age of the expectant mother (less than 19 or over 35 years old).
- Little or polyhydramnios.
- The woman has a chronic somatic pathology: diabetes mellitus, autoimmune thyroiditis, systemic diseases such as lupus erythematosus or vasculitis, hypertension.
- Multiple pregnancy, especially with signs of fetofetal transfusion.
- Conflict between the fetus and mother regarding the Rh factor or blood type.
- Umbilical cord entanglement.
- Suspicion of a congenital heart defect or an anomaly in the development of one or another organ in the fetus.
- The woman has a history of miscarriage, intrauterine fetal death, etc.
- Inconsistency between the fetometric data of the fetus and its gestational age.
- Doubtful or unsatisfactory changes on fetal CTG.
Interpretation of Doppler measurements
The Doppler device records information about the speed of blood in the blood flow system. Each artery has its own standard indicators. Blood flow is assessed throughout the entire cardiac cycle - from the systole of the heart muscle to its relaxation during diastole.
A Dopplerogram contains all indicators of the functionality of the cardiac organ in all phases of its cycle.
MSS (maximum systolic velocity) occurs during the period of myocardial contraction, and the minimum, or terminal velocity, occurs during diastole (CDS). These indicators carry information in the Dopplerogram.
Dopplerogram indicators:
- SDO (systole-diastolic ratio) is an indicator of the relationship between the speed of blood flow during the diastolic period and the maximum speed during systole. This coefficient is calculated using the MCC/KDS division method;
- The pulsation index is calculated using the formula - (MSS - KDS / SS). The final diastolic velocity is subtracted from the maximum speed and this indicator is divided by the average blood flow speed;
- The resistance index is calculated using the formula - (MCS - KDS / MSS).
The results of the study may be higher than the normative indicators, then we can talk about the resistance of the placental-fetal vessels, and the indicators may also be lower.
This means that in any deviation from the norm, pathology develops during pregnancy.
Preparation for the procedure and methodology
Ultrasound scanning with Doppler does not require any special preparation from the woman. It is only recommended to arrive on an empty stomach, and before that, do not eat gas-forming foods for a couple of days. In the short term, the doctor may ask you to fill the bladder; the second and third ultrasound screening does not require such a procedure, since the amniotic fluid sufficiently displaces the bladder, “exposing” the uterus.
The study is carried out relatively quickly and completely painlessly:
- After the pregnant woman lies down comfortably on the couch, the doctor applies a transparent gel that removes the air gap between the skin and the sensor, and then begins the procedure.
- The examination is performed in several projections with the sensor localized in the suprapubic region. The doctor selects the best cut and takes all the necessary measurements.
- The obtained indicators are entered into the ultrasound examination protocol.
At what time period is such research considered informative?
This study during pregnancy is carried out after the complete formation of the fetal placenta. The first Doppler ultrasound is done at 16 to 18 weeks. At this time, there is a low level of vascular resistance. Experts also recommend combining ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound at 20-22 weeks of pregnancy. Also, Doppler testing is considered mandatory at 30-34 weeks. But all studies can be adjusted by the doctor who is observing you, depending on the course of pregnancy and fetal development.
Twisting of umbilical cord vessels around the fetal neck
Around the end of the first trimester, the umbilical cord is already fully formed and you can undergo an ultrasound, which will help identify possible pathologies. It is difficult to call the umbilical cord entwined around the baby’s neck a pathology, but this problem occurs in approximately twenty percent of cases, and let’s immediately say that it does not always require an emergency caesarean section.
Doctors say that the main reason that the umbilical cord is wrapped around the neck is that the umbilical cord is too long (more than 70 centimeters), as a rule, the length of the umbilical cord is already genetically predetermined. The second most common reason is fetal hypoxia, that is, the baby does not have enough oxygen and he begins to actively move to take a more comfortable position and, without knowing it, gets caught in the loops. And of course, high water, with it the umbilical cord floats freely and twists itself into loops.
But remember that the fetus can not only create loops, but also unravel them on its own.
Therefore, do not worry in advance if the second planned ultrasound reveals that the umbilical cord is entangled; perhaps the baby will soon get out of it on his own. And most importantly, only five percent of the umbilical cord entanglement is dangerous; all the rest ends favorably and does not affect the birth in any way.
How many vessels are in the umbilical cord
So, as we said above, normally the umbilical cord has three vessels: 2 arteries and one vein. This is necessary for the proper supply of oxygen and all necessary nutrients to the developing fetus. Two arterial vessels are necessary to cleanse the blood of carbon dioxide and harmful substances; cleansed at the placenta, they are sent back to the baby through a vein. Thus, constant circulation and work of these three vessels of the umbilical cord is necessary for the proper development of your baby.
Diagnosis of the umbilical cord condition
The most reliable information about the condition of the umbilical cord and its vessels can be obtained by ultrasound examination with color Doppler mapping. A transverse “section” of the umbilical cord shows the presence of a larger vessel – a vein, and a smaller diameter – an artery.
The number of vessels is assessed from the longitudinal image. Data on the number of vessels can be obtained by the end of the first trimester, at about 12 weeks, when the woman is sent for the first screening test.
The accuracy of diagnosing the number of umbilical cord vessels can be influenced by various factors: the impossibility of good visualization of the organ too early or on the eve of birth, a small amount of amniotic fluid, more than one fetus in the uterus, excess weight in a pregnant woman. The qualifications of the doctor conducting the study also play a significant role.
In general, the condition of the umbilical cord and its possible pathologies are quite difficult to detect during pregnancy. As a rule, ultrasound diagnostics are performed, which makes it possible to identify the entanglement of the umbilical cord around the neck, limbs and torso of the fetus, as well as its presentation.
With the help of phonocardiography and auscultation, not only heart defects can be detected, but also the murmur of the umbilical cord vessels, which appears in connection with the entanglement of the child’s torso or neck. Doctors can also use the color mapping method, in which all umbilical arteries, veins and Doppler measurements are clearly visible, allowing one to assess, among other things, the state of the uteroplacental blood flow.
Vaginal examination reveals prolapse of the umbilical cord loops. After the birth of the placenta, the placenta and umbilical cord are examined and, if necessary, the material is sent for histological examination.
Formation and structure of the umbilical cord
The umbilical cord is a cord that connects the fetal surface of the placenta to the abdominal wall of the fetus.
Its main components are blood vessels. On the outside, the umbilical cord is covered with a single layer of epithelial cells, and the vessels are surrounded by a jelly-like substance (Wharton's jelly), which plays a protective role, enveloping them on all sides. By the end of pregnancy, the thickness of the umbilical cord reaches one and a half to two centimeters, the length is 50-70 cm, which allows the fetus to move freely in the uterine cavity even before birth, and the expectant mother feels peculiar tremors and movements. An excessively long or short umbilical cord is a sign of pathology.
As mentioned above, the umbilical cord must have two arteries and one vein. It is generally accepted that venous blood with carbon dioxide moves through the veins, and arterial blood rich in oxygen and nutritional components moves through the arteries. With the umbilical cord, the situation is somewhat different: the vein carries oxygenated blood to the tissues of the fetus, and the arteries carry venous blood away from the unborn baby.
The umbilical arteries exist only during fetal development. Departing from the internal iliacs, they pass along the inner surface of the abdominal wall, on the sides of the bladder in the form of a triangle, heading to the umbilical ring, where they are included in the umbilical cord. After birth, these vessels become empty, and only thin folds of peritoneum on the back of the abdominal wall remind of them.
There is only one umbilical vein, although initially there are two of them (the left one is reduced). Nature provides that only one vessel is sufficient to ensure adequate blood flow, so neither the fetus nor the mother experiences “inconvenience” due to an azygos vein. The umbilical vein delivers about 80% of the blood to the developing baby's inferior vena cava, and the remaining 20% is used for blood flow to the liver.
Uteroplacental blood flow system
The amount of blood that flows through the vessels of the umbilical cord during pregnancy is enormous. By the end of gestation, the fetus receives about 240 ml of arterial blood per minute through the vein, the same volume goes through the arteries to the placenta. About 5-20 minutes after the birth of a child, blood flow through the vessels of the umbilical cord remains, and at this time it can be taken for research and other purposes (preparation of medicines, for example), however, already during the birth process, under the influence of the release of the hormone oxytocin, the vessels of the umbilical cord begin to empty, and the organ quickly atrophies as unnecessary.
This is interesting: Complications of hemorrhoids - thrombosis and phlebitis: signs, treatment methods, consequences