Baby protection
While in the mother's womb, the baby's entire body is covered with a viscous gray substance - vernix lubrication. It serves to protect the baby’s delicate skin and makes it easier for him to pass through the birth canal. Immediately after birth, the child is covered in a not very attractive “protective shell”. But after a couple of days, the skin absorbs this lubricant.
Doctors believe that this lubricant cannot be removed on purpose, because it actually helps the newborn’s skin adapt to a new life. And it will prevent the possible problem of dry skin in infants. Remaining lubricant should be removed two days after birth if it remains in the folds of the arms and legs, neck or behind the ears. Well-known vegetable oil will help with this, which needs to be heated a little in a water bath.
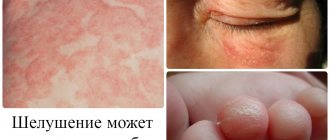
Why does a newborn's skin peel?
The most important reason for peeling skin in a newborn is the exfoliation vernix lubricant that has not had time to be absorbed . Throughout pregnancy, the baby is in the womb, its skin is covered with lubricant (mucus), which protects the delicate skin of the fetus and facilitates the movement of the baby through the birth canal into the birth process. Previously, vernix was carefully wiped off the skin of a newborn, but now pediatricians have come to the conclusion that there is no need to do this. Lubrication on the skin helps the baby more easily adapt to a change in environment and most of it is absorbed into the baby’s skin within 2-3 days. What is not absorbed dries out and crusts form on the skin, which we mistake for peeling.
Along with this harmless flaking of lubricant, actual drying of the top layer of newborn skin is often encountered for a number of reasons. It is in such cases that mothers panic and turn to the pediatrician for help.
Causes of peeling skin
- One of the most important reasons why a child’s skin peels is the period of adaptation of the baby’s skin to the unusual living conditions in the new world. In the womb, the baby was protected by lubricant, and it was humid and warm there.
Now the baby’s skin must adapt to continuous contact with air (not humid), clothing (consisting of different materials), and little by little learn to moisturize and renew itself in an unfamiliar environment. The main thing to remember is that if the skin of newborns is without redness and swelling, and the children themselves are not restless, then the peeling will disappear on its own, you just need to perform basic hygiene in infants.
- A child’s skin may peel off because the air in the building is very dry. Mostly the skin on the body peels off during the heating season. Radiators in homes dry out the air very much, and parents of children do not use humidifiers. Parents should know and ensure that the humidity level is 55-75% for the proper functioning of the baby’s entire body, the skin is no exception.
You should humidify the air not only to avoid peeling of the baby's skin, but also to prevent the mucous membrane in the nose from drying out, and this can lead to a malfunction of the respiratory system and problems with sleep. If you do not have a humidifier and you are unable to purchase one, then you need to do wet cleaning much more often, place dishes with water in the rooms so that it evaporates, and hang wet towels on the radiators.
- Often, a newborn's skin peels due to the fact that most parents do not care for it correctly. Most mothers use a weak solution of potassium permanganate for bathing, and its main property is to dry the skin. And then the baby’s arms and legs may peel off. Potassium permanganate is used only in certain cases, and it is better to bathe the baby every day in ordinary tap water.
If parents are worried about the quality of such water, you can make a bath of boiled water, but do not add anything to it. Use soap products infrequently, no more than once a week. In addition, after using personal hygiene products, observe the reaction of the baby’s skin to their use.
If a newborn's skin peels, it means he is allergic to some of the components of these products. Then you need to change the brand of cosmetics, and it is possible that you will only be able to choose a good product after several attempts. Try to buy all products from a quality place and from trusted brands.
- If the skin on the head of newborns peels off, this is a normal process that occurs due to intensive fat production. But besides this, the skin of newborns peels, perhaps due to seborrheic dermatitis, which, as a rule, occurs by 2 months of life. Then you should contact your pediatrician, who will explain the rules for treating seborrheic “crusts”.
Some people recommend not touching them and leaving them (by the first year of life they often go away on their own). And some advise steaming them or softening them with oil, and slowly picking them out with a comb after taking a bath.
- Peeling skin on the face of infants occurs due to a reaction to cold air, chapping, or very active, long-term exposure to sunlight. To avoid such manifestations, it is best to protect the baby from cold air, gusts of wind and direct sunlight while walking, and in winter, 30 minutes before going outside, smear the child’s face with a special cream.
- Skin may also peel due to food allergies.
If a baby is breastfed, it means that his body responds in this way to the product that his mother uses. If the baby is bottle-fed, then an allergy occurs to the baby formula and it needs to be changed. Due to an allergic reaction, the scalp, torso, arms and legs may begin to peel off, and the baby may also be covered, which is sometimes accompanied by itching. - If the allergy does not go away even after eliminating the possible source among food and cosmetics, then it is likely that the reason for this is hidden in the powder or fabric softener. In such a situation, you need to use special hypoallergenic products for children.
- The cause of scabies, peeling, and rashes can also be the baby’s clothing, or rather the composition from which it is made. Carefully choose clothes for your baby, read the composition of children's clothing, give preference to natural fabrics.
There are also other sources of flaking baby skin. But only a doctor can accurately determine them, and he will give recommendations for treatment if your baby needs it. Diseases of fungus, ringworm, mites, and scabies require medical intervention, because self-medication can only make the situation worse and waste valuable time.
Main types of peeling
- Crusts on the head or Gneiss. This phenomenon is caused by a lack of fat. Only the scalp is affected. The disease manifests itself in the form of peeling and crusts. Requires brushing and moisturizing.
- Allergy - affects the baby's face, arms and legs. This peeling has a bright red color and is accompanied by itching, which bothers the baby. Sometimes there is even a fever. Treatment is prescribed by a pediatrician, as a complication may occur, such as angioedema.
- Diathesis - most often peeling appears on the cheeks. May cause itching and redness. Sometimes sores appear. The disease most often manifests itself from the consumption of sweets and allergens.
- Synthetic peeling is a skin reaction to various types of fabrics, such as synthetics.
How to avoid the problem
Eliminate all possible sources of peeling of the baby's skin. And you just need to properly care for your baby’s skin.
- Use baby moisturizer or cosmetic oil. Apply to areas where the skin is peeling only after a bath, and do not apply moisturizer to your baby before going outside.
- If you are allergic to a cosmetic product, you should change it to olive oil.
Before using it, it should be boiled in a water bath, allowed to cool, and only then can it be used. Soak a swab in oil and apply to the areas where the skin is peeling. - Use a special sunscreen for babies. It protects the child's skin from the negative effects of the sun during summer walks. If the baby is mainly in the shade, then there is no need to use such cosmetics.
- After a bath, always wipe your baby dry and change his diapers promptly.
Impact of adaptation
It is not surprising that the skin of a newborn baby reacts to changes in living conditions with such manifestations as: flaking on the body, dryness, irritation . Many books have been written about why this happens; many doctors advise new parents on this topic every day.
It is very difficult for a baby, who has been developing under the 100% protection of his mother’s body for 9 long months, to adapt to the peculiarities of the outside world. Moreover, not only the child’s skin, but also other systems and organs experience discomfort from the need to go through an adaptation path.
If the baby only experiences peeling, it is enough to simply provide the baby’s skin with proper care.
Note! If the baby's skin is peeling, but the baby does not experience any discomfort, there is no inflammation or redness on his body, then it is enough to provide timely care and nutrition of the skin. This will make adaptation easier.
In addition, it is recommended to carefully monitor the nutrition of the baby and mother (if breastfeeding), in order to avoid the addition of an allergic component to the adaptation period.
Taking proper care of the baby
What to do if newborns have flaky skin - take proper care of it. How to do it? It is necessary to wipe all the folds of the baby with an oil swab, namely:
- neck;
- ears;
- rub well between fingers;
- palms - it is on them that threads and fibers often remain that allow diaper rash to develop, and therefore everything needs to be cleaned in detail;
- bends at the elbows;
- armpits;
- all folds on the legs - from the toes to the thigh;
- groin area;
- fold between the buttocks.
A new cotton swab should be used for each area, and this should be done after each bath for three months. If there are no problems with it, then you can stop doing these manipulations. But not all. If a baby's skin begins to peel, then all possible aspects should be taken into account.
Symptoms of desquamation
The skin of a person (even a newborn) is constantly renewed. The upper layer of the dermis peels off imperceptibly and is replaced by new dermal cells - this is a completely normal process for a healthy body. Peeling of the skin is called desquamation. There are normal (physiological) and pathological forms of desquamation. Why does the second form develop? This is often due to an illness and requires treatment.
| Pathology | Characteristic symptoms | Note |
| Staphylococcus aureus infection | The bacterial infection can spread to internal organs. Lesions on the scaly, rough dermis may resemble a burn or abscess. | The pathogens are resistant to alcohol, ultraviolet radiation, high temperatures and even a number of antibiotics. |
| Microsporia | Small bright spots form on the arms and legs, as well as under the hairline. There is no itching or burning with microsporia. | Can be transmitted through pets. |
| Ringworm Zhibera | The lesions have an oval or regular rounded shape, pink or pale brown. Usually appear on the back, sides, and limbs of the patient. In the central part of the lesions, the rough skin peels off in scales. | The infection spreads intensively in early autumn and more often affects girls and women. |
| lupus erythematosus | Painless bright red rashes on the face (including around the eyes), abdomen, and in the area of the lymph nodes. The disease affects not only the skin of the face, but also joints and internal organs. | Autoimmune disease |
| Eczema | The skin of the extremities (feet, hands) becomes red, and the formation of scales increases. | It develops due to a genetic predisposition (including in newborns), as well as due to untreated dermatitis or constant stress. |
| Ichthyosis | The skin is excessively flaky, peeling, and flaking particles look like fish scales. | Hereditary pathology. Symptoms appear in the first 1.5 – 2 years of a child’s life (including in newborns). |
| Atopic dermatitis (we recommend reading: what are the causes of atopic dermatitis in children?) | A red, bumpy rash that is itchy and very uncomfortable. Can occur on any area of the skin. Sometimes complicated by infection. | Most often it develops in younger preschoolers. |
The main symptom of desquamation is peeling, flaking of the skin. The epithelium is removed in “scales”. Peeling patches can form on any part of the body - from the palms and feet to the face (including around the eyes) and head. If a child’s skin peels for an unknown reason, you should not ignore it - desquamation can act as a symptom of a pathology that requires urgent medical attention.
Prevention
- You should not bathe your baby more than once a day, otherwise the skin will become very dry.
- After the bath, the baby should not be wiped, but simply soaked until all the water is absorbed into the towel.
- After swimming, use a moisturizer.
- Cosmetics for children can be replaced with olive or peach oils - something to which the baby will not be allergic.
- Change your baby's diapers in a timely manner, and leave the baby without them for a certain period so that the skin can rest.
- In summer, use children's sunscreen.
- Don't use moisturizer before going outside.
- Do not purchase cosmetic products containing lanolin, which is a strong allergen.
- Don't forget to humidify the air in your home.
- Adjust the feeding mother's diet and eliminate possible allergens.
What to do if the skin on your palms peels off?
If your child begins to peel off the skin on his palms, you should consult a doctor to find out the cause of the pathological process. Peeling, itching (increasing at night), spots on the arms, palms, legs and tummy can be symptoms of scabies (see also: a child has a red, rough spot on his arm: causes and photos). This disease spreads quickly (especially in children's groups), so the little patient needs to be isolated from other children as soon as possible.
Peeling of the skin on the arms and legs, in the groin area, accompanied by a burning sensation that intensifies after water procedures, may indicate a fungal infection. Neglecting treatment is dangerous, since such diseases can become chronic after a short development in the acute stage. One type of fungal infection is athlete's foot. It only affects the arms (palms and fingers).
Contact dermatitis is usually caused by external causes - chapping or interaction with aggressive chemicals. The main signs are that the skin on the hands becomes very inflamed and looks very dry. Small red rashes form on the affected areas, causing discomfort to the patient.