general information
Hernia of the white line of the abdomen in children - photo:
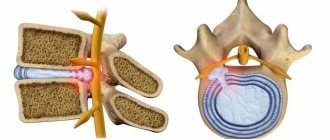
The linea alba is a vertical muscular stripe starting at the xiphoid process of the sternum and passing through the umbilical region. It ends at the pubic symphysis (pelvic part).
The width of the tendon layer is on average 2-3 mm, and its widest part reaches 20 mm. A hernia of the linea alba develops when the tendon bundles diverge at the level of the navel.
, protrusion of the omentum and intestinal loops occurs . The width of the lumen can reach several centimeters.
Stages of development of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen:
- formation of preperitoneal lipoma;
- transformation of lipoma into a hernial sac;
- formation of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen.
What are the signs of increased intracranial pressure in an infant? Find out about this from our article.
Causes of the disease
Photo: umbilical hernia in a newborn
A hernia in a child can occur due to a genetic predisposition if, after birth, the abdominal walls do not develop correctly. Also, a hernia can be acquired due to anatomical weakness.
All this leads to tissue depletion and loss of their former elasticity. They are not able to cope with the loads exerted, so round or slit-like holes begin to form.
The most common cause of the development of abdominal hernia in children is underdevelopment of the tendon plate, which includes collagen fibers and tissues responsible for the elasticity of the peritoneum.
There are also frequent cases when the disease is provoked by increased intra-abdominal pressure. The following factors contribute to this:
- Overweight child, in rare cases even obesity;
- Abdominal injury. A hernia may begin to develop in places where the surgical suture was previously located;
- Prolonged crying of the baby, chronic bronchitis or whooping cough.
Reasons for appearance
The development of a hernia of the linea alba in infants and older children can be provoked by congenital characteristics or the influence of certain external factors.
In newborn children, the cause of pathology is constant and severe crying, overeating or constant stress on the abdominal area (for example, when coughing as a result of chronic bronchitis).
With age, the number of provoking factors increases.
Factors related to the causes of pathology development :
- genetic weakness of fibrous fibers;
- congenital defects of the abdominal wall;
- underdevelopment of the broad tendon plate;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- regular overeating;
- abdominal injuries;
- development of obesity;
- consequences of surgery;
- regular accumulation of gases and constipation;
- constant increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
Causes of hernia of the white line of the abdomen
In children, pathology is usually detected at the age of 5 years, but it also occurs in newborns. Prerequisites for the formation of hernias are:
- scars from abdominal surgery;
- heredity;
- obesity;
- frequent constipation;
- hysterical cough and scream;
- ascites;
- congenital defect of the abdominal muscles;
- underdevelopment of tendons;
- binge eating.
The symptoms of the disease are unclear, so they are determined by the doctor during examination. Under certain conditions, a bulge in the abdomen is noticeable, which increases when lifting heavy objects or after eating. Painful sensations are found in the upper abdomen when pressed with hands. In the lying position, the hernia is barely noticeable; with pressure, it also decreases.
Some signs should alert mothers and fathers of children. These include abdominal pain after eating, heartburn and a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, possibly indigestion and decreased or absent appetite. In infants, the pathology may be the result of constant strong crying or coughing, which increases pressure in the abdominal cavity.
In infants, the cause of a hernia can be constant continuous crying.
With hernias of significant size, pain is localized in the sternum and on the back, and there may also be pain under the shoulder blades. When you sneeze or cough for a long time, the hernia increases. If the child’s well-being sharply deteriorates and the pain worsens, then a complication of the disease in the form of injury to the hernial sac is possible.
In newborns, the main causes of this defect are prolonged loud crying, severe coughing and bad stool. When screaming and constipation, the abdominal wall becomes very tense, causing the connective tissue inside it to weaken and separate. The cause of a hernia of the linea alba in an older child may be any trauma to the abdomen or large excess weight. There is also a genetic predisposition to this disease.
Symptoms, clinical picture
The symptoms of hernia of the white line of the abdomen in children depend on the stage of development of the pathology. At the first stage, the disease occurs in the form of protrusion of muscles in the umbilical region .
When the child relaxes his stomach or is in a horizontal position, the signs of a hernia become invisible.
In the presence of complications, the protrusion remains in a permanent form and is accompanied by pain . Symptoms of the pathology manifest themselves in the following conditions:
- Painful sensations in the abdominal area after eating or exercising.
- Pain in the abdominal area combined with pain in the hypochondrium or lower back.
- Heartburn, belching and bad breath in combination with the main signs of the disease.
- Bloating, diarrhea or constipation combined with abdominal pain.
- Attacks of nausea combined with spasmodic pain in the peritoneum.
- Protrusion of muscles in the navel area.
Types and stages of hernia development
The development of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen in a child goes through three stages:
- a small amount of fatty tissue passes through the gap between the tendons, thereby forming a benign tumor;
- then a hernial sac is formed from this tumor, into which the internal organs partially extend;
- the hernial sac falls out through the gaps between the tendons along with parts of the internal organs located in it.
Quite often, the development of a hernia stops at the first stage, but you shouldn’t count on such luck. If the third stage is reached, there is a possibility of serious complications.
- Strangulated hernia. Those parts of the internal organs that are located in the hernial sac are subject to constant pressure in the area of the intertendinous gap. Because of this, blood flow to them becomes limited. The functioning of the organs first deteriorates, then inflammation, diffuse peritonitis and even gangrene may occur. A strangulated hernia is usually accompanied by severe pain, and in this case, urgent surgery is required.
- Irreversible hernia. With prolonged absence of treatment, those parts of the organs that are located in the hernial sac begin to fuse with each other. This leads to the inability to repair the hernia.
- Since the protruding organs are less protected than usual, they can be easily damaged in the event of any trauma to the abdomen. Considering that children are quite active creatures, the occurrence of such a situation is quite real.
All complications resulting from the lack of treatment for a hernia are fraught with very serious health problems. Therefore, the best preventative measure in this case is timely diagnosis of the disease.
Depending on the location, the following types of hernias are distinguished:
- Epigastric. This pathology accounts for about 80% of all cases of the disease. It is located above the navel. Also known as supra-umbilical and epigastric hernia.
- Paraumbilical. It is localized near the navel, but not in it (see also: what to do if pus appears in the navel of a newborn?). This type of pathology is very rare - about 1% of all cases.
- Subumbilical. Localized under the navel. Occurs in 10% of sick children.
When forming, pathology goes through several stages of development:
- Preperitoneal lipoma. Usually not accompanied by any symptoms, there is no pain. A piece of fatty tissue emerges through the hole between the weakened tendons of the linea alba. The hernial sac is not yet formed. It is almost impossible to establish pathology.
- Initial stage. The process of formation of the hernial sac is activated. It is already possible to diagnose pathology in children.
- Formed hernia. The stage at which the intestinal loops and internal organs of the abdomen fill the hernial sac. The disease is accompanied by certain symptoms and is easily diagnosed.
Possible complications and consequences
An advanced form of hernia of the white line of the abdomen can cause serious infringement or necrosis of certain internal organs.
Compression of the intestine or omentum impairs blood circulation, resulting in a risk of developing peritonitis.
If this pathology is detected in a child, it is necessary to treat the disease or perform surgical intervention as soon as possible.
A hernia of the linea alba can cause the following complications :
- rupture of an internal organ damaged by a hernia;
- development of peritonitis;
- intestinal obstruction;
- development of an inflammatory process or suppuration.
Why is a hematoma on the head of a newborn after childbirth dangerous? Find out the answer right now.
Acquired umbilical hernia in a child
An acquired umbilical hernia is most often discovered in the first year of a baby’s life and its formation occurs due to low muscle tone of the umbilical ring. The presence of concomitant diseases in a child such as rickets or malnutrition can further aggravate the situation. A few more reasons are frequent constipation in the baby, prolonged crying, colic . All of them do not in any way contribute to the rapid healing of the muscles of the umbilical ring and thereby create the most favorable conditions for the appearance of a hernia.
Diagnostics
A doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis of a hernia of the linea alba on the basis of a visual examination of the child and palpation of certain areas of the abdominal cavity.
To confirm the pathology, additional examinations and consultations with specialized specialists are prescribed.
Based on the collected data, a course of treatment is drawn up or a referral for surgery is given.
Methods for diagnosing the disease are the following procedures:
- palpation of the area of the white line of the abdomen;
- general blood and urine analysis;
- EGDS;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- MRI of the abdominal organs;
- X-ray of the stomach and duodenum;
- computed tomography of the abdominal organs;
- herniorrhaphy;
- gastroscopy.
Recommendations for the treatment of hyperexcitability syndrome in newborns can be found on our website.
Massage for umbilical hernia
Special massage helps young children well. Parents can perform basic techniques independently.
1. Lightly stroke the tummy in a circle in a clockwise direction. 2. Smoothing movements in the oblique muscle area. 3. Stroking in the area of the large intestine. Performed with fluttering movements, without pressure. 4. Counter movements of both palms of the hands (up and down) along the posterolateral plane of the chest.
Stroke the baby with a warm, full palm around the navel. All movements are performed only clockwise. Gently grab the oblique abdominal muscles with your palm from the sides to the center. Next, perform stroking “discriminately”, i.e. in the opposite direction. Regularly performing simple massage movements will help strengthen your abdominal muscles. Leave more complex manipulations to a professional to avoid making things worse. Before performing an independent massage, consult your surgeon about the correct actions.
Treatment methods
Conservative treatment of a hernia of the linea alba in children is prescribed only if the pathology is diagnosed early and there is no tendency for rapid development of the pathology.
Drug therapy is carried out to eliminate additional symptoms.
The child may be prescribed painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs appropriate for his age.
Such medications have no effect , but alleviate the general condition.
Non-surgical methods of treating pathology:
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- massage treatments;
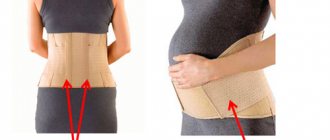
- wearing a bandage;
- hernia reduction;
- taking medications.
Umbilical hernia: do we treat or wait?
Umbilical hernias in children are among the conditions that become the subject of a wide variety of rumors, speculation and misconceptions. Some parents believe that a hernia can be eliminated with the help of spells, others stick coins to the child’s navel... What is an umbilical hernia, does it require treatment - and what kind?
An umbilical hernia most often occurs during the neonatal period and, as a rule, in the first month after the birth of a child. Some time after the umbilical cord has fallen off, a protrusion may appear in the navel area, which is easily retracted into the abdominal cavity.
The size of the hernial protrusion depends on the size of the umbilical ring. The umbilical ring is the muscle surrounding the navel; During labor, the midwife cuts the umbilical cord and the muscles surrounding the navel contract because the baby no longer needs to receive nutrition through the umbilical cord. When its size is small, a hernia can only sometimes appear when the child is crying or when he is restless. When the pediatrician palpates the navel area, the finger “falls” into the abdominal cavity; this method allows the doctor to determine the size of the umbilical ring and clearly define the edges of the hernial orifice. The edges of the hernial orifice are the area surrounding the hernial protrusion. With a significant size of the umbilical ring (and, accordingly, the hernia), swelling in the navel area is constantly visible, which increases during crying and when straining.
The size of the hernia may gradually increase in the first months after its appearance.
Causes of umbilical hernia in children
The main cause of umbilical hernias is a hereditary predisposition to weakness of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. This means that if the father or mother of the child themselves had this pathology in childhood, then the probability that their child will have a hernia is approximately 70%. However, there are cases when parents did not have this pathology in childhood, and the baby suddenly develops an umbilical hernia.
There is an opinion that an umbilical hernia can occur due to the fact that the midwife “wrongly” cut off the umbilical cord during childbirth and the child developed a wide umbilical ring. However, this is not true: the technique of applying an umbilical staple does not affect the occurrence of umbilical hernia in children. An umbilical hernia occurs due to anatomical weakness of the muscle tissue in the navel area.
The contents of an umbilical hernia are usually intestinal loops. With light pressure, the hernial protrusion is freely retracted inward. With a very wide umbilical ring and a large hernia, intestinal peristalsis is sometimes visible outwardly, that is, contraction of the intestinal muscles and the movement of food through it, which is very frightening for many parents, but this does not cause inconvenience to the baby.
The diagnosis of “umbilical hernia” is made during examination by the pediatrician observing the child. In the future, the doctor may refer the baby for a consultation with a surgeon to receive additional recommendations on the treatment of this condition.
Umbilical hernias in children are prone to self-healing, even with fairly large sizes of the umbilical ring and hernial protrusion.
Infringement of umbilical hernias, that is, compression of the contents of the protrusion, is practically not observed. However, many pediatricians notice that children with hernias are more restless than their peers, and also sensitive to weather changes. The child does not experience pain due to the hernia itself, but the presence of this condition in the baby is often accompanied by bloating, which leads to anxiety in the baby. The presence of an umbilical hernia in a child is largely a cosmetic defect.
Treatment
As mentioned above, umbilical hernias tend to heal themselves, regardless of size. It is recommended to carry out a number of conservative measures to eliminate the existing pathology. With proper treatment, a hernia can be eliminated within six months. What methods of conservative treatment of umbilical hernia exist?
The most effective measure for preventing the occurrence of an umbilical hernia, as well as treating an already existing condition, is to place the baby on his tummy.
It is recommended to lay the baby out 10-15 minutes before feeding 2-3 times a day on a flat, hard surface. This could be a changing table or a table covered with a diaper. Be sure to be close to the child, do not leave him for a second, even if your baby does not yet know how to roll over.
During laying out, it will be useful to give a light massage to the back, legs and arms of your baby; just stroking from the tips of the fingers upward, from the buttocks to the shoulders is enough.
The second method of conservative treatment of umbilical hernia, as well as a method of preventing the occurrence of this condition, is abdominal massage. Massage in a clinic as prescribed by the observing pediatrician is usually carried out after the child reaches two months. However, you can massage yourself immediately after the umbilical wound has healed. For the smallest babies, it is enough to carry out only three or four light stroking movements of the tummy clockwise, starting from the right iliac region to the left, that is, from the right lower abdomen to the left lower region. A stroking massage relaxes the muscles, so movements should be very gentle and comfortable for the child. This technique is performed using the palmar surface of the hand.
Older children can have a massage using the “I love U” method. This massage will help with flatulence (bloating), colic and umbilical hernia. Imagine an inverted U shape on the surface of your baby's tummy; the intestines look the same. Apply a little massage oil to your palms and knead your baby's tummy with your fingers lying flat in a circular motion. First, go from top to bottom along the left side of your baby's tummy, writing the letter "I" (for you it will be on the right). With this movement, you move gases downward, expelling them from the descending colon. Then draw an inverted "L" shape, moving peristalsis and gases across the transverse colon, then back down the descending colon (this is the upper abdomen) and then back down the left side of the baby's abdomen. Then draw an inverted letter “U”, going up the ascending part of the colon, then along the transverse one and further down the descending part, that is, from the right from bottom to top, then along the upper abdomen and then from top to bottom along the left side of the baby’s abdomen.
Particular attention should be paid to the peri-umbilical region, since it is due to the weakness of the rectus abdominis muscles that an enlarged umbilical ring and, consequently, an umbilical hernia is formed. The rectus abdominis muscles are located to the right and left of the navel and cover almost the entire anterior abdominal wall. Place your thumb and index fingers to the right and left of the baby's navel at a distance of approximately 1-2 cm from the center of the navel and make ten presses with small point movements. Make the same pressures above and below the navel. Movements should be gentle and not cause discomfort to the baby. Then, at the same distance from the navel, use your index and middle fingers to make ten clockwise circular movements. Finally, press the hernial protrusion inside the tummy. The intensity of these procedures should be comfortable for your baby. It is advisable to massage the umbilical area two to three times during the day. The duration of the procedures is no more than 5 minutes; It is advisable to carry them out before feeding the baby. Some babies prefer to have their tummy massaged before bathing, while others prefer to receive the treatment after the bath. This issue is decided individually each time, depending on the child’s condition. As mentioned above, children with umbilical hernias are sensitive to changes in weather, and if the baby is capricious, then it is better to postpone the massage until a more favorable moment.
The third method of conservative treatment is the application of an adhesive bandage. The application of such a bandage as a method of treating an umbilical hernia may be recommended by the observing pediatrician or surgeon. There are several ways to apply the patch. Plasters for the treatment of umbilical hernias are produced by various companies (Chicco, Hartmann); Such patches are sold in pharmacies and children's stores. The doctor applies an adhesive bandage for 10 days in a wide strip (preferably 4 cm), from one lumbar region to the other, that is, the bandage will be applied around the abdomen. In this case, the hernial protrusion is reduced with a finger, and the rectus abdominis muscles are connected above the umbilical ring in the form of two longitudinal folds. If applied correctly, these folds under the patch should remain (not straighten out). If, after removing the bandage, it turns out that the umbilical ring has not closed and the hernia remains, then the bandage can be applied for another 10 days. A course of applying a bandage three times (3 times for 10 days) is often enough for a complete cure. Modern pediatricians rarely use this version of the plaster method, since the plaster can irritate the child’s delicate skin.
There is also a technique for applying the patch directly to the umbilical area for several weeks, without forming a fold. The patch must be changed every two to three days, and the baby is bathed every day without removing the bandage. This method is more gentle, and parents can change the patch themselves without the help of a doctor. When using this method, it is recommended to use the hypoallergenic patch “Cosmopor E” 5x7.5 cm from Hartmann, which does not need to be removed while swimming. If there is a question about using a patch bandage as a treatment for an umbilical hernia, then the tactics and method of applying the bandage are determined by the doctor when examining a child with an umbilical hernia. For children who have the patch applied, we also recommend a light tummy massage using the method described above, as well as placing it on the stomach. The entire complex of conservative measures (laying on the stomach, abdominal massage, applying an adhesive bandage) should be carried out only after the umbilical wound has completely healed and in the absence of skin changes, including inflammatory and allergic reactions in the navel area.
If the entire complex of conservative treatment measures turned out to be ineffective and the child’s hernia persists after 1 year, then surgical intervention is performed to eliminate the cosmetic defect. This issue is decided jointly by the pediatrician and the surgeon who are observing the baby.
Conspiracy against hernia
It is worth mentioning such methods of “getting rid” of an umbilical hernia as applying a copper five-kopeck coin to the hernial protrusion, applying bandages, using grandmothers’ spells and other methods of alternative medicine. Without a doubt, at present it is necessary to give preference to traditional medicine, which will be many times more effective and safer for your child.
Prevention of umbilical hernia
Prevention of the occurrence of umbilical hernias is, first of all, the prevention of excessive straining of the child and bloating, which is usually caused by increased gas formation and constipation.
To prevent excessive intestinal bloating in a child and the development of constipation, the most favorable option for young children is breastfeeding, but the mother must follow a diet. We can advise mothers to temporarily exclude the following foods from their diet: whole milk, white cabbage, legumes, nuts, sweets, smoked meats, sausages. It is preferable to consume fermented milk products, bran, whole grain cereals, fresh vegetables and fruits. During breastfeeding, prunes and dried apricots (no more than 3-5 berries per day) are useful for preventing constipation.
If for any reason the baby is bottle-fed, in order to exclude constipation, bloating, colic, or an allergic reaction, the formula should be selected by a pediatrician.
The doctor observing your baby may recommend medications: SAB-SIMPLEX, ESPUMIZAN, PLANTEX, BABY-CALME, etc.
To prevent constipation, which can occur in a baby due to improperly selected artificial nutrition, due to errors in the diet of a nursing mother, as well as in dysbacteriosis and other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, in which excessive straining occurs, pediatricians recommend taking DUPHALAC among medications. , as well as the introduction of GLYCERIN SUPPLIES and microenemas - MICROLAX. Your pediatrician will tell you the dosage and specifics of administering these medications, since the prescription of drug therapy is purely individual and can only be done by the doctor monitoring your baby’s development.
Children with lactose intolerance (lactase deficiency) quite often have umbilical hernias. Lactase deficiency occurs in children who were born prematurely or at term, but remain functionally immature. In this condition, breast milk is partially or completely not digested, resulting in fermentation in the intestines and bloating. In addition, one of the forms of lactase deficiency may be a tendency to constipation. The most effective means of prevention for such children is a rational selection of feeding; during breastfeeding, additional administration of the lactase enzyme is often recommended.
At an early age, many children suffer from intestinal dysbiosis, that is, a violation of the intestinal microflora, which can occur against the background of lactase deficiency and other conditions. At the same time, constipation, as well as bloating, which accompanies dysbacteriosis, quite often provoke the occurrence of an umbilical hernia in babies. Treatment in this case should be aimed primarily at eliminating the symptoms of the underlying disease.
Do you need a diet?
Compliance with a special diet is an integral part of the treatment of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen at any stage and during the rehabilitation period after surgery.
Meals should be balanced and fractional. Starvation and overeating of the child must be excluded. The diet must include foods rich in vitamins and beneficial microelements.
Diet features:
- The last meal should be taken no later than three hours before bedtime .
- The diet should not contain foods that can cause flatulence (grapes, white bread).
- Cheeses, seafood, and lean meats will help replenish the calcium supply
- The menu should include fermented milk products and natural yogurt with a minimum percentage of fat content.
- Flour products should be consumed in limited quantities .
- The consumption of carbonated drinks is excluded .
- Sweets in a child's diet should be present in minimal quantities .
- The child’s menu should include fruit jelly, jellies, and natural juices.
- Spicy, smoked, fried and fatty foods are excluded .
- The diet should include porridge, light soups and broths.
How to help an umbilical hernia?
Ninety-nine percent of umbilical hernias up to half a centimeter in size will close on their own. Hernias larger than three centimeters are also often closed. And at the same time, you can help them. We are talking about sealing the hernia with a plaster. It is very important to use an “umbilical patch” product specially designed for this purpose, since a regular patch causes serious irritation to the child’s skin. Allergy, infection and even inflammation - this is the list of consequences of using a “regular” patch. The umbilical patch is hypoallergenic and - in addition to its auxiliary effect in the fight against hernia - preserves the health of the skin and the comfort of the baby's life.
Indications for surgery
The hernia may be reducible or unreducible . The first type implies the possibility of treatment without the use of surgery.
In the second case, surgery is the only way to eliminate the pathology.
Before surgery, the child is given a comprehensive examination. The development of some acute diseases may cause the procedure to be rescheduled.
Indications for surgery are the following conditions:
- pathology develops at a rapid pace;
- conservative treatment methods do not lead to improvement in the child’s condition;
- strangulated hernia;
- the presence of serious pathological complications.
How serious is this?
An umbilical hernia is safe for children. There were no cases of strangulated umbilical hernia before the age of fourteen. Its presence can threaten health if an eighteen-year-old young man regularly engages in heavy physical activity.
An umbilical hernia closes on its own at the age of three to five years. It is not recommended to operate on a child under three years of age because most hernias close before this age. If the hernia has not closed after five years, it will not close on its own. And the solution here is surgical intervention. The main indication for surgery to eliminate an umbilical hernia is cosmetic - due to psychological discomfort.
How is the defect removed?
The procedure for removing a hernia of the linea alba in medical practice is called hernioplasty . This is carried out using general anesthesia.
The purpose of surgery is not only to open the hernial sac and remove its contents, but also to eliminate the existing discrepancy of the rectus muscles.
The procedure is carried out in two ways, depending on the tissues used during the operation. Two operation options :
- using your own tissues and synthetic non-absorbable thread;
- using a special synthetic mesh frame.
The duration of the operation to remove a hernia of the white line of the abdomen does not exceed one hour. The period of a child’s stay in the hospital and the rehabilitation process depend on the individual characteristics of the child’s body.
The doctor may discharge the patient after a few days or leave the child under the supervision of specialists for a week.
Read about the symptoms and treatment of umbilical hernia in children here.
Hernia in children: what is it?
In children, hernias most often occur - protrusion of the small intestine in the abdominal cavity and other types of this disease. The most common umbilical hernia occurs in children, but other types may occur. It is much easier to get rid of such defects in children than in adults. The earlier the disease is detected and treatment started, the better. As you age, this condition can cause more negative health consequences.
You can often notice the occurrence of this pathology in children under one year of age; in some cases it is said that it can disappear on its own. However, in any case, when it appears, the child should be under the supervision of a doctor.
The exact cause of protrusion in children is quite difficult; its appearance may be due to the structural features of the abdominal tissues; in this case, they speak of a congenital hernia. Other factors can affect the protrusion, these include strong child crying and screaming, severe constant cough. In any case, regardless of the cause, you need to start therapy as quickly as possible and straighten the protrusion of the organ.
Under no circumstances should you try to reduce or cure a hernia by any other method, Dr. Komarovsky warns about the same. This disease requires medical supervision; self-medication can lead to worsening of the condition and serious problems.
Important! If this condition is not addressed in childhood, a hernia can cause much more problems in later life.
Why is it dangerous?
The main danger when such a condition occurs is the possibility of pinching of the protruding organ. If the organ is pinched by surrounding tissues, there is a possibility of complete disruption of its functioning. In the case of the intestines, this can lead to dire consequences.
Other possible complications that occur without timely treatment include inflammation and rupture of organs inside the hernia, and various strangulations inside the hernia. Over time, the defect may also become irreparable; getting rid of this condition will be extremely difficult.
Post-intervention care
After surgery to remove a hernia of the linea alba, the child is prescribed a special diet .
During the rehabilitation period, significant physical activity is prohibited.
Violation of these rules can cause complications and relapse of the disease.
Experts recommend conducting courses of vitamin therapy to increase the protective functions of the child’s body and speed up the recovery process.
Features of care after surgery:
- exclusion of spicy, fatty and fried foods from the diet;
- control of fiber intake;
- avoiding constipation;
- the child’s physical activity should be minimal;
- the child will need to wear a postoperative bandage for a certain time;
- restoration of the body with the help of vitamins B, C and calcium;
- The diet must include vegetable and fruit juices and purees.
How is surgery to remove an inguinal hernia performed in girls? Read about this in our article.
Stages of development of hernial protrusion
Photo: hernia of the white line of the abdomen
Most often, a child experiences a hernia of the linea alba. There are three stages of its development:
- The first stage is characterized by the protrusion of peritoneal cells through the opening, which is still small in size. A lipoma is formed located in front of the peritoneum. Basically, in children at this stage, the development of a hernia stops;
- When the lipoma begins to form into a hernial sac, the second stage of the disease begins. The sac contains the omentum and small intestine. An already formed hernia forms a gate for exit. In complicated cases, the walls of the stomach are located inside the hernial sac;
- The third stage of the disease is visible to the naked eye. It is easily detected by palpating the abdominal area. The hernial sac begins to fall out.
Features of the appearance of hernias in children
The peculiarities of the appearance of hernias in a child include the fact that they are local only in rare cases. Often several hernias form at once, which are located one after another. They can be near, under or above the navel.
In children, hernias are not large. Usually its parameters do not exceed two centimeters. In appearance, it looks like a small round-shaped swelling; you can view the photo for reference.
[Show as slideshow]
Symptoms of abdominal hernia in children
Signs of an abdominal hernia in children include pain, discomfort and the presence of a protrusion, which may disappear when lying down. If such symptoms occur, then you definitely need to visit an experienced doctor. Only he will confirm or refute the diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Symptoms of a hernia vary depending on the location and degree of development. However, several important signs have been identified, which include:
- Aching and nagging pain at the location of the hernia;
- Poor functioning of the digestive system. Nausea accompanied by vomiting and frequent constipation are observed;
- Problems with the urinary system. This is possible if the bladder gets into the hernial sac.
If such symptoms are observed, you should immediately consult a doctor!
Diagnostics. Preparing for treatment
Every mother should be wary if her child constantly has a stomach ache. When the pain does not go away, but only gets worse, you need to visit a doctor. Only he will be able to properly examine the little patient, and then, if necessary, refer him for examination.
In addition to palpation, an abdominal hernia can be diagnosed using ultrasound and computed tomography of the peritoneum. The doctor may also perform an X-ray of the gastrointestinal tract. During the final examination, a special substance will be injected into the peritoneum, which will allow a thorough examination of the hernia.
If the diagnosis has been confirmed, then it is necessary to immediately set up the child for surgery. If a hernia was detected in a baby, the date of surgical intervention will be postponed.
On average, most clinics undertake to operate on children over five years of age. However, it will be necessary to undergo a thorough examination by a doctor, who may postpone the treatment period or, conversely, shorten it.
To prepare your child for surgery, you will need to create a proper and balanced diet, excluding some foods from it. These include:
- Spicy and fatty dishes, food with added herbs and spices;
- Chocolate, lemonade, butter;
- Snacks, semi-finished products.
You need to feed your baby five times a day in small portions to avoid problems with the digestive system.
Operation
Surgery to remove an abdominal hernia in children is called hernioplasty. The operation will be performed under general anesthesia, but with a lower dosage. Hernioplasty can be performed using two methods:
- By stitching the peritoneal walls using your own tissues;
- Carrying out an intervention using a specially designed mesh.
During the operation, the surgeon makes small incisions and then opens the hernial sac. He removes its contents, then works to eliminate the discrepancy of the rectus muscles. This allows you to avoid the progression of diastasis. Only this will guarantee a complete cure for the hernia.
When performing hernioplasty with native tissues, the aponeurosis defect is eliminated using a non-absorbable thread made of synthetic materials. This form of intervention can lead to relapse, because subsequently there is a large load on the sutures.
Therefore, surgery during which synthetic materials are used has become more widespread. The mesh frame covers the aponeurosis, which leads to an even distribution of the load on the peritoneum. At the same time, the possibility of relapse is minimal, since the tissue can quickly and easily grow through the allomaterial.
Features of surgical intervention (hernioplasty):
- The operation lasts no more than an hour;
- The next day the child can go home, complications are no longer observed. Only in some cases may the doctor leave the patient for a few more days for ongoing examination;
- Sutures are removed after two weeks.
Rehabilitation period
After the operation, a rehabilitation period begins. During this time, it is necessary to adhere to proper nutrition and also avoid physical activity and heavy lifting. As before the operation, the child is advised to avoid fried, spicy and smoked foods. To facilitate the digestion of food, you should try to eat liquid foods: porridge and soups.
It is recommended to eat in small portions. To ensure regular bowel movements, the child needs to be given oatmeal or kefir.
To restore the body after surgery, it is necessary to consume vitamin B and C complexes.
How to prevent a hernia?
To prevent a hernia from developing in infants, it is necessary to achieve constant and regular bowel movements and the absence of excess weight. It is worth taking care that the baby does not overeat or cry for a long time.
If the child is between five and ten years old, then the development of a hernial protrusion can be prevented through moderate exercise. Thanks to them, the abdominal walls are significantly strengthened.