You wouldn't wish this on any woman. This news will certainly come as a shock. Such diagnoses are always perceived emotionally. But we hasten to console you as much as possible: an ectopic pregnancy is not a death sentence.
In fact, ectopic implantation of the ovum is not such a rarity: although there is little pleasant in this, but due to the frequency of occurrence, doctors have already learned to quickly identify an ectopic pregnancy and take the necessary measures to prevent risks and minimize the consequences. However, future forecasts for a woman will depend on a number of factors.
It is of great importance at what stage an ectopic pregnancy makes itself known, and how exactly. Unfortunately, in 5-10% of all cases, a woman really cannot have any more children. But timely actions help to avoid many troubles, including preserving the functionality of the female reproductive system. So, the main thing is not to waste time.
Why is the egg not in the uterus?
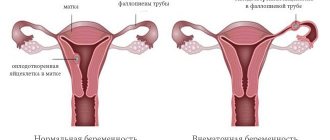
When a sperm fertilizes an egg, the latter begins to move along the fallopian tube and at the end of the path is attached to the wall of the uterus for further development and growth - implantation occurs. This is how a normal pregnancy begins, during which the egg improves, constantly divides, a fetus is formed, from which by the end of the term a full-fledged child grows, ready for life outside the mother’s womb. For this complex process to take place, a certain “home” for the egg and space for its growth are necessary. The uterine cavity is an ideal option.
However, it happens that the egg does not reach its destination and settles earlier. In 70% of cases, it is attached to the fallopian tube, but other options are possible: to the ovaries, to the cervix, to any of the abdominal organs.
Causes of ectopic pregnancy
There are several reasons why the egg cannot reach the uterus:
- Disturbances in the condition of the walls and functioning of the fallopian tubes (when they contract poorly and are not able to move the egg further). This often happens due to previous diseases of the pelvic organs, as well as chronic inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, in particular STDs.
- Anatomical features of the fallopian tube (for example, infantilism): a tube that is too narrow, tortuous, scarred or scarred makes it difficult and slows down the passage of the egg.
- Previously undergone tubal surgery.
- Previous abortions, especially if the woman’s first pregnancy was artificially terminated.
- Slowness of sperm: the egg is “waiting” for fertilization, which is why it does not have time to get to the right place in time, that is, to the uterus - hunger forces it to settle earlier.
- Hormonal disorders in the body of a pregnant woman.
- Tumors on the uterus and appendages.
- Changes in the properties of the fertilized egg.
- A woman wearing a contraceptive intrauterine device.
- Some artificial insemination technologies.
- A woman’s constant nervous overstimulation, in particular, the fear of getting pregnant and unreliable methods of contraception, do not allow her to relax, which is why the fallopian tubes spasm.
Of course, ideally, it is necessary to try to exclude all possible causes of the development of an ectopic pregnancy at the planning stage.
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
How do you know that the pregnancy that has occurred is ectopic? In fact, it is not easy to “see” it. The symptoms of this pregnancy are exactly the same as a normal physiological one: the next period does not occur, the breasts become full, the uterus enlarges and can stretch, toxicosis is possible, a change in appetite and taste preferences, and so on. But some things may still cause some suspicion.
With an ectopic pregnancy, dark spotting and spotting may be observed from the first days. It happens that the next menstruation occurs on time or with a slight delay, only the discharge is weaker than usual. In this case, the nagging pain in the lower abdomen radiates to the anus, and if the fallopian tube ruptures, it becomes unbearably strong, acute, even to the point of loss of consciousness, and bleeding begins. With internal bleeding, weakness and pain are accompanied by vomiting and low blood pressure. In such cases, the woman must be urgently taken to the hospital for immediate surgery.
An ectopic pregnancy is most easily confused with a threatened miscarriage. But this is precisely how it makes itself felt: it begins to be interrupted, which usually happens at 4-6 weeks. To prevent the worst from happening, it is necessary to make a diagnosis in time. Therefore, as soon as you find out that you are pregnant, immediately undergo a gynecological examination and ultrasound. This will allow you to sleep peacefully, because in such cases the location of the fertilized egg immediately becomes known (in most cases).
Signs of an ectopic: how not to miss important symptoms
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy differ depending on the course of its course, age, and characteristics of the female body. For some, these are vivid symptoms from the first days of conception, while others begin to notice something closer to the fatal outcome. That is why, at the first suspicion of pregnancy, you need to responsibly monitor the manifestations of the body and immediately undergo an examination at the antenatal clinic, first of all, for the level of the hCG hormone, and then an ultrasound examination.
The initial signs of an ectopic pregnancy are similar to those of a normal pregnancy. Women watch:
- weakness and drowsiness;
- delayed menstruation;
- swelling of the mammary glands;
- manifestations of toxicosis from mild nausea to vomiting and fainting, etc.
All these signs of an ectopic pregnancy can make themselves felt even before the delay, the main thing is not to attribute them to ordinary malaise or fatigue. Already at this stage you need to immediately consult a doctor for examination.
At home, it is worth trying to do a test with results indicating an ectopic pregnancy. This is a common rapid test to determine the level of hCG in urine. The downside is that real results will be noticeable only 2-3 weeks after the delay, and for an ectopic pregnancy this is too late. Therefore, you should not think about how to independently determine an ectopic pregnancy at home, rather than wasting time and trusting specialists.
You can determine the same low level of hCG in the early stages, even before the delay, in the laboratory by taking a blood test. Positive results will be the first indicator of pregnancy anomaly and an indication for an in-depth study of the situation.
The usual signs and symptoms of early ectopic pregnancy may be supplemented by:
- spotting dark-colored discharge and bleeding associated with improper attachment of the fertilized egg;
- increasing pain of a cramping nature in the solar plexus and lower back, caused by constant tone of the uterus;
- general malaise with increasing attacks of drowsiness, fatigue and dizziness up to sudden loss of consciousness;
- increased toxicosis with vomiting up to 10 times a day and the initial stage of dehydration.
Closer to the resolution of the situation, the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy intensify and eventually develop with rapid force. A woman feels overwhelmed and tired due to dropped blood pressure, experiences incessant dizziness, chills, and, less often, anemia when hemoglobin levels drop.
When the organ on which the fertilized egg is attached ruptures, sharp pain appears and shock and coma may develop. Surgery will help avoid disaster.
***
How to determine an ectopic pregnancy?
The success of resolving the situation with an ectopic pregnancy will depend on at what stage of its development the diagnosis was made. Pregnant women are registered in the second or third month, and this is already too late... Therefore, as soon as you have the slightest suspicion that something is wrong, you need to immediately verify the existence of a problem or rule it out. This happens through examination.
First, you need to make sure that pregnancy has actually occurred. The easiest and fastest way is to do a home pregnancy test. However, you should not rely only on the test in any case: a gynecologist will be able to confirm guesses about the conception that has taken place during an in-person examination. However, this is not always the case: if the period is not long enough or the egg is still too small, then the only way to reliably find out whether pregnancy has occurred or not is a pelvic ultrasound with the introduction of a transvaginal sensor and a blood test for hCG.
If it’s too late to guess - there are all the signs of a pipe rupture or abdominal bleeding - call an ambulance immediately: this condition is life-threatening! And under no circumstances do you take any action on your own: don’t take painkillers, don’t use ice packs, don’t give enemas!
More on the topic
Ectopic pregnancy and pregnancy test
HCG for ectopic pregnancy
Signs of an ectopic pregnancy in the early stages
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
Signs of an ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy: signs in the early stages, symptoms at 5 and 6 weeks of pregnancy
Motherhood is the cherished dream of many women, but it is not always easy to achieve. On the way to the intended goal, there are serious obstacles and one of the most dangerous is an ectopic pregnancy. No one is immune from it, and every woman can be at risk, so to effectively prevent the consequences, you need to clearly know the signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy, otherwise this pathology can lead to death. Today we will tell you how to prevent this and what to do if dangerous symptoms appear.
Causes of ectopic pregnancy?
The causes of ectopic pregnancy are not fully understood; in approximately 35% of cases, doctors are unable to answer the question of why the embryo is fixed in an atypical place. The risk of developing pathology is increased by genital infections, intrauterine contraception, abortion, endometriosis, and problems with the thyroid gland.
Usually, if a woman's period is late, she takes a home pregnancy test and is happy if she sees two lines. However, an ectopic pregnancy cannot be determined independently - hCG tests and tests will show the presence of pregnancy, and not its quality. Even doctors cannot always determine in the first weeks that the egg is developing in the wrong place. First, let's answer the question, what is an ectopic pregnancy?
An ectopic or ectopic pregnancy is a condition in which a fertilized egg is implanted not in the uterus, but outside it. Most often it develops in the fallopian tube, but other types of pathology also occur when the embryo develops in the cervix, abdominal cavity, or even on internal organs.
The fertilized egg (embryo with membranes) grows and develops, and its cells turn into organs and tissues of the unborn child. However, a fertilized egg can only fully develop in the uterus; the whole process is clearly thought out by nature. In other places, the egg is doomed to death, and there can be serious consequences for the woman. For the development of the fetus, certain conditions are needed, including good blood supply, a thick and elastic wall of the organ that will not rupture, will serve as good protection from damage and can provide adequate nutrition.
Most often, an ectopic pregnancy develops in the tube on the side of the ovary in which the egg has matured. During ovulation, a mature egg leaves the ovary and moves into the tube, where fertilization occurs. In this case, the egg encounters many sperm, but chooses the fastest and most active one. After conception, the egg moves through the tube due to contraction of the muscular layer and wave-like movements of the villi of the mucous membrane. On average, the journey takes 3-4 days, during which time the egg secretes special cells, due to which it then attaches to the uterus.
Sometimes there are obstacles on the way of the egg, and it does not have time to get into the uterus, so it is attached where it is at the moment.
The main causes of ectopic pregnancy:
- Previous inflammatory diseases of the fallopian tubes and genital organs are the most common cause. Treated inflammation leads to the formation of adhesions and fibrous cords in the tubes, which make it difficult for the egg to pass through. It does not have time to pass into the uterus before enzymes begin to be produced that melt the mucous membrane for implantation.
- The inflammatory process in the fallopian tubes leads to the death of the villi on the mucous membrane, which help the egg move into the uterus.
- Sometimes women experience abnormalities in the development of the fallopian tubes, for example, additional fallopian tubes or holes in their lumen.
- Surgical operations that lead to the formation of adhesions in the area of the appendages, which prevent the advancement of the zygote.
- Hormonal imbalance leads to disruption of the menstrual cycle and provokes immobilization of the smooth muscles of the tube. When taking hormonal medications, sometimes the embryo develops faster and begins to attach ahead of time.
- Removal of one fallopian tube can also cause the development of an ectopic pregnancy. If the egg matures on the side where the tube is removed, then the path of the egg becomes several times longer, and it does not have time to travel all the way to the uterus.
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy in the first weeks
In the early stages (5-6 weeks), ectopic pregnancy proceeds in the same way as a normal one. There are no specific symptoms of pathology; standard signs of pregnancy are noted:
- Delay of menstruation
- Early toxicosis
- Increased breast sensitivity
Unfortunately, most often an ectopic pregnancy is detected only after it is terminated. It can be recognized by ultrasound at a period of 5-6 weeks, and not in all cases. The main symptoms of termination of ectopic pregnancy:
- Abdominal pain. The very first symptom, which in combination with other signs should alert a pregnant woman. The pain can be constant or cramping, radiating to the lower back or collarbone.
- Uncomfortable sensations in the anus, when a false urge to defecate appears.
- Bloody spotting discharge. Almost no blood comes out through the pipes, and light spotting may appear.
- Weakness, dizziness, low blood pressure, pale skin are signs of internal bleeding.
- A high temperature indicates an inflammatory process in the body.
The first signs of ectopic embryo development
The main sign of fallopian tube rupture during ectopic pregnancy is sharp pain during vaginal examination. If the test shows the presence of pregnancy, external signs are present, but the ultrasound does not show the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity, then other organs are examined - the appendages, abdominal cavity and cervix. Another sign is the accumulation of fluid in the pouch of Douglas.
To accurately diagnose the pathology, a puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix is performed to identify the accumulation of blood due to internal bleeding. The presence of blood in the retrouterine space indicates the need for surgical intervention. Modern medicine often makes it possible to solve the problem without abdominal surgery using laparoscopy, when several small punctures are made in the anterior abdominal wall. In more advanced cases, abdominal surgery is performed.
Laparoscopy allows the most accurate diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. Using an optical system, the doctor can thoroughly examine the abdominal cavity, after which, using special instruments, he removes the embryo and stops the bleeding. Thus, laparoscopy is prescribed for diagnosis, and then can develop into surgery.
When diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy, doctors pay attention to the following signs:
- Reduced level of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin)
- Lack of fertilized egg in the uterus
- Pain in a pregnant woman
If an ultrasound shows the presence of a fertilized egg in the uterus, then the diagnosis can be removed. If the size of the uterus is smaller than it should be for the duration of pregnancy, then a frozen pregnancy or a threatened miscarriage can be suspected.
An ectopic pregnancy is dangerous because it can result in death due to blood loss, so if you suspect an ectopic pregnancy, you should immediately consult a gynecologist for advice.
Types of ectopia and characteristic signs
There are different types of ectopic pregnancy, but according to statistics, most often the pathology occurs in the fallopian tube, especially on the right. Studies have shown that this type of ectopic pregnancy accounts for 95% of all cases. The signs and timing of termination of pregnancy depend on which part of the tube the fertilized egg is attached to. In a narrow channel, the rupture will occur already at 6 weeks, in a denser place - later.
Ovarian pregnancy is considered the most dangerous, but according to statistics, it develops no more often than in 1% of cases. What happens in this case? A sperm fertilizes an egg when it is already mature, but has not yet left the ovary. Sometimes the egg leaves the ovary and is immediately fertilized, and then attaches to the ovary. During ovarian pregnancy, there are no obvious signs; the diagnostic picture is blurred and similar to acute pathological conditions in the ovaries. This situation ends with complete rupture of the ovary.
If the egg enters the abdominal cavity, an abdominal pregnancy develops. Sometimes during a tubal pregnancy, the egg is pushed into the abdominal cavity and begins to develop there. The fetus grows and as a result puts pressure on the woman’s internal organs. There are known historical facts of successful abdominal pregnancy. The birth takes place by caesarean section, but this requires a highly qualified surgeon.
If the fertilized egg attaches to the cervix or isthmus, a cervical pregnancy occurs. The main danger is that the cervix is abundantly supplied with blood and when it ruptures, severe bleeding occurs; due to acute pain, the woman may lose consciousness. Sometimes, in order to save the patient’s life, doctors are forced to completely remove the uterus.
The following pathologies are extremely rare:
- Simultaneous intrauterine and ectopic pregnancy
- Attachment of the egg in the uterine horn
- Location of the zygote in the body of the uterus
All types of ectopic pregnancy are dangerous to the life and health of a woman, can cause death or deprive further chances of having a child, so it is extremely important to diagnose the pathology in a timely manner.
Will a pregnancy test help?
When diagnosing pregnancy, the doctor relies on the patient’s complaints and ultrasound results. In this case, you cannot trust home pregnancy tests, because they can show either two stripes, indicating a healthy pregnancy, or one strip, completely denying pregnancy. There are two types of tests, one simply shows the presence of hCG in the urine, and the second determines the ratio of intact and modified human chorionic gonadotropin. The ratio of fractions allows one to suspect the development of an ectopic pregnancy from 5 weeks. The test results can be confirmed or refuted using ultrasound.
Treatment Options for Ectopic Pregnancy
The only treatment for a ruptured ectopic pregnancy at the moment is to remove the fallopian tube because it is necessary to stop the bleeding. In addition, the functionality of a pipe cannot be restored after a rupture. Modern medicine uses two methods of surgical intervention:
- Laparotomy (abdominal surgery)
- Laparoscopic (special equipment is inserted into the cavity through small punctures and surgery is performed)
The most accurate diagnosis is made using a laparoscope. Through a special thin telescope, the doctor sees where the fertilized egg is located and at an early stage can remove only the embryo. With such an operation, the pipe can be saved, but if it is affected by adhesions, then it is better to remove it, even if the pipe does not rupture. If at the time of detection of an ectopic pregnancy the diameter of the tube exceeds 5 cm, then the tube will also have to be removed. In the early stages, treatment without surgery is possible with the drug Methotrexate. Sometimes drug sclerosis of the ovum is used. In order to resolve it, a special chemical composition is introduced, however, it is impossible to guarantee that the patency of the pipe will be maintained. Most often, this method is used if there is only one fallopian tube left.
Modern treatment methods make it possible to cut the tube and remove the embryo, after which the organ is restored plastically, however, even in this case the patency of the tube cannot be guaranteed. With early detection, fimbral evacuation of the fertilized egg is possible - the embryo is pulled out of the tube under vacuum from the part of the tube that is adjacent to the ovary.
A repeat ectopic pregnancy usually results in both tubes being removed, so if the couple has no children, in vitro fertilization (IVF) is the only way to get pregnant. However, if one tube is preserved, then ectopic pregnancy is not a death sentence and there is a chance to get pregnant naturally.
Basal temperature during ectopic pregnancy
Women who keep a basal temperature chart may suspect pregnancy at the earliest stages. After conception, the expectant mother’s body begins to intensively produce progesterone, which is necessary to ensure the vital activity of the egg and create favorable conditions for its further development. It is the increase in the level of this hormone that causes the increase in basal temperature. You can focus on indicators only if measurements are made from month to month according to all the rules, at least for 4-6 cycles in a row.
With the onset of pregnancy, the basal temperature rises to an average of 37.2-37.3 ° C (for different women these indicators may differ slightly) and is maintained at this level. This occurs regardless of whether the pregnancy develops intrauterine or outside the uterus. Basal temperature during ectopic pregnancy is no different, since progesterone is produced in any case.
A decrease in basal temperature (below 37°C) occurs only when the fetus freezes, which often happens during an ectopic pregnancy. But this is not necessary: often the BT indicators remain at the same levels in this case.
Does the test indicate an ectopic pregnancy?
It is impossible to give an exact unambiguous answer to this question. Firstly, not every test and does not always show a normal pregnancy. Secondly, in the case of attachment of the fertilized egg outside the uterus, there may indeed be nuances.
So, almost all pregnancy tests show the fact of fertilization. It does not matter where exactly the egg has stopped: the level of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) will certainly increase (since the developing placenta begins to produce it), which is what the test systems actually react to.
In principle, there are expensive cassettes that in most cases are able to detect not only pregnancy in the earliest stages, but also its ectopic development (read about this in the article Ectopic pregnancy and pregnancy test). But if we talk about ordinary home tests, they can only establish the fact of pregnancy, and even then with reservations.
The test for an ectopic pregnancy may “work” later than for a physiological one. That is, at a time when a normally developing pregnancy can already be diagnosed using a home test, a pathological pregnancy is sometimes still “hidden”. An ectopic pregnancy can often be detected using a delayed test, that is, 1-2 weeks later than the usual situation. Or the second test strip appears very weakly. What is this connected with?
Timing of pathology detection
At 1-2 weeks it is difficult to determine the disease. A woman has a delay in menstruation, as in a normal pregnancy. Symptoms of the pathology appear at 3–4 obstetric weeks. Diagnostic methods:
- Transvaginal ultrasound. Screening is carried out at 4–5 obstetric weeks. The vaginal sensor does not detect the embryo in the uterus. The doctor examines the ovaries, cervix, and peritoneal area.
- Blood analysis. The increase in the level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is insignificant. With ectopic attachment of a fertilized egg, the progesterone level is below normal.
- Laparoscopy. An invasive diagnostic method is prescribed for open uterine bleeding. If the diagnosis is confirmed, surgery is performed.
HCG level during ectopic pregnancy
It's all about hCG. Wherever the fertilized egg attaches itself, its membrane (chorion) still begins to produce this hormone. This is why a pregnancy test will show a positive result even with an ectopic pregnancy. But doctors say that in the latter case, the level of hCG is lower than during intrauterine pregnancy and does not grow as dynamically. Therefore, at a time when a home test already shows a normal pregnancy, with an ectopic pregnancy the hCG level may still be insufficient for detection.
In the blood, the concentration of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin increases earlier and faster than in the urine. Therefore, a blood test for hCG will be more informative. If a woman has unkind suspicions and the gynecologist, after examination and consultation, does not exclude the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy, then it is better to take this test and undergo an ultrasound.
By itself, a blood test for hCG cannot be a reason for making a final diagnosis, but together with an ultrasound it can clarify the picture. HCG during an ectopic pregnancy, although it increases, is not so rapid and dynamic. Regular monitoring of the level of hCG in the blood (with a break every 2-3 days) allows us to draw preliminary conclusions: during normal pregnancy it will double, during pathological pregnancy it will increase only slightly.
Main signs of pathology
At first, an ectopic pregnancy manifests itself in exactly the same way as a normal one: there is a delay in menstruation, the mammary glands become engorged, nausea and mild malaise occur. It is impossible to determine from these signs that pregnancy is developing incorrectly. The only difference between the normal process and pathology is the degree of severity of the pregnancy test stripes. And although this method cannot be called reliable, it should not be completely ignored.
Pay attention to the severity of the dough strips
So, you have cause for concern if:
- the second stripe is noticeably paler than the first;
- when conducting several tests at intervals of 2-3 days, the brightness of both strips decreases each time;
- with characteristic symptoms of pregnancy, the test shows a negative result.
Pregnancy test photo
As you know, the test reacts to a special hormone produced in the body only during pregnancy. When the embryo is located outside the uterine cavity, the concentration of the hormone is reduced, which is manifested by the pale color of the strip on the test. At very low concentrations the result is usually negative. And yet, this is not a direct indication of an ectopic pregnancy, because much depends on the characteristics of the body and the quality of the test itself.
Pregnancy tests from different manufacturers
Characteristic signs of pathology, which appear a little later, include bleeding and pain in the lower abdomen. The earliest symptom is changes in the menstrual cycle: periods come late or are scantier than usual. In some cases, mucus and fragments of the rejected membrane come out along with blood. This is how the endometrium reacts to the presence of an embryo in the fallopian tube. Many people do not attach importance to such changes, as a result of which an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed too late.
Discharge and pain as a symptom
In some cases, on the contrary, the discharge is profuse, especially if an ectopic pregnancy develops in the cervix. There are many blood vessels in this area, and therefore any damage to the membrane can provoke severe bleeding, sometimes even life-threatening.
Heavy bleeding may occur
The pain has a pulling nature and usually occurs on the side where the embryo is attached. If it is the tubes, then it hurts on the left or right side of the abdomen; with pathology in the abdominal area or cervix, the pain appears in the middle.
Pain may appear on the side where the embryo is implanted
When walking, bending and turning the body, changing position, it intensifies. The dependence of the timing of the onset of pain on the location of the embryo is noted: in the ovaries and abdominal zone the pain begins from 4 weeks, in the isthmuses of the tubes from 5-6 weeks, in the ampullary part from 8 weeks. The development of the embryo in the cervix is accompanied by pain in rare cases, so the dangerous condition goes unnoticed for a long time.
In rare cases, the embryo detaches spontaneously and comes out along with blood and mucus. This is the most favorable option, the most gentle for the body. Of course, a woman cannot independently determine the rejection of the fertilized egg, so a visit to a gynecologist is mandatory.
A visit to a gynecologist and tests are a must if you suspect an ectopic pregnancy
Does an ultrasound show an ectopic pregnancy?
Transvaginal ultrasound allows you to see the location of the fertilized egg already in the second week of pregnancy, although reliable data can certainly be obtained from approximately the fourth week. If the embryo is not found in the cavity of the fallopian tube or uterus (when the period is too short and the fertilized egg is not visible due to its extremely small size), and there is suspicion of an ectopic pregnancy, the procedure is repeated after a while or the woman is immediately hospitalized and a medical examination is performed. According to indications, it is even possible to perform laparoscopy: the pelvic organs are examined under anesthesia during an operation, which, if an ectopic pregnancy is confirmed, immediately turns into a medical procedure.
Ultrasound with intravaginal insertion of a sensor is considered the most reliable method for diagnosing ectopic pregnancy. However, it does not provide a 100% guarantee that the diagnosis will be made correctly. In 10% of all cases when an ultrasound is performed during an ectopic pregnancy, it is not installed because an accumulation of fluid or a blood clot located in the uterine cavity is mistaken for the fertilized egg. Therefore, even such highly accurate diagnostics are recommended to be combined with other methods for greater reliability, in particular with a blood test for hCG.
Ectopic pregnancy: forecasts
No organ of the female body is designed to bear a child, except the uterus. Therefore, the embryo attached “in the wrong place” must be removed. If this is not done in advance, for example, a rupture of the fallopian tube may occur (if the egg is implanted here) or it may enter the abdominal cavity when bleeding opens. Both situations are extremely dangerous for a woman and require immediate surgical intervention. When a fallopian tube ruptures, a woman experiences severe acute pain, shock, fainting, and intra-abdominal bleeding are possible.
It is very important to detect an ectopic pregnancy in time in order to successfully solve the problem. Previously, in such cases, the fallopian tube was removed, which meant the inability to become pregnant and give birth in the future. Today this is a last resort. In most cases, for an ectopic pregnancy, an operation is performed during which the fertilized egg is removed and the fallopian tube is sutured to preserve reproductive capabilities.
More and more doctors are studying and putting into practice the drug treatment of ectopic pregnancy using hormones. However, even if you have one damaged fallopian tube removed, you have every chance of getting pregnant and carrying a child to term if the other one is preserved.
True, first you need to undergo a rehabilitation treatment course. Also, a woman who has experienced an ectopic pregnancy should not become pregnant for at least another six months. Be extremely careful when choosing a contraceptive method. You must understand that there remains a fairly high chance of repeating such an abnormal pregnancy. And to prevent this, you must find out the reason why the fertilized egg in your case cannot reach the uterus. Well, of course, eliminate it.
Especially for beremennost.net - Elena Kichak
General information
Ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy is rightfully considered one of the most dangerous pathologies in the field of gynecology. Indeed, if the diagnosis is not carried out in a timely manner, the diagnosis is incorrectly established and, accordingly, without adequate treatment, a woman who develops an ectopic pregnancy may die due to blood loss and pain shock. The incidence of ectopic pregnancy is about 2% of all pregnancies .
There are two stages of ectopic pregnancy: progressive and interrupted . After the fertilized egg during an ectopic pregnancy is implanted primarily into the fallopian tube, changes occur in the pregnant woman’s body that are characteristic of the normal course of pregnancy. Next, the egg grows, and the pipe wall stretches. Gradually it is destroyed, and the pregnancy is terminated. In this case, the pipe often ruptures and internal bleeding threatens the woman’s life.